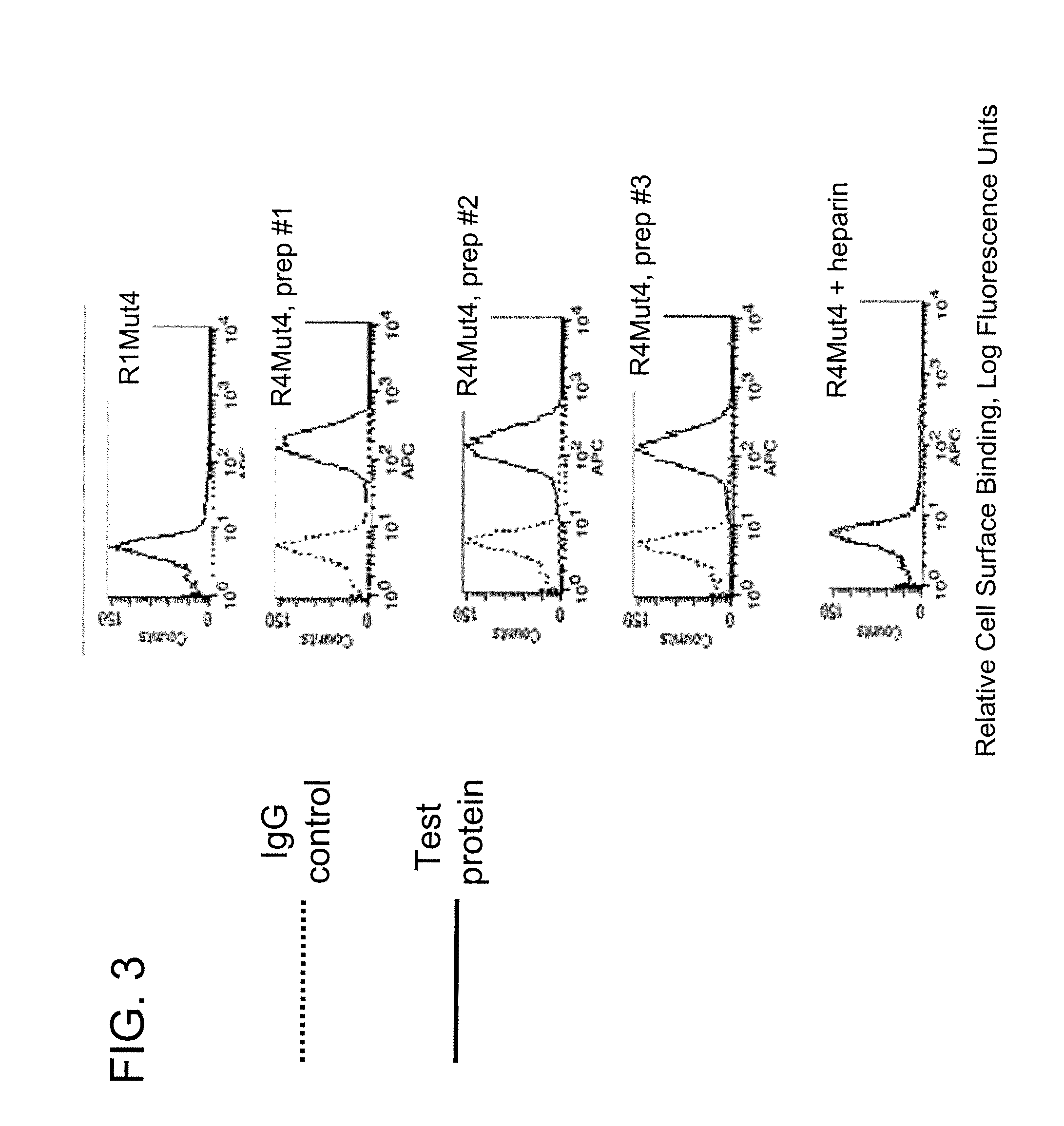
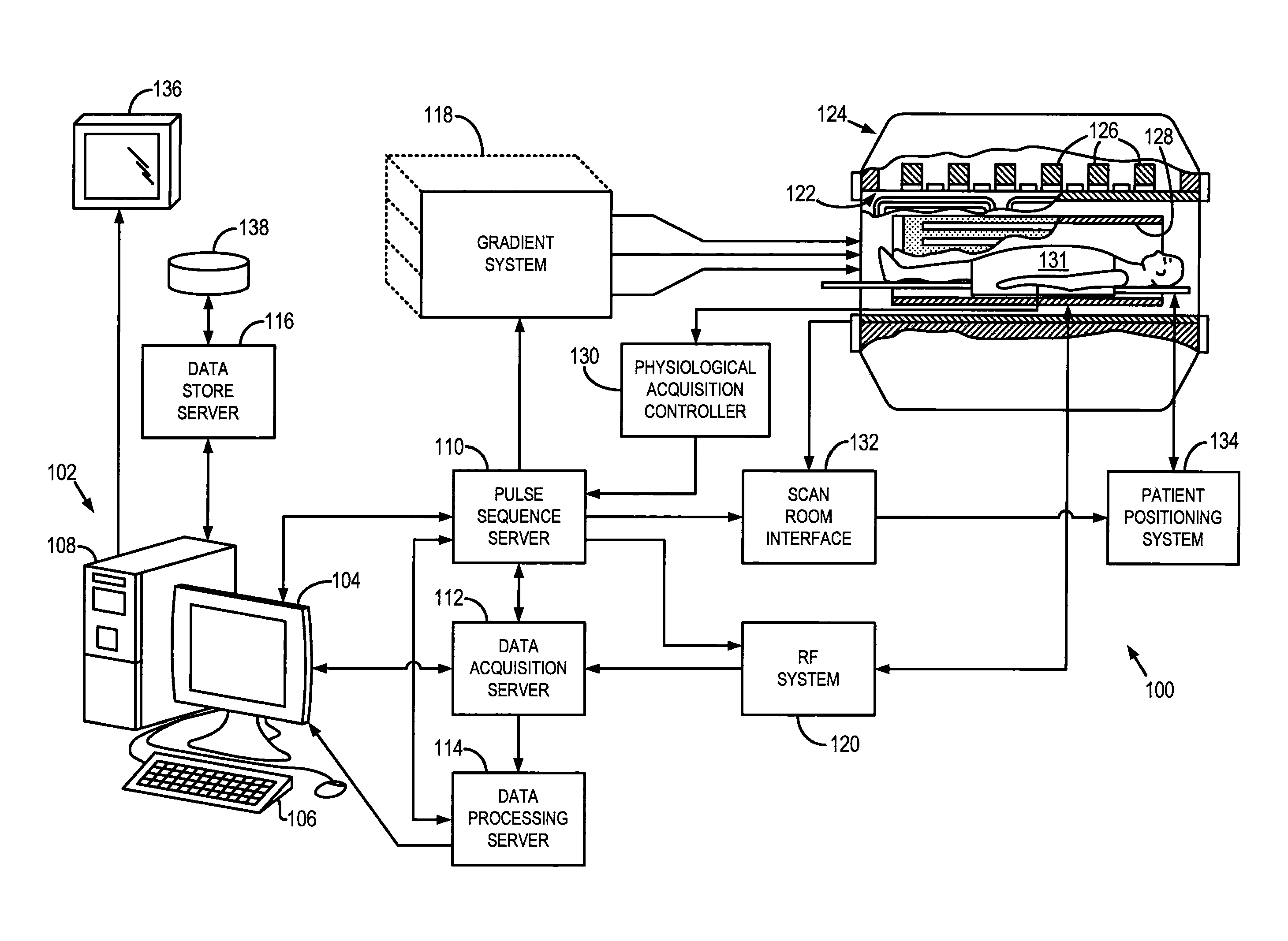
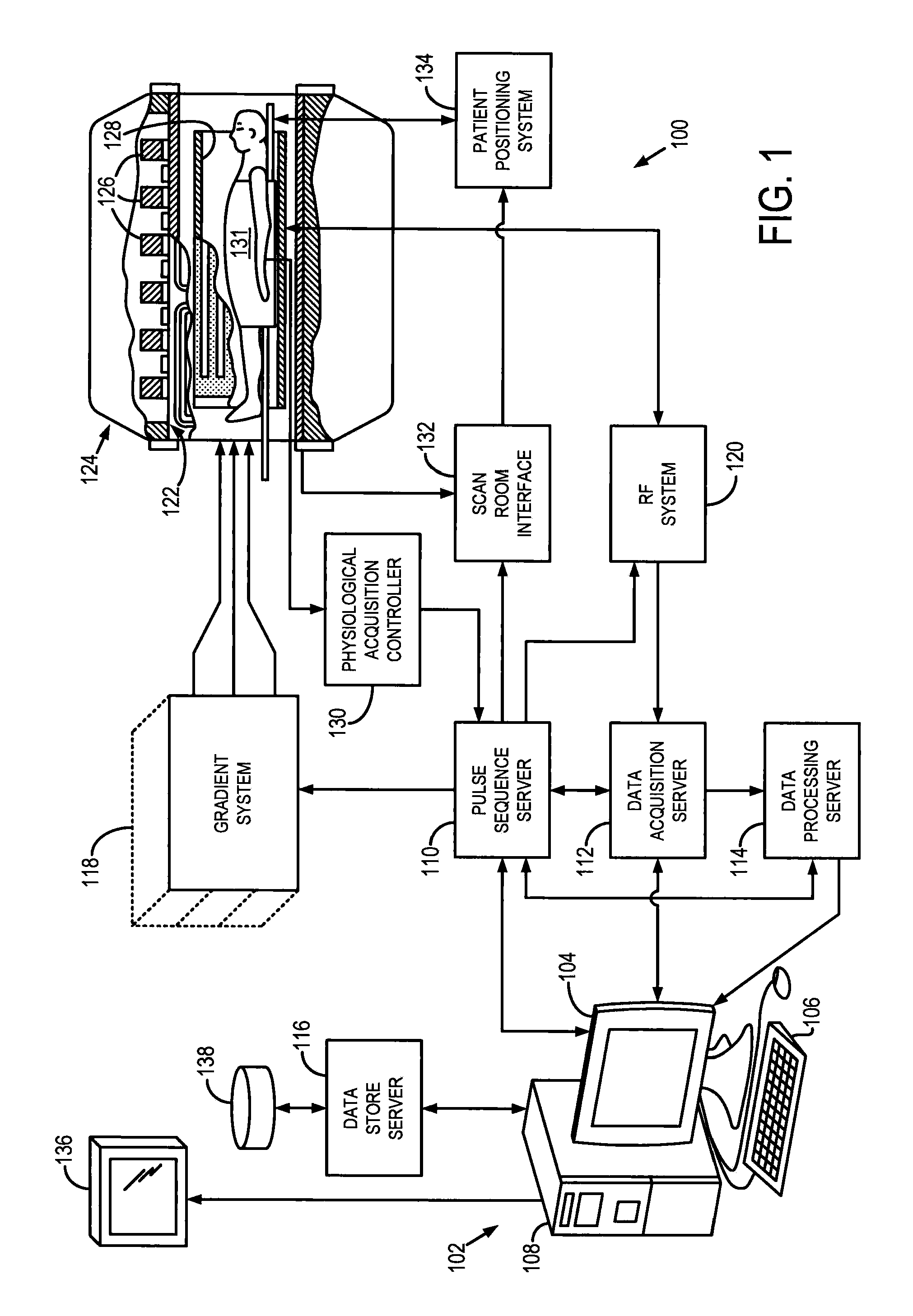
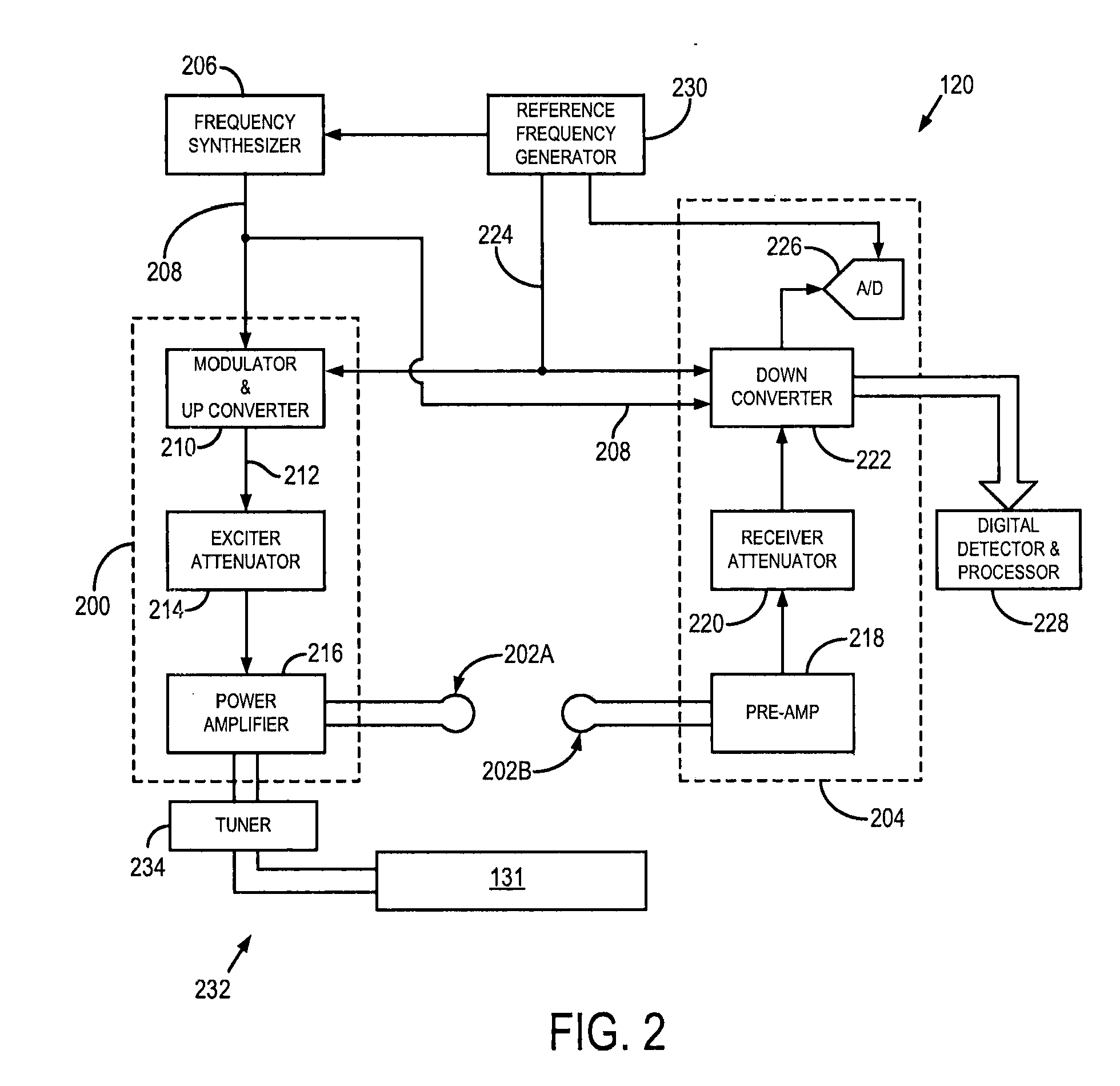
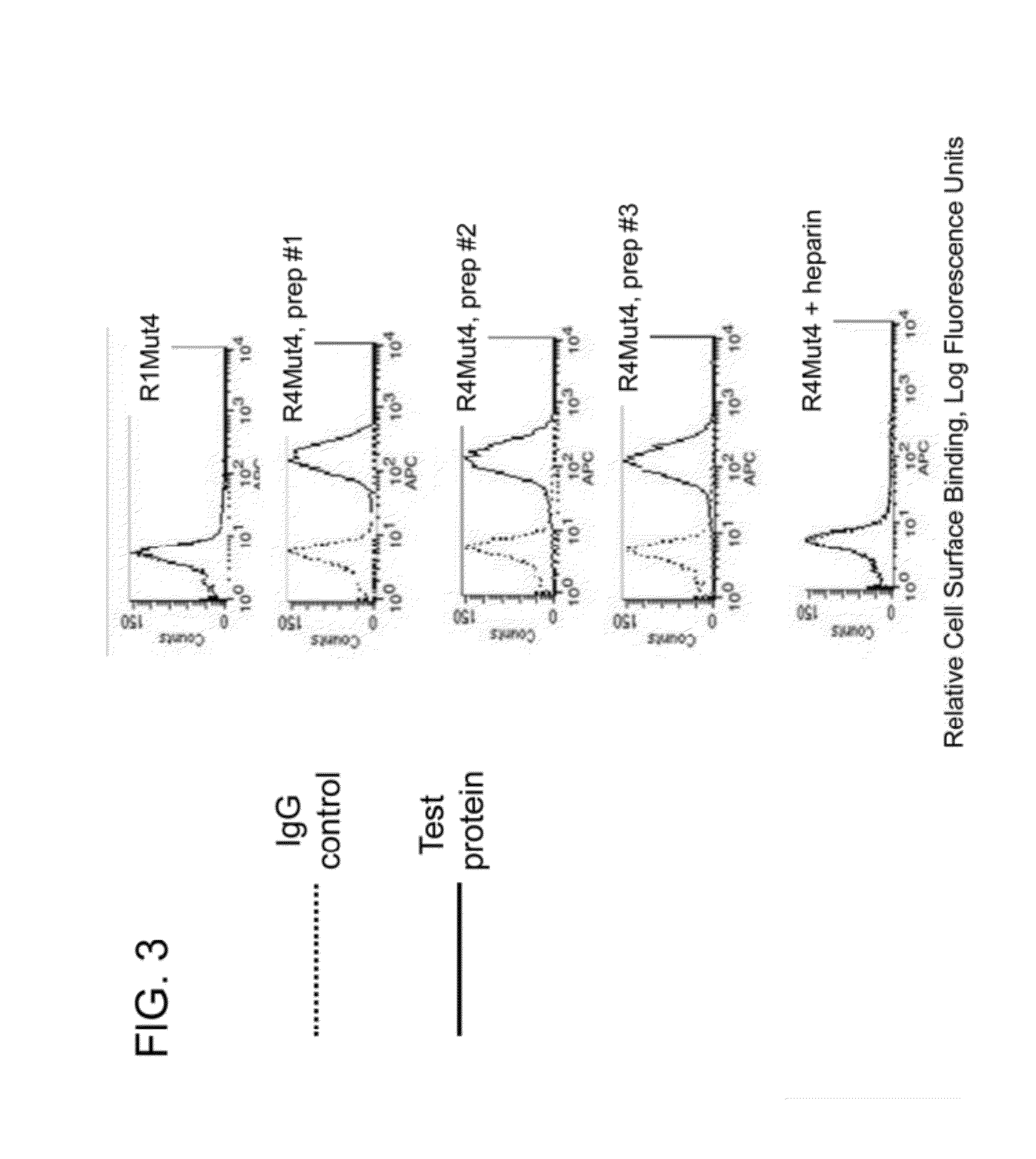
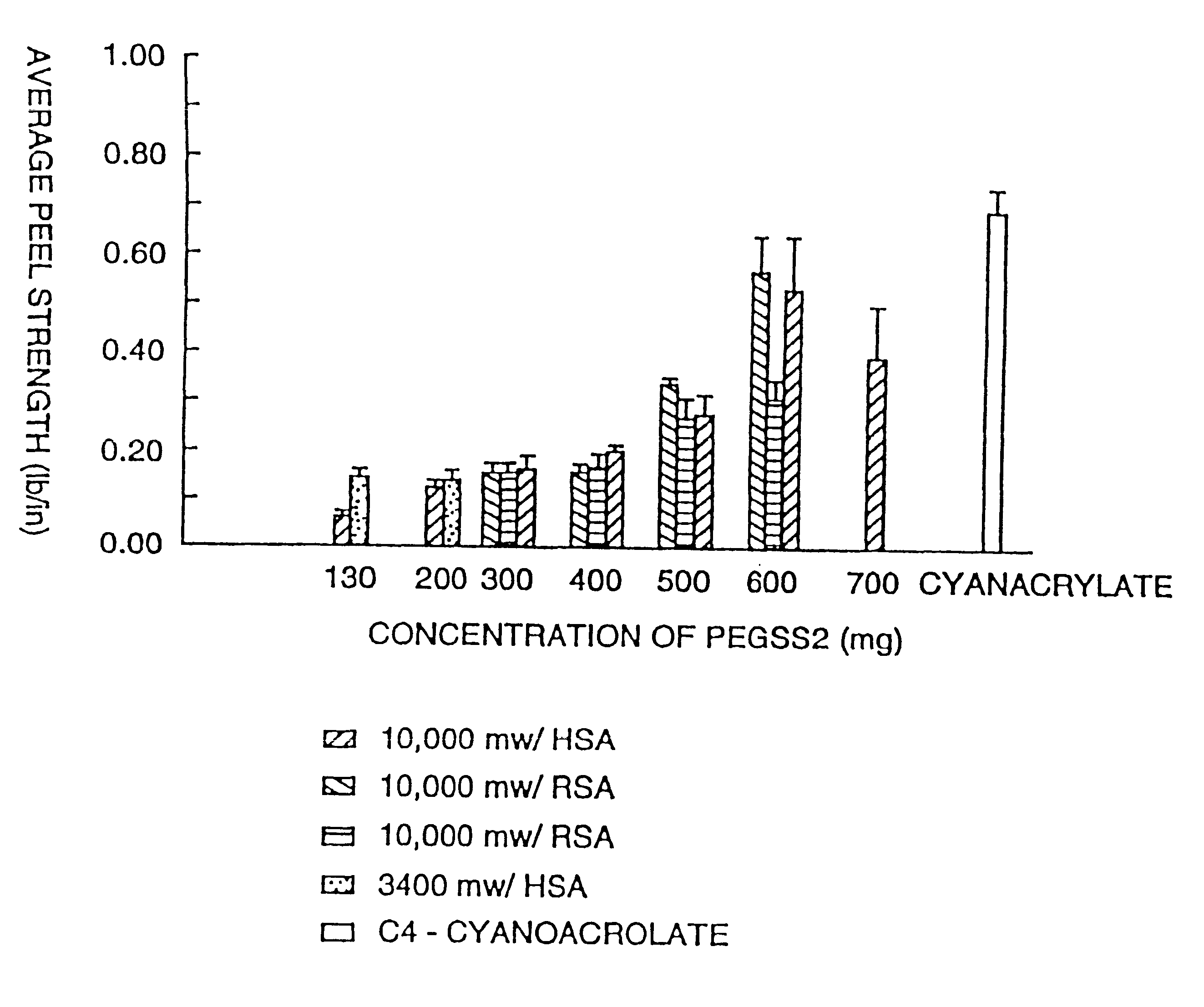
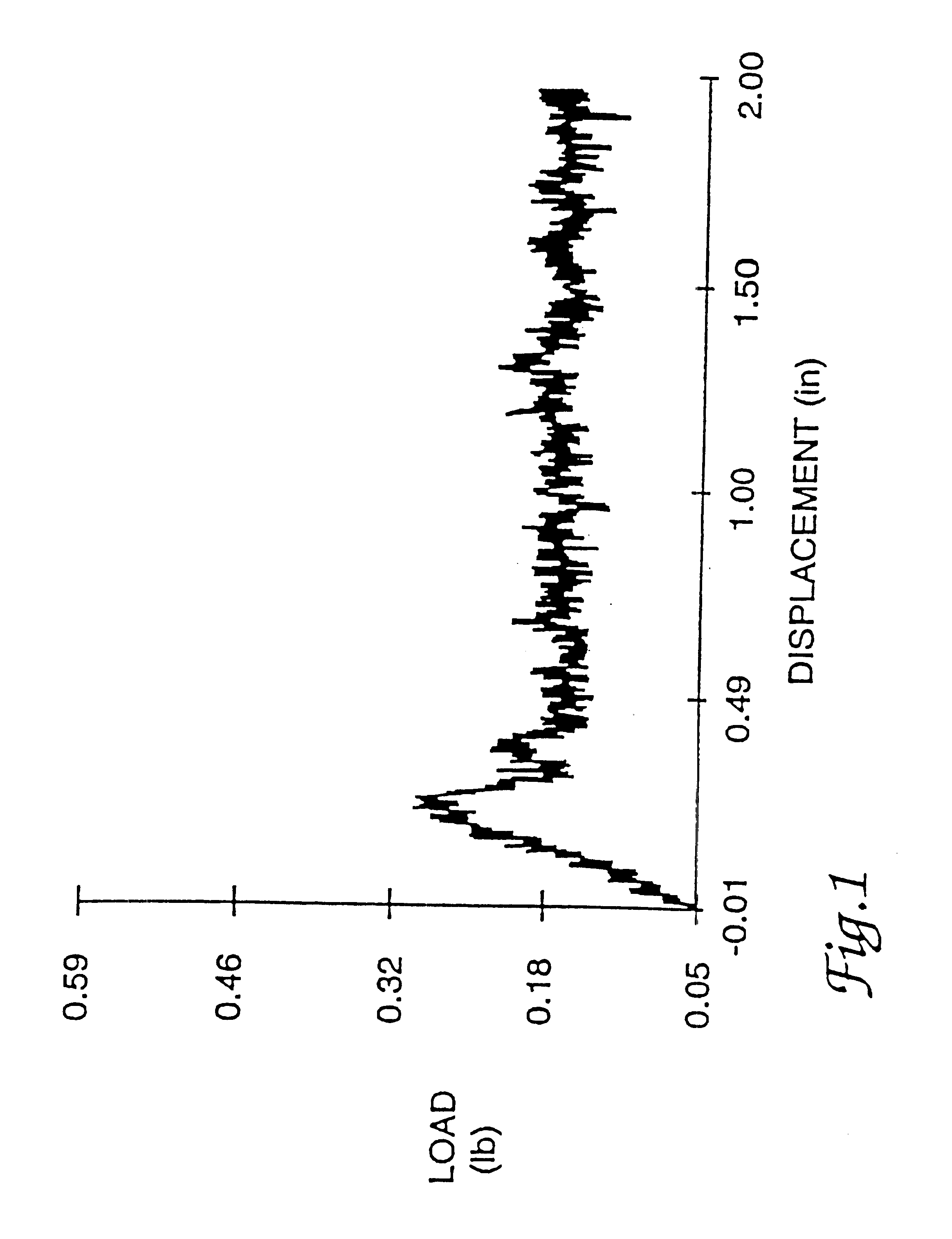
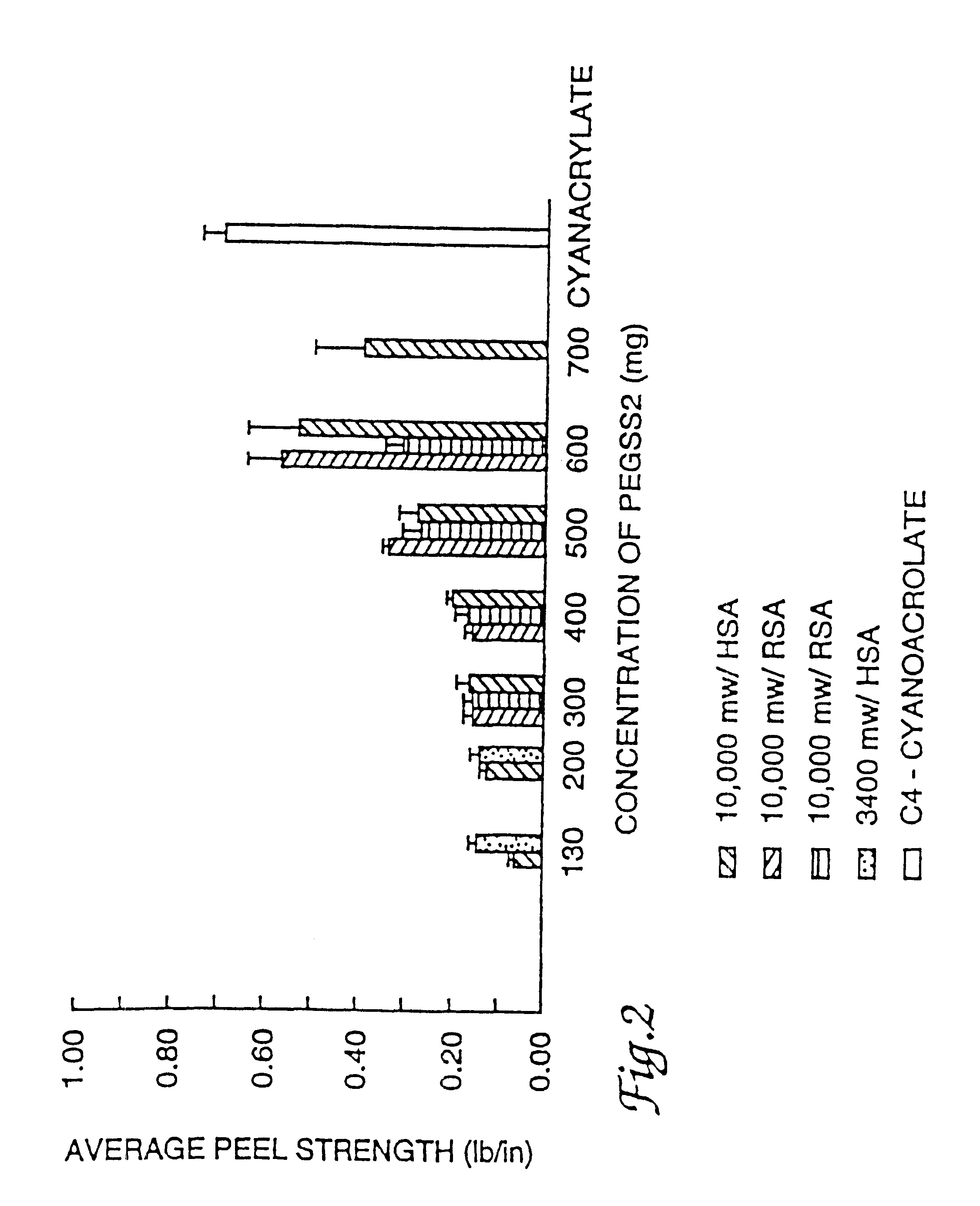
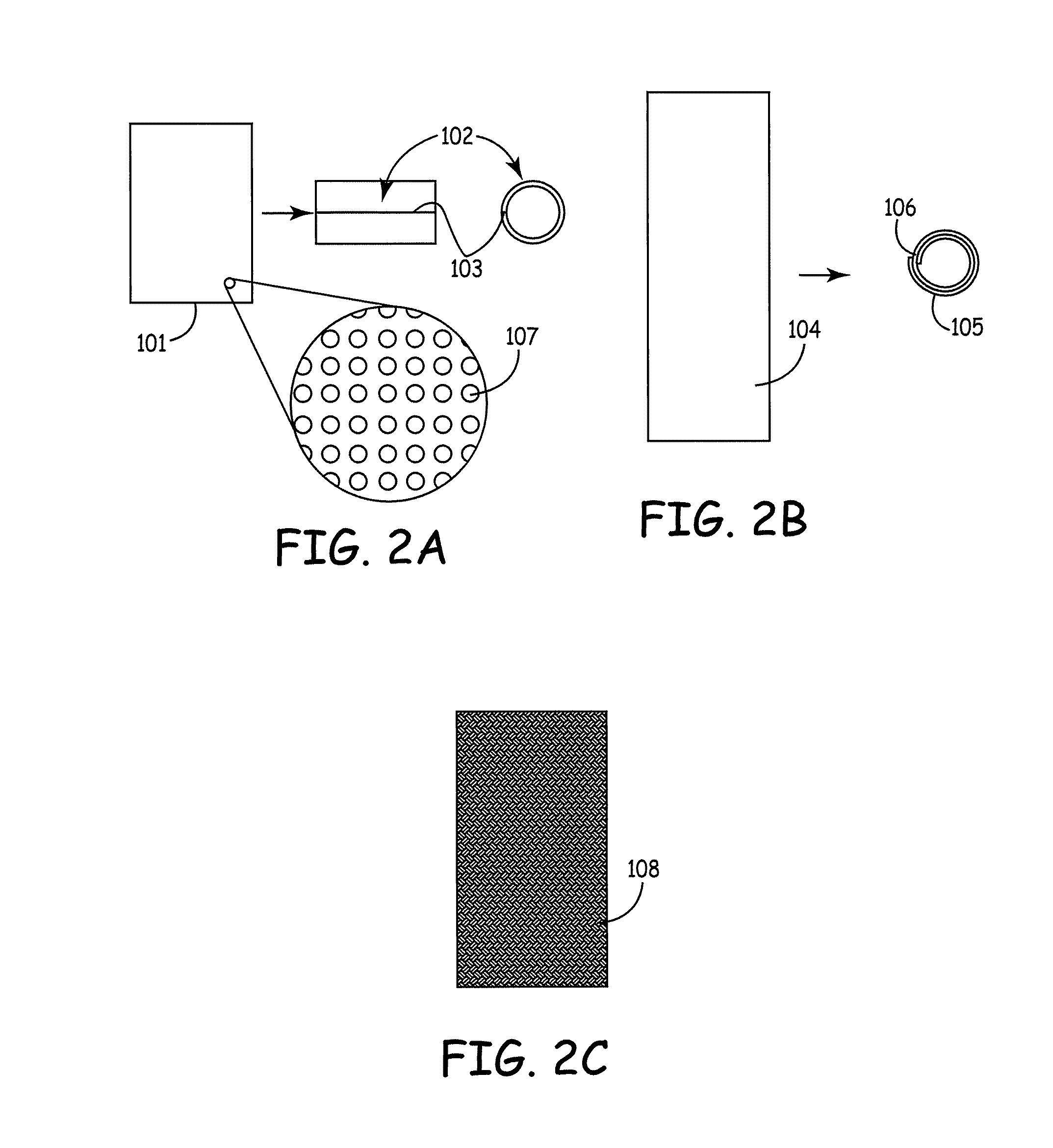
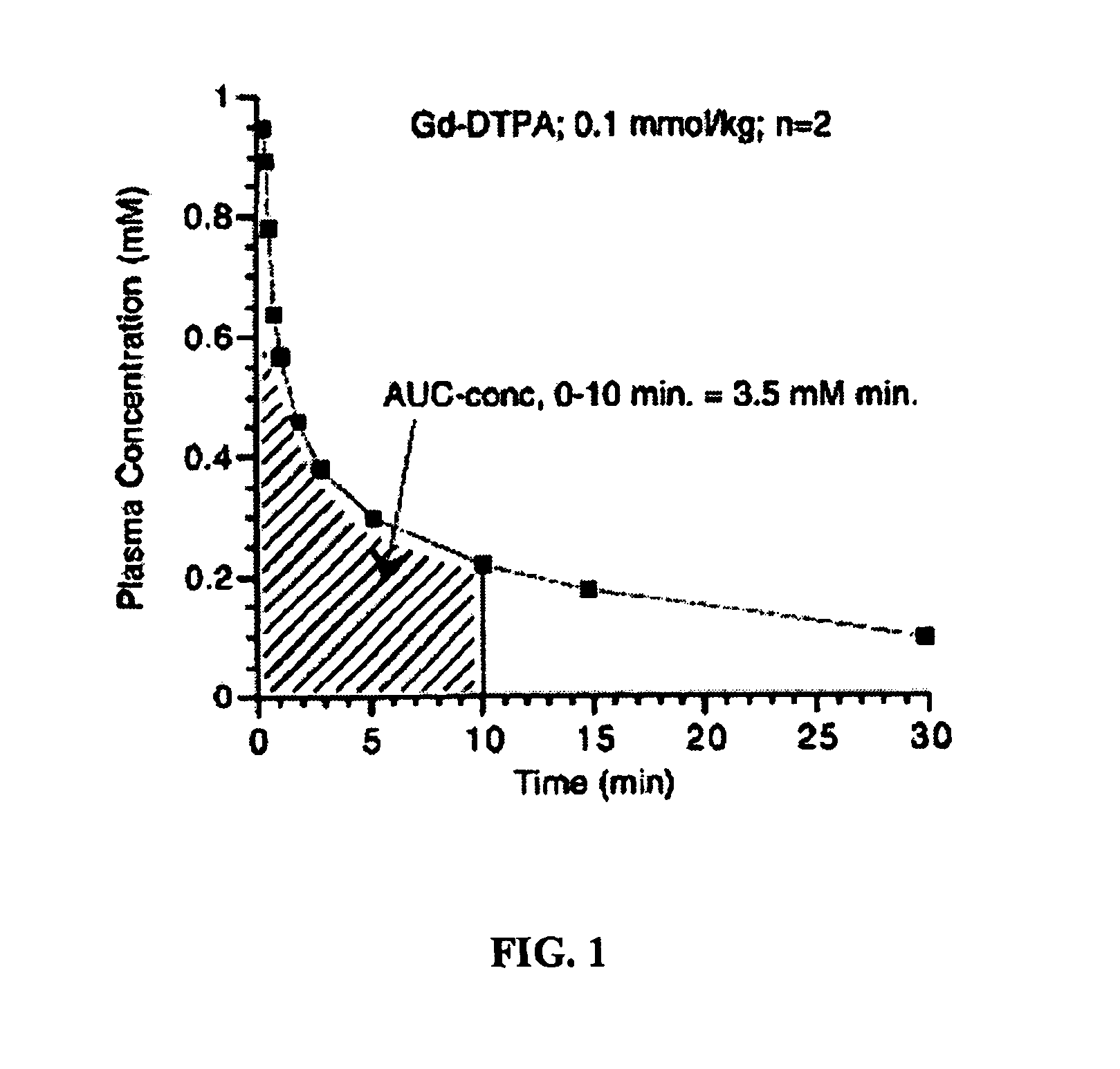
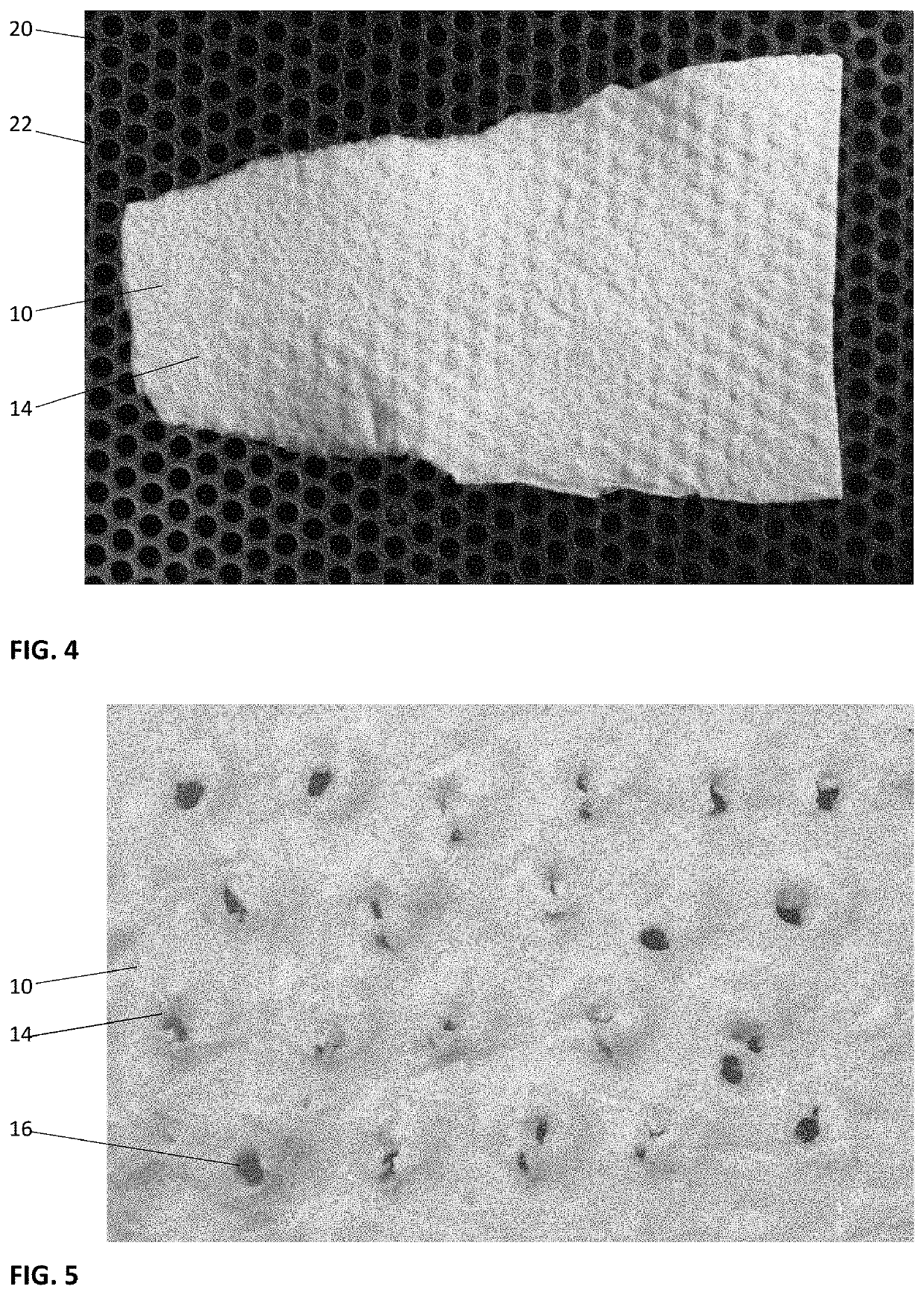
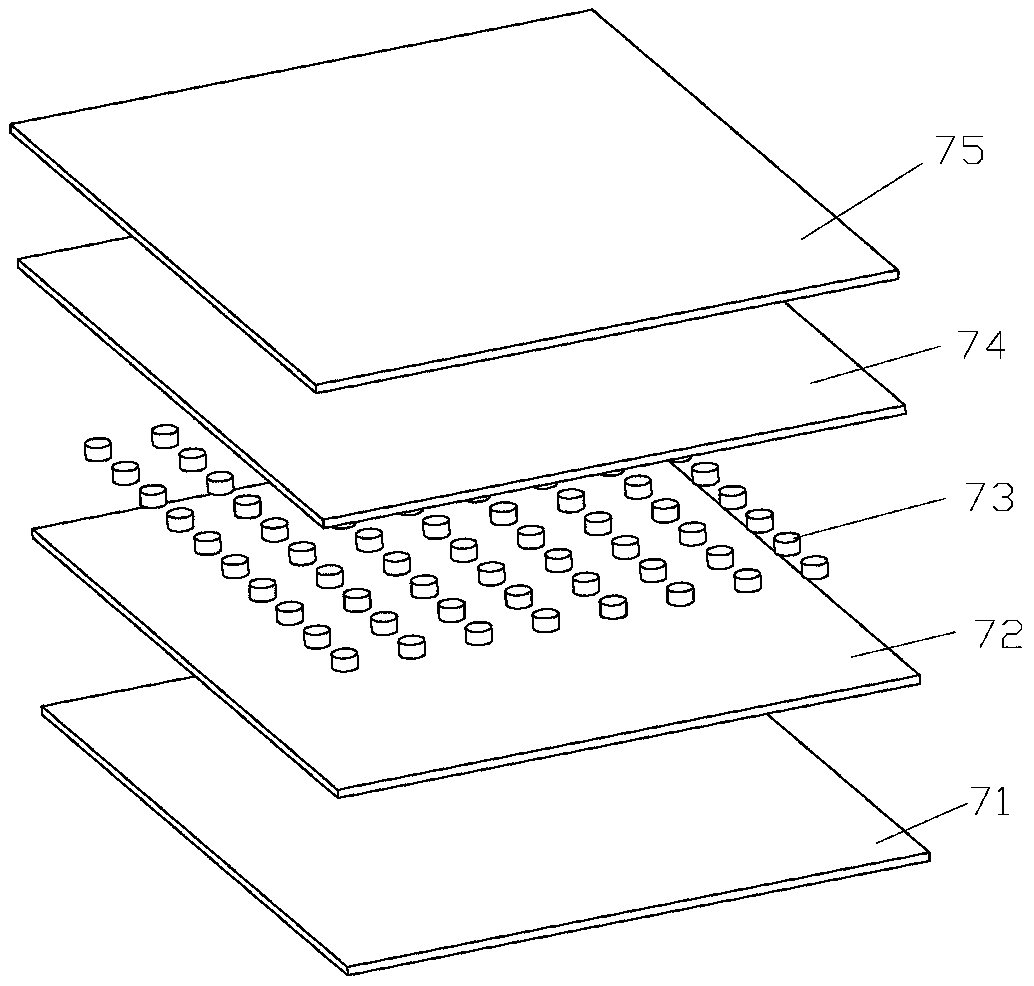
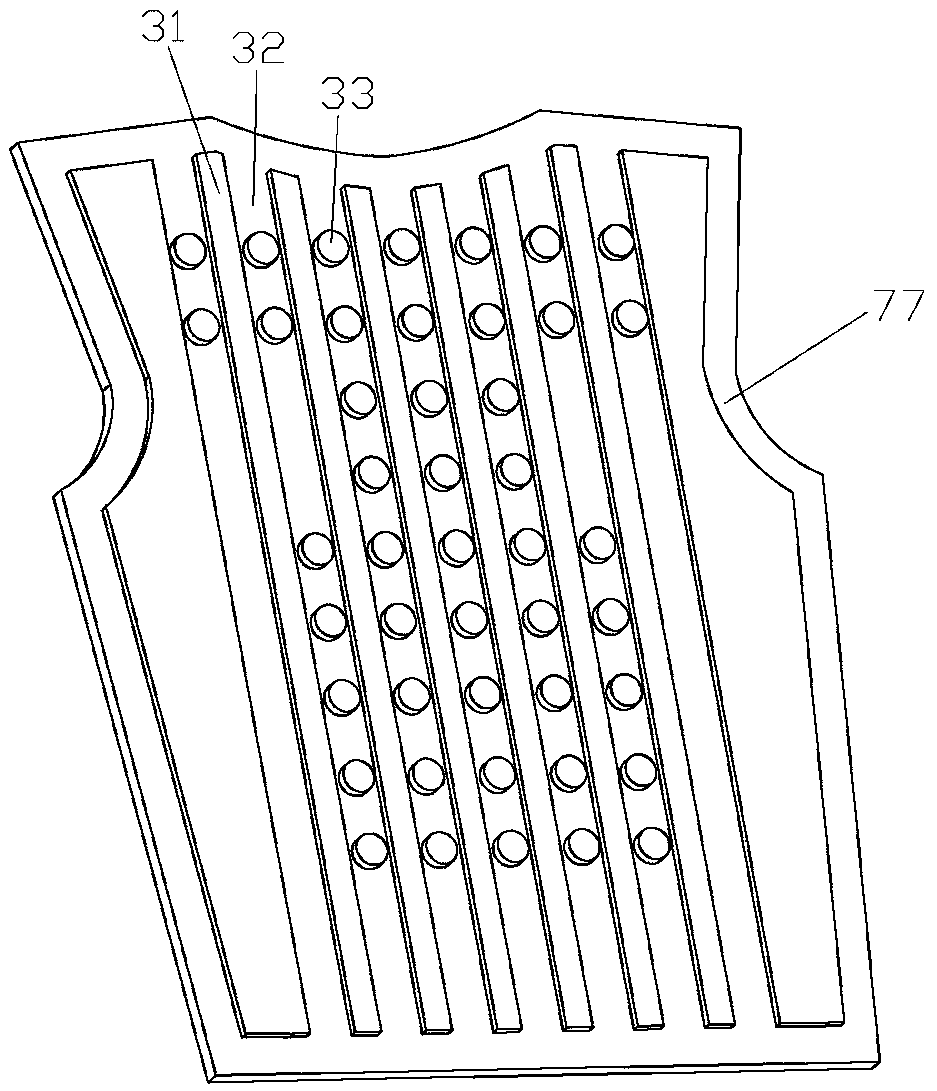
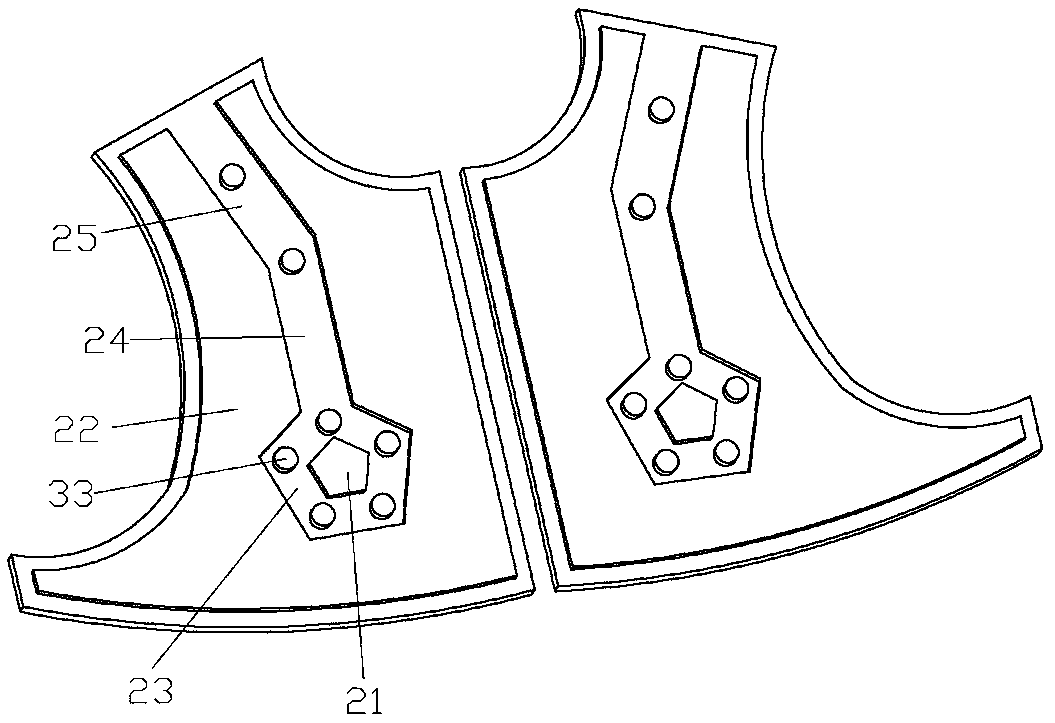
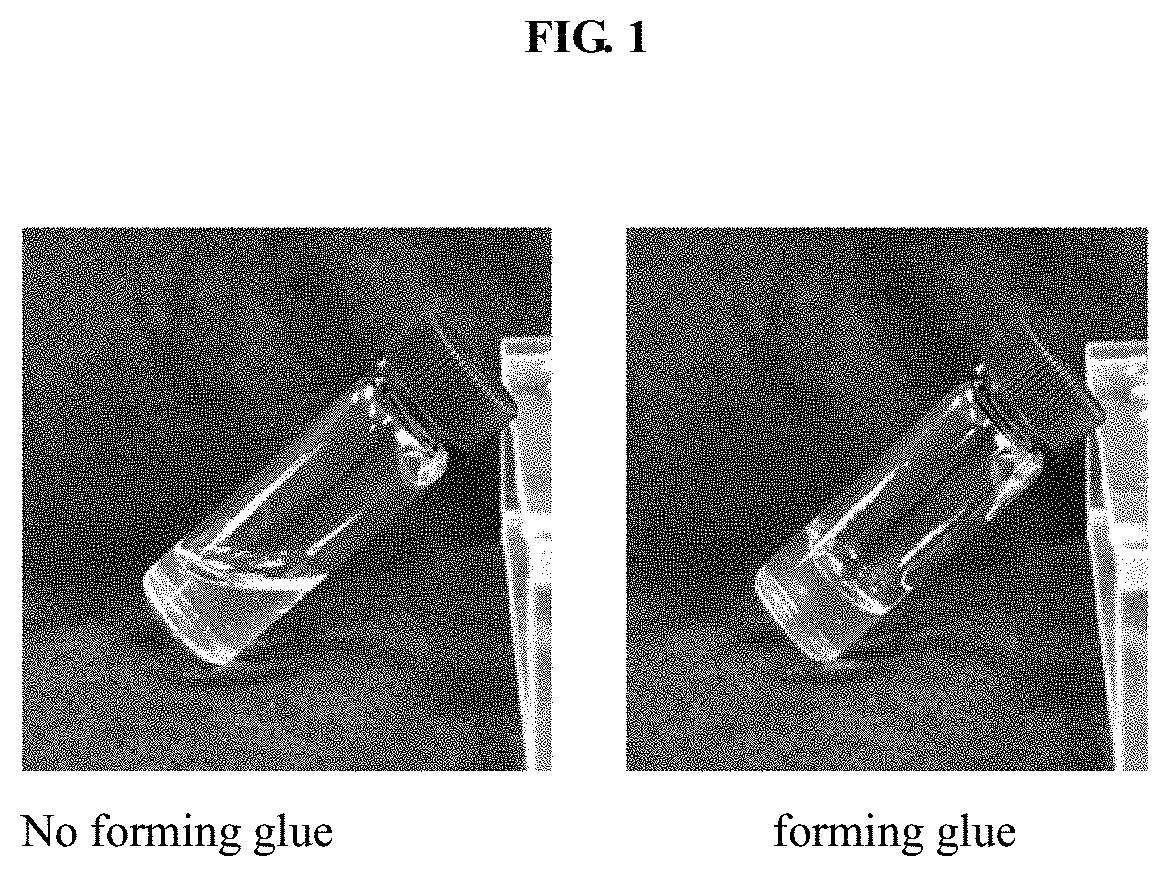
