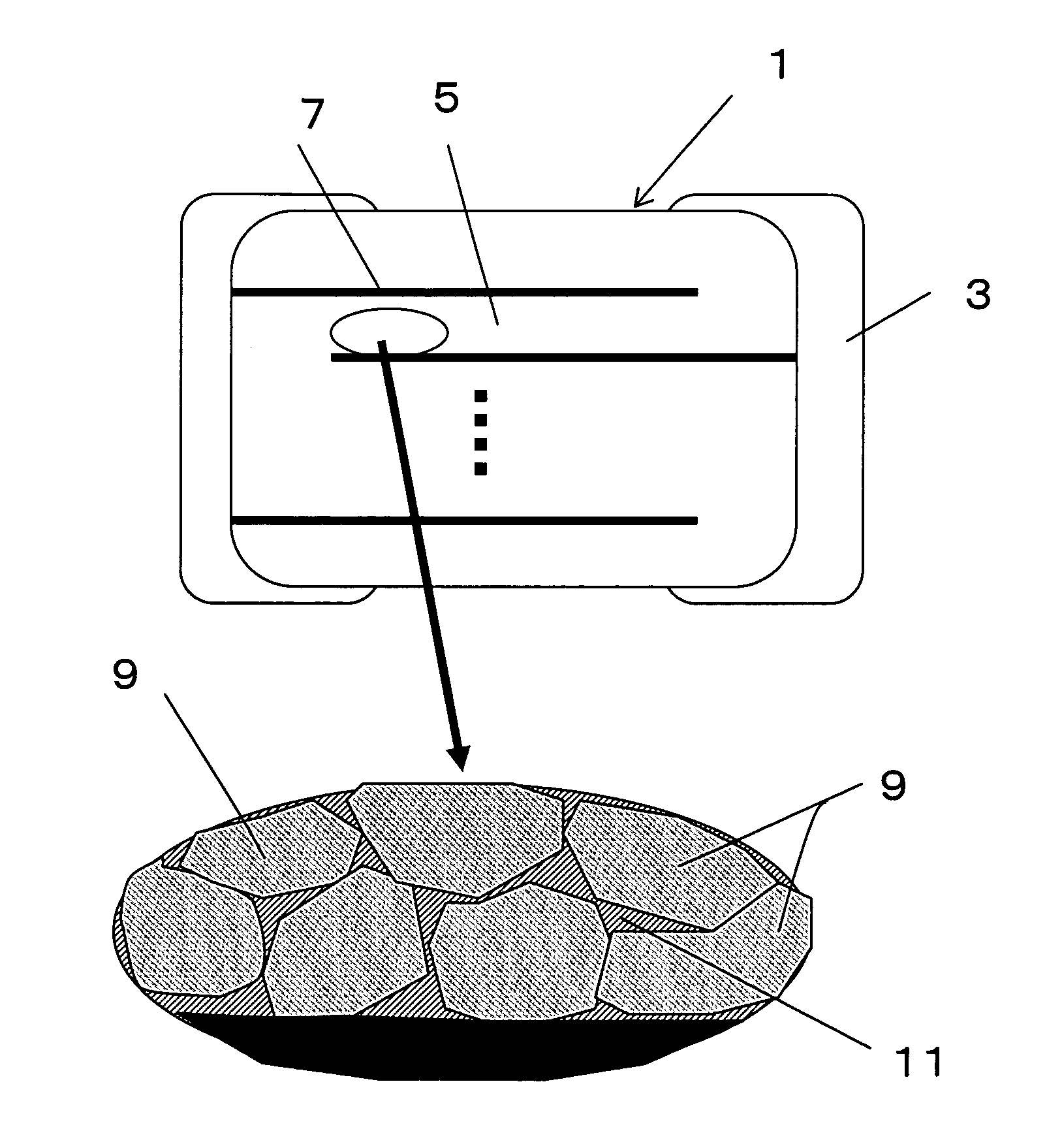
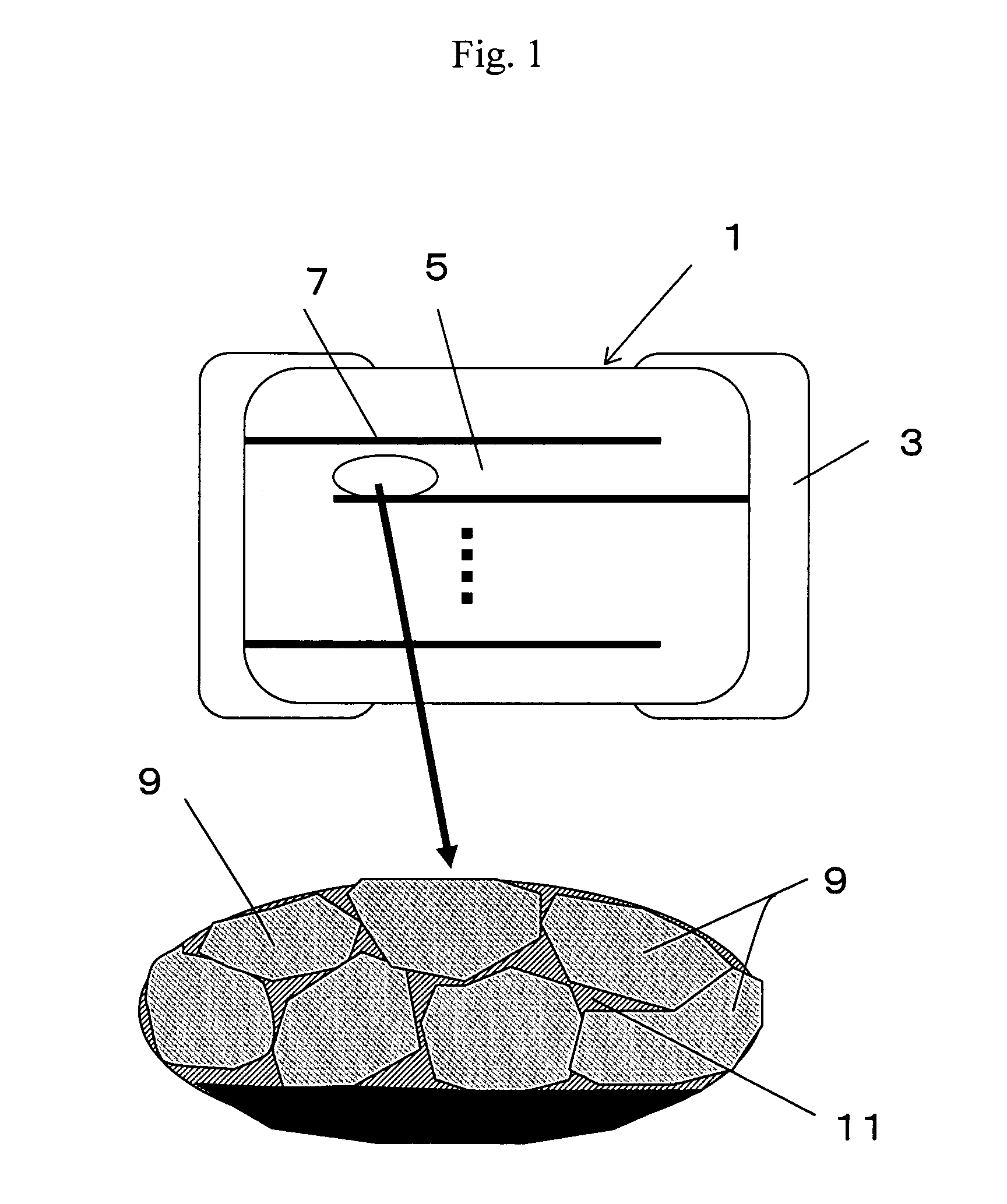
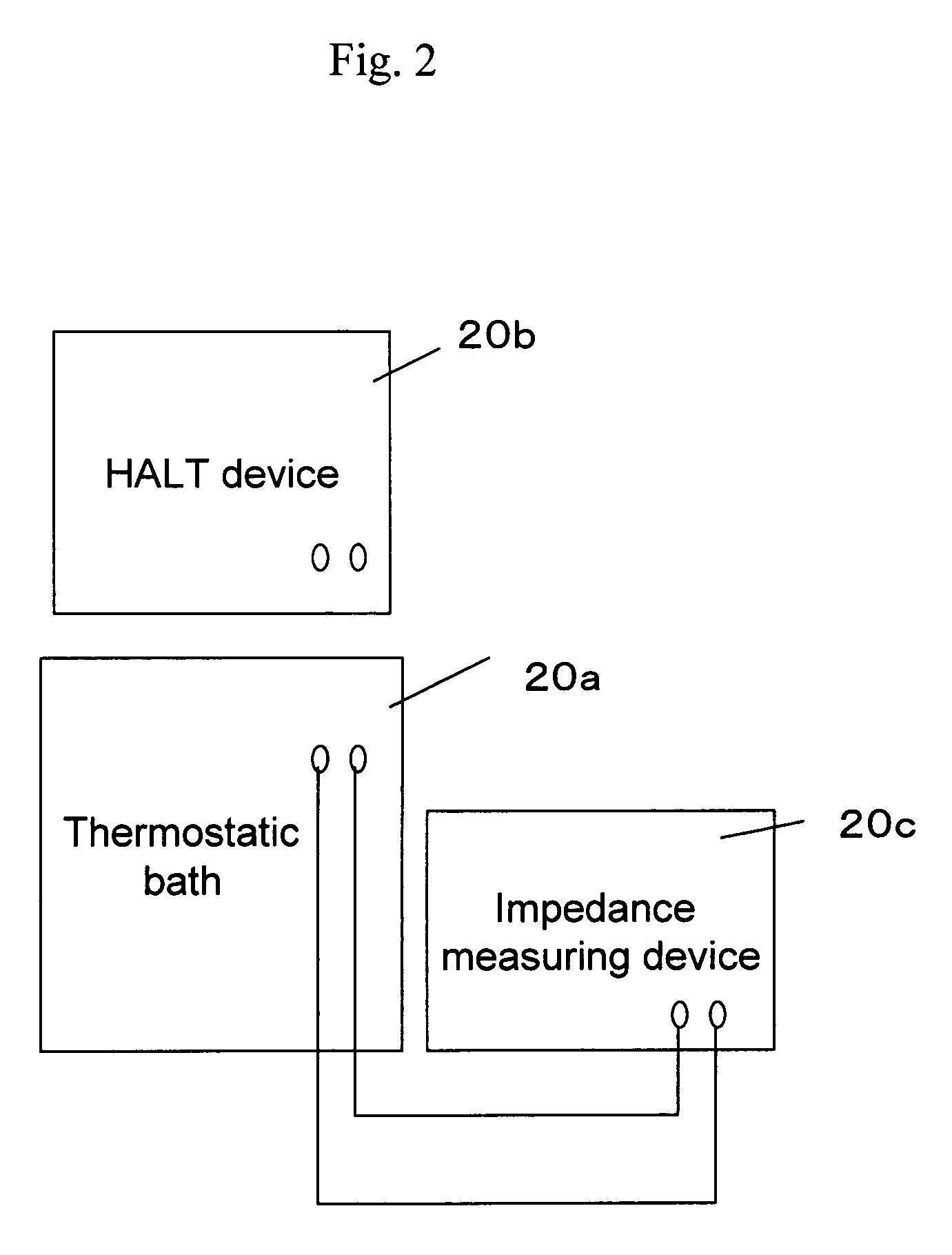
Dielectric ceramics, multilayer ceramic capacitor and method for manufacturing the same
a multi-layer ceramic and capacitor technology, applied in the direction of fixed capacitors, stacked capacitors, fixed capacitor details, etc., can solve the problems of abnormal grain growth during firing at atmospheric pressure, low relative dielectric constant of dielectric ceramics, and inability to uniformly size crystal grains constituting dielectric layers, etc., to achieve high relative dielectric constant, stable temperature characteristic, and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0081]The following examples illustrate the manner in which the present invention can be practiced. It is understood, however, that the examples are for the purpose of illustration and the invention is not to be regarded as limited to any of the specific materials or condition therein.
example i
