Mineral fortification systems
A technology of minerals and compounds, applied in the fields of added substances water/sewage treatment, food science, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the cost of preservatives
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0103] Preparation of Liquid Compositions
[0104] The liquid compositions of the present invention can be prepared from a variety of liquid sources. Most preferred is deionized, demineralized or distilled water.
[0105] The present invention provides processing steps in which mineral and vitamin fortification of water is achieved without undesirable color, solubility, taste and bioavailability by redox modulation, in which case redox modulation lowers the redox potential. A preferred treatment method involves the removal and / or cleanup of the main species with a high redox potential in the water, which is dissolved oxygen. This method involves deoxygenating the water to reduce the concentration of oxygen in the water, or to remove all dissolved oxygen. A preferred water deoxygenation method involves the removal of oxygen (and other dissolved gases) with carbon dioxide or other inert gases. Preference is given to inert gas such as nitrogen. The oxygen content can also b...
Embodiment 1
[0112] Prepare a mineral fortified powder containing the following ingredients in the indicated amounts:
[0113] Element
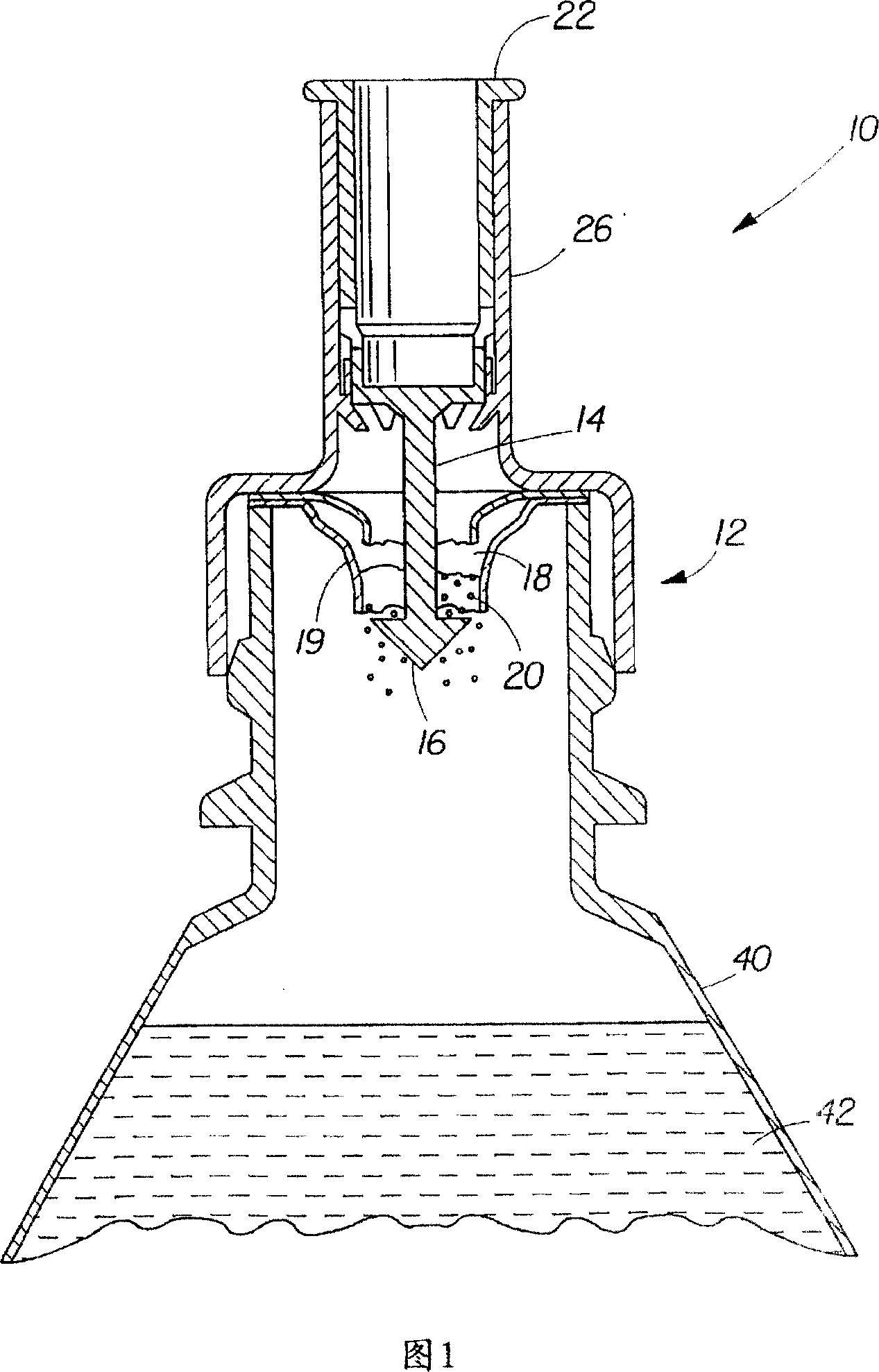
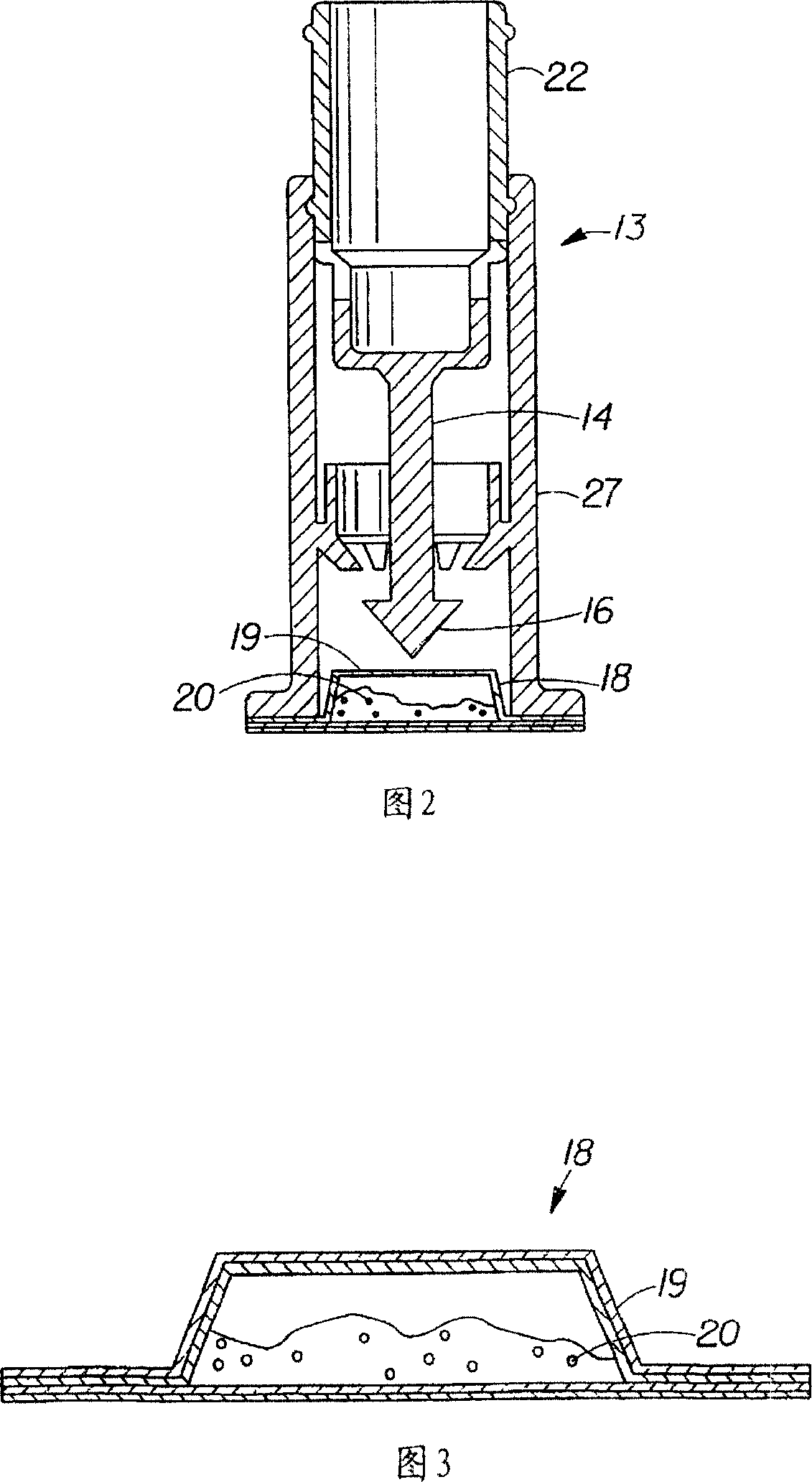
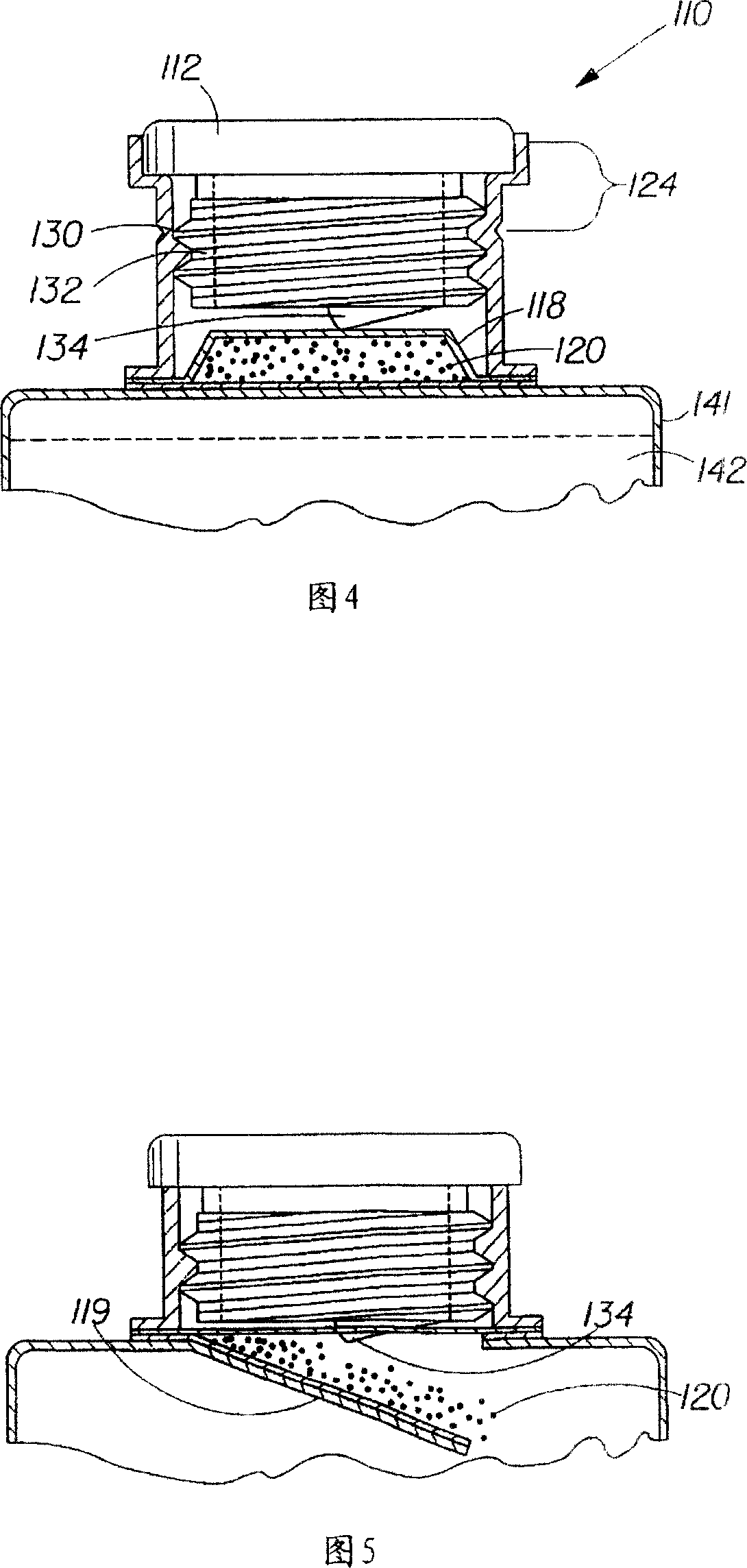
[0114] When preparing the mineral fortified powder, it is placed in a sealed sachet and inserted into the lid, as shown in Figure 1. The cap was then placed over a bottle of reverse osmosis / Millipore (Milli-Q) water and the plunger depressed. Gently swirling the bottle of water mixes the powders and creates a fortified liquid composition with no discoloration or rust, no sedimentation or cloudiness, and a low redox potential. The taste of the liquid composition was not significantly different in terms of metallic taste or aftertaste compared to liquid solvent alone (reverse osmosis / Millipore (Milli-Q) water).
Embodiment 2
[0116] As described herein, and more specifically, mineral fortified liquid compositions as described in Example 1 were compared with normal tap water, conventional reverse osmosis treated distilled water and various commercially available bottled waters. Some commercially available bottled waters are supplemented with vitamins. Using the measured values of the redox potential (listed in "mV" in Table 2A) and the pH value, the inequality 0≥RP-(A-B*pH) was calculated for different values of "A" and "B". The results of these calculations are given in Table 2A. Table 2B presents additional data comparing these products.
[0117] Table 2A
[0118]
mV
pH value
A=400
B=20
A=380
B=18
A=360
B=16
A=340
B=14
The water of embodiment 1
reverse osmosis water
fresh milliQ 1
Stored milliQ
Aquafina with Calcium 2
Aquafina Multi-V
Aquafina Da...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| turbidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com