Preparation method of allose 6-phosphate, acetyl phosphate and acetyl coenzyme A
A technology of allose phosphate and allulose phosphate, which is applied in the fields of biotechnology and medicine, can solve the problems of low reaction rate, low efficiency, and difficulty in accumulating high concentrations of glycolaldehyde, and achieves high catalytic activity and reaction efficiency. High and affinity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1、6
[0039] Preparation of embodiment 1, allose 6-phosphate
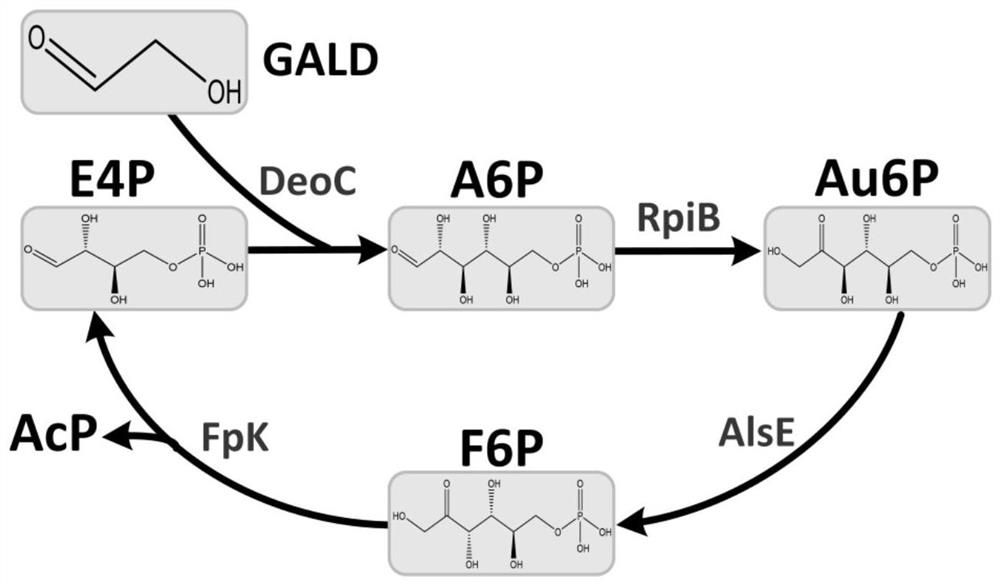
[0040] At an initial concentration of 10 mM of glycolaldehyde GALD, under the action of deoxyribose aldolase (EC 4.1.2.4, NP_418798.1) derived from Escherichia coli, 2.5 mM erythrose 4-phosphate was added to carry out 6-phosphate aldolase For the preparation reaction of Lulose, react at 37°C for 0.5h.
[0041] Detection of Au6P: take 50 μL of the reaction solution, lyophilize the reaction solution, and derivatize with 30 μL of methoxyamine hydrochloride and 90 μL of trimethylsilyltrifluoroacetamide for 1 h respectively, the derivatization temperature is 37 ° C, and the GC-MS Detection of allose 6-phosphate content. The content of allose 6-phosphate quantitatively detected by GC-MS was 1.5 mM, and the average synthesis rate of allose 6-phosphate was 50 μmol (allose 6-phosphate) / min / mg (enzyme protein).
