Reagent for modifying extracellular vesicles and preparation method thereof
A cell and vesicle technology, applied in the field of reagents and preparations for modifying extracellular vesicles, can solve problems such as affecting the biological function of extracellular vesicles, hindering the process of visualization research of extracellular vesicles, and low labeling efficiency, and achieves The effect of good visualization, efficient and controllable retouching, efficient and controllable labeling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Milk-derived extracellular vesicles were obtained by separating and purifying fresh milk through acid precipitation (pH 4.0), ultracentrifugation, and column chromatography, and the particle size distribution of milk-derived extracellular vesicles was characterized by nanoflow detection technology , observing the morphology of extracellular vesicles by transmission electron microscopy, detecting the marker proteins of extracellular vesicles by Western blot, and detecting the purity of extracellular vesicles by ultra-high liquid phase-size-exclusion chromatography. The results will be as follows: image 3 E. Image 6 C. Figure 7 with Figure 8 Shown in B.
Embodiment 2
[0075] Embodiment 2: Preparation of fluorescent labeling reagent
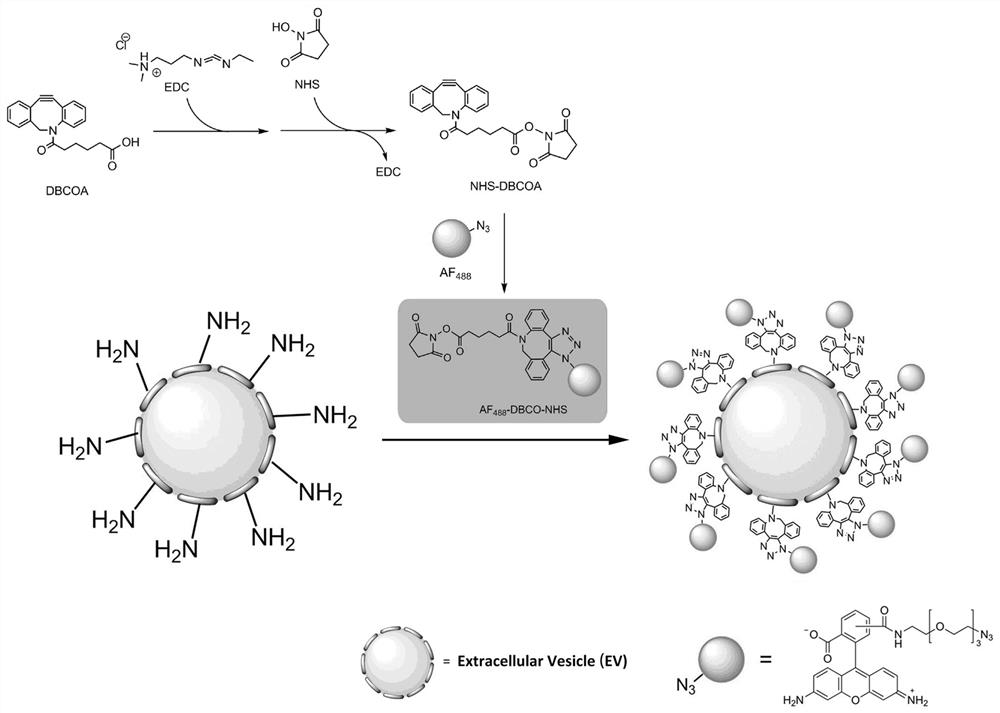
[0076] EDC·HCl (5.8 mg, 30 μmol, 1.0 eq.) was mixed with NHS (3.5 mg, 30 μmol, 1.0 eq.), and DMSO (832 μL) was added to prepare 36.1 mM activated crosslinker. Add diphenylcyclooctyne adipic acid (10 mg, 30 μmol, 1.0 eq.) into the activated cross-linking agent, mix well at room temperature, and activate the carboxyl group to obtain diphenylcycloctyne succinimide ester.
