Preparation method of starch-derived maltodextrin for nephropathy
A maltodextrin and starch technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of low starch branched chain content, high process control difficulty, extremely high process control requirements and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
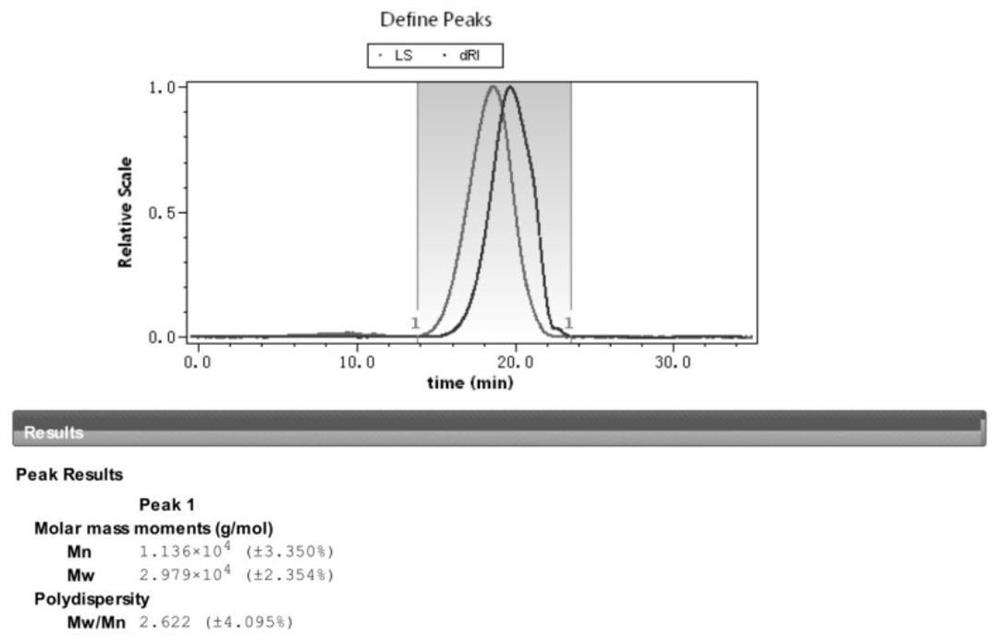
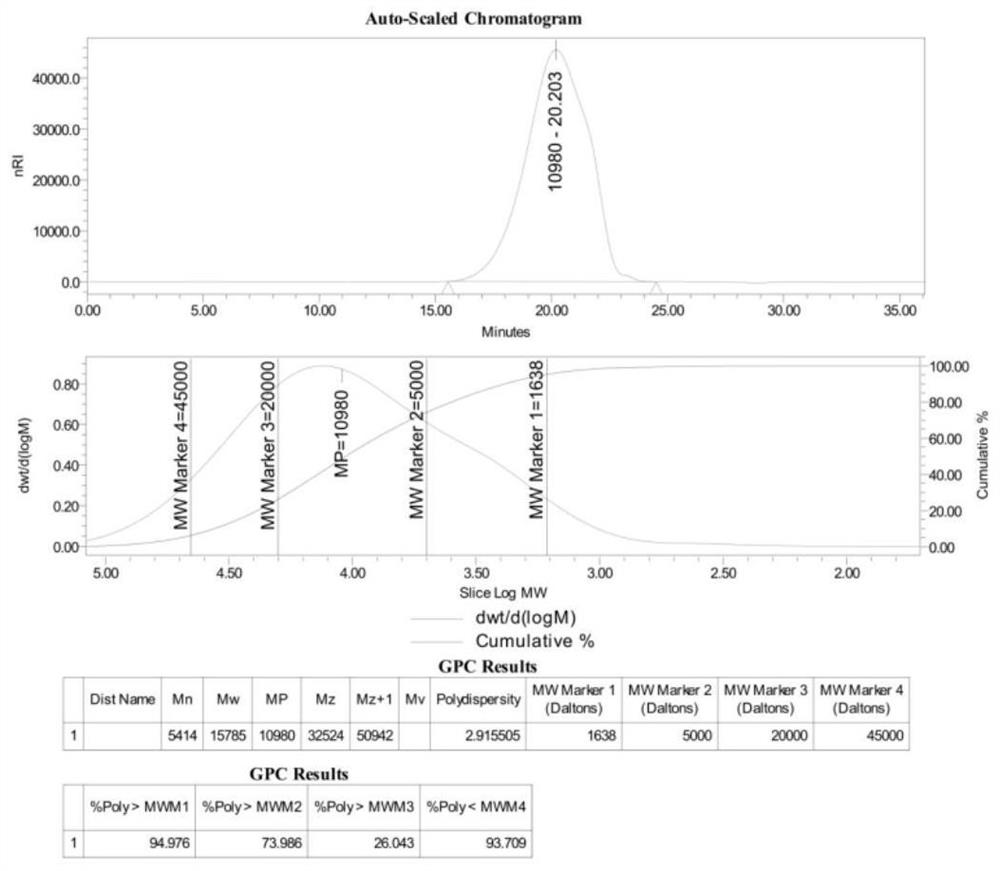
[0075] (1) Add cornstarch to purified water at 30°C to make the concentration reach 25wt%, stir and mix well, keep stirring all the time, add hydrochloric acid in an amount of 0.36mmol per gram of dry starch, turn on the temperature rise, and lower the temperature of the reaction solution Raise to 85°C, control the heating time between 0.5-1.5h, keep the temperature at 85°C±2°C, and react for 1h, add sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH to 6.5, terminate the acid hydrolysis reaction, obtain acid hydrolyzate, and measure the molecular weight : Number average molecular weight Mn6371, weight average molecular weight Mw32240 (such as Figure 14 );
[0076] (2) Heat the hydrolysis solution in (1) above to 95°C, add α-amylase in an amount of 50 U per gram of dry starch, keep the temperature at 95°C±5°C, stir for 40 minutes, and add a certain amount of dilute Adjust the pH to 2.0 with hydrochloric acid, keep it for 15 minutes to rapidly inactivate the enzyme, add a certain amo...
Embodiment 2
[0082] (1) Add cornstarch to purified water at 30°C to make the concentration reach 25wt%, stir and mix well, keep stirring all the time, add hydrochloric acid, the dosage is 0.36mmol per gram of dry starch, turn on the temperature rise, and raise the temperature of the reaction solution To 80°C, control the heating