Method for treating radioactive waste liquid containing nitric acid through electrolytic tank
A technology of radioactive waste liquid and electrolytic cell, which is applied in the field of nuclear chemical industry, can solve problems such as difficult operation, difficult adjustment of formaldehyde, and treatment of radioactive gas, so as to achieve the effects of improving current efficiency, ensuring reduction potential, and controllable reaction process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
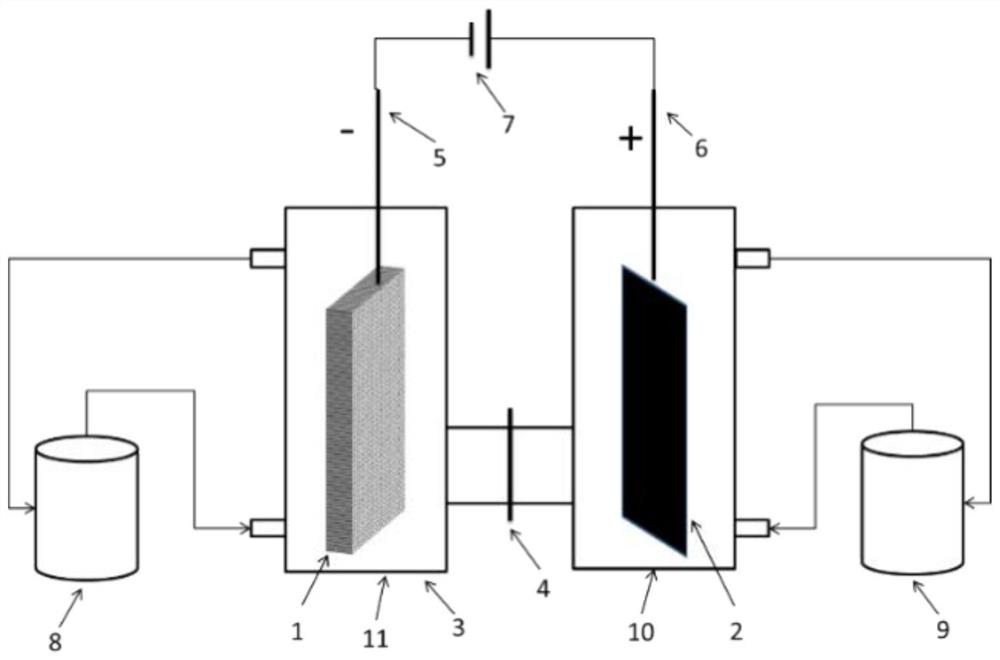
[0048] Electrolytic denitrification device such as figure 1 As shown, the DC power supply provides the current and voltage required for the electrolysis reaction.
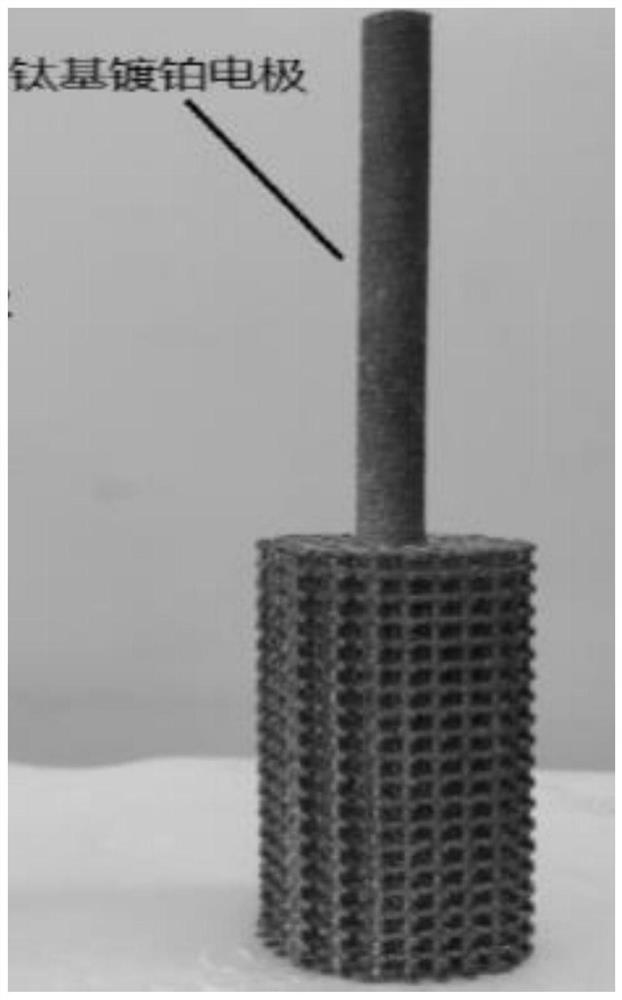
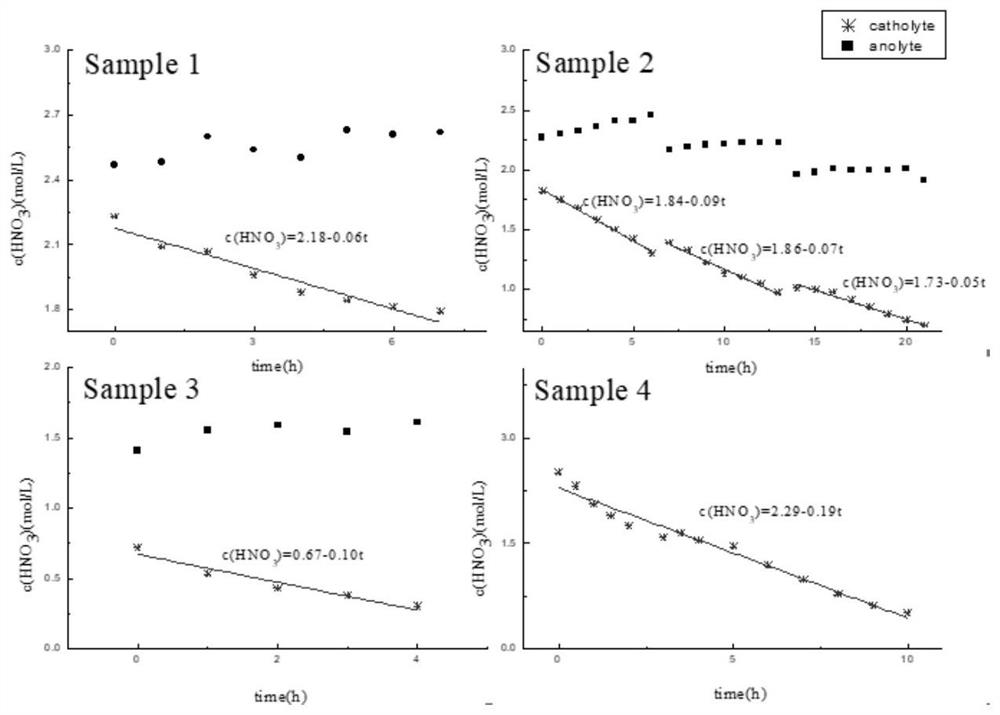
[0049] Inject 200mL, 2.47mol / L nitric acid solution into the anode area solution storage tank 9, simulate high-level radioactive waste liquid of 2.23mol / L nitric acid concentration of 200mL (containing 100mg / L uranium, 500mg / L zirconium, 200mg / L molybdenum, 200mg / L ruthenium, 300mg / L iron, 100mg / L cesium, 100mg / L barium, the same below) are injected into the solution storage tank 8 in the cathode area. Add a 50mm×100mm platinum mesh as the anode, 50mm×5mm×100mm 3D printed porous titanium (porosity 72%, pore diameter 2mm) as the cathode in the above electrolytic denitrification device, and use Nafion117 proton exchange membrane between the anode area and the cathode area As a diaphragm material; pass through a constant current of 3.0A for 7 hours, and measure the change curve of the concentration of nitric acid in ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that the liquid in the anode region is a mixed solution of 2.27mol / L nitric acid and 0.5mol / L hydrazine nitrate solution of 200mL, and the liquid in the cathode region is 1.82mol / L nitric acid concentration of 200mL The simulated high-level radioactive waste liquid, constant current 3.0A, intermittent electrolysis, electrolysis time a total of 21h. During the electrolysis process, the solution in the nitric acid storage tank was regularly sampled, the concentration of nitric acid was analyzed, and the denitrification rate of nitric acid was calculated based on the change of the total volume of the solution. The results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0053] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that the liquid in the anode region is a mixed solution of 200mL of 1.41mol / L nitric acid and 0.50mol / L hydrazine nitrate, and the liquid in the cathode region is 200mL of 0.72mol / L nitric acid concentration. Simulate high-level waste liquid, constant current 3.0A, electrolysis time 4h. During the electrolysis process, the solution in the nitric acid storage tank was regularly sampled, the concentration of nitric acid was analyzed, and the denitrification rate of nitric acid was calculated based on the change of the total volume of the solution. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com