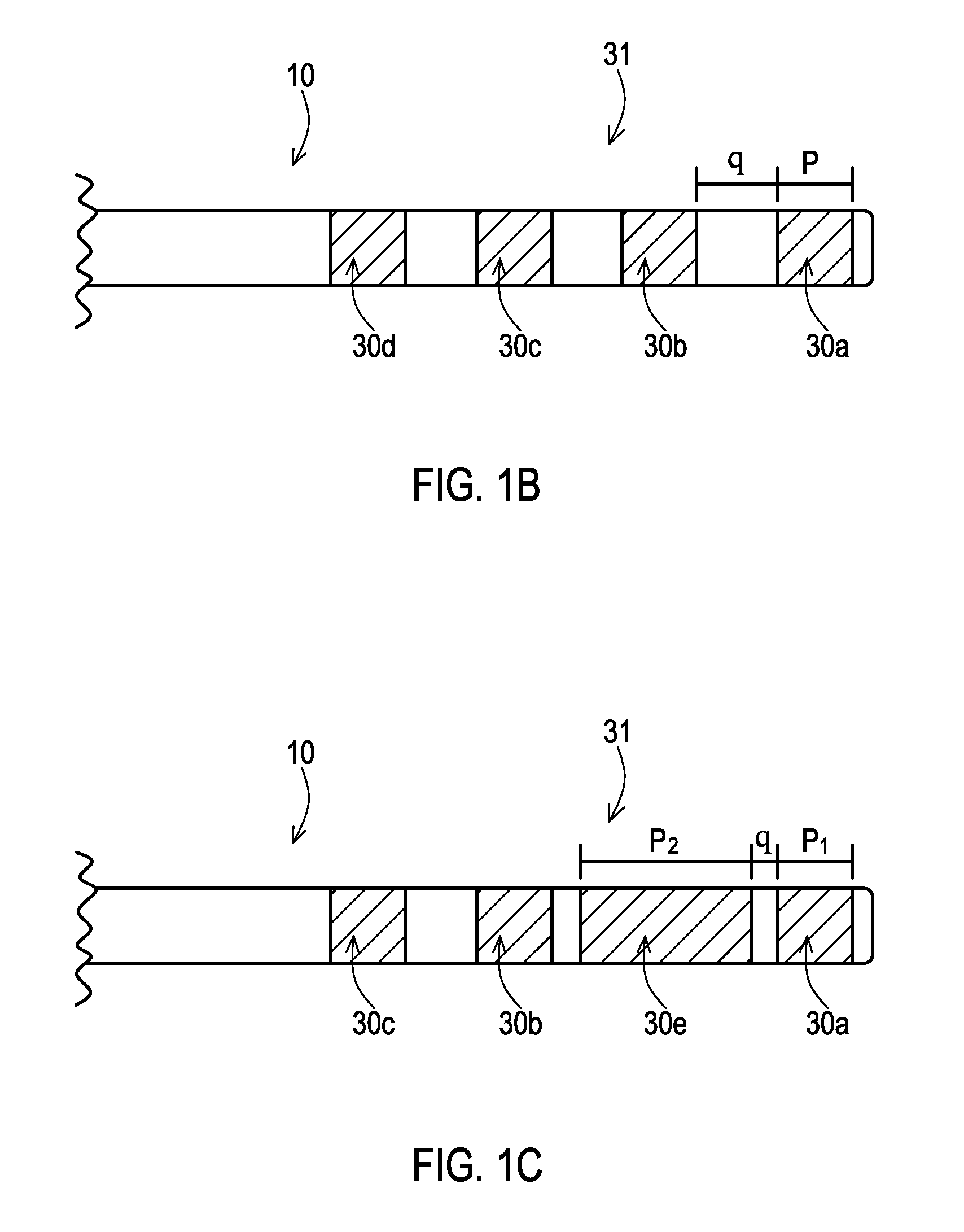
