Preparation method and application of injectable hemostatic adhesive hydrogel based on gelatin particles
A hydrogel and gelatin technology, which is applied in the field of materials science and biomedical materials, can solve the problems of difficult sealing, the inability of cells and tissues to provide active regulation and response, and the difficulty of minimally invasive applications, so as to achieve the effect of improving mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] (1) Preparation of gelatin particles
[0033] 10g of A-type gelatin was dissolved in 100mL of deionized aqueous solution, and kept heated to 50°C to obtain a clear and transparent aqueous gelatin solution. Hydrochloric acid was added dropwise to adjust the pH of the solution to 2.5, and 240 and 350mL of acetone solution were added dropwise to the above gelatin solution. In and keep heating at 50 ° C and continuous stirring (1000 rpm), the total dropwise addition time is 40 min, and 84 μL of the crosslinking agent glutaraldehyde (25wt% aqueous solution) is added to the above nanoparticle suspension. The crosslinking time is 16h, and the reaction is completed. Then, 100 mM glycine was added to the mixture to terminate unreacted end groups of glutaraldehyde. The nanoparticle suspension was repeatedly centrifuged and resuspended in deionized water. The suspension was freeze-dried at -80°C to obtain dry powder of gelatin nanoparticles.
[0034] The particle size and surfac...
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) Preparation of gelatin particles
[0047] Positively charged gelatin nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 were used.
[0048] (2) Grafting of polyethylene glycol polymer groups
[0049] Use polyethylene glycol diacrylate with molecular weights of 0.6kDa and 20kDa (purchased from China Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Reagent Company)
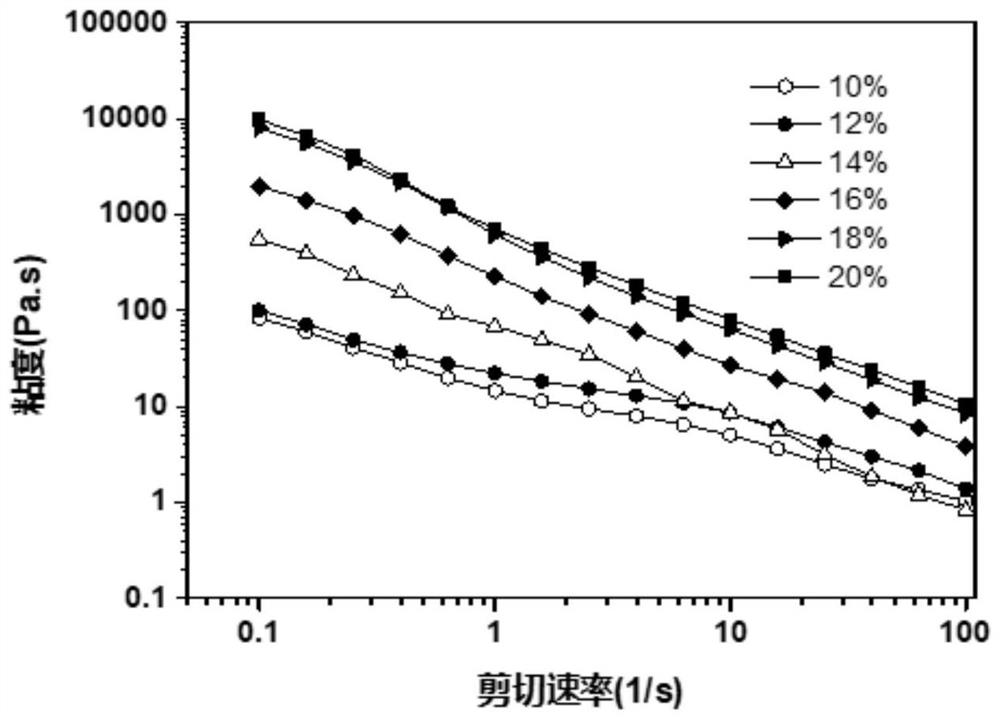