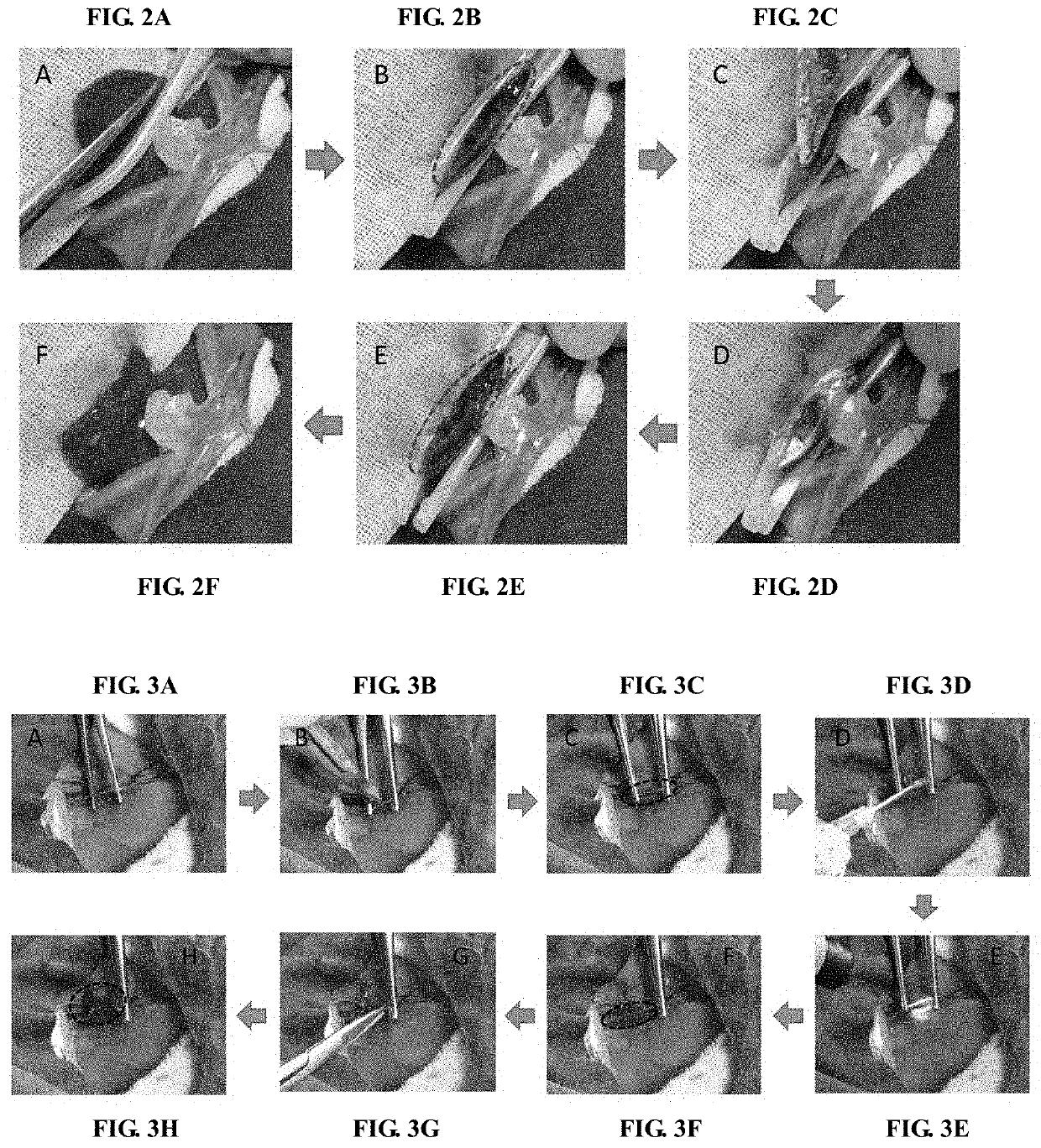
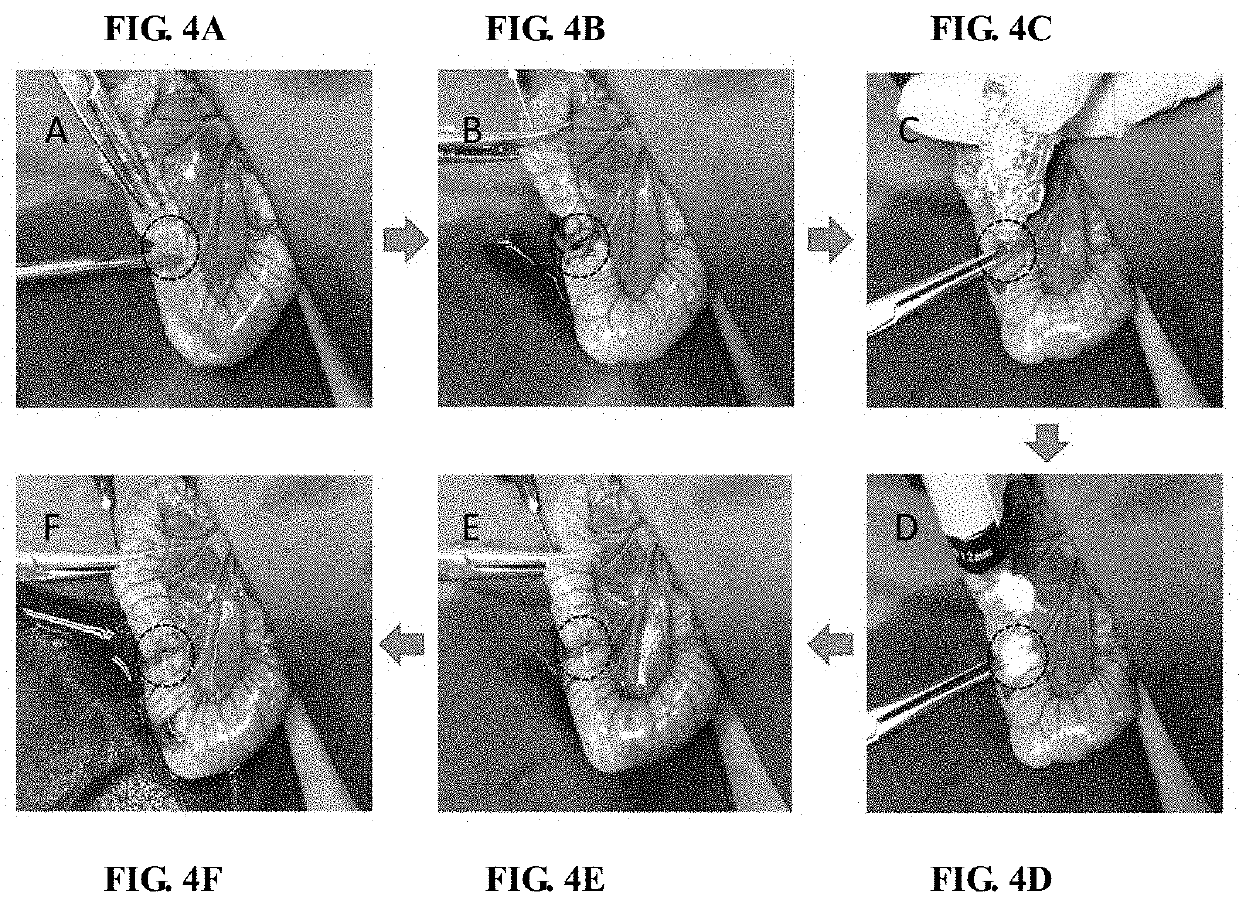
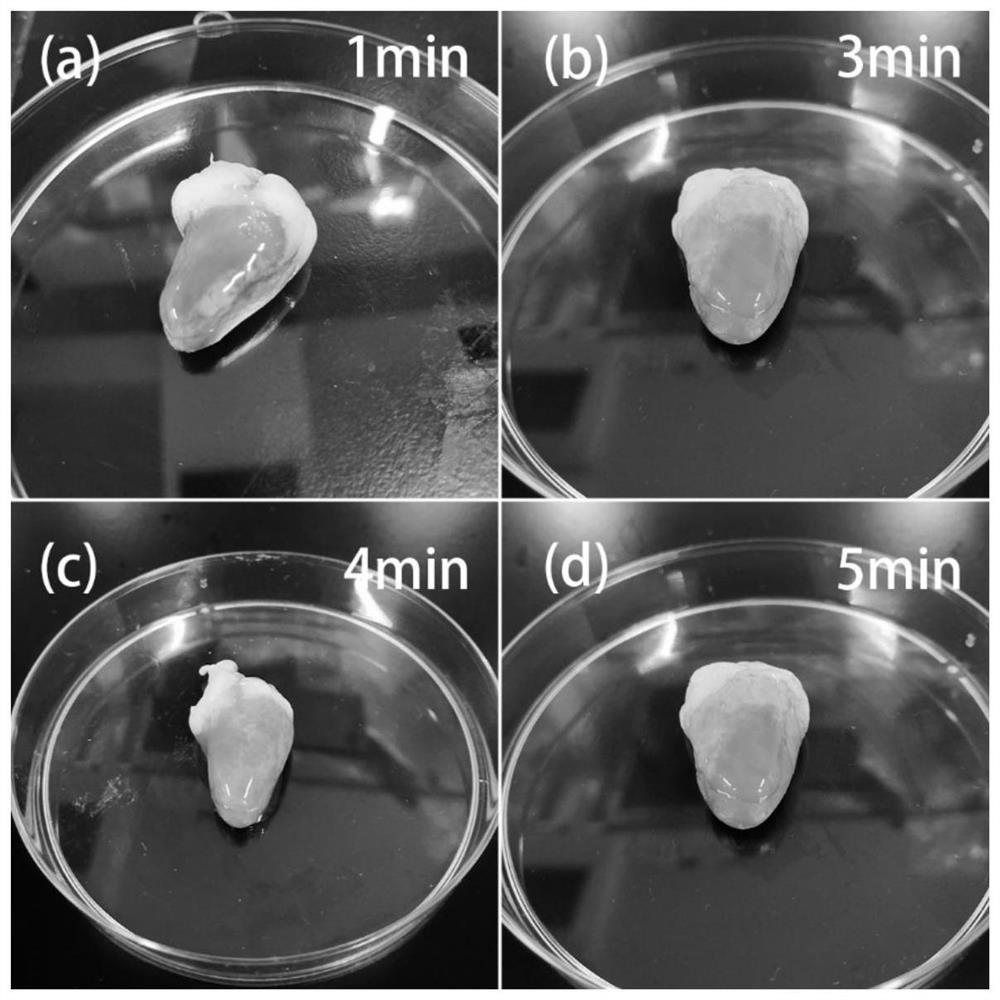
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Tissue binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
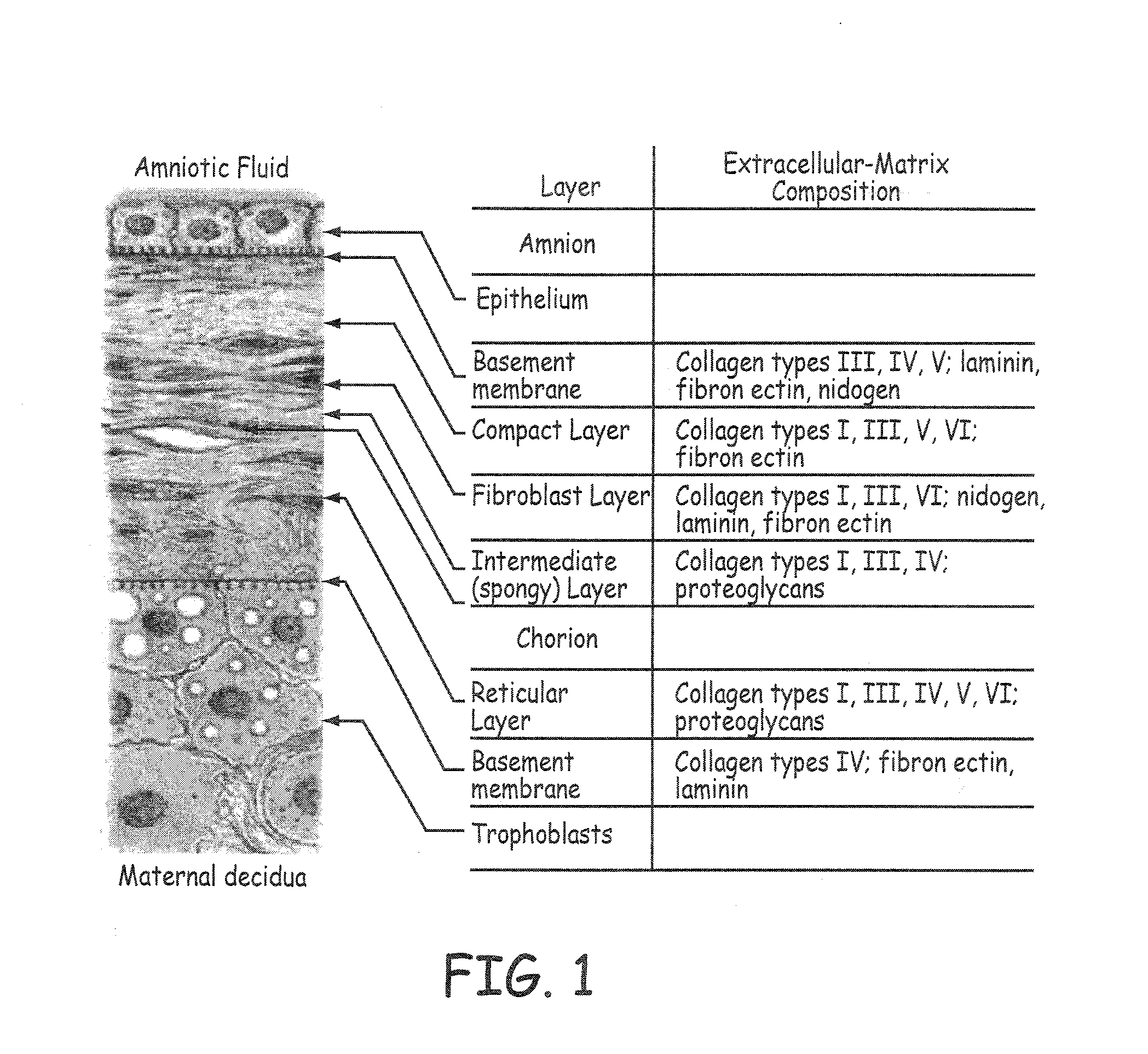
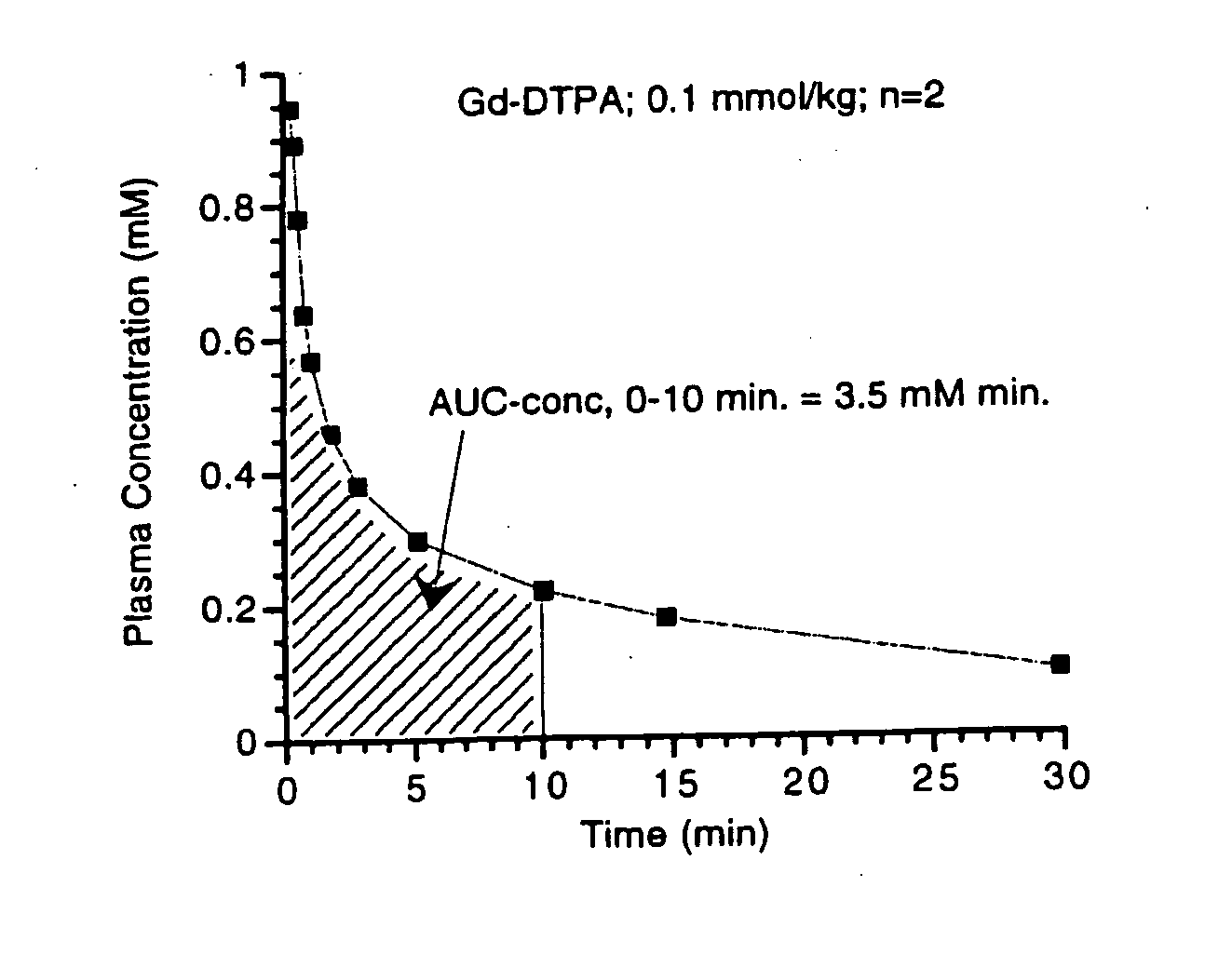
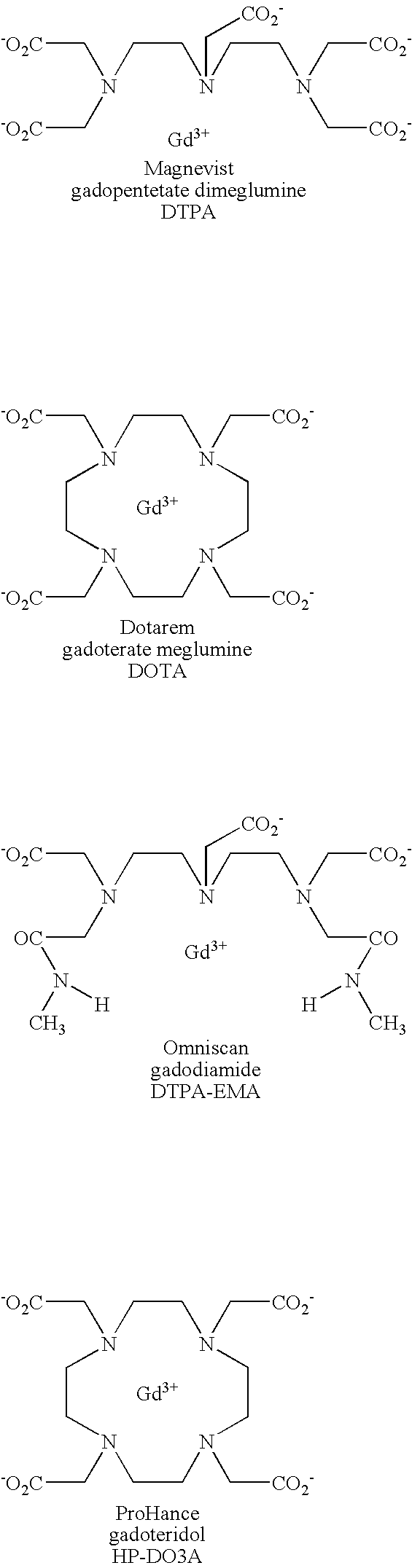
Tissue Binding. According to their physicochemical properties (e.g. lipophilicity and solubility) compounds can bind to different kinds of tissues, such as fat, brain, liver, and kidney, causing accumulation of the compound in the body outside of blood circulation.