[0082]Regarding the dielectric ceramics of the present invention, the effect of volume per unit cell represented by a product of lattice constant (a, b, c) figured out from X-ray diffraction pattern was checked. First, dielectric primary powders obtained through sol-gel method, hydrothermal synthesis method, oxalic acid method and solid phase method shown in Table 1 were prepared. These powders were prepared so as to have the ratio Ba / Ti of 1.005.
[0083]The next step was to dry powders. When a zeolitic drying agent was not employed, the above powders went through preliminary drying at atmospheric pressure and in the atmosphere of temperature 200° C.
[0084]Meanwhile when a zeolitic drying agent was employed, the dielectric primary powders so prepared went through dry-heat process at atmospheric pressure and 400° C. The zeolitic drying agent used was mainly composed of aluminosilicate and had the specific surface of 600 m2 / g. Thereby, dielectric powders were obtained. The quantity of th...
example 2
[0092]First, to check the effect of glass softening point and thermal expansion coefficient, dielectric powder was molded into a 1 mm-thick tablet-like shape having a diameter of 12 mm and fired. Then, evaluation was made. The results were presented as dielectric ceramics in Tables 2 and 3. The mean grain size of barium titanate that was used, the ratio A / B, the ratio c / a, the added amount, firing temperature and glass composition were shown in Tables 2 and 3. By plating, 0.1 parts by weight of Mg, 1 part by weight of Y and 0.2 parts by weight of Mn in terms of oxide to 100 parts by weight of barium titanate powder were contained in the barium titanate powder used here. 1 part by weight of glass component to 100 parts by weight of barium titanate powder was contained in glass powder. The ratio of A site / B site in BT powder used here was 1.003 or 1.001.
[0093]The softening point of glass powder was measured with a TG-DTA after molding glass powder into a tablet-like shape. The thermal...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mean grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com