Saccharomyces cerevisiae bred by space breeding technology and mutation site application thereof
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of reducing carotenoid synthesis efficiency, growth retardation and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
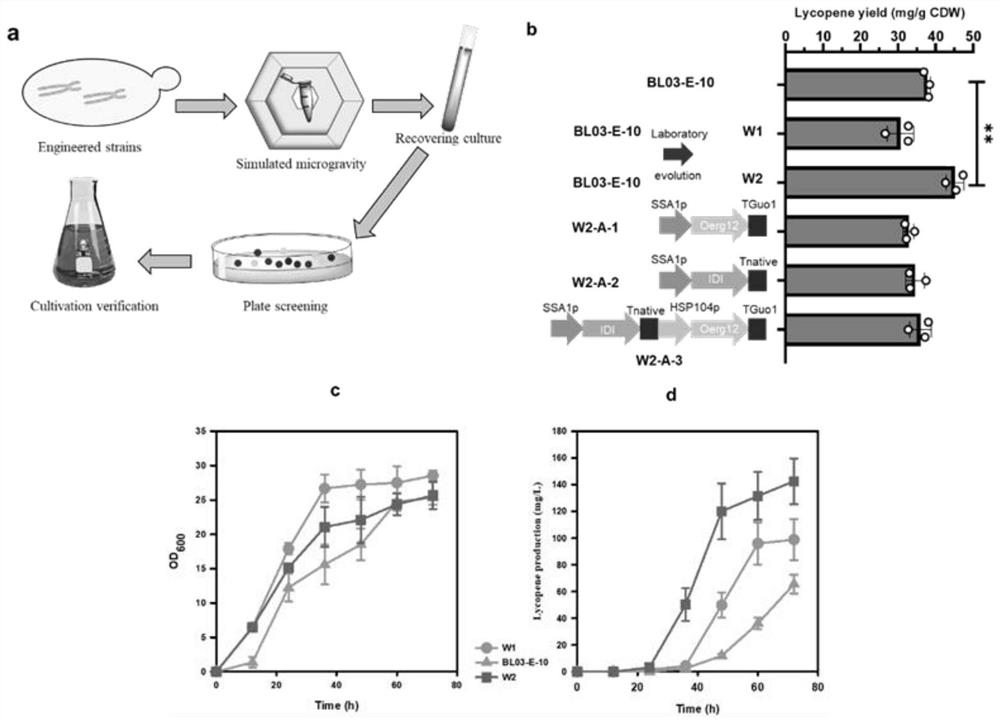
[0023] Embodiment 1 microgravity mutagenesis
[0024] The Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation medium of the present embodiment is: YPD medium: yeast extract 10g / L (OXOID company), peptone 20g / L, glucose 20g / L, solvent is water; Or YPM medium: yeast extract 10g / L L (Angel Yeast Co., Ltd.), peptone 20g / L, glucose 20g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 10g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 5g / L, potassium sulfate 3.5g / L, sodium phosphate 2.5g / L, TMS Solution 1ml / L (magnesium chloride hexahydrate 250mg / L, calcium chloride dihydrate 104.5mg / L, mg / L, copper sulfate pentahydrate 0.4mg / L, sodium iodide 0.08mg / L, manganese chloride tetrahydrate 0.1mg / L, sodium molybdate dihydrate 0.5mg / L, boric acid 1mg / L, cobalt chloride hexahydrate 0.3mg / L, zinc sulfate heptahydrate 6.25mg / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 3.5mg / L), the solvent is water. Its preparation method is to mix each component uniformly and sterilize to prepare. The solid medium is based on the liquid medium by adding 2% a...
