Vaccine composition for vaccinating dogs against canine infectious respiratory disease(CIRD)
a technology for respiratory diseases and vaccine compositions, applied in the field of vaccine compositions, can solve the problems of large treatment costs, no new data to support the involvement, and disruption of schedules in training kennels, so as to increase the immunogenicity of the agent and improve the antigenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
The Association of Streptococcus Equi Sub Species Zooepidemicus with Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease
Summary
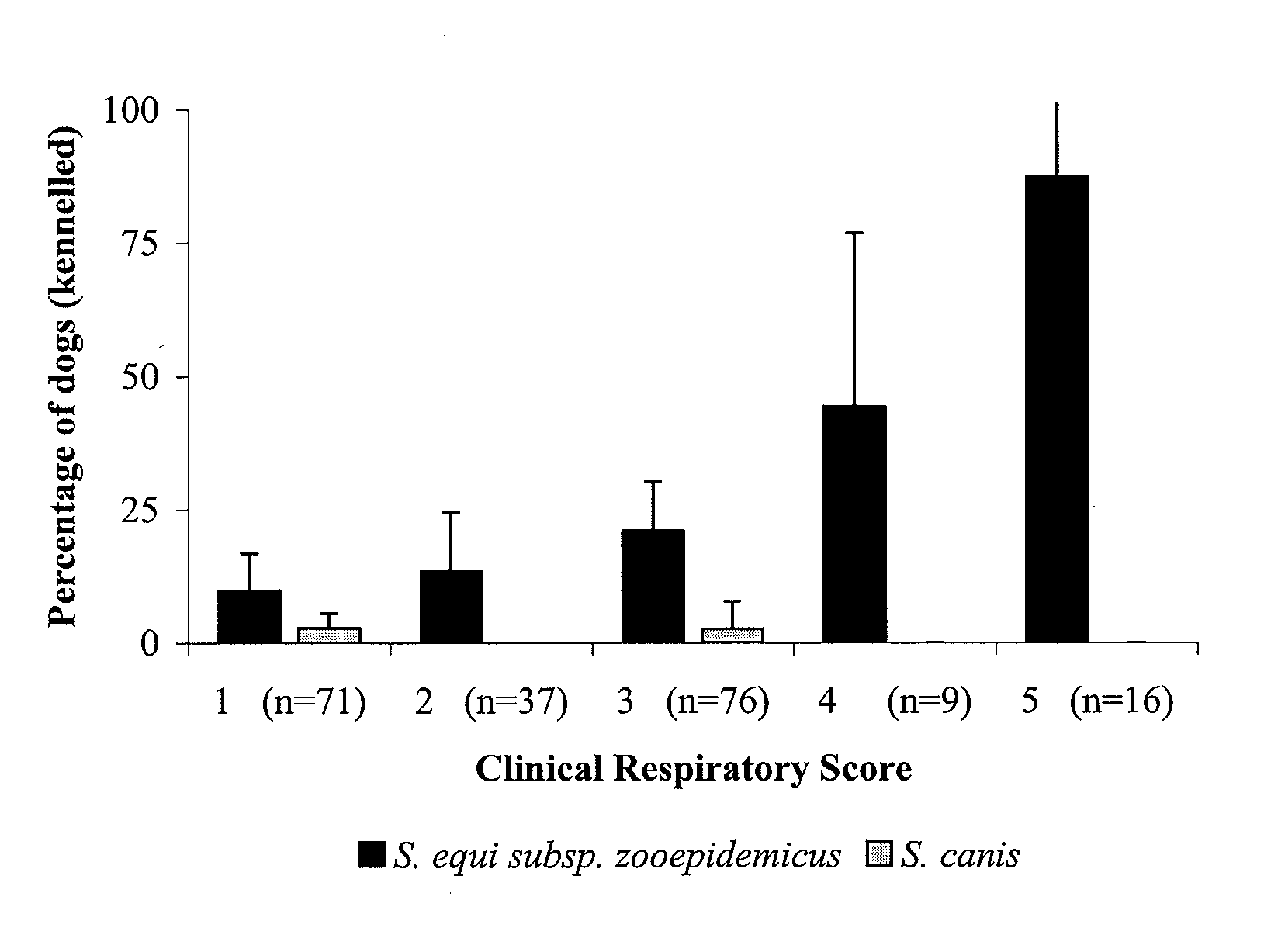
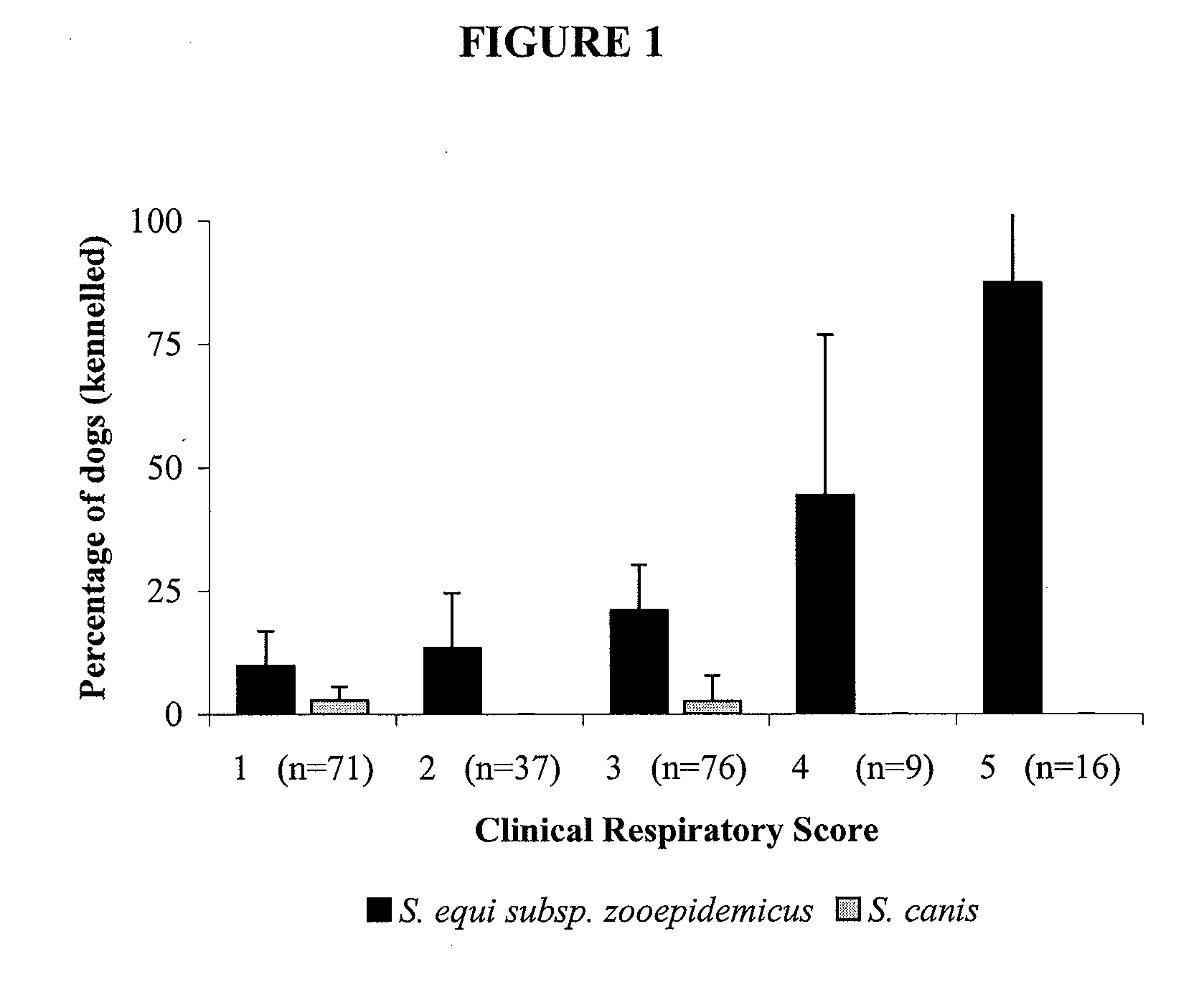
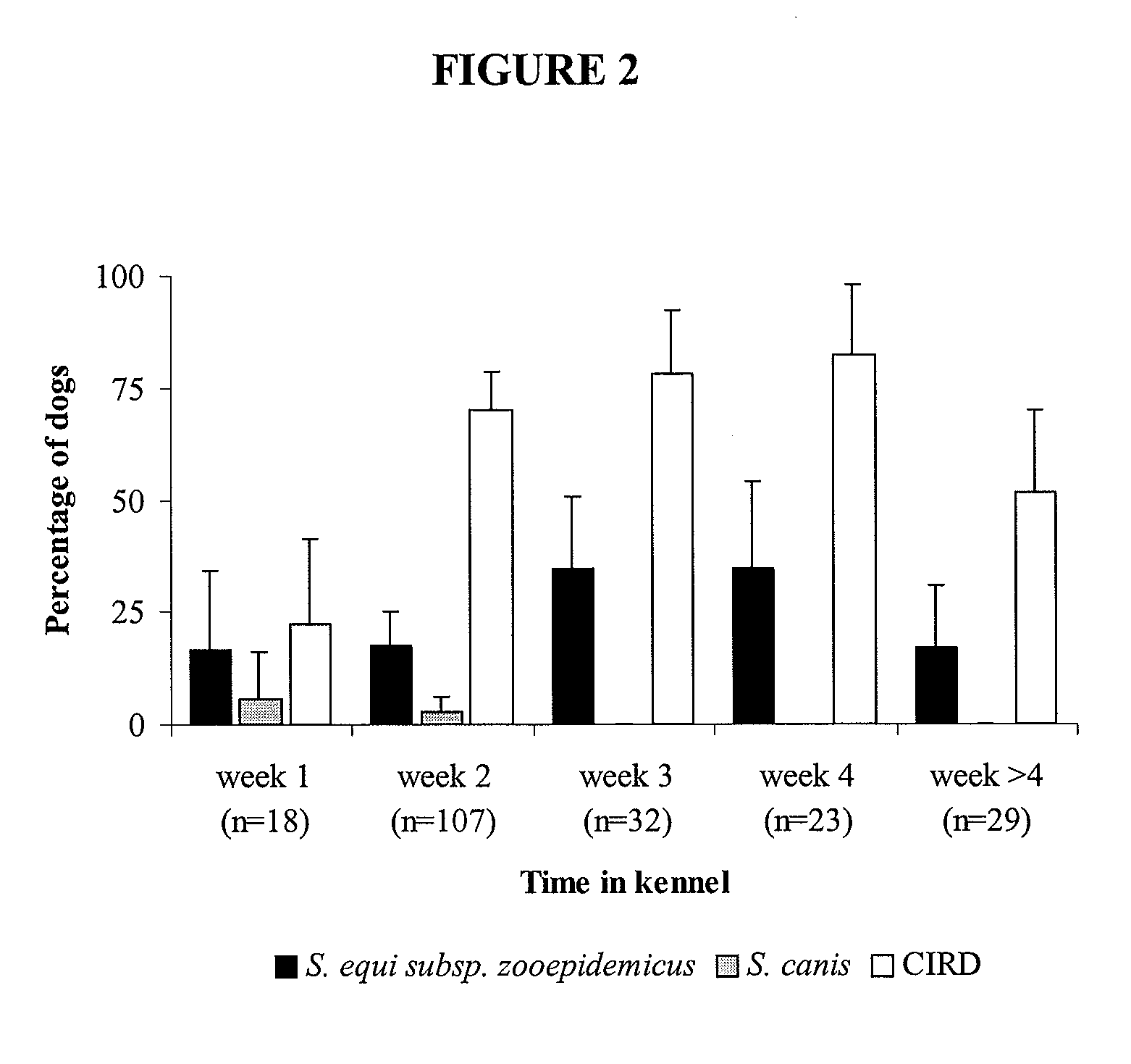
[0358]Canine infectious respiratory disease (CIRD) is a multi-factorial infection that affects many kennelled dogs despite the wide use of vaccination. Current vaccines aim to protect against viral agents and a single bacterial agent, Bordetella bronchiseptica. We examined the role of streptococcal species in CIRD. The isolation and identification of streptococci in the lower respiratory tract of clinically healthy dogs and those with CIRD were used to correlate