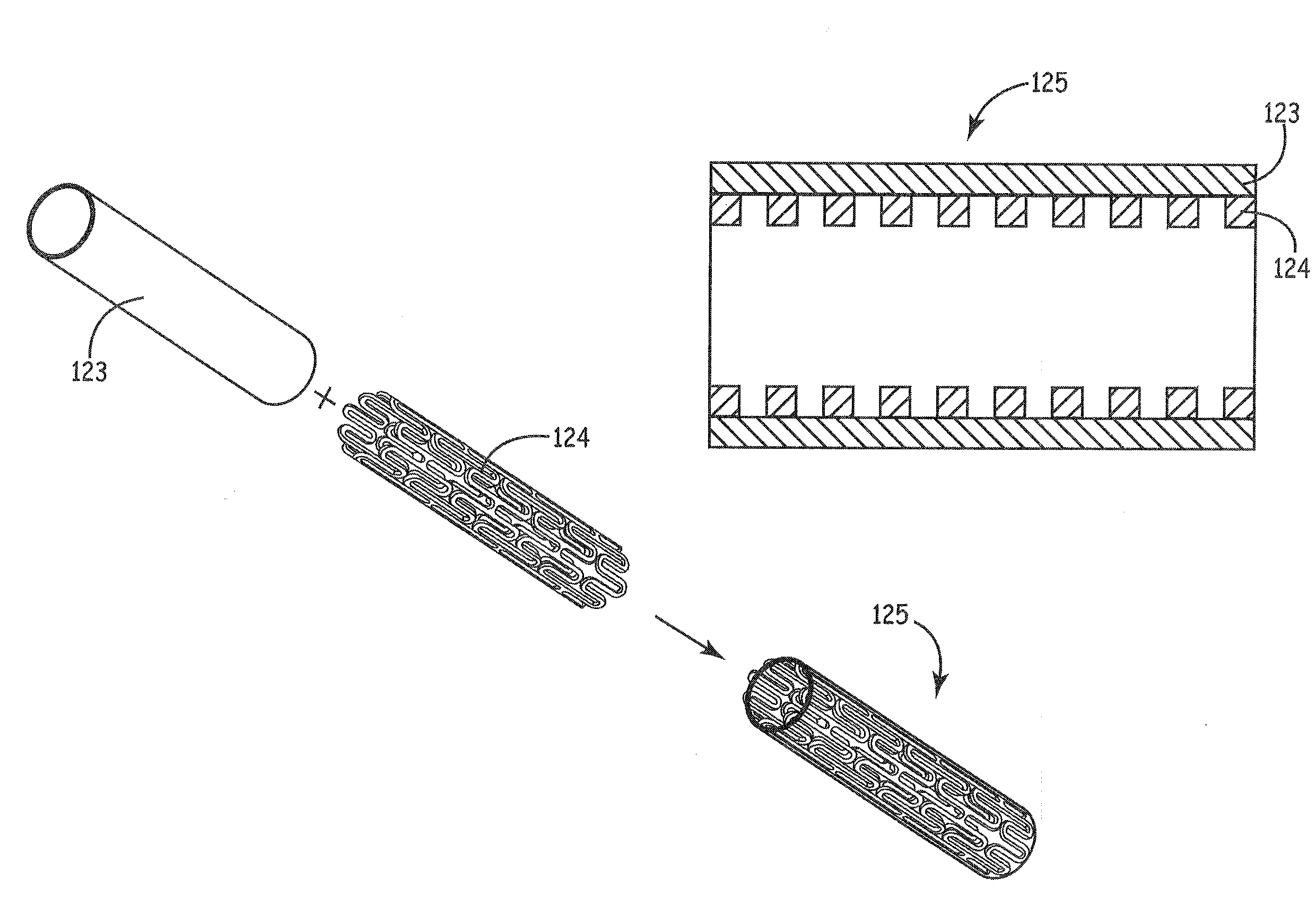
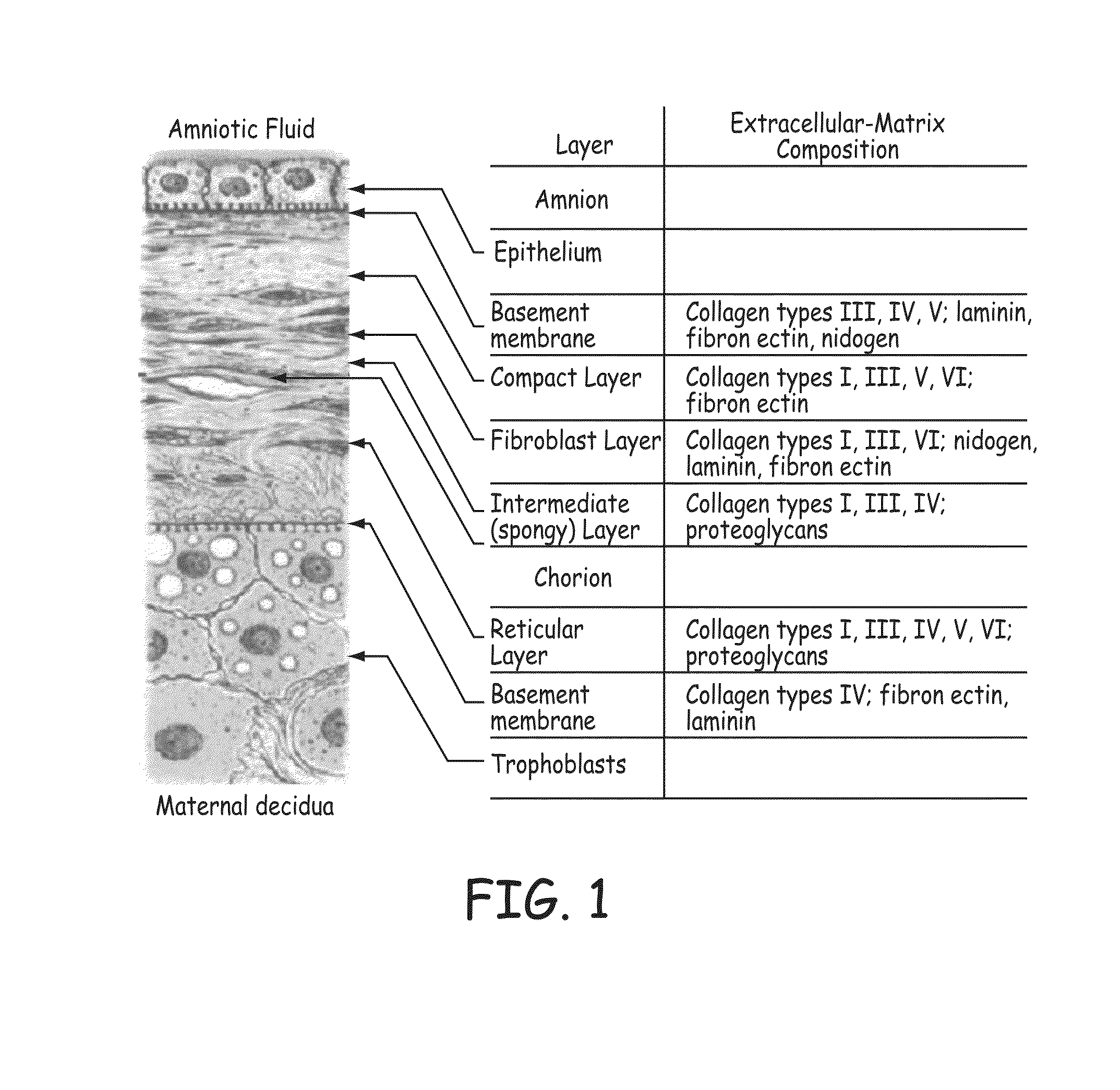
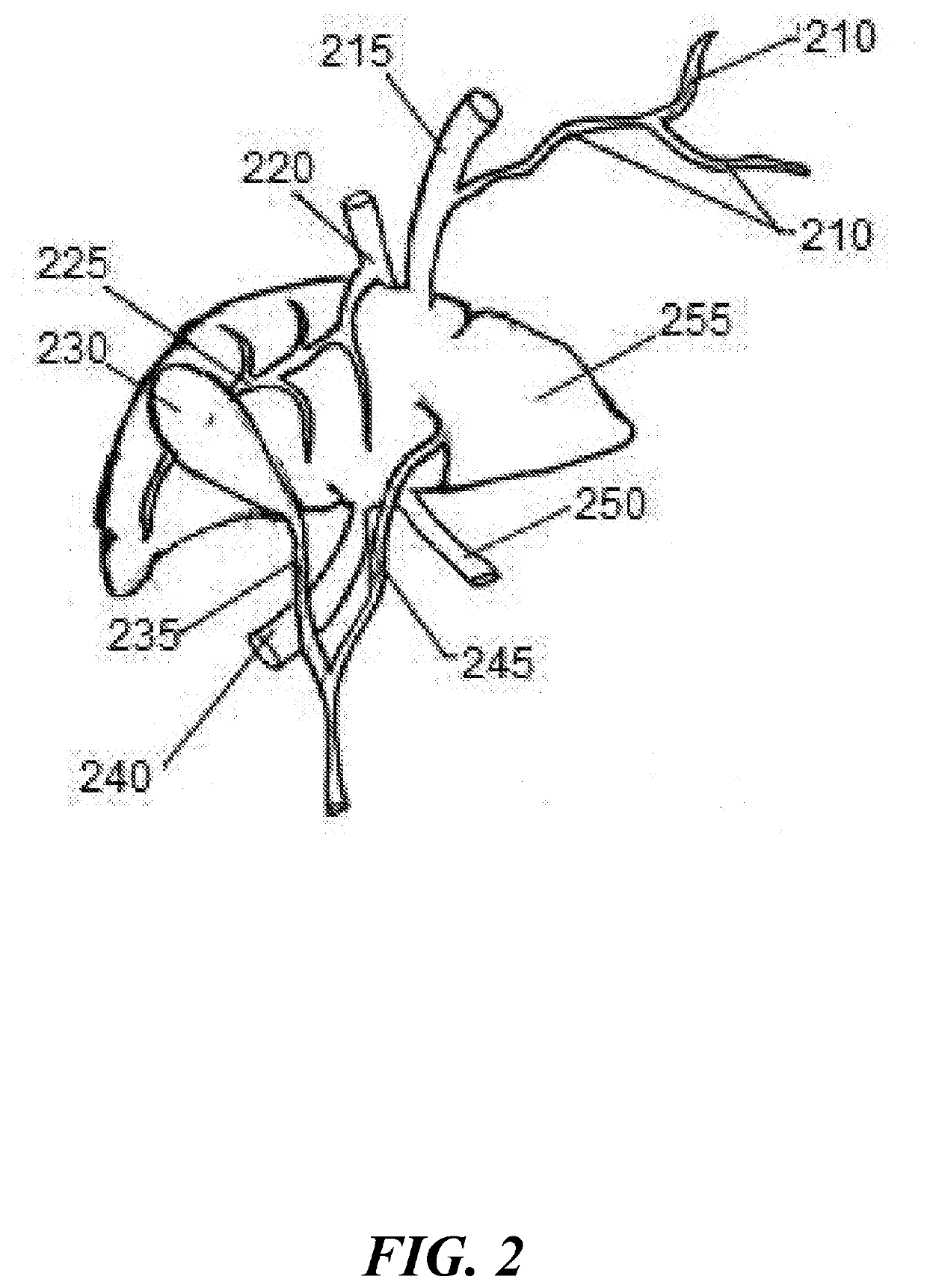
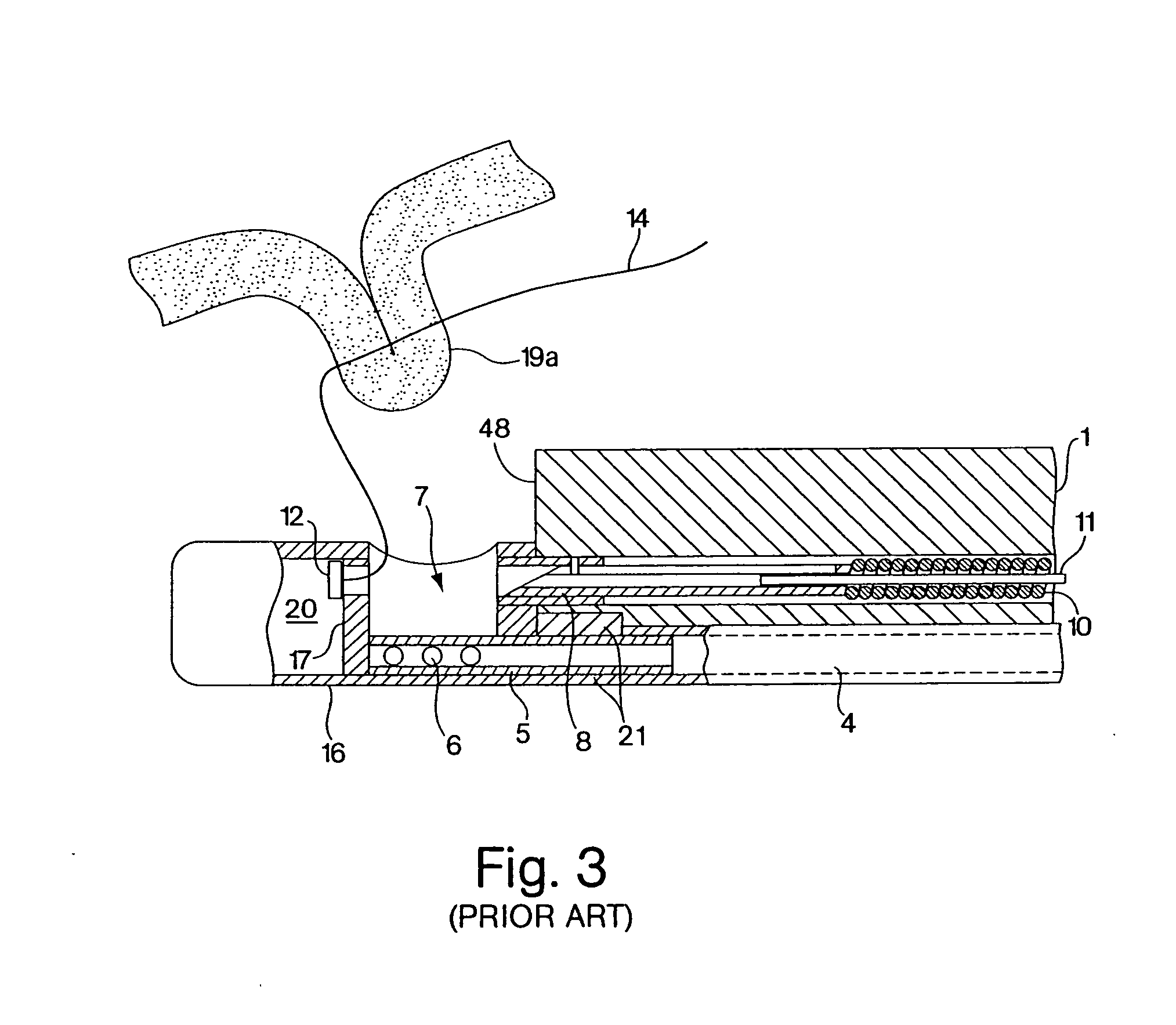
Stents modified with material comprising amnion tissue and corresponding processes
A stent scaffold combined with amniotic tissue provides for a biocompatible stent that has improved biocompatibility and hemocompatibility. The amnion tissue can be variously modified or unmodified form of amnion tissue such as non-cryo amnion tissue, solubilized amnion tissue, amnion tissue fabric, chemically modified amnion tissue, amnion tissue treated with radiation, amnion tissue treated with heat, or a combination thereof. Materials such as polymer, placental tissue, pericardium tissue, small intestine submucosa can be used in combination with the amnion tissue. The amnion tissue can be attached to the inside, the outside, both inside and outside, or complete encapsulation of the stent scaffold. In some embodiments, at least part of the covering or lining comprises a plurality of layers of amnion tissue. The method of making the biocompatible stent and its delivery and deployment are also discussed.
