Method for recovering papermaking black liquor liquid soda
A paper-making black liquor and liquid alkali technology, applied in the regeneration of alkali liquor, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the salt content of organic fertilizer, affecting the quality of organic fertilizer, and high conversion cost, so as to increase the compressive strength and anti-osmotic pressure Impact ability, fast resin exchange speed, and improved wear resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
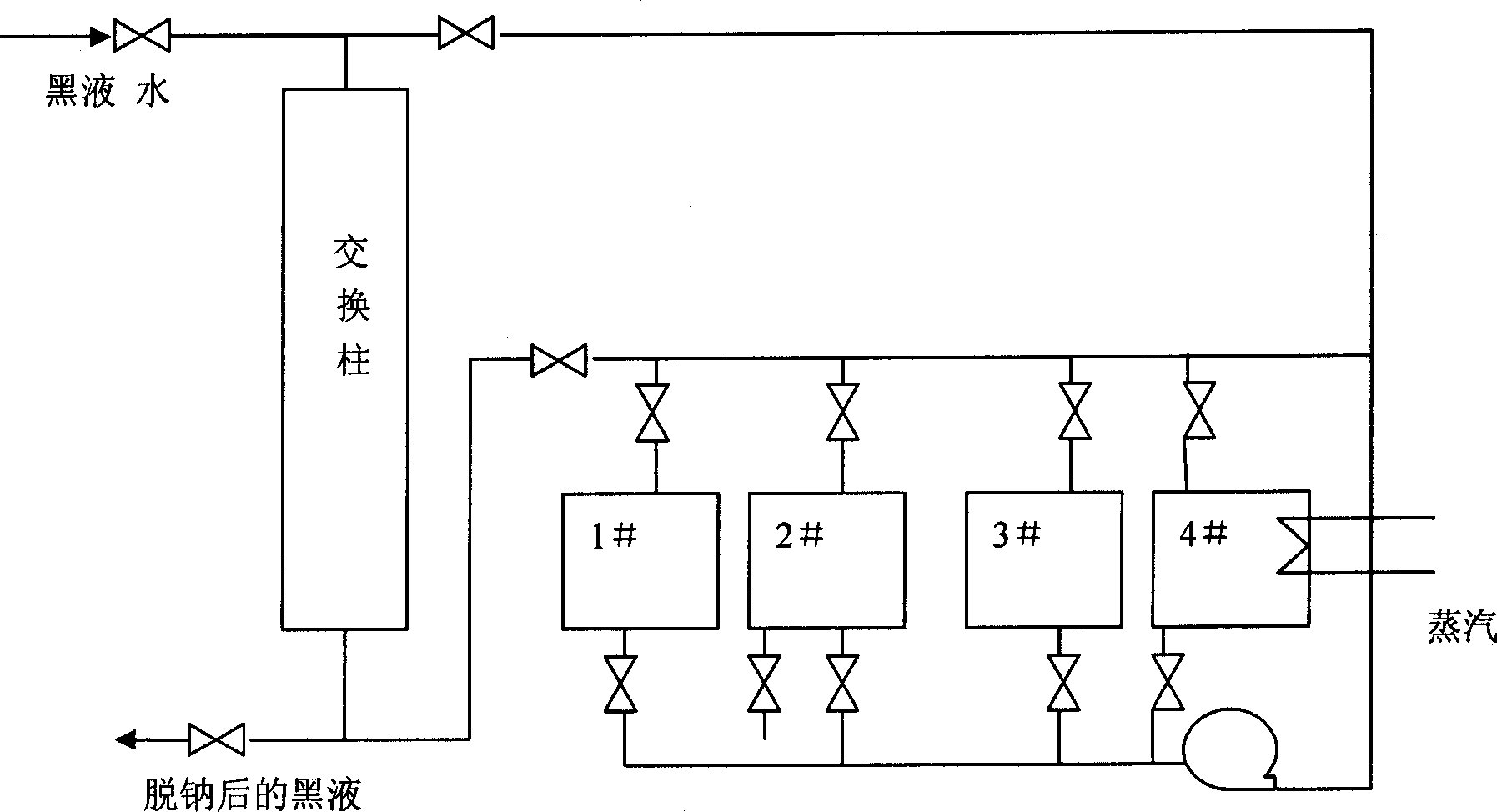
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1. Styrene 82.0g, 55.60% divinylbenzene 18.0g, vinyl acetate 8.0g, dicyclopentadiene 1.0g, benzoyl peroxide 1.1g, 300# liquid paraffin 81.8g. Stir for more than 0.5 hours to make it evenly mixed. Add to the water phase which has been warmed to 40°C. The aqueous phase consists of 400ml of 10% saline and 3.2g of pre-swollen gelatin. After putting the oil phase into the water phase, let it stand for 10 minutes. Start stirring, heat up to 80°C, adjust the stirring speed during the heating process, so that the particle size of the beads is within the required range. The reaction was incubated at 80°C for 3 hours to finalize the beads. Then the temperature was raised to 90° C., and the temperature was kept for 2 hours. Then the temperature was raised to above 95°C and kept for 8 hours. Polymerization is complete. The beads are filtered out, loaded into an exchange column, and the porogen in the beads is extracted with acetone, and the acetone used for extract...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2. Styrene 77.0g, 55.60% divinylbenzene 10.8g, acrylonitrile 5.0g, triallyl isocyanate 6.0g, benzoyl peroxide 1.0g, 200# solvent naphtha 60.0g. Stir for more than 0.5 hours to make it evenly mixed. Add to the water phase which has been warmed to 40°C. The aqueous phase consists of 400ml of 10% saline and 1.0g of pre-swollen hydroxymethylcellulose. After putting the oil phase into the water phase, let it stand for 10 minutes. Start stirring, heat up to 65°C, adjust the stirring speed during the heating process, so that the particle size of the beads is within the required range. The reaction was held at 65°C for 2 hours, then raised to 80°C for 3 hours. Then the temperature was raised to 90° C., and the temperature was kept for 2 hours. Then the temperature was raised to above 95°C and kept for 8 hours. Polymerization is complete. The beads are filtered out, loaded into an exchange column, and the porogen in the beads is extracted with acetone, and the a...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3. Methyl acrylate 77.0g, 55.60% divinylbenzene 5.4g, acrylonitrile 5.0g, triallyl isocyanate 6.0g, benzoyl peroxide 1.0g, 200# solvent naphtha 60.0g. Stir for more than 0.5 hours to make it evenly mixed. Add to the water phase which has been warmed to 40°C. The aqueous phase consists of 400ml of 20% saline and 1.0g of pre-swollen hydroxyethylcellulose. After putting the oil phase into the water phase, let it stand for 10 minutes. Start stirring, heat up to 65°C, adjust the stirring speed during the heating process, so that the particle size of the beads is within the required range. The reaction was held at 65°C for 2 hours, then raised to 80°C for 3 hours. Then the temperature was raised to 90° C., and the temperature was kept for 2 hours. Then the temperature was raised to above 95°C and kept for 8 hours. Polymerization is complete. The beads are filtered out, loaded into an exchange column, and the porogen in the beads is extracted with water vapor....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com