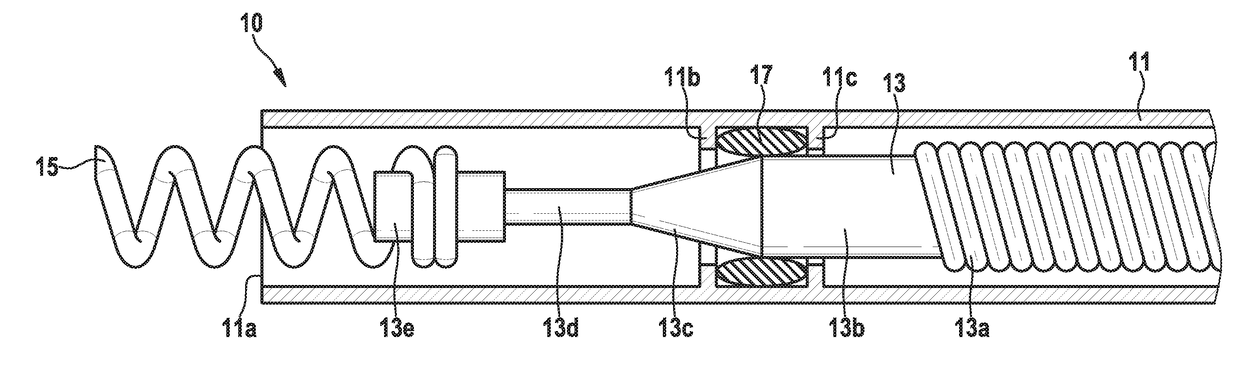
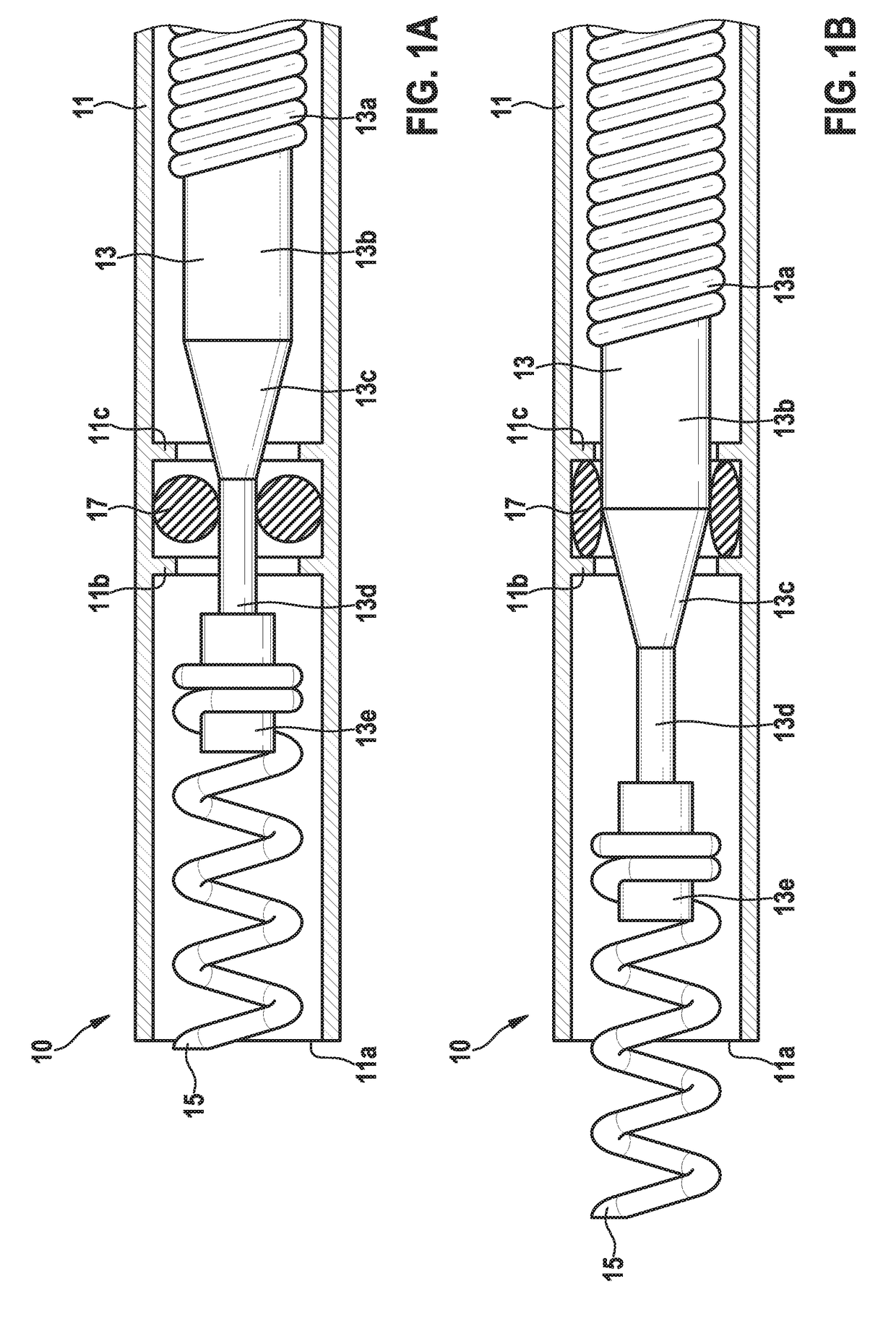