time between 30-80min, keep the temperature at 80°C±2°C, and react for 40min, add sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH to 6.5, stop the acid hydrolysis reaction, and obtain the acid hydrolyzate, measure the molecular weight: number Average molecular weight Mn8917, weight average molecular weight Mw55850 (such as Figure 18 );
[0083] (2) Heat the hydrolysis solution in (1) above to 95°C, add α-amylase, the dosage is 50U per gram of dry starch, keep the temperature at 95°C±5°C, stir for 60min, add a certain amount of dilute Adjust the pH to 2.5 with hydrochloric acid, keep for 10 minutes to rapidly inactivate the enzyme, then add a certain amount of dilute s...
Embodiment 3
[0089] (1) Add cornstarch to purified water at 40°C to make the concentration reach 20wt%, stir and mix well, keep stirring all the time, add α-amylase, the dosage is 45U per gram of dry starch, turn on the temperature rise, and lower the temperature of the reaction solution Raise to 100°C, control the heating time between 40-50min, monitor the dynamic viscosity during the reaction, measure the dynamic viscosity value between 5-20mPa·s, add citric acid to adjust the pH to 2.5, and the dosage is 0.9% of the volume of the reaction solution ( w / V), keep 20min to make enzyme inactivation, get enzyme hydrolyzate, measure molecular weight, number average molecular weight Mn 8122, weight average molecular weight Mw100900 (such as Figure 22 ).
[0090] (2) Reduce the temperature of the above (1) enzyme hydrolyzate to 75°C, add hydrochloric acid, the dosage is 0.2mmol per gram of dry starch, keep the temperature at 75±2°C, monitor the dynamic viscosity during the reaction process, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com