Transdermal delivery systems for active agents
a technology of active agents and transdermal or transmucosal injection, which is applied in the direction of biocide, plant growth regulators, pharmaceutical non-active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of lack of sex drive, clinical symptoms, and undesirable clinical symptoms, and achieves the effect of avoiding undesirable odor and irritation effects, facilitating formulation use, and facilitating patient complian
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0123]One embodiment of the formulation according to the invention is a topical gel having Testosterone 1.25% w / w, propylene glycol 5.95% w / w, Ethyl alcohol 45.46% w / w, Distilled water 45.67% w / w, Carbomer (Carbopol 980 NF) 1.21% w / w, Triethanolamine 0.39% w / w, Disodium EDTA 0.06% w / w.
example 2
[0124]One embodiment of the formulation according to the invention is a gel composed by testosterone 1.00% w / w, diethylene glycol monoethyl ether 5.00% w / w, propylene glycol 6.00% w / w, ethanol 47.52% w / w, purified water 38.87% w / w, carbomer (CARBOPOL™ 980 NF) 1.20% w / w, triethanolamine 0.35% w / w, and disodium EDTA 0.06% w / w.
example 3
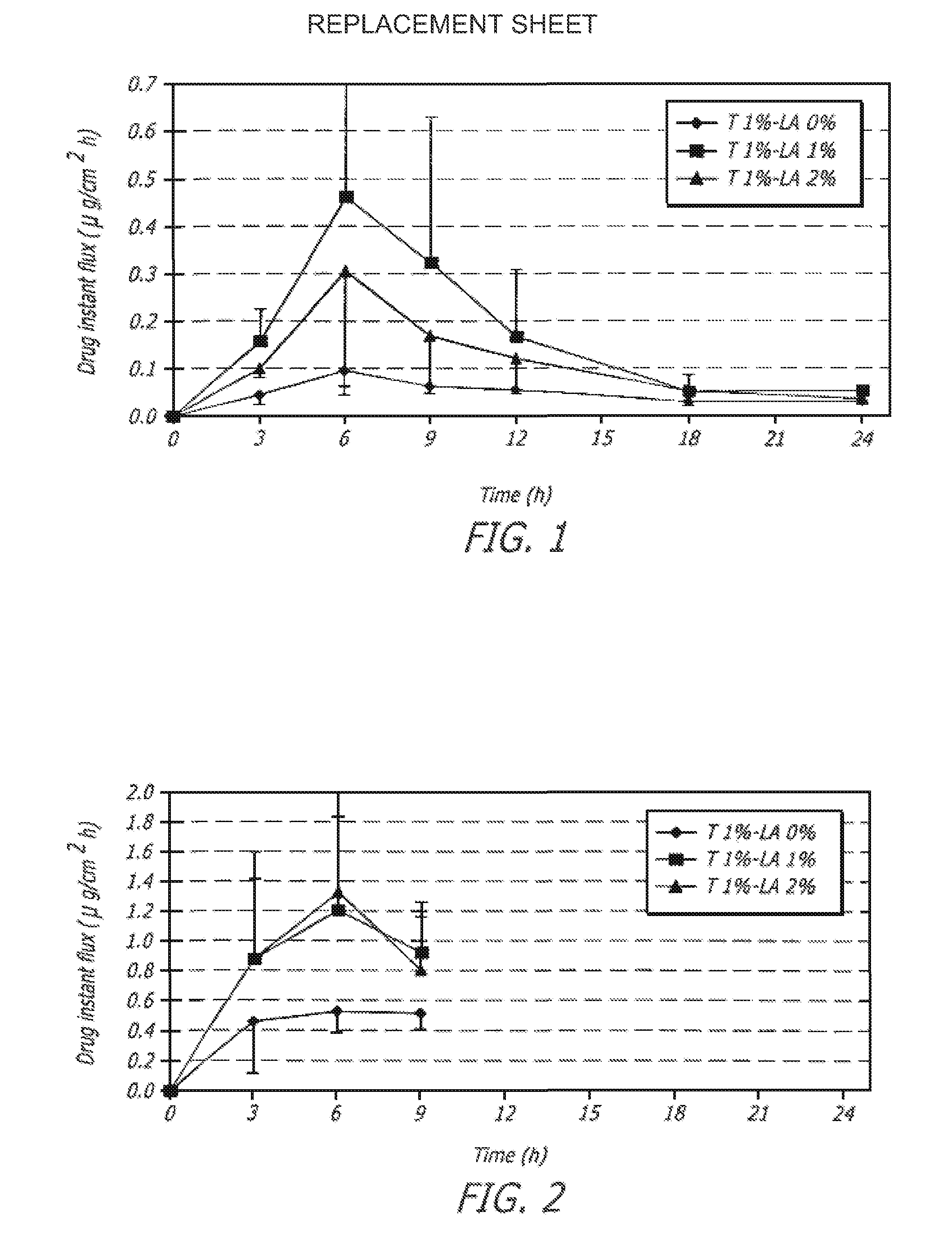
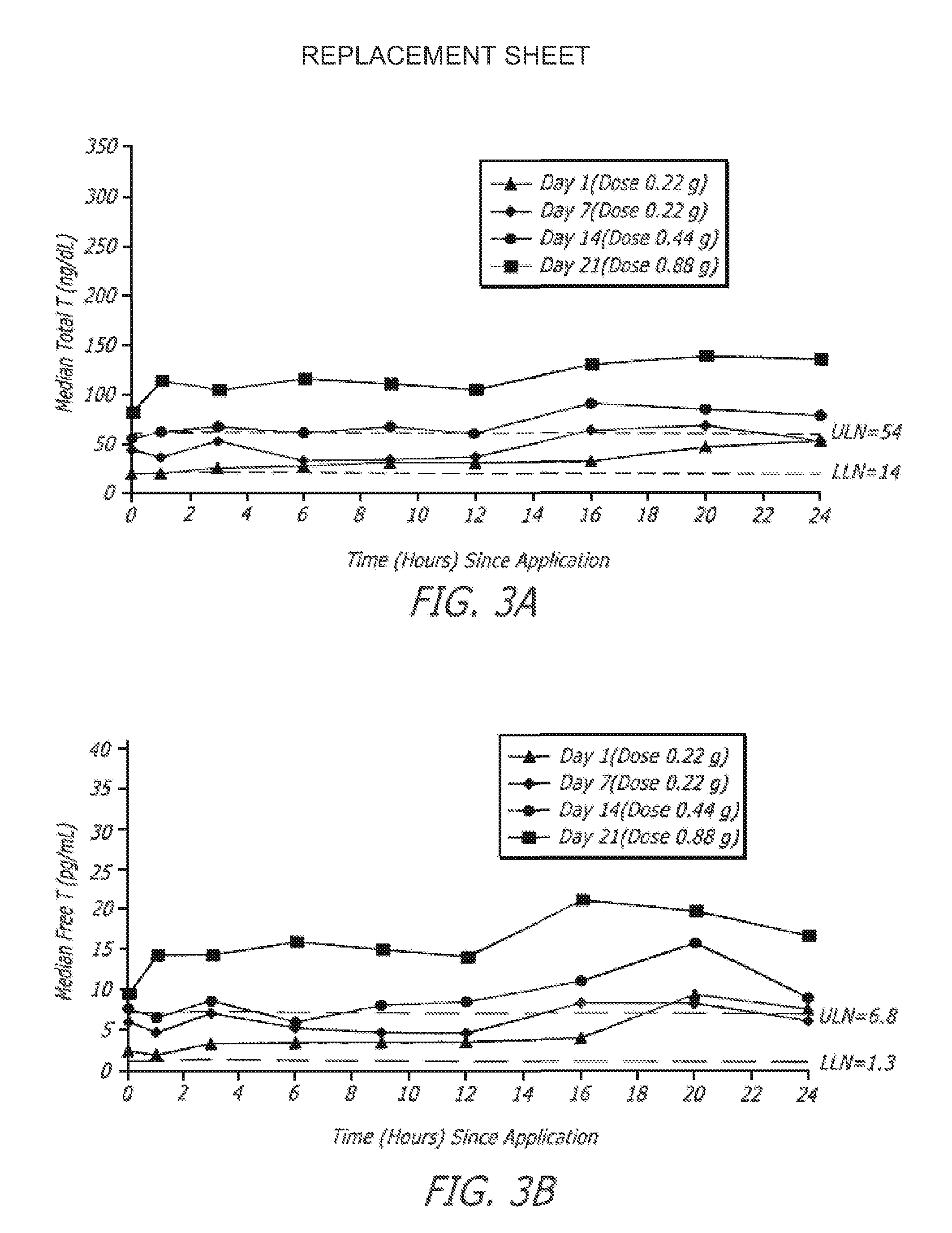
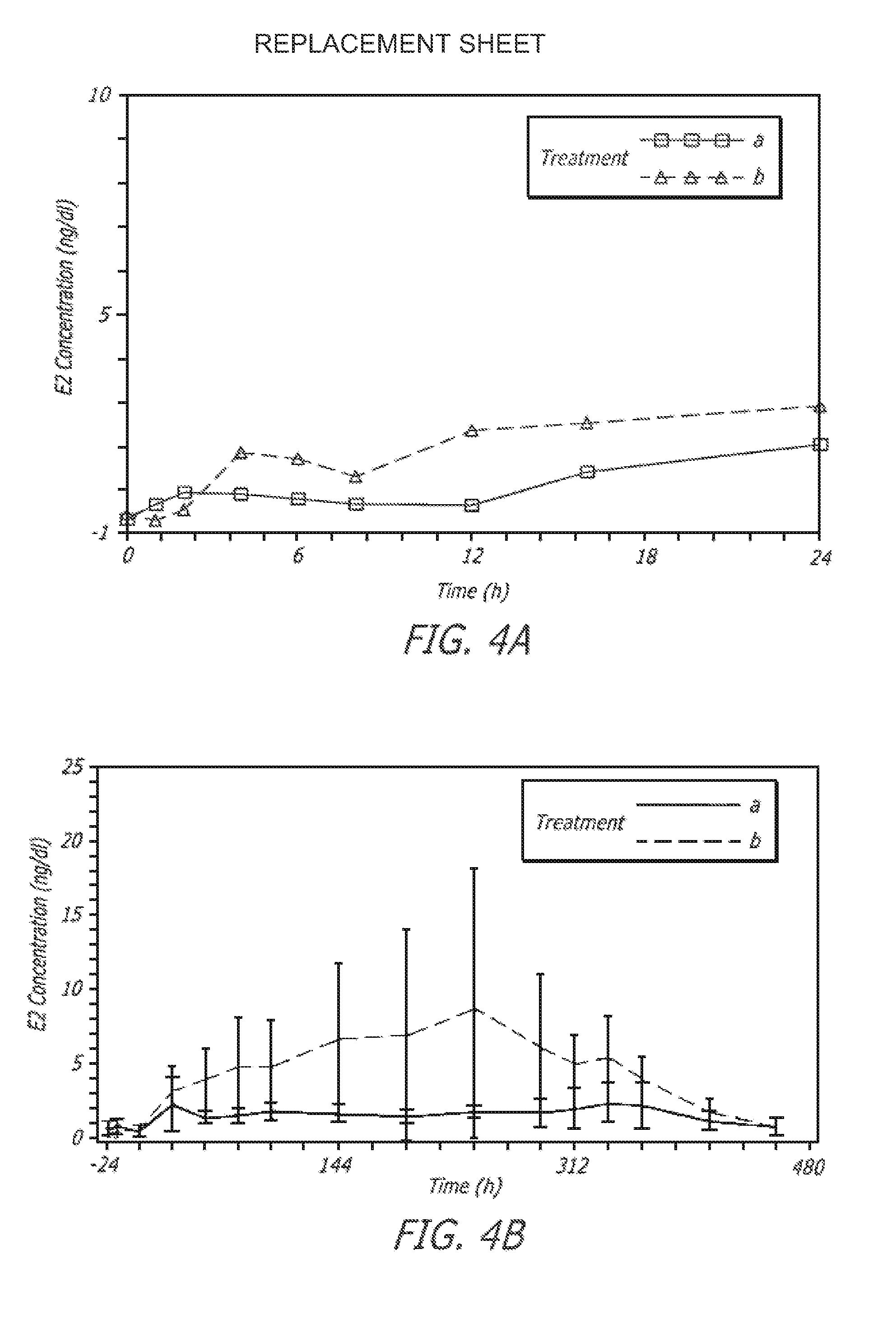
[0125]One embodiment of a formulation according to the invention is a topical hydroalcoholic gel formulation with 1% testosterone as the active ingredient. The formulation has been studied in one Phase I / II multiple dose, dose escalating clinical study in women. The study was conducted to determine the effectiveness of the formulation for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (“HSDD”), in subjects including surgically menopausal women with low testosterone levels.
[0126]This study showed that the testosterone gel dosing between about 0.22 g to about 0.88 g formulation (2.2 to 8.8 mg / day testosterone) daily for 7 days resulted in average total and free testosterone serum concentrations within the normal range or somewhat above the normal range for pre-menopausal women.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| skin temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com