the presence of specific streptococcal species with respiratory disease. We show that the presence of S. equi sub species zooepidemicus (S. zooepidemicus) is associated with increasing severity of disease in a population of kennelled dogs with endemic CIRD.
Introduction
[0359]CIRD is an infection that affects dogs of all ages and commonly occurs when large numbers of dogs are housed together in close confinement. Th...
example 2
The Association of Mycoplasma Cynos with Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease
[0379]The presence of M. cynos was investigated by culture of the organism and identification by PCR analysis. In a survey of 184 kennelled dogs we have found that the percentage of dogs with M. cynos in the trachea or lung increases with signs of respiratory disease from 10% in healthy dogs to 31% in diseased dogs (FIG. 3).
[0380]We have also noted that respiratory disease increases with time in the kennel and during the first week in the kennel dogs have no detectable M. cynos in the trachea, whereas by the second week 24% of the 184 dogs were positive for M. cynos in the trachea—indicating 24% of the population are being infected with this bacterium. A smaller but similar increase was also seen for colonization of the lung (from 15% to 23%) (see FIG. 4).
example 3
The Association of Chlamydophila with Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease
[0381]We surveyed 210 dogs by PCR analysis for the presence of Chlamydophila.
[0382]A 218 bp fragment of the 23S rRNA gene was amplified from the Chlamydophila by the following PCR. Reaction conditions, 95° C. 5 min (×1 cycle), 95° C. 30 seconds, 50° C. 30 seconds, 72° C. 1 minute (×40 cycles) and 72° C. 5 mins. The PCR reaction mix of 50 μl total, included 5.0 μl 10× magnesium free buffer (promega), 1.5 mM MgCl2 (Promega), 0.5 μl (0.5 Units) Taq DNA polymerase (Promega), 0.2 mM PCR nucleotide mix (Promega), 0.025 μg forward primer C1 (5′-GATGCCTTGGCATTGATAGGCGATGAAG GA-3′, SEQ ID NO: 9) and reverse primer C2 (5′-TGGCTCATCATGCAAAAGGCA-3′, SEQ ID NO: 10), 40 μl water and 2 μl sample tissue DNA.
[0383]A PCR product obtained from 8 dogs was confirmed as a Chlamydophila by sequence analysis and comparison of the PCR product to all available sequences in GenBank by Fasta analysis. The partial sequence of the 23S rR...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com