Owner:PEYTANT SOLUTIONS INC
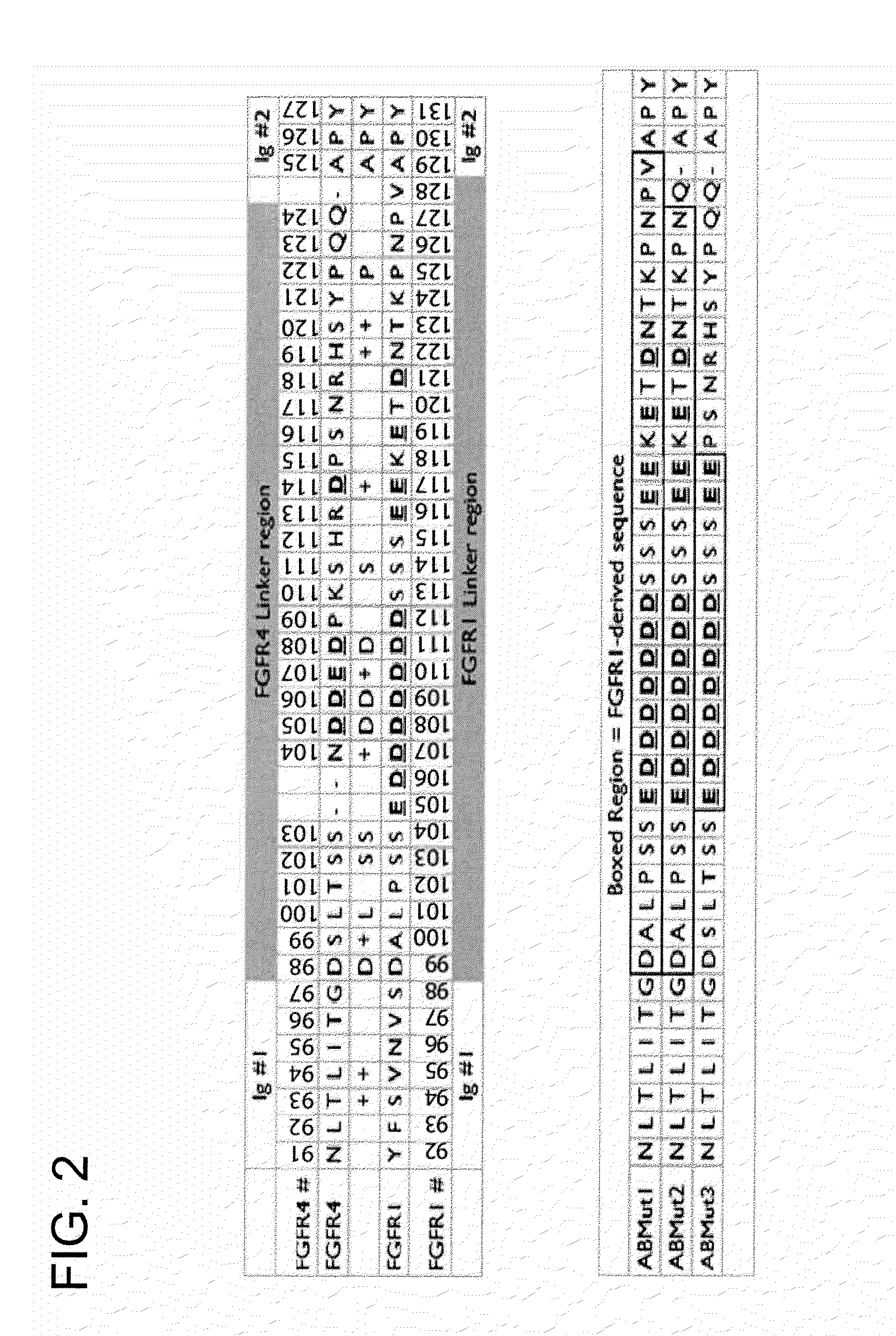
FGFR Extracellular Domain Acidic Region Muteins
InactiveUS20100087627A1Decreased ECM bindingImprove bioavailabilitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMutated proteinPolynucleotide
Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) extracellular domain (ECD) acidic region muteins that have been engineered to exhibit decreased tissue binding by increasing the number of acidic amino acid residues within the D1-D2 linker region are provided. Polynucleotides encoding FGFR ECD acidic region muteins are also provided. Methods of making FGFR ECD acidic region muteins, and methods of using such molecules to treat proliferative disorders, including cancers, disorders of angiogenesis, and macular degeneration, are also provided.
Owner:FIVE PRIME THERAPEUTICS
System and Method For Magnetic-Nanoparticle, Hyperthermia Cancer Therapy
InactiveUS20100292564A1Overcomes drawbackElectrotherapyMagnetic measurementsMedical imaging dataMagnetite Nanoparticles
A system and method is provided for performing and monitoring a magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia process on a subject having received a dose of a magnetic nanoparticle configured to bind to tissue within a target area of the subject. A low-field MRI system is utilized having a static magnetic field and a radio frequency (RF) system configured to receive MRI data from the target area. A hyperthermia system is coupled to the low-field MRI system and configured to generate a hyperthermia excitation field configured to cause the magnetic nanoparticle to rotate at a lag with respect to a magnetic field experienced by the magnetic nanoparticle to cause a temperature increase in the target area. The MRI system is configured to acquire medical imaging data from the target area and reconstruct images therefrom indicating at least one of a spatial distribution of the nanoparticle in and a temperature of the target area.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
FGFR extracellular domain acidic region muteins
InactiveUS8338569B2Preventing tissue bindingGreater ECM bindingSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMutated proteinPolynucleotide
Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) extracellular domain (ECD) acidic region muteins that have been engineered to exhibit decreased tissue binding by increasing the number of acidic amino acid residues within the D1-D2 linker region are provided. Polynucleotides encoding FGFR ECD acidic region muteins are also provided. Methods of making FGFR ECD acidic region muteins, and methods of using such molecules to treat proliferative disorders, including cancers, disorders of angiogenesis, and macular degeneration, are also provided.
Owner:FIVE PRIME THERAPEUTICS
Adhesive sealant composition
InactiveUSRE38158E1High bonding strengthOrganic active ingredientsNon-fibrous pulp additionAqueous bufferWater soluble
This invention is related to an adhesive composition which may be used to bond or seal tissue in vivo. The adhesive composition is readily formed from a two component mixture which includes a first part of a protein, preferably a serum albumin protein, in an aqueous buffer having a pH in the range of about 8.0-11.0 and a second part of a water-compatible or water-soluble bifunctional crosslinking agent. When the two parts of the mixture are combined, the mixture is initially a liquid which cures in vivo on the surface of tissue in less than about one minute to give a strong, flexible, pliant substantive composition which bonds to the tissue and is absorbed in about four to sixty days. The adhesive composition may be used either to bond tissue, to seal tissue or to prevent tissue adhesions caused by surgery.
Owner:NEOMEND INC
Tissue container with auxiliary compartment
A tissue container comprising a tissue receiving enclosure and a re-closable opening for dispensing tissues there through, and an associated auxiliary compartment holding a preparation for use in conjunction with the tissues.
Owner:DE VRIES LIAT
Phage displayed cell binding peptides
InactiveUS7704953B2Peptide-nucleic acidsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCell bindingBinding peptide
The present disclosure relates to the construction, expression, and selection of genes that encode novel Trp cage polypeptides with desirable cell and / or tissue binding properties, as well as the novel Trp cage polypeptides themselves. A polypeptide of this disclosure may contain all or part of amino acid sequence AAADX1YX2QWLX3X4X5GPX6SGRPPPX7 (SEQ ID NO: 4), wherein Xn represents an amino acid found in position n, the polypeptide comprising a tryptophan cage (Trp cage).
Owner:MDRNA
Contrast-enhanced diagnostic imaging method for monitoring interventional therapies
InactiveUS20050118103A1Increase contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryState dependentImage contrast
The present invention relates to a contrast-enhanced diagnostic imaging method for monitoring the efficacy of interventional therapies. The contrast agents useful in this method comprise an image-enhancing moiety (IEM) and a state-dependent tissue binding moiety (SDTBM). These contrast agents exhibit state-dependent binding to one or more components of a targeted tissue or tissue component and provide a detectable change in the signal characteristics of the agent once bound to the targeted tissue. As a result, these agents exhibit a binding affinity for, and thus image contrast of, the targeted tissue which changes as the tissue-state changes during therapy.
Owner:LANTHEUS MEDICAL IMAGING INC
Stents modified with material comprising amnion tissue and corresponding processes
A stent scaffold combined with amniotic tissue provides for a biocompatible stent that has improved biocompatibility and hemocompatibility. The amnion tissue can be variously modified or unmodified form of amnion tissue such as non-cryo amnion tissue, solubilized amnion tissue, amnion tissue fabric, chemically modified amnion tissue, amnion tissue treated with radiation, amnion tissue treated with heat, or a combination thereof. Materials such as polymer, placental tissue, pericardium tissue, small intestine submucosa can be used in combination with the amnion tissue. The amnion tissue can be attached to the inside, the outside, both inside and outside, or complete encapsulation of the stent scaffold. In some embodiments, at least part of the covering or lining comprises a plurality of layers of amnion tissue. The method of making the biocompatible stent and its delivery and deployment are also discussed.
Owner:PEYTANT SOLUTIONS INC
Contrast-enhanced diagnostic imaging method for monitoring interventional therapies
InactiveUS6861045B1Increase contrastBiocideNMR/MRI constrast preparationsState dependentImage contrast
The present invention relates to a contrast-enhanced diagnostic imaging method for monitoring the efficacy of interventional therapies. The contrast agents useful in this method comprise an image-enhancing moiety (IEM) and a state-dependent tissue binding moiety (SDTBM). These contrast agents exhibit state-dependent binding to one or more components of a targeted tissue or tissue component and provide a detectable change in the signal characteristics of the agent once bound to the targeted tissue. As a result, these agents exhibit a binding affinity for, and thus image contrast of, the targeted tissue which changes as the tissue-state changes during therapy.
Owner:LANTHEUS MEDICAL IMAGING INC
Kit for adhering biological hard tissues
A kit for bonding to biological hard tissues, containing a phosphorylated polysaccharide, a polyvalent metal salt other than phosphates, and a solvent. The adhesive composition for biological hard tissues provided by the kit for bonding to biological hard tissues is suitably used in for medical uses, such as cement for bones or dental cement. In addition, since the adhesive composition has excellent bio-absorbability, it is useful as fusion materials for artificial joint prosthesis, fusion materials for spine fracture, fusion materials for extremity fracture, filling materials for bone tumors in the region of orthopedics, filling materials and restorative materials at dental caries-defective sites, luting materials for prosthetic restorative materials such as inlay and crown, pulp-capping and lining materials, implant surface treatment materials, periodontal disease therapeutic materials, hyperesthesia preventive materials, dental pulp capping materials, substrates for DDS, substrates for systems engineering, and tissue bonding materials in the dental region.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA +1
Tissue specific markers for preoperative and intraoperative localization and visualization of tissue
PendingUS20210106696A1Accurate distinctionDiagnostics using lightLuminescence/biological staining preparationRadiologyTissue specific
Surgeons may face the difficulty of preoperatively selecting the location for making an incision and intraoperatively identifying and differentiating targeted tissue for removal or for identification so that it is not removed along with neighboring or non-target tissue or so that neighboring or non-target tissue is not nicked, harmed, or removed accidentally. A tissue specific marker can include an aptamer or an affimer configured to bind to a pre-selected target tissue and one or more indicator elements coupled with the aptamer or the affimer. The one or more indicator elements produce a signal thereby allowing identification of the target tissue in a preoperative and operative manner.