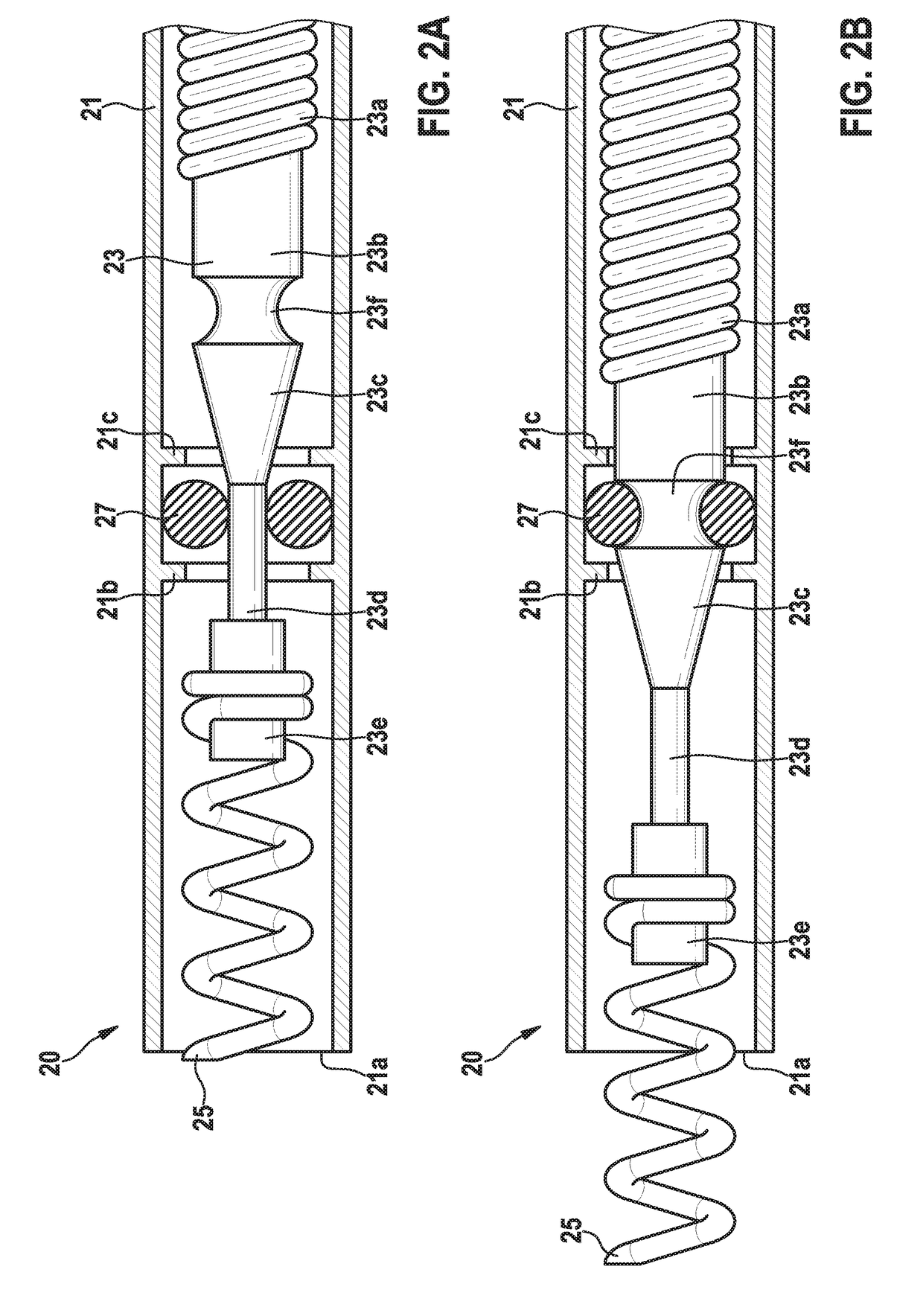
Patents