Embodiment 2
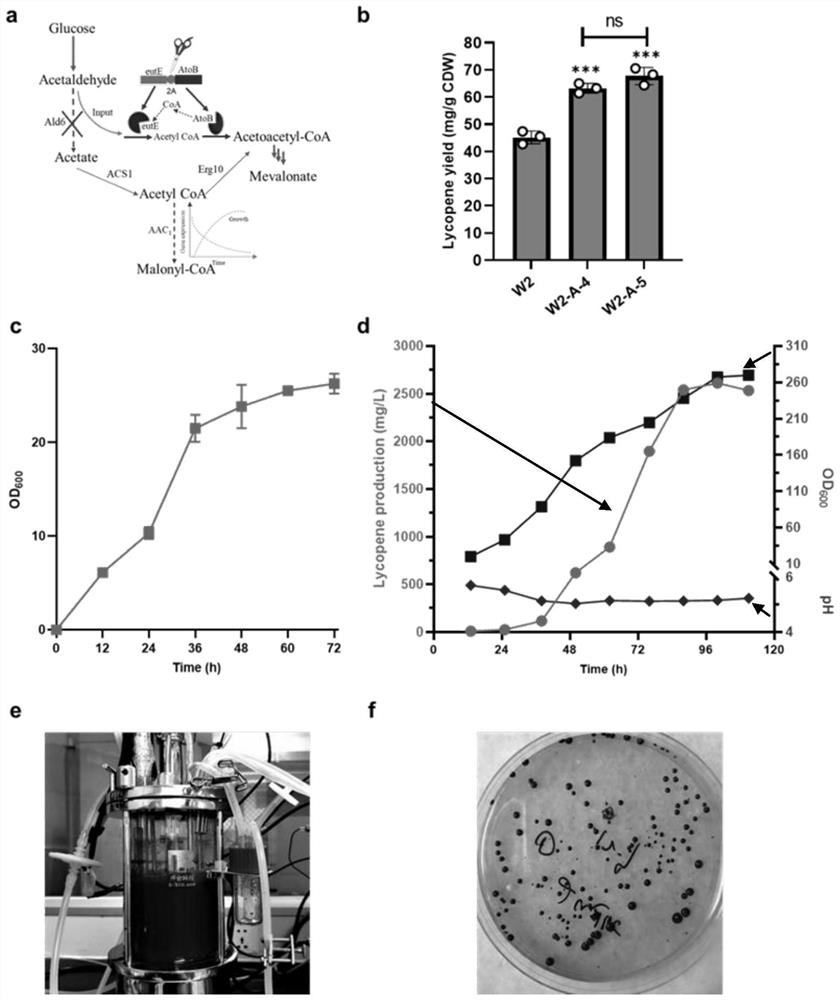
[0027] Embodiment 2: Further modification of W2 bacterial strain
[0028]In order to further enhance the carotenoid synthesis ability of S. cerevisiae W2 strain, we replaced the ACC1 gene promoter (its nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1) with PDC1 (its nucleotide sequence) on the basis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae W2 strain The sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2), references (Xie ZX, et al. Rapid and Efficient CRISPR / Cas9-Based Mating-Type Switching of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.8,173-183(2018).) and construct diploid cells Strain W2-A-5 was obtained. It was deposited in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center (GDMCC) on December 3, 2020, address: 5th Floor, Building 59, Compound, No. 100 Xianlie Middle Road, Yuexiu District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province, postcode 510070, and the deposit number is: GDMCC No :61337.
[0029] Streak the obtained strains in fresh YPD solid medium respectively. After 48 hours, pick a single colony and inoculate it in 5ml of YPD l...
Embodiment 3
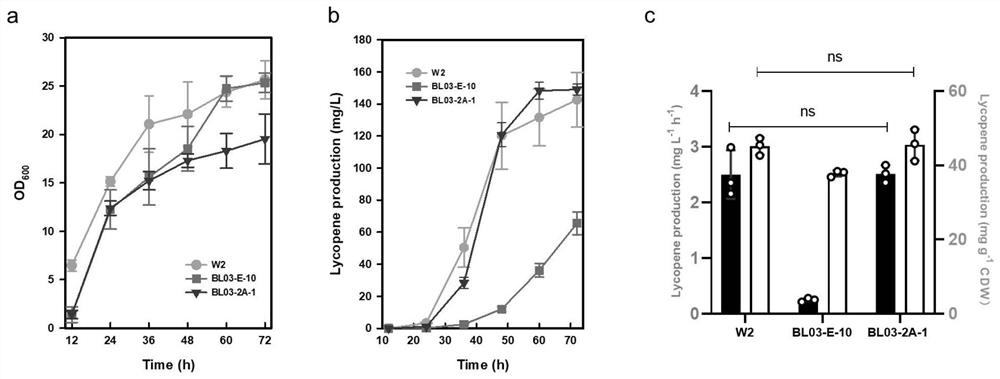
[0034] Example 3 Determination of the Mutation Site of the W2 Strain
[0035] In order to determine the mutation site of the mutant strain W2, we performed genome resequencing on the starting strain-S. Four single-nucleotide mutations were found, one of which was meaningful and produced a stop codon inside the CHO2 gene, resulting in gene inactivation. Subsequently, we carried out reverse metabolic engineering research on the starting strain, and used the CRISPR / Cas9 system to knock out the CHO2 gene (Gene ID: 853061) of the BL03-E-10 strain to obtain the CHO2 gene knockout mutant strain BL03-2A-1 .
[0036] Primers used in the construction of BL03-2A-1 and BL03-D-5 strains
[0037]
[0038] Inoculate BL03-E-10, Saccharomyces cerevisiae W2, and the modified strain BL03-2A-1 into YPM medium according to the method of Example 1, and culture them at 30°C and 200rpm for 96 hours, measure the carotenoid content in cells, and calculate As a percentage of dry weight, the result...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com