[0077] The fluorescent probe azide fluorine 488 (1 mg, 1.74 μmol) was dissolved in DMSO (205 μL) to prepare 8.5 mM azide fluorine 488 fluorescent dye. Add 168 μL azide fluorine 488 fluorescent dye (1.428 μmol) to diphenylcyclooctyne succinimide ester, and mix thoroughly at room temperature to prepare a dichromate that is coupled with a fluorescent probe azide fluorine 488. Fluorescent labeling reagent for phenylcycloctyne succinimide ester (1 mL), store at 2-8 ℃.
[0078] Mix 5 μL of fluorescent labeling reagent with 150 μL of milk-derived ext...
Embodiment 3
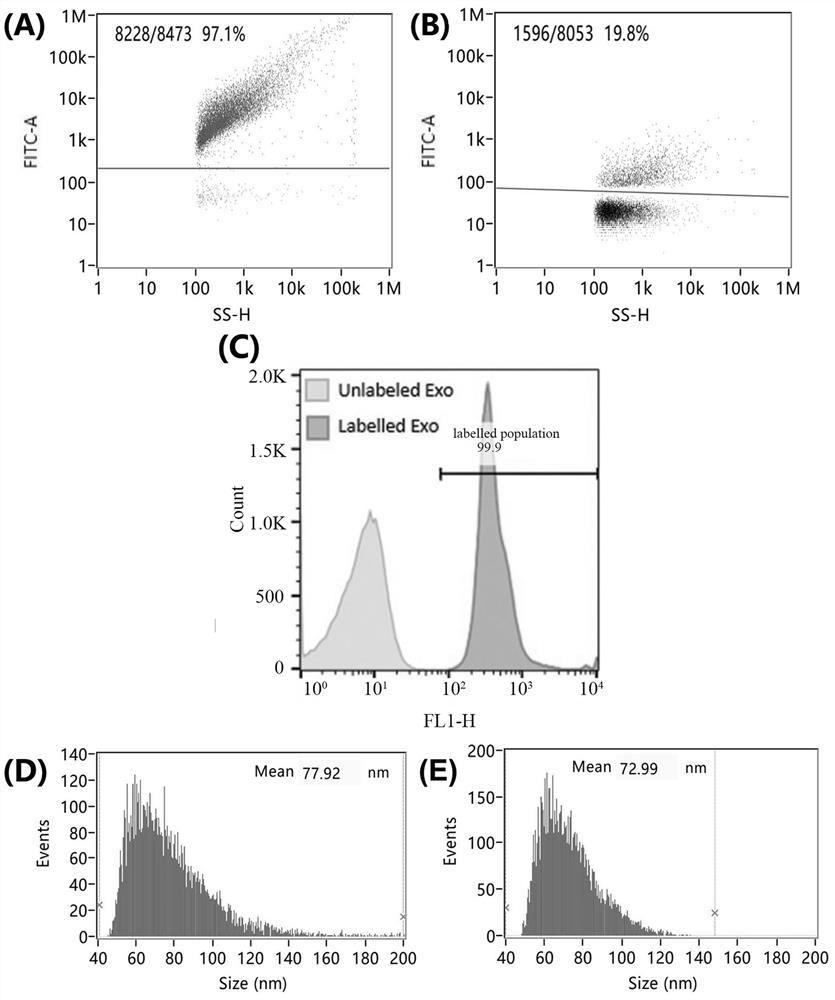
[0088] Example 3: Characterization of Fluorescence Labeling Rate and Particle Size Distribution of Extracellular Vesicles Using Nanoflow Detection Technology
[0089] The extracellular vesicles labeled with fluorescent molecules in Example 2 and Comparative Example were diluted 1000 times with PBS, and 250 ± 5 nm monodisperse nano-fluorescent silicon spheres were selected for optical calibration and counting standards of the nano-flow detector. Select A group of nano-silicon spheres with particle sizes of 68 ± 2 nm, 91 ± 3 nm, 113 ± 3 nm, and 155 ± 3 nm were used as particle size standards for the nano flow detection instrument, and the nano flow detection technology (Nano flow cytometry, NanoFCM) respectively detect the fluorescent labeling rate of at least 5000 extracellular vesicles in Example 2 and the comparative example.
[0090] Detection conditions: 488 nm laser, the detection channels are scattering channel and FITC fluorescence channel, the attenuation coefficient is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com