Literature
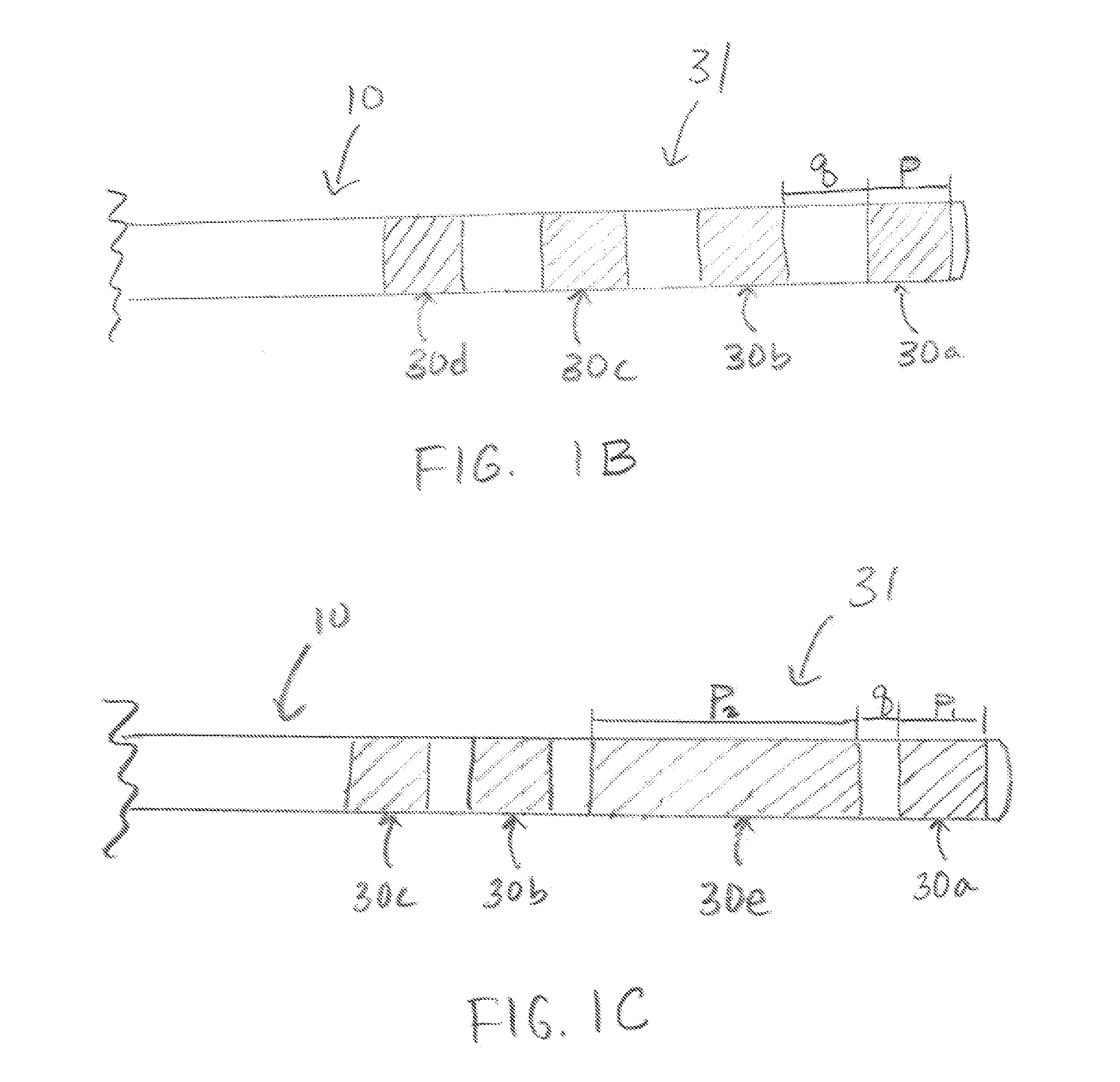
31 results