Owner:INVUITY
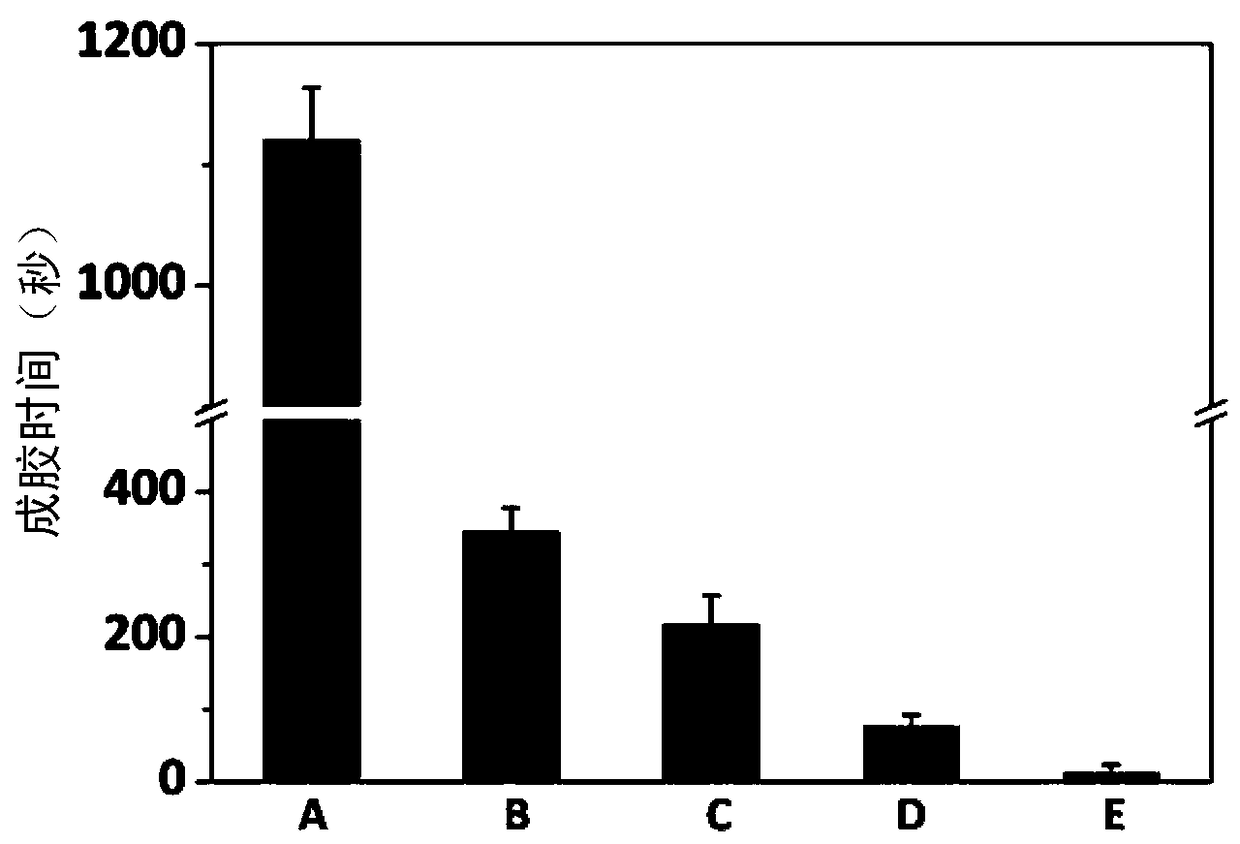
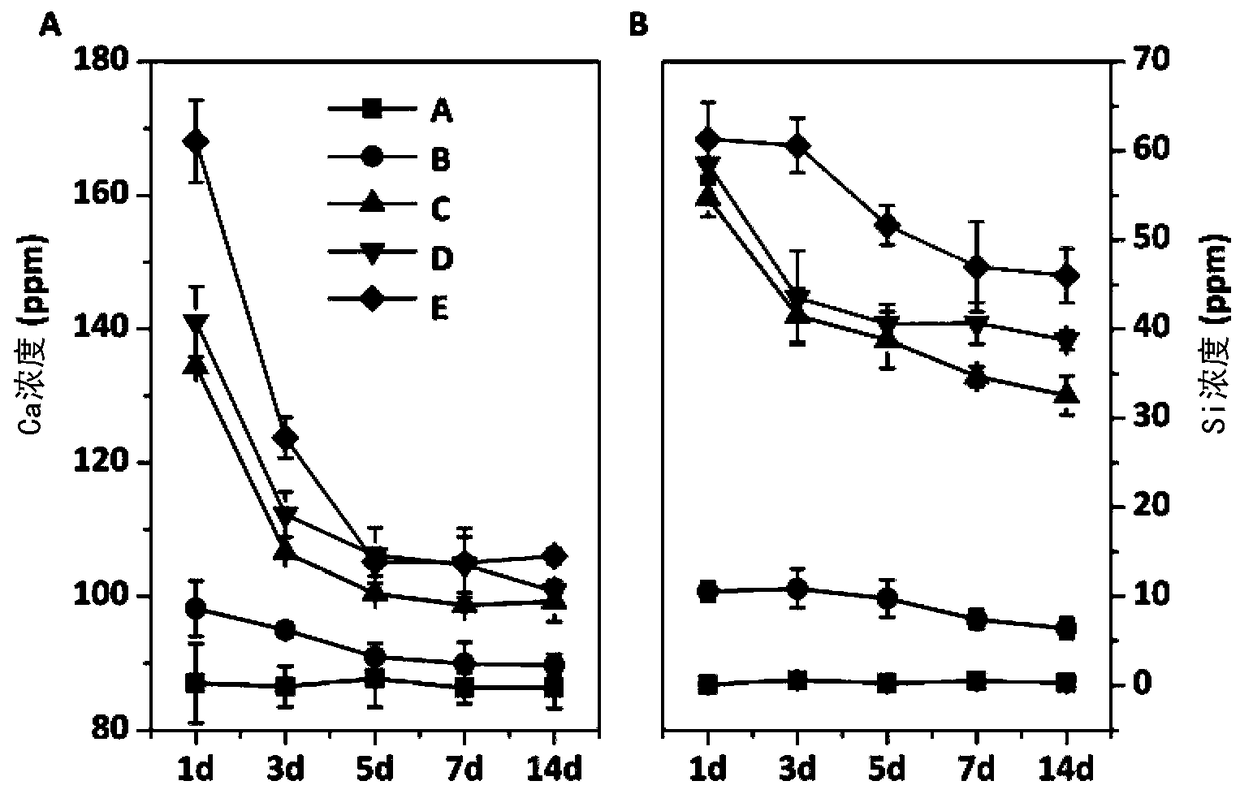
Compound wound dressing with tissue binding performance and preparation method of compound wound dressing
The invention provides a compound wound dressing with tissue binding performance and a preparation method of the compound wound dressing. Bioactive glass / albumin composite hydrogel at least comprisesbioactive glass, albumin, polyethylene glycol containing an electrophilic functional group and buffer solution, pH (potential of hydrogen) of the buffer solution ranges from 5.0 to 8.0, and the raw materials are mixed into gel to obtain the composite hydrogel. The composite hydrogel comprises albumin hydrogel and the bioactive glass loaded into the albumin hydrogel, the content of the albumin hydrogel is 95% or more, and the content of the bioactive glass is 5% or less.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lymph targeted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent with brown algal polysaccharide serving as carrier and preparation method and application of lymph targeted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent with brown algal polysaccharide serving as carrier
ActiveCN105343900AAchieve the purpose of combiningImprove bindingEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsLymphatic vesselLymphatic/immune
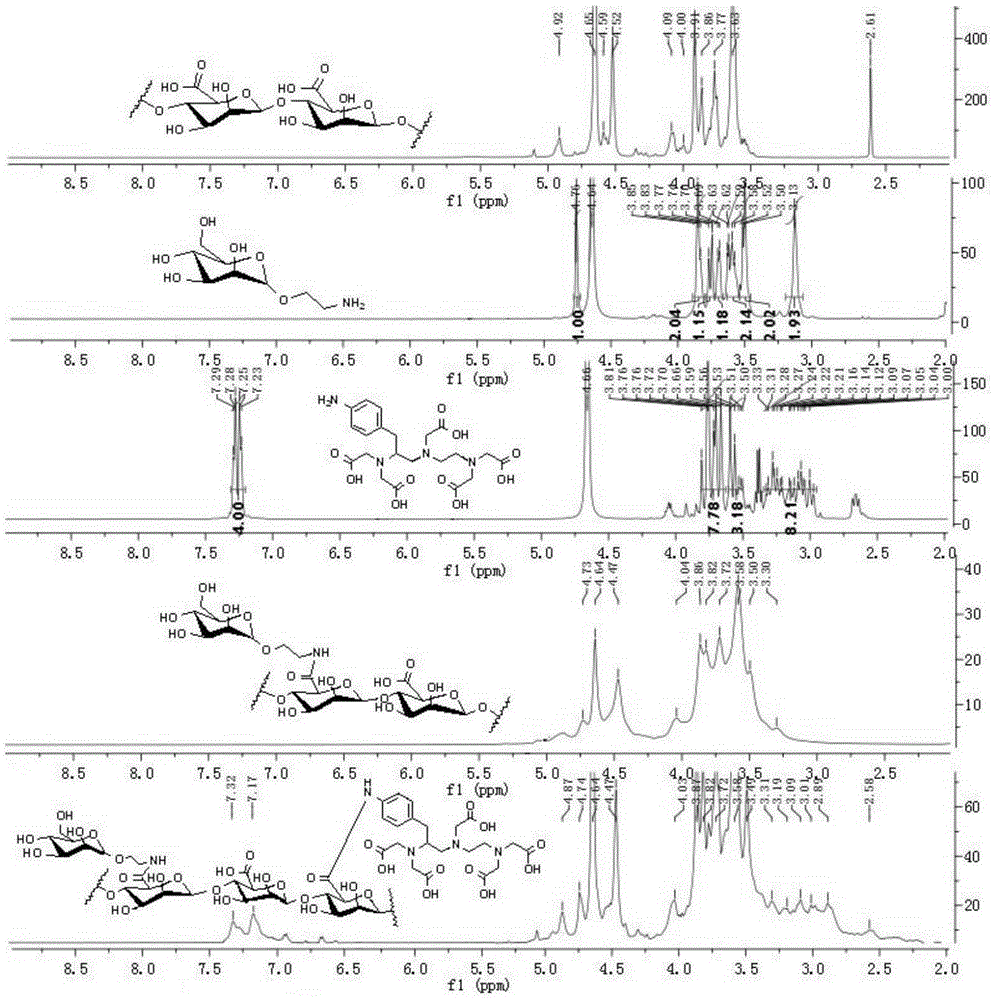
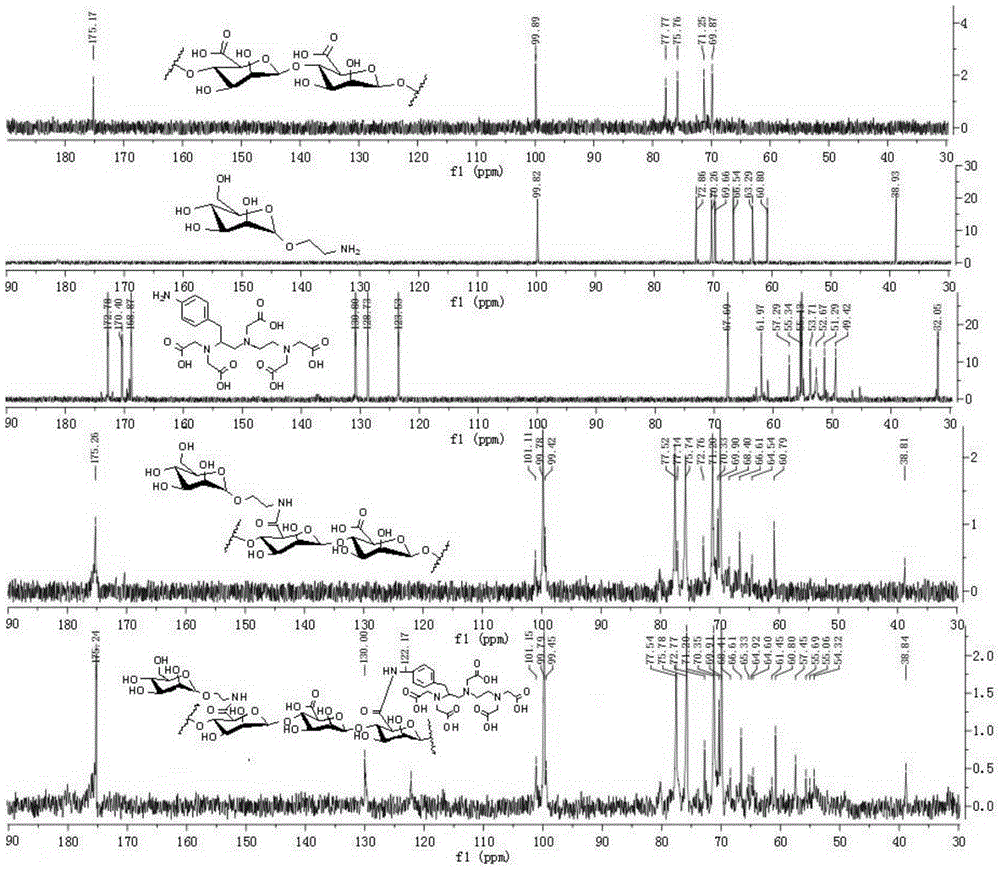
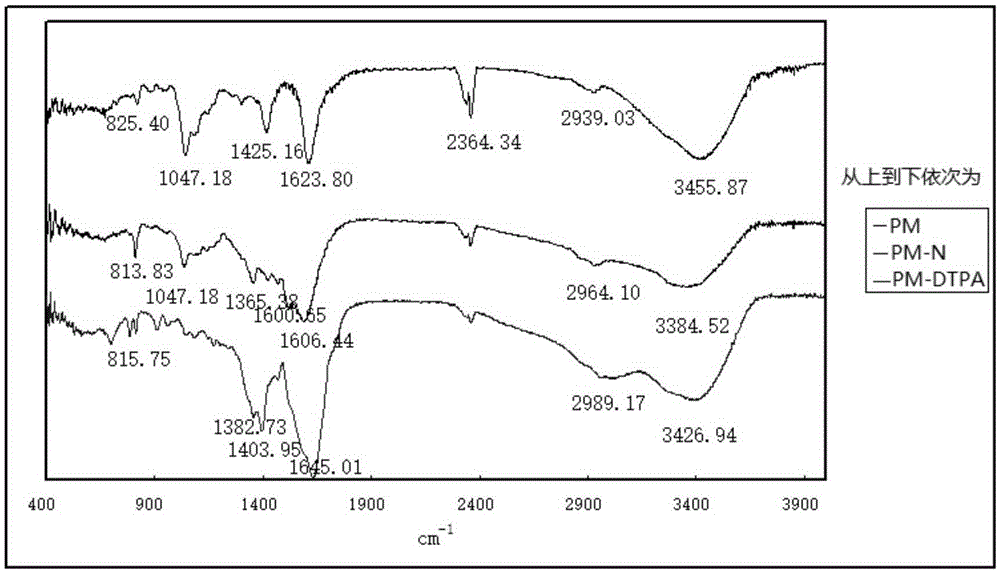
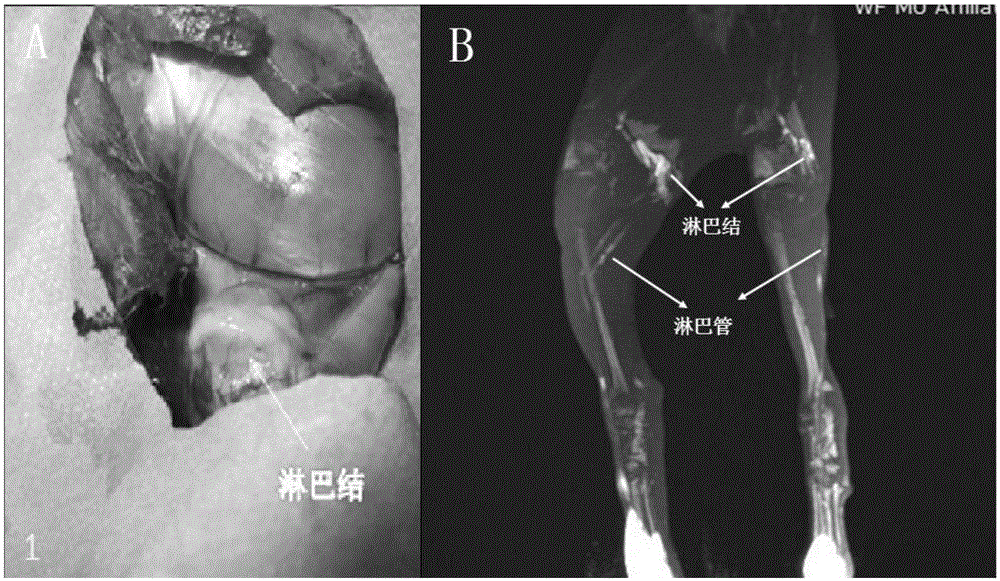
The invention relates to contrast agents for medical science, in particular to a lymph targeted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent with brown algal polysaccharide serving as a carrier and a preparation method and application of the lymph targeted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent with the brown algal polysaccharide serving as the carrier. The macromolecular contrast agent high in water solubility is prepared by taking the brown algal polysaccharide as the carrier, taking mannose or mannose derivatives as a mannose receptor MBP (mannose binding protein) recognition group and taking paramagnetic metal ion chelates as a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging group. Lymph tissue binding force is increased, and combination of the mannose or mannose derivative group introduced into the synthetic contrast agent with mannose receptors enriched in lymph tissues is realized. In addition, after hypodermic injection of the contrast agent, lymph vessels and lymph glands are clearly developed under scanning of a nuclear magnetic resonance equipment, lymph gland signal enhancement rate of one side, with the contrast agent injected, of an animal body is remarkably increased while enhancement time is remarkably prolonged, distinct drawing and precise positioning of the lymph glands and the lymph vessels are realized, and a great significance to examination and diagnosis of lymphatic diseases is achieved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Vital staining contrast agent by using polyuronide as vector, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105148291AActive targetingAids in dissectionIn-vivo testing preparationsSolubilityLymph fluid
The invention relates to medical contrast agents, and particularly relates to a vital staining contrast agent by using polyuronide as a vector, as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. A macromolecular contrast agent with excellent water solubility is prepared by using polyuronide as the vector, mannose or mannose derivatives as a mannose receptor (MBP) recognition group and a paramagnetic metal ion chelate as a magnetic resonance imaging group, the lymphoid tissue binding force is improved, and the aim of binding mannose or mannose derivative group which is introduced into the synthesized contrast agent molecules with the mannose receptor enriched in the lymphoid tissues can be achieved. Furthermore, preoperative lymph imaging mapping is beneficial to intraoperative sentinel lymph node mapping and lymph node cleaning operation in a delicate tumor surgical operating process, and can be widely applied to breast cancer, head and neck cancer, melanotic cancer and other preoperative sentinel lymph node mappings. The contrast agent can be used for simultaneously meeting the requirement for biopsy and magnetic resonance imaging, and is an excellent difunctional lymph target contrast agent.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Endoscopic tissue apposition device with multiple suction ports
InactiveUS20080215069A1Safely abrades tissue sufficientlySuture equipmentsSurgical needlesTherapeutic Endoscopic SurgeryAnatomy
Owner:CR BARD INC
Nucleic acid aptamer capable of binding specifically to pancreatic cancer cells or tissues and use thereof
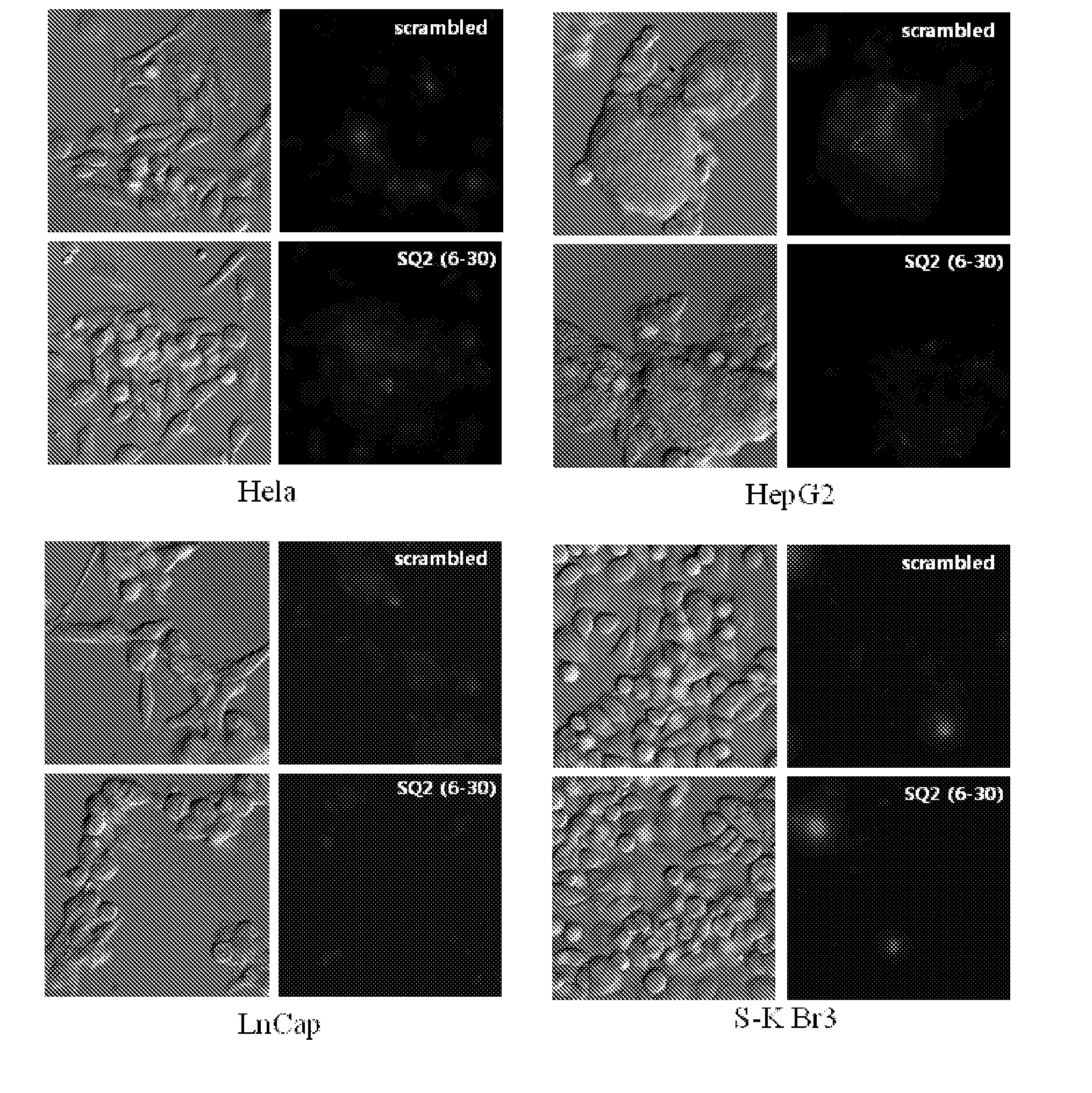
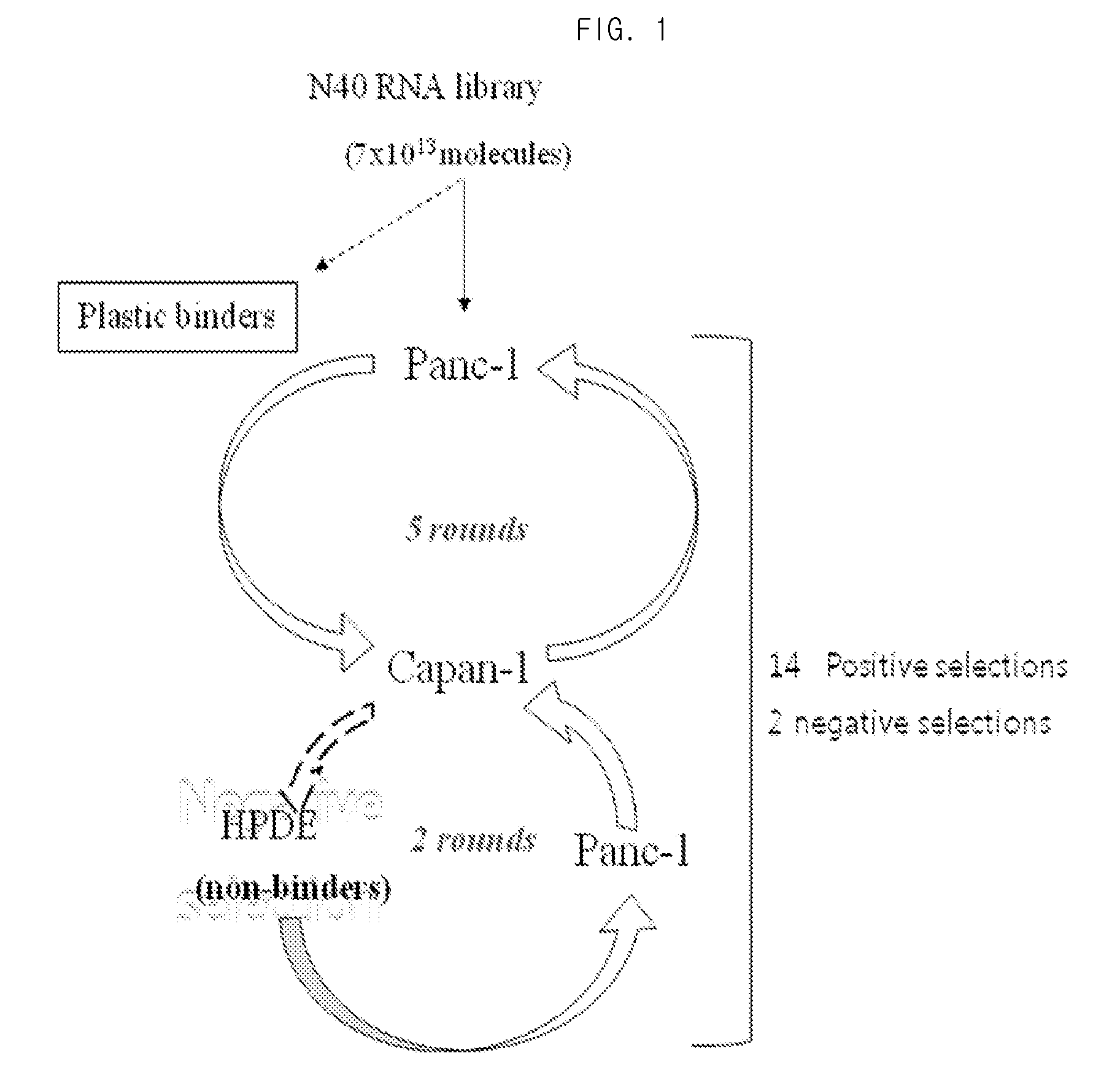
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer which can specifically recognize and bind to pancreatic cancer cells or tissues. The nucleic acid aptamer can bind specifically only to pancreatic cancer cells or tissues without binding to normal pancreatic cancer tissue, and thus can be effectively used as a composition for diagnosing and treating pancreatic cancer. In addition, the nucleic acid aptamer can detect not only the terminal pancreatic cancer cell line Capan-1, but also the early pancreatic cancer cell line Panc-1, and thus can be used for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, thereby contributing to increasing the survival rate of pancreatic cancer patients.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
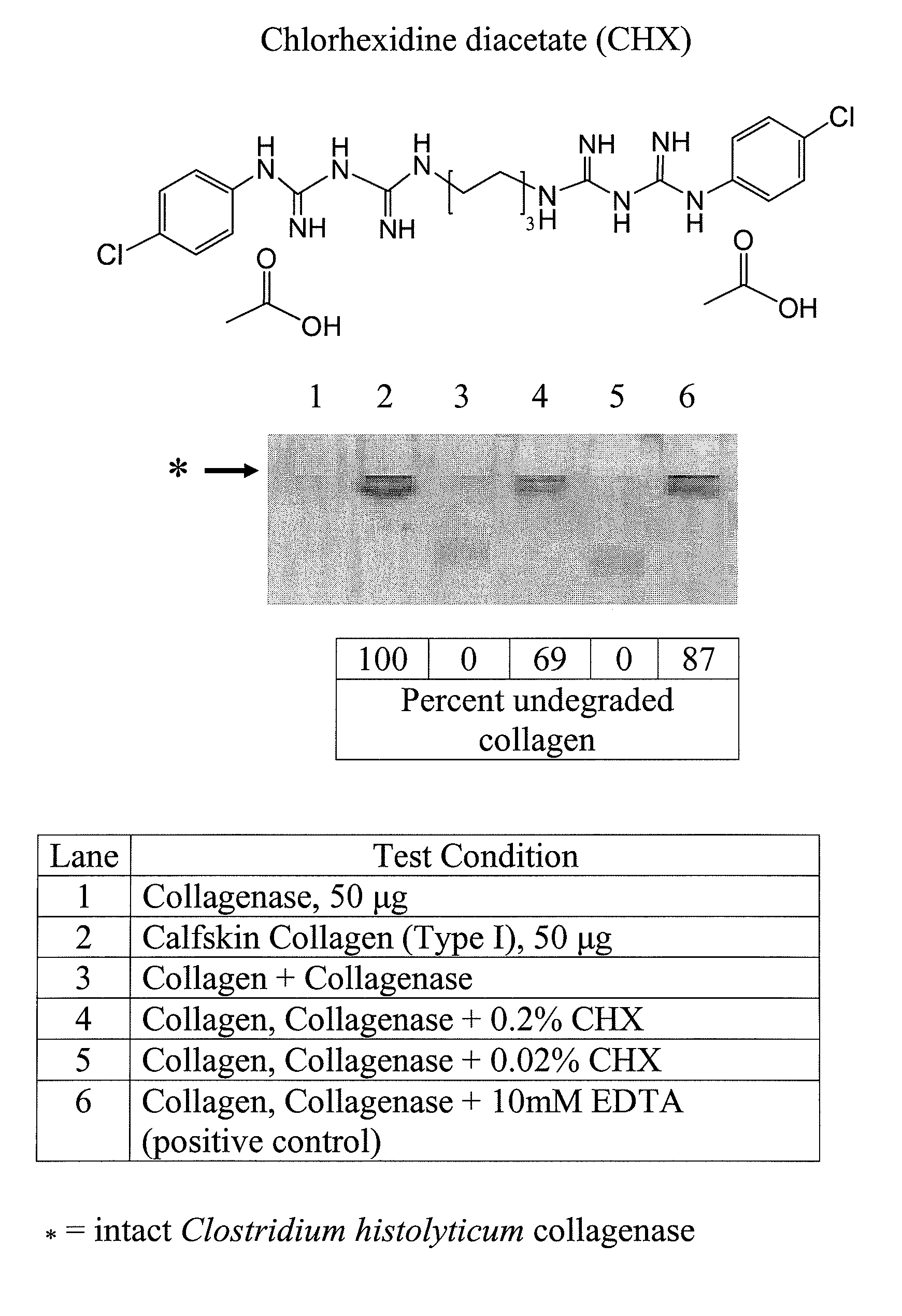
Use of Quaternary Ammonium Compounds to Inhibit Endogenous MMPs in Tooth Dentin
InactiveUS20110256510A1Prevent degradationIncreased durabilityBiocideImpression capsAmmonium compoundsRestorative material
Disclosed are compositions and methods of using such compositions for inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase activity in dental tissue. The compositions, methods and uses may prevent degradation of the bonding between restorative materials and dental tissues, thereby increasing durability and longevity of the restorative material-dental tissue bonds. For example, the compositions, methods, and uses of the present invention may be used for treating carious dental tissue such as by the creation of dental fillings, crowns, bridges, among other techniques, as well as the creation of esthetic laminate restorations.
