Nanometer metal or alloy composite material and preparation and usage thereof
A nano-metal and composite material technology, applied in the field of nano-metal or alloy composite materials, to achieve high ion conductivity, good cycle characteristics and safety, and the effect of inhibiting damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
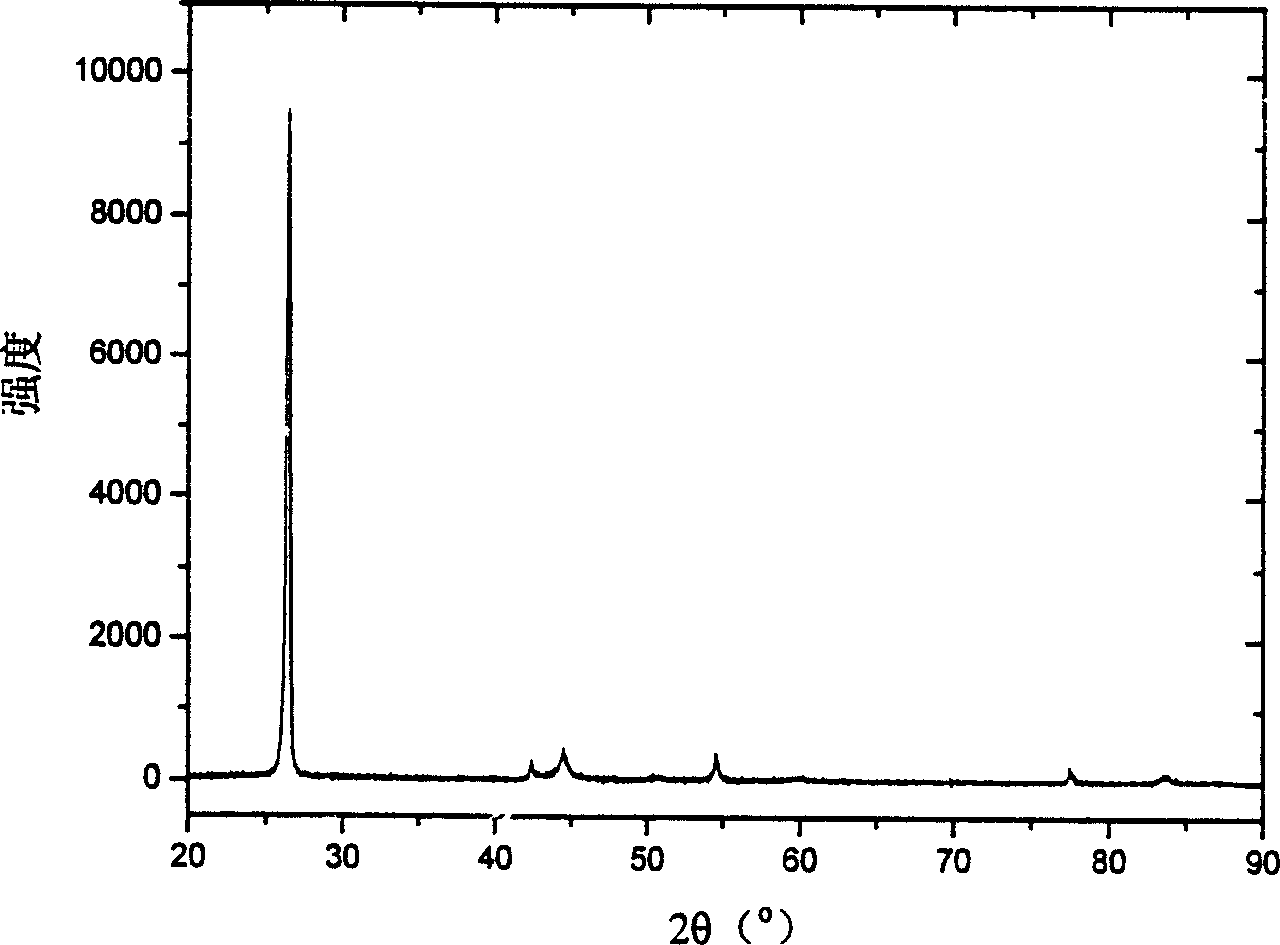
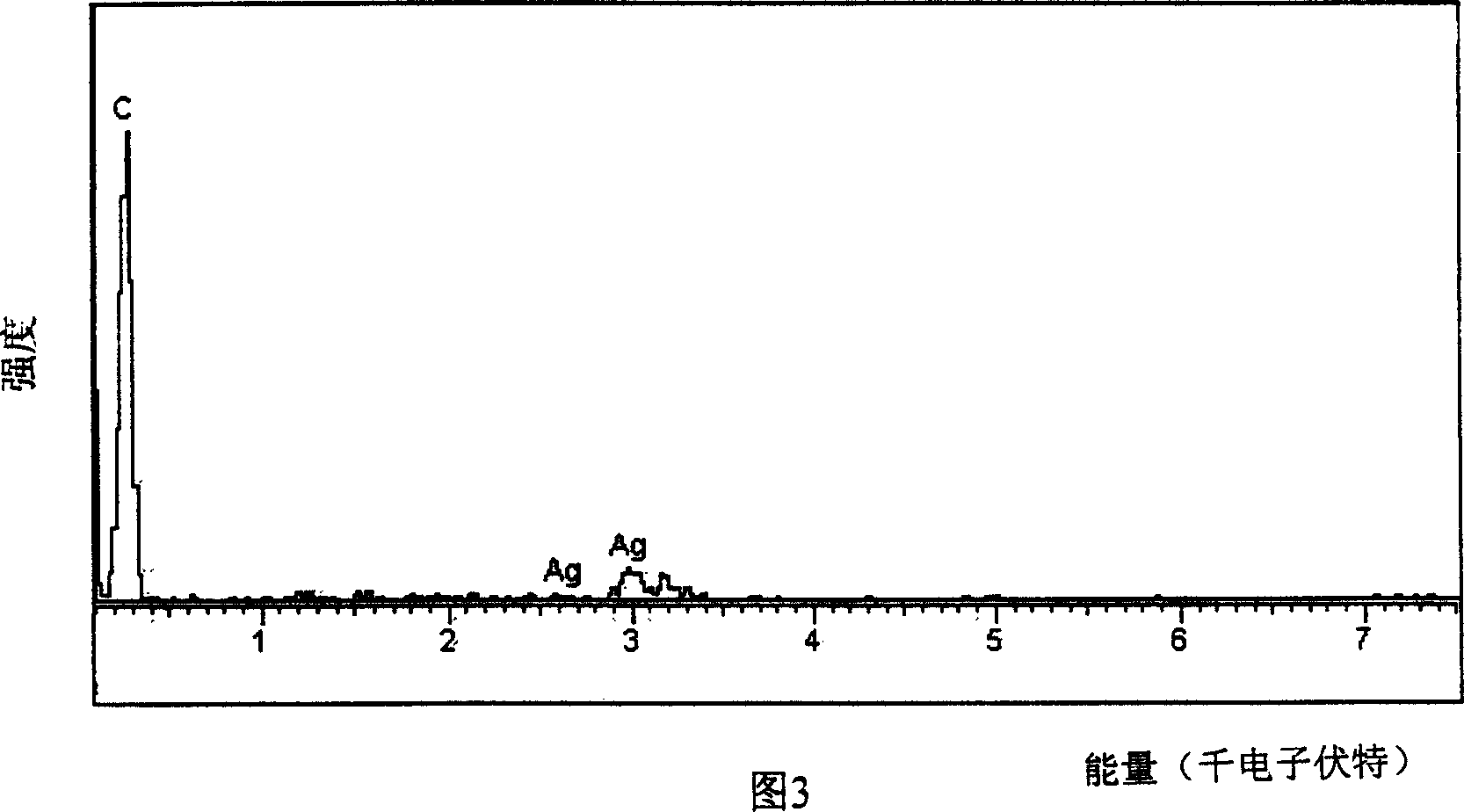
[0047] Embodiment 1, using preparation method one (electroless plating method) to prepare Ag / graphitized mesophase carbon pellets (hereinafter referred to as GMCMB) composite material
[0048] Ag 0.1 / GMCMB 0.9 Preparation of the composite material: (1) Weigh 0.85 grams of silver nitrate and put it into 20 milliliters of anhydrous ethylene glycol to heat and dissolve to form solution 1; (2) Weigh 5 grams of graphitized mesophase carbon pellets and put them into 20 milliliters of ethylene glycol Alcohol and 1,3 propanediol (volume ratio: 1:1) in the mixed solution, stir and mix evenly, then heat to 160 degrees, add the solution 1 obtained in step 1, continue to reflux at 130 degrees for 14 hours and then cool naturally, during the heating and reflux process (3) the black suspension obtained in step 2 is filtered, first rinsed several times with ethylene glycol, and then rinsed with ethanol, and the black substance obtained is in a hollow oven at 100 degrees. After drying for ...
Embodiment 21
[0054] Example 21. Preparation of Al / natural graphite powder (hereinafter referred to as NG) composite material by preparation method three (chemical vapor deposition method)