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2, the preparation of acetyl phosphoric acid
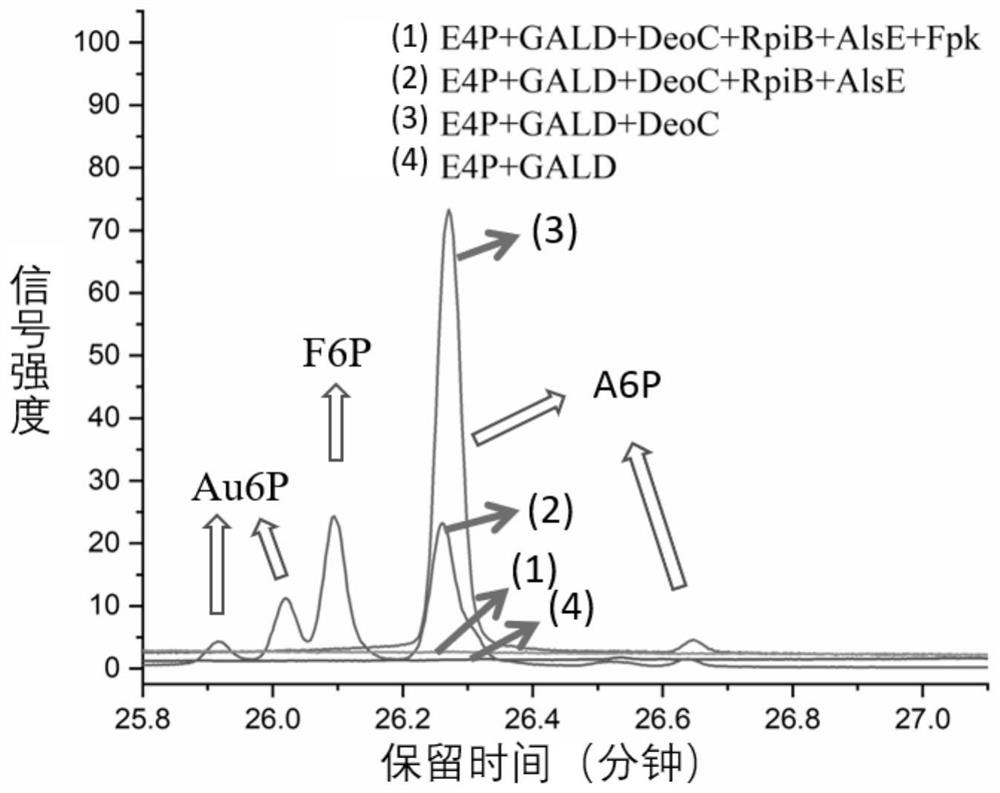
[0043] Glycoaldehyde GALD at an initial concentration of 10 mM, thiamine pyrophosphate ThDP at a concentration of 1 mM, PO 4 3+ Add fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase Fpk (EC 4.1.2.22) from Bifidobacterium adolescentis, deoxyribose aldolase DeoC (EC 4.1.2.4) from Escherichia coli, and allose-6 at a concentration of 2 mM. -Phosphate isomerase RpiB (EC 5.3.1.6), psicose-6-phosphate 3-epimerase AlsE (EC 5.1.3.-) and 2.5mM erythrose 4-phosphate for acetyl phosphate Reactions were prepared to detect the production of acetyl phosphate and the consumption of glycolaldehyde.
[0044] Detection of acetyl phosphate: mix 40μL reaction sample with hydroxylamine solution (2M, pH 6.5), react for 10min, then add trichloroacetic acid solution (15g / 100mL), hydrochloric acid solution 1 (4M) and ferric chloride solution (5g / 100mL of hydrochloric acid solution 2, wherein the concentration of hydrochloric acid solution 2 is 0.1...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Embodiment 3, the construction of the recombinant bacteria of synthesizing poly-3-hydroxybutyrate
[0047] The gene for the synthesis of phosphoketolase was integrated into the genome of Escherichia coli K-12MG1655, and then the genes (PhaA, PhaB and PhaC) for the synthesis of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) and the aldolase The plasmid of the gene of DeoC was transferred into the above-mentioned strains. IPTG-inducible promoters were selected for the above plasmids (the rest of the required enzymes already exist in Escherichia coli). The above strains were cultured in LB medium. After 2.5 hours of culture, the bacterial cell OD 600 When the value reaches 0.8-1.0, add IPTG to a final concentration of 0.5mM to induce (16°C, 12h) expression of the target enzyme protein on the above plasmid. After collecting the bacteria by centrifugation (4°C, 8000r / min, 30min), suspend the bacteria with M9 medium without adding carbon source and nitrogen source, and re-centrifuge to colle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com