Owner:GEORGIA HEALTH SCI UNIV RES INST
Technology for repairing dentures by using 3D printing titanium-based composite material
InactiveCN110946665AShort preparation cycleImprove comfortAdditive manufacturing apparatusArtificial teethDenturesFixed prosthodontic
The present invention provides a technology for repairing dentures by using a 3D printing titanium-based composite material. The technology combines 3D printing with an existing digital technology anda new titanium alloy formula is used to solve problems that existing fixed denture restorations are high in porcelain-falling rate and poor in binding with human body tooth tissues.
Owner:山西万佳康齿科技术有限公司
Method of monitoring a biological system by labeling with an apo metal binding protein
InactiveUS7045312B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingMetal binding proteinsProtein insertion
The present invention is directed to reporter molecules and tags that may be used to monitor a target substance in a biological system. More particularly, the present invention relates to the use of an apo metal binding protein as a reporter molecule or tag. An apo metal binding protein may be bound to a protein or tissue or introduced into a cell. The invention also relates to methods of utilizing the apo metal binding protein for detecting a cell expressing a protein of interest, localizing a protein in a cell, and designing a therapeutic agent for treating a disease or infection.
Owner:TIBOTEC NV
Medical hydroxybutyl chitosan sponge and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107033258AGood hemostasisAnti-adhesion tissue repairSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismChemistryTissue engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and hygiene and particularly relates to medical hydroxybutyl chitosan sponge and a preparation method thereof. The sponge is prepared from hydroxybutyl chitosan, sodium chloride, disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate and a plastic agent which is one or more of glycerin and polyethylene glycol. A cross-linking agent is not needed, and the sponge has a thermal-sensitive characteristic after absorbing tissue fluid or blood, can be converted to a gel state when reaching the normal temperature of a human body, is firmly bonded with tissue, has effects of stopping bleeding, preventing adhesion and promoting tissue repair, can be combined with a sterilizing agent, growth factors and other drugs for use, and can also be applied to the fields of tissue engineering and artificial organs.
Owner:惠众国际医疗器械(北京)有限公司
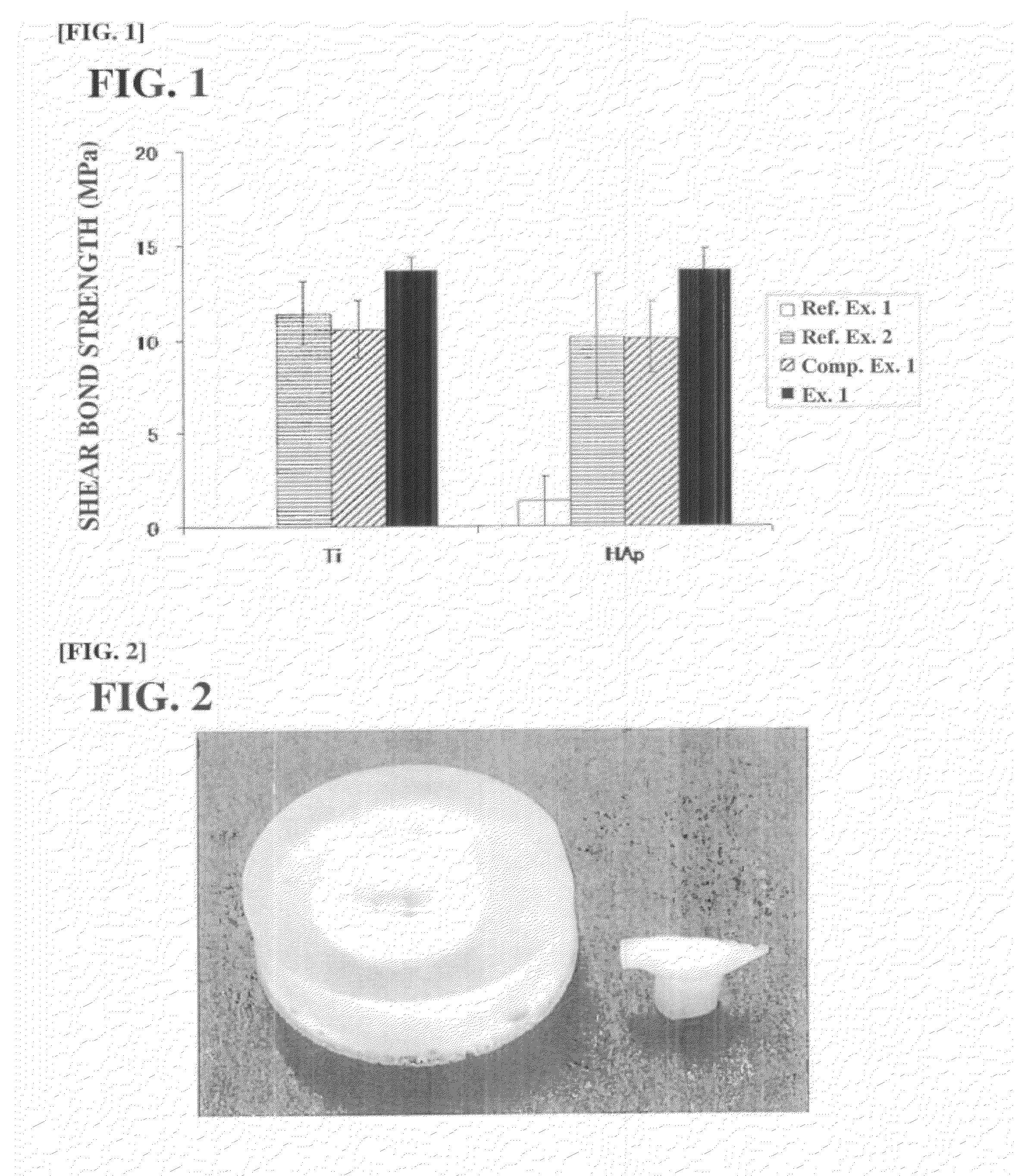
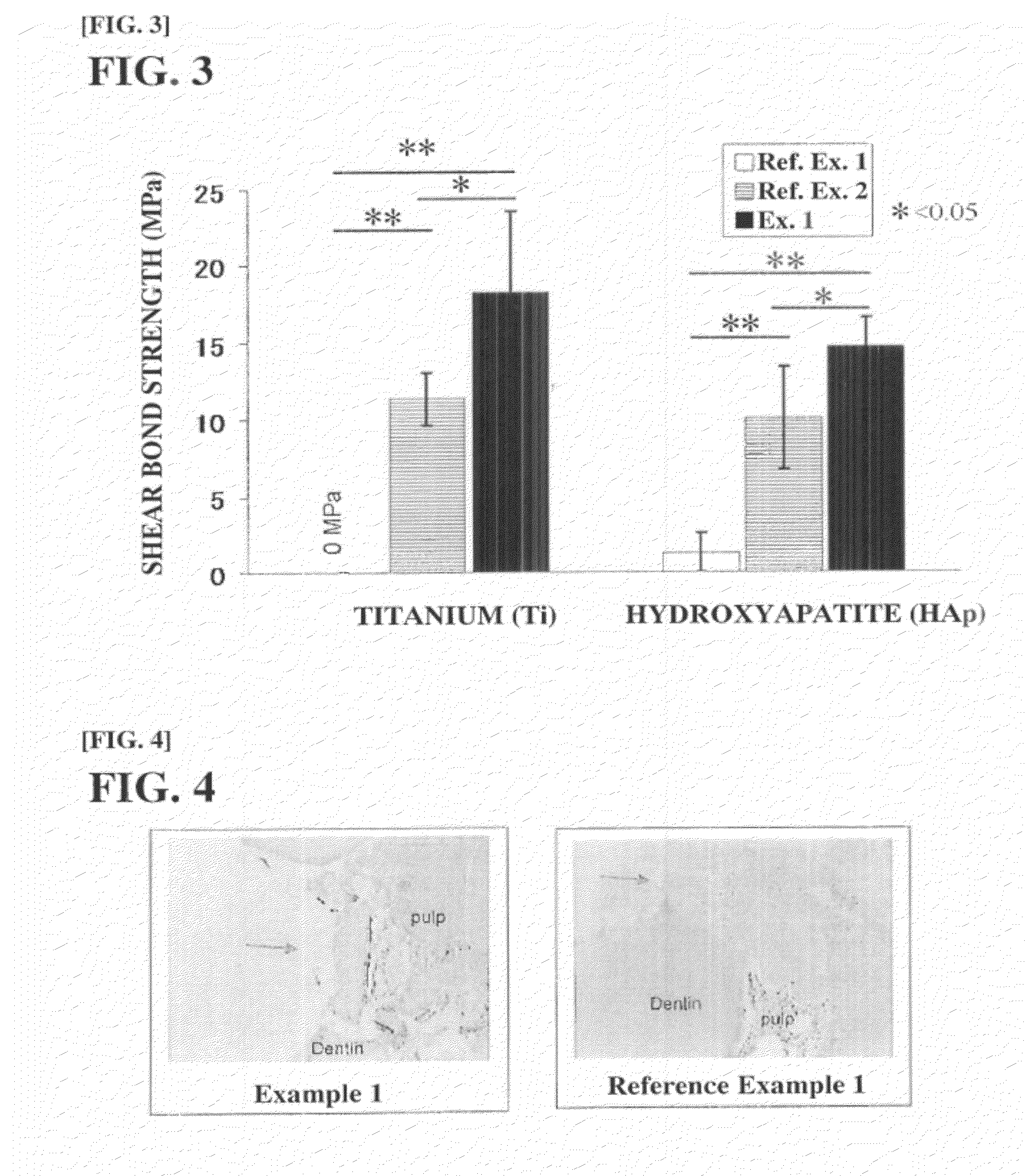
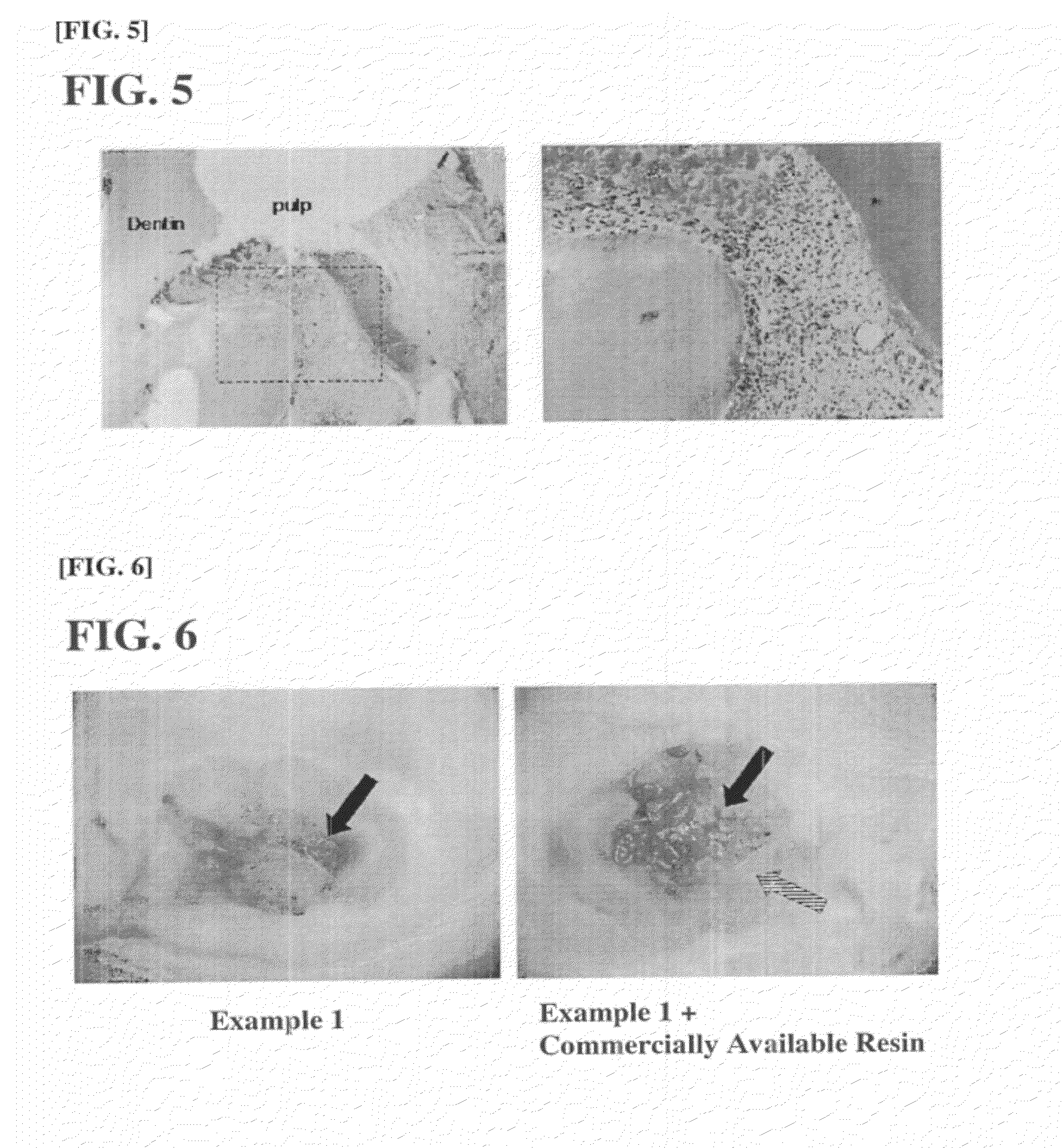
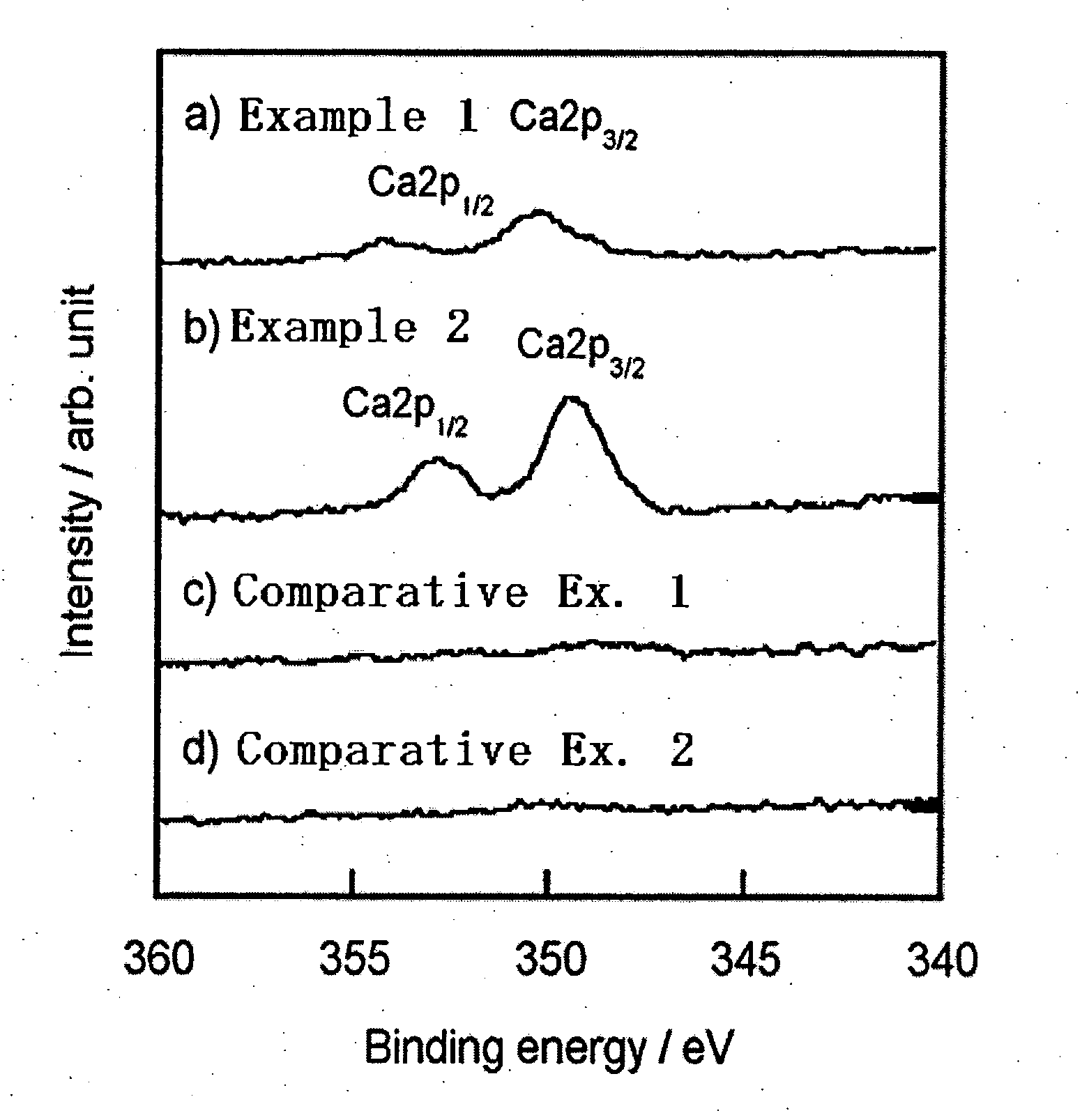
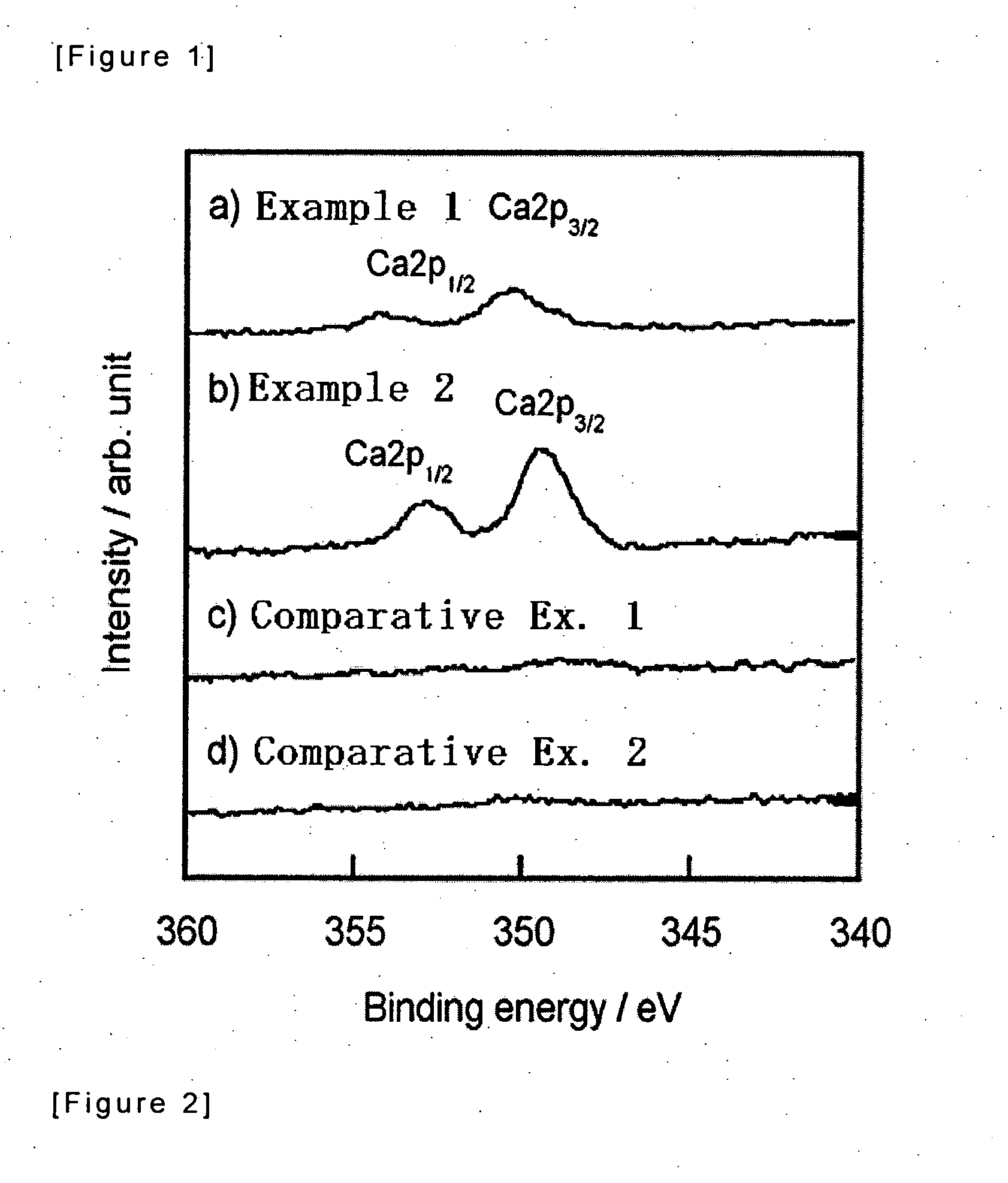
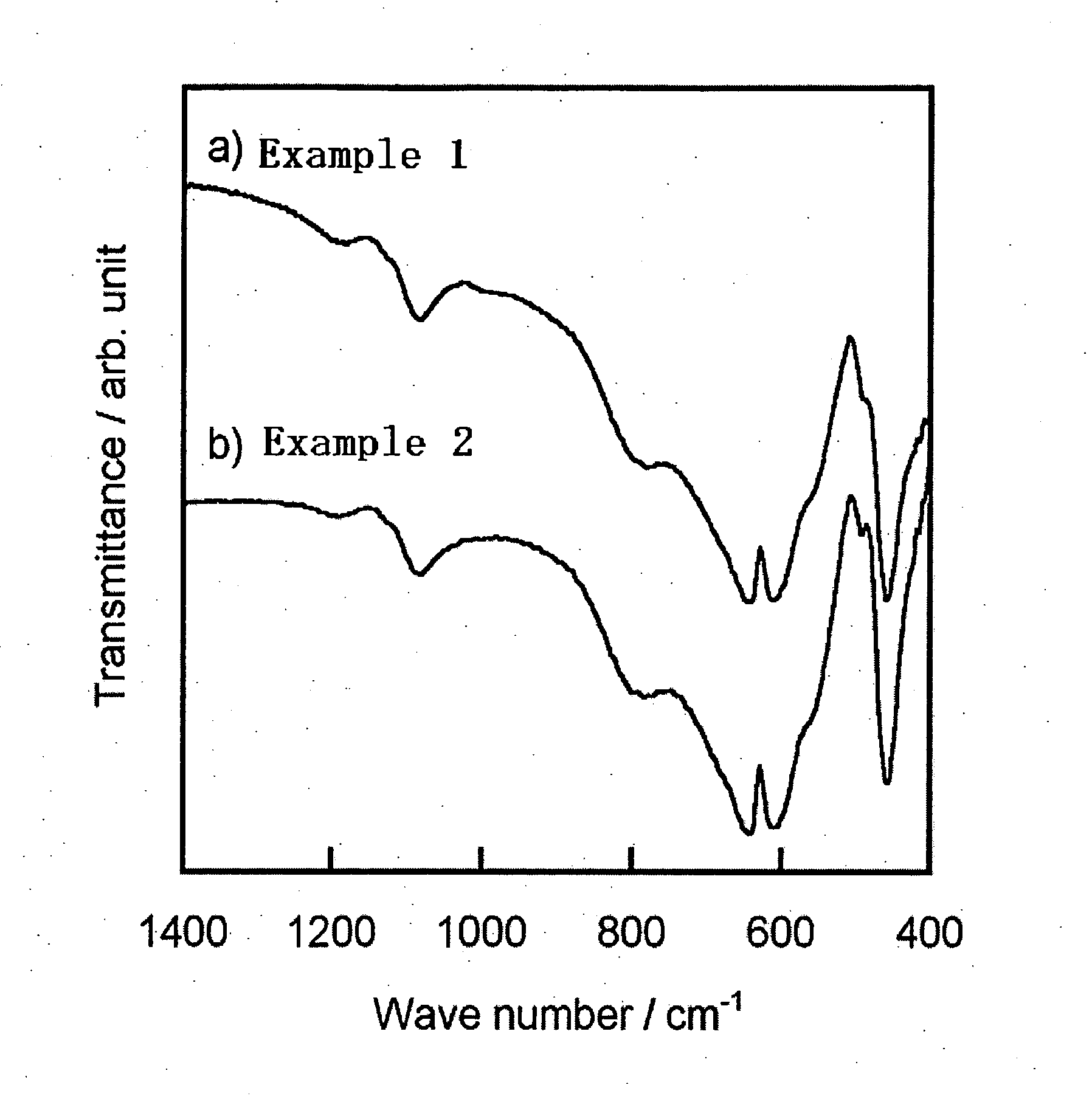
Tissue-bondable material for medical use
The present invention relates to a medical tissue-binding material, especially a soft tissue-binding material capable of attaching to a soft biological tissue such as a bone reconstruction material or a transdermal terminal, and a method for preparation thereof. In particular, the present invention relates to a medical tissue-binding material which comprises a base material having calcium binding onto the surface, provided that the base material is not titanium or titanium alloy. Also, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a medical tissue-binding material which comprises soaking a base material into a calcium ion containing solution. Introduction of at least one group selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl, carboxyl, sulfonate, amino, silanol and phosphate to the surface of the base material is effective for said method.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Agent for biological damage repair or hemostasis and the method thereof
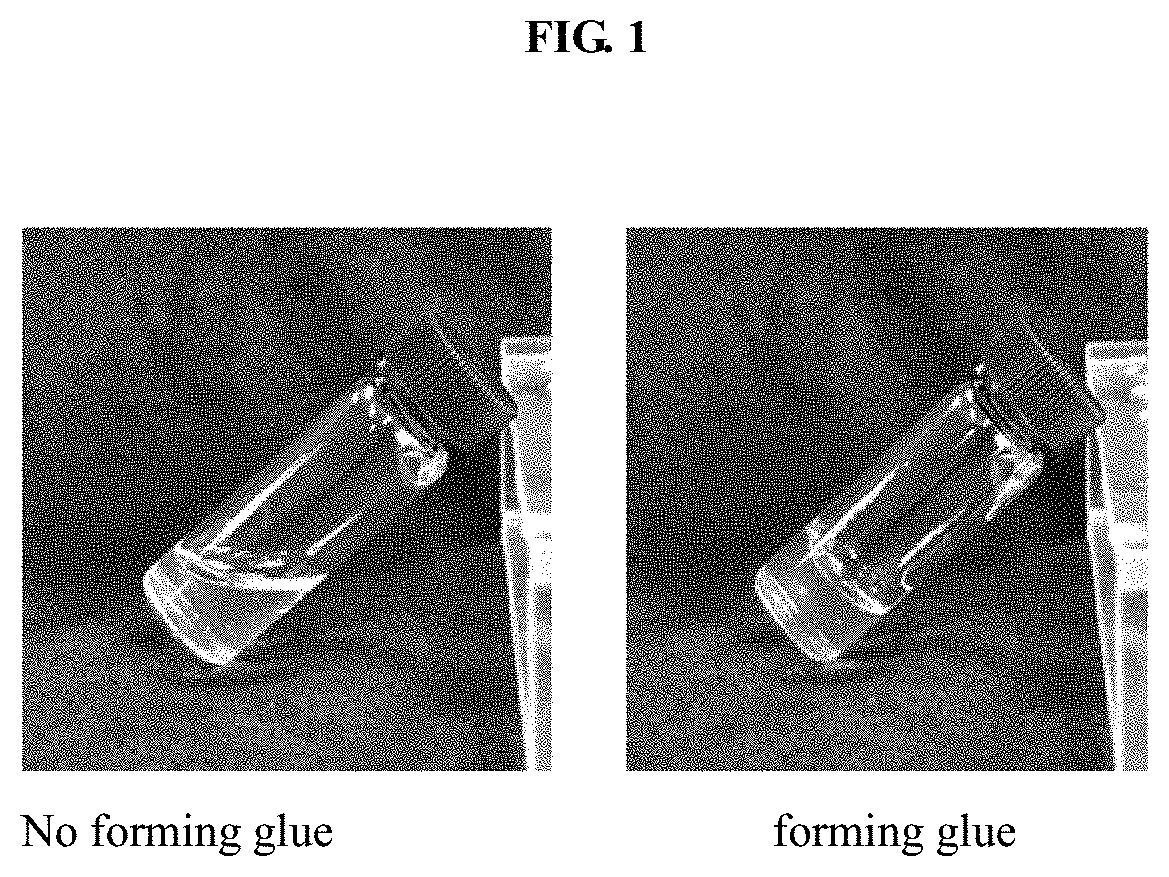
ActiveUS20200206383A1Improve tissue binding force and convenienceConnective tissue peptidesSurgical adhesivesDamage repairBiochemistry
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a light control agent and explore its application, and is expected to improve the tissue binding force and convenience of the existing biological glue material by providing a new reagent or material for biological damage or homeostasis. In one of embodiment, this invention provides an agent for repairing biological damage or homeostasis, wherein the agent comprises a natural biological macromolecule modified by the photo-responsive cross-linking group.
Owner:HAINING ZHULUOJI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Membranous tissue with evenly spaced elevated projections on one side and concave depressions on the other side method and use
InactiveUS20200289708A1Enhance vascular ingrowth and tissue incorporationEasy to keepPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationAnatomyTissue binding
The present invention discloses the method of preparation and use of soft tissue membranous structures into slip resistant membranes with regularly spaced surface projections on one side and concave depressions on the other side with perforations or without perforations which enhance vascular ingrowth and tissue incorporation.
Owner:MALININ THEODORE I
Magnetic health-care lining for human body wearable device and production process of magnetic health care lining
PendingCN107899136AComfortable to useImprove bindingElectrotherapyDevices for pressing relfex pointsHuman bodyInterlining
The invention belongs to the health-care equipment technical field and relates to a magnetic health-care lining for a human body wearable device and a production process of the magnetic health-care lining. The magnetic health-care lining comprises a first screen cloth layer, a first fusible interlining layer, magnetic particles, a second fusible interlining layer, and a second screen cloth layer which are sequentially stacked from the inner side to outer side of a human body. According to the magnetic health-care lining of the invention, massage portion regions which can abut against the humanbody and are provided with recessed portions and protrusion portions are formed at one side of the first screen cloth layer, and therefore, the magnetic health-care lining is more comfortable, has abetter magnetic health care effect, and can be better combined with the tissue of the human body.