[0055] al 0.2 / NG 0.8 Preparation of composite materials: In a chemical vapor deposition furnace, organic aluminum butylaluminum is used as a precursor, argon is used as a carrier gas, and natural graphite particles are used as a deposition substrate. The deposition temperature is 400 degrees and the deposition time is 15 minutes.
[0056] The nanometer metal or alloy / electrode active material composite material in this example is used in the method of Example 1 to prepare an electrode and assemble it into an experimental battery. Other materials, structures, assembly and testing methods in the battery are the same as those in Embodiment 2. Embodiment 22~30, use the same method as embodiment 21 to obtain nine kinds of different composite materials, the test conditions are the same as embodiment 1, lis...
Embodiment 31
[0057] Example 31. Preparation of Zn / carbon fiber (hereinafter referred to as CF) composite material by preparation method four (physical mixing method)
[0058] Zn 0.3 / CF 0.7 Preparation of composite material: directly mix 0.6 g of nano-zinc powder with 1.4 g of carbon fiber and set aside.
[0059] The nanometer metal or alloy / electrode active material composite material in this example was prepared by the same method as in Example 1 to prepare an electrode and assemble it into an experimental battery. Other materials, structures, assembly and testing methods in the battery are the same as those in Embodiment 2.
[0060] Embodiments 32 to 40, using the same method as in Example 31 to obtain nine different composite materials, the test conditions are the same as in Example 1, listed in Table 1
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com