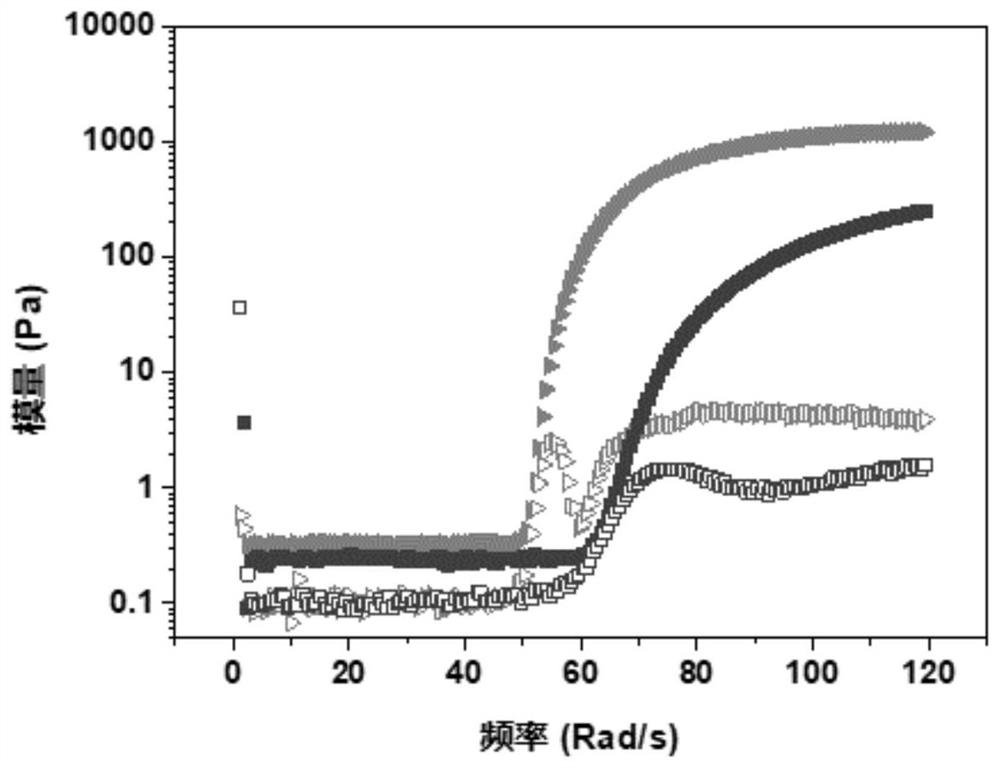
[0050] (3) Dissolve 0.1g of 0.6kDa and 20kDa polyethylene glycol diacrylate and 0.005g of 2-hydroxy-4′-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2-methylpropiophenone photoinitiator respectively In 1 mL of aqueous solution, 0.2 g of gelatin particles were repeatedly pipetted through a luer adapter syringe for 10 times to obtain a prepolymerized colloidal gel with injectable and self-healing properties such as figure 2 shown, figure 1 It is shown that the prepolymerized colloidal gel has shear-thinning mechanical properties when no polymer network is formed, and optical images show that it has excellent injectable properties, figure 2 It is shown that the prepolym...
Embodiment 3
[0057] (1) Preparation of gelatin particles
[0058] Positively charged gelatin nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 were used.
[0059] (2) Grafting of polyethylene glycol polymer groups
[0060] Use polyethylene glycol diacrylate with molecular weights of 0.6kDa and 20kDa (purchased from China Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Reagent Company)
[0061] (3) Dissolve 0.05g of 0.6kDa, 20kDa polyethylene glycol diacrylate and 0.005g of 2-hydroxy-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2-methylpropiophenone photoinitiator respectively In 1 mL of aqueous solution, 0.2 g of gelatin particles were repeatedly pipetted through a luer adapter syringe for 10 times to obtain an injectable, self-healing prepolymerized colloidal gel;
[0062] (4) The above prepolymerized colloidal gel is at 365nm, 50mw / cm 2 Double-network hydrogels were obtained by crosslinking under UV light for 20 s.
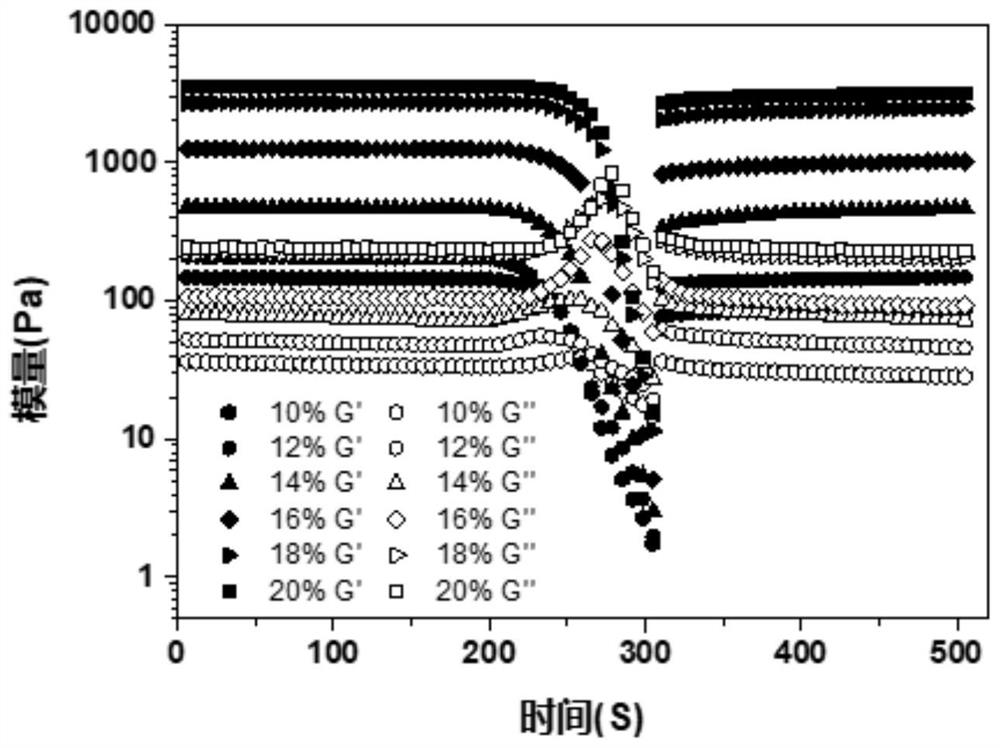
[0063] (5) The storage moduli and loss moduli (Table 4) of the above composite hydrogels were obtained using the time-sweep mode o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface charge | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com