about "Icd lead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
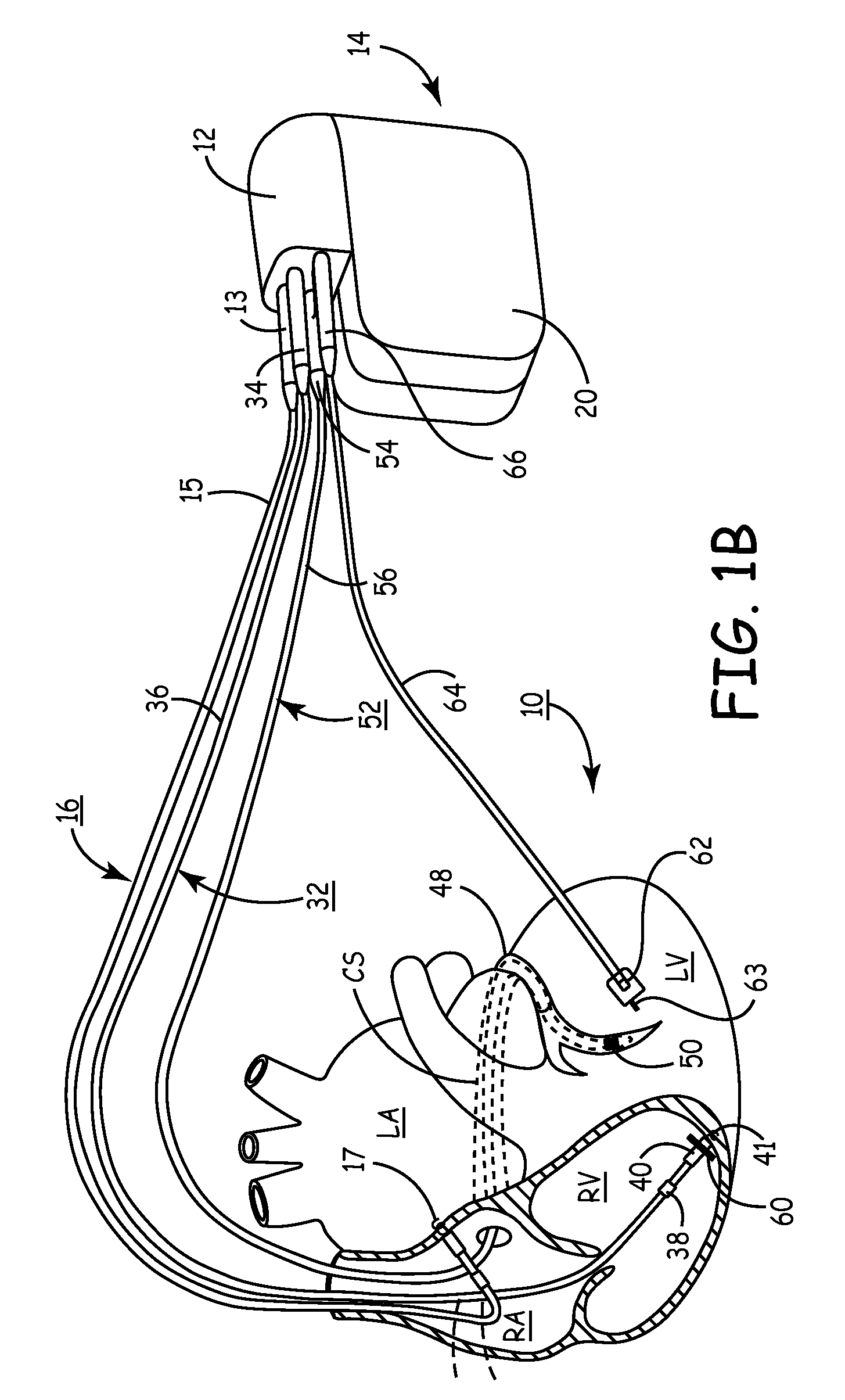
