Methods for direct synthesis of compounds having complementary structure to a desired molecular entity and use thereof
a technology of complementary structure and compound, applied in the field of indirect drug identification methods, can solve the problems of inability to test the number of compounds, inability to directly synthesis compounds, and inability to meet the requirements of the drug, and achieve the effect of increasing hea
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0131] This example describes the formation of amolecularly imprinted material using two differently reacting crosslinking monomers, A, and B. By virtue of choosing the mutual reactivity ratios (r) so that the product r.sub.Ar.sub.B<1, these monomers will preferably form stretches of homopolymers, rather than random, or alternating, copolymers. Polymerization of a mixture of these. crosslinkers will lead to segment polymer formation: -A-A-A-A-B-B-B-B-A-A-A-A.
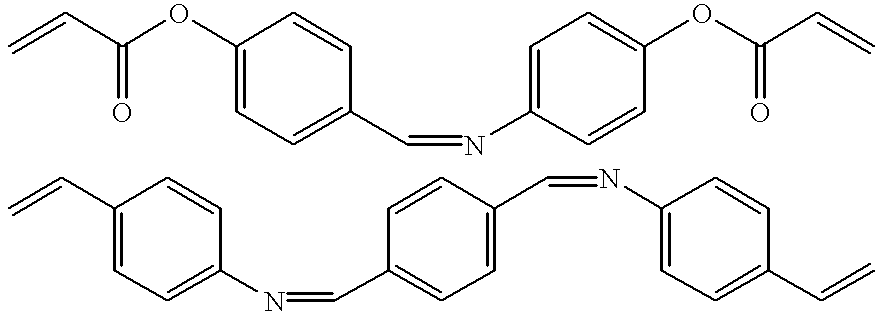
[0132] A solution comprising the two different crosslinkers, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EDMA) (FIG. 4, 23) and N1-((E)-1-(4-vinylphenyl)-m-ethylidene)-4-vinylaniline (VMVA) (FIG. 6, 2), together with the functional monomer methacrylic acid (MAA) (FIG. 4, 3), in acetonitrile is spraycoated onto the print molecule, immobilized onto a silicon wafer support (FIG. 3A). Upon exposure to UV-irradiation at 366 nm, polymerization takes place, during which a continuous three-dimensional segment polymer is formed around the print mole...
example 2
[0134] This example demonstrates the use of two-dimensional movement in order to acquire anti-idiotype ligand formation.
[0135] A self-assembled monolayer (SAM), consisting of long-chain alkyl thiols (FIG. 9, 1) is built on a gold surface (FIG. 5A). On top of this layer, a second layer is built, consisting of long-chain alcohols (FIG. 9, 2) as well as crosslinkable, and functional alkenyl-structures (FIG. 9, 3-6)(FIG. 5B). In the second layer, the molecules are free to move within the layer in a random manner. Addition of a solution containing the target molecule, e.g., acetylcholine esterase (AChE), on top of the second layer, results in a directed arrangement of the functional alkenyl-molecules towards the enzyme. Patches of complexes between the functional alkenes and the enzyme takes place on the surface (FIG. 5C). These complexes are subsequently "frozen" by the addition of a crosslinker, such as tetramethyldisiloxane (TMDS)(FIGS. 9, 7)(FIG. 5D). After breakage of the layers, an...
example 3
[0136] This example represents the use of molecular scaffolds to "freeze" a self-assembled complex between ligand building elements in their interaction with a binding site.
[0137] Crosslinked trypsin (from Altus), a proteolytic enzyme specific for the cleavage of peptide bonds (-X-Y-) where X can be any amino acid residue and Y is a positively charged residue, is mixed together with ligand building elements labeled with photoactive groups, e.g., perfluorophenylazido groups (FIG. 10, 1-2), chosen so as to be able to fit into the active site of the enzyme, and a preassembled scaffold-ligand element (FIG. 10, 3) (FIG. 11A). The ligand elements, including the scaffold-bearing element, are prone to interact with the enzyme randomly. In order to enhance non-covalent interactions between the ligand building elements and the enzyme, and to reduce the amount of non-specific hydrophobic interactions, the process is performed in acetonitrile. After a period of time when self-assembly is allowe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| chain length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| chain length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| chain length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com