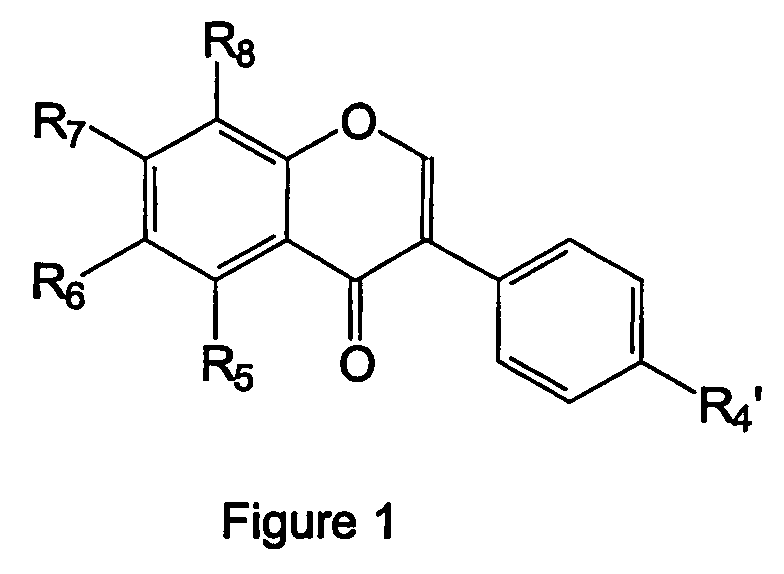
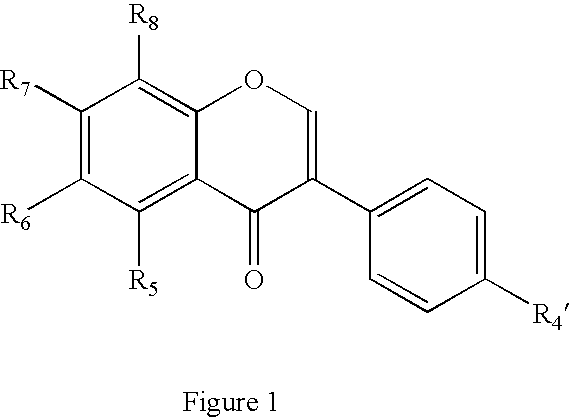
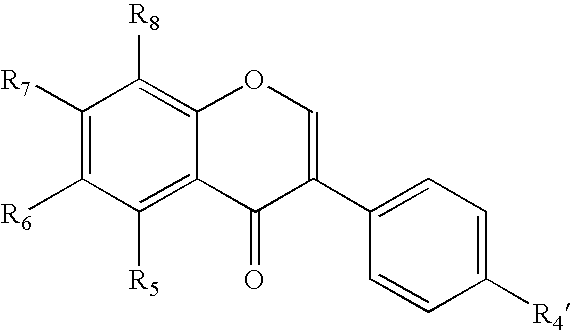
Isoflavone derivatives
a technology of isoflavones and derivatives, which is applied in the field of isoflavones, can solve the problems of difficult formulation of foodstuffs, low solubility of isoflavones, and insoluble water insoluble nature of isoflavones, and achieves the effect of increasing the bioavailability of isoflavones and being easy to hydrolyzed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Mixed Phosphate Esters of Genistein
[0028] A solution of genistein (135 mg, 0.5 mmole) and di-tert-butyl phosphoramidite (330 ul, 1.0 mmole) in DMF (1 ml) was stirred under argon while 1H-tetrazole (210 mg in 0.5 ml of DMF; 3.0 mmole) was added dropwise. After a few minutes, the solution was cooled to −20° C., then a solution of m-chloroperbenzoic acid (260 mg in 0.5 ml of methylene chloride, 1.5 mmole) was added dropwise. After warming to room temperature, the mixture was diluted threefold with ethyl acetate, then washed with 10% sodium metabisulfie and 10% sodium bicarbonate. A wash with 5% sodium carbonate removed a trace of unreacted genistein.
[0029] The ethyl acetate solution, containing the butyl esters of the genistein phosphates, was washed with 1M HCl and dried over sodium sulfate. After removal of the solvent in vacuo, the residue was treated with 30% TFA in acetic acid for 90 minutes at room temperature. The solvents were removed in vacuo, and the residue was taken up in...
example 2
[0032] a) Genistein-7-tosylate: p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (540 mg, 2.8 mmoles) was added during 4 hours to a stirred mixture of genistein (730 mg, 2.7 mmoles) and potassium carbonate (2 g) in 25 ml of acetone. After stirring overnight , the mixture was poured into brine and extracted with ethyl acetate. The extract was evaporated under vacuum, and the residue chromatogrammed through silica gel with dichloromethane and chloroform. Crystallization from methanol yielded 920 mg (80.2% yield) of genistein-7-tosylate. The proton magnetic resonance spectrum was consistent with the expected structure.
[0033] b) 4′,5-Di(methoxymethyl)-genistein-7-tosylate: Chloromethyl methyl ether (90 ul, 1.12 mmoles) was added to a solution of genistein-7-tosylate (106 mg, 0.25 mmoles) and diisopropylethylamine (200 ul, 1.15 mmoles) in 0.6 ml of dioxane, under argon atmosphere, and stirred overnight. The mixture was poured into brine, extracted with ethyl acetate, and chromatogrammed...
example 3
Mixed Hemisuccinate Esters of Genistein
[0038] A solution of genistein (135 mg, 0.5 mmole) in 2.0 ml of pyridine was stirred at room temperature while succinic anhydride (100 mg, 1.0 mmole) was added in several portions. After stirring overnight at room temperature, the solvent was removed in vacuo. The gummy residue was taken up in water, adjusted to pH 3.0, and extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate extracts were washed with water, then evaporated to dryness in vacuo. The crude mixture of mixed hemisuccinic acid esters weighed 205 mg.
[0039] Thin layer chromatography of the product showed principally the presence of mixed mono- and disuccinate esters of genistein. The product was completely soluble in phosphate buffer at pH 7.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| a wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com