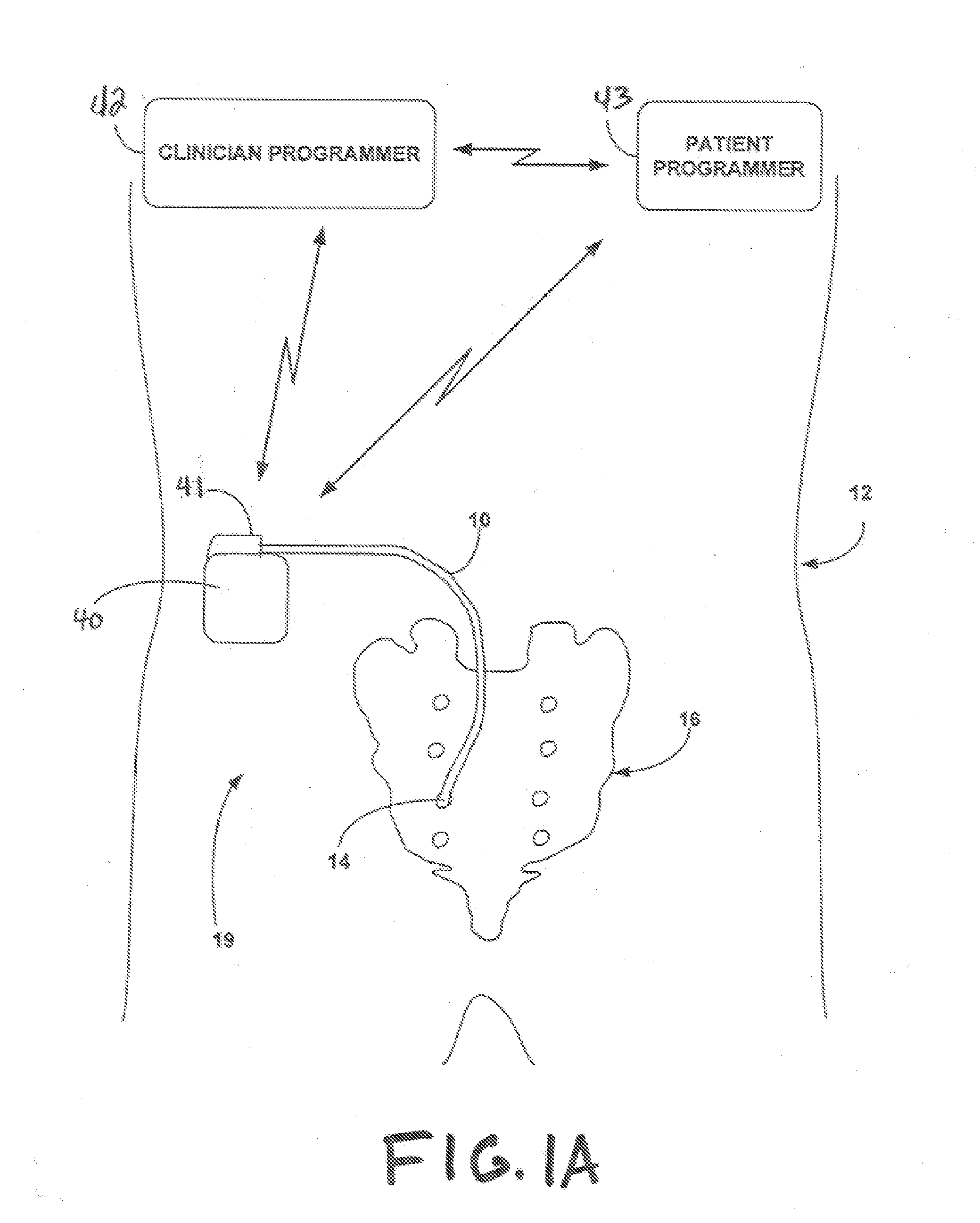
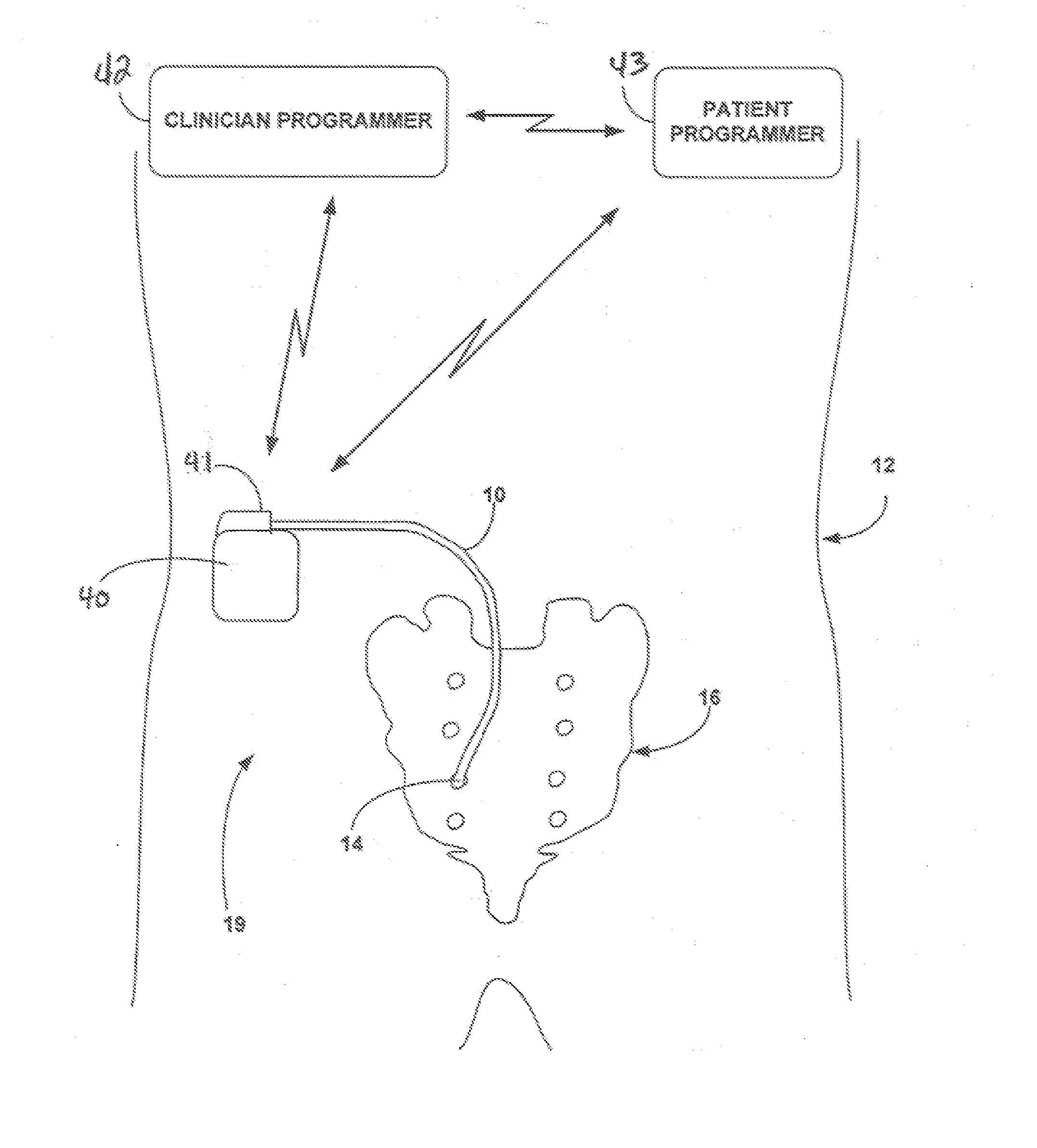
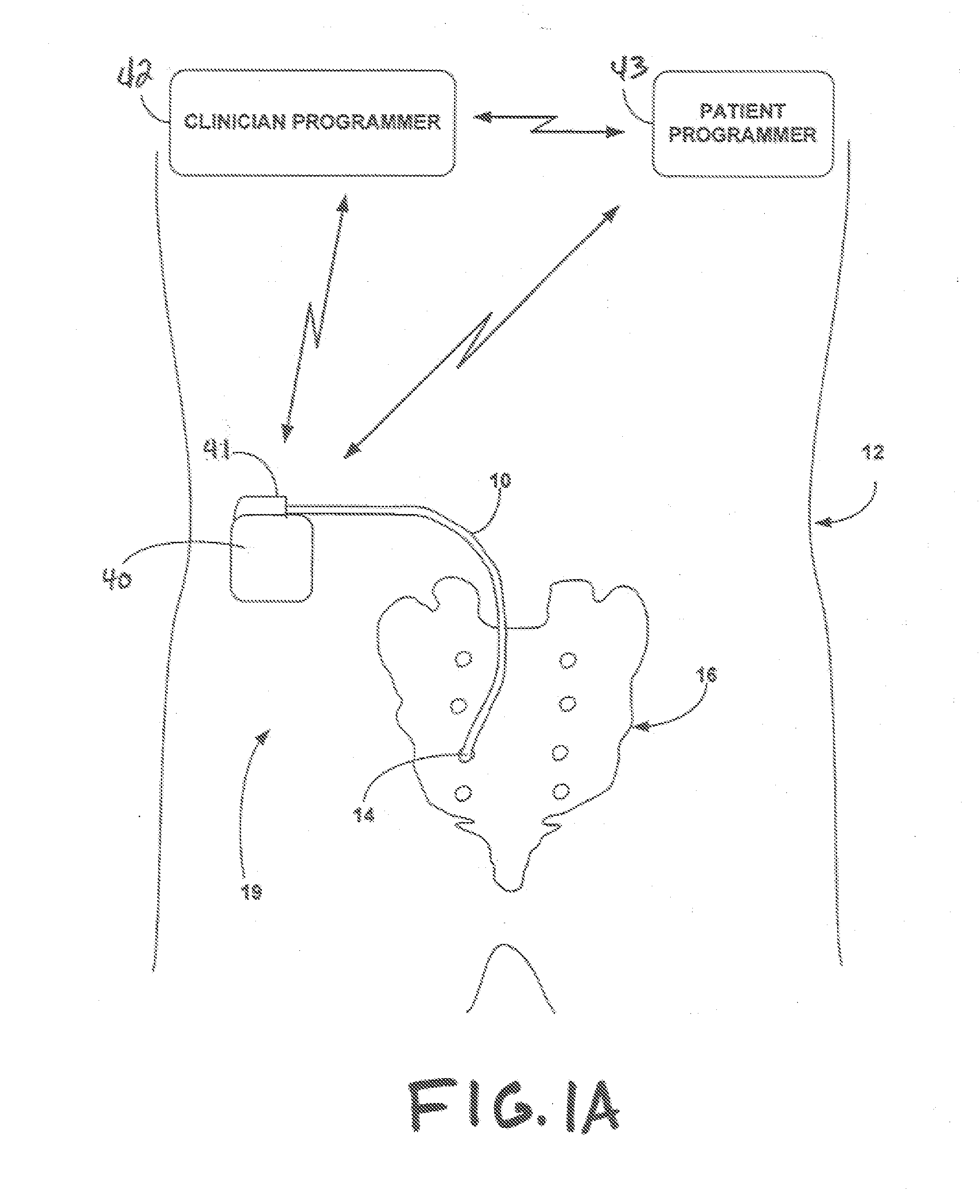