Owner:HEYE HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Agent for biological damage repair or hemostasis and the method thereof
ActiveUS11446409B2Improve tissue binding force and convenienceConnective tissue peptidesSurgical adhesivesDamage repairBiochemistry
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a light control agent and explore its application, and is expected to improve the tissue binding force and convenience of the existing biological glue material by providing a new reagent or material for biological damage or homeostasis. In one of embodiment, this invention provides an agent for repairing biological damage or homeostasis, wherein the agent comprises a natural biological macromolecule modified by the photo-responsive cross-linking group.
Owner:HAINING ZHULUOJI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
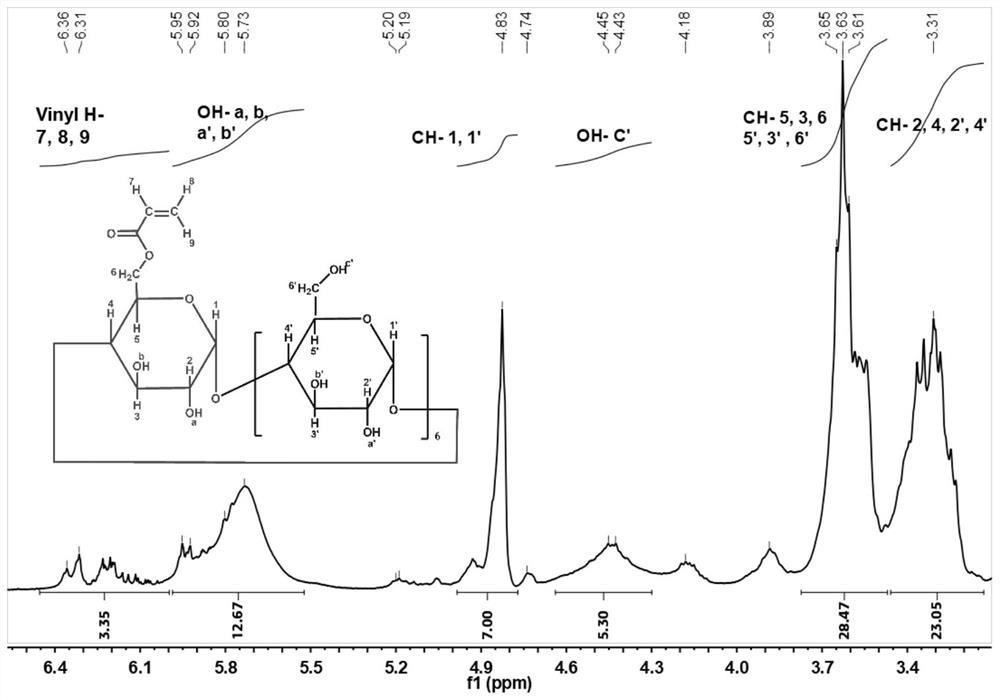
Host-guest supramolecular hydrogel induced by visible light in situ polymerization and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112538170ATightly boundStrong interactionTissue regenerationProsthesisIn situ polymerizationArginine
The invention discloses a host-guest supramolecular hydrogel patch induced by visible light in situ polymerization and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprisesthe following steps of: dissolving gelatin and acryloyl cyclodextrin (Ac-beta-CD) into water according to a certain mass fraction, and adding a certain amount of visible light initiator (riboflavin and L-arginine) to prepare a gel precursor solution; and then coating the myocardial surface with the gel precursor solution, and initiating in-situ gelling under visible light with a certain wavelength. The hydrogel myocardial patch induced by visible light in situ polymerization has proper mechanical strength, is tightly combined with tissues, and can be completely degraded after being stored ina PBS solution (containing type I collagenase) at 37 DEG C for 28 days.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of titanium implant with surface controllable micro-nano composite structure biofilm
ActiveCN112170841BHigh speedHigh strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurface reaction electrolytic coatingSelective laser meltingTissue binding
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical materials, and discloses a method for preparing a titanium implant with a surface-controllable micro-nano composite structure biofilm, comprising the following steps: (1) designing a titanium implant model with micro-pores on the surface; (2) Using the selective laser melting (SLM) technology in the additive manufacturing method to print the titanium implant model to obtain the initial product of the titanium implant; (3) Using the plasma micro-arc oxidation (PEO) technology with hydrothermal A hydroxyapatite film layer with a micro-nano composite structure is formed in situ on the surface of the initial titanium implant by post-treatment or electrophoretic deposition, so as to obtain a finished titanium implant. The invention improves the detailed structure design of the implant and the overall process design of the preparation method, imitates the biological bone tissue structure, obtains a micro-nano composite structure biofilm layer with controllable surface morphology and composition, and can increase the number of implants and surrounding areas. Tissue binding efficiency and binding strength.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
A kind of composite wound dressing with tissue bonding performance and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108404199BGel forming time is controllableHas tissue bonding propertiesBandagesWound dressingBioactive glass
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A bacterial cellulose-based asymmetric bilateral heterosexual biological patch and its preparation method
ActiveCN110639065BImprove mechanical propertiesImprove stabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProsthesisTissue repairEngineering
The invention provides a bacterial-cellulose-based asymmetric bidirectional isomerism biological mesh and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps that a smooth semi-drymembrane of bacterial cellulose is obtained by slow dehydration and drying, then micropores are formed in the bacterial cellulose side, then the side with the micropores is closely attached to the mold-controlled modified surface, and finally, through hydrolytic condensation deposition of a long carbon chain hydrophobic modifier on the other side under high temperature and high pressure, the biological mesh with good adhesion resistance on one side and good tissue bonding and tissue repair ability on the other side is obtained. According to the bacterial-cellulose-based asymmetric bidirectional isomerism biological mesh and the preparation method thereof, on the premise of ensuring excellent comprehensive mechanical properties and biocompatibility of the bacterial cellulose, anti-adhesionproperties are improved, the preparation method is simple, the preparation cost is relatively low, the sample shape and size are easy to control, and the bacterial-cellulose-based asymmetric bidirectional isomerism biological mesh is expected to be widely used in clinical practice; and in addition, the bacterial-cellulose-based asymmetric bidirectional isomerism biological mesh can be used for repairing hernia, dura mater, tendon, myocardium, pelvic floor and other soft tissues, and can be further used for artificial blood vessels and artificial skin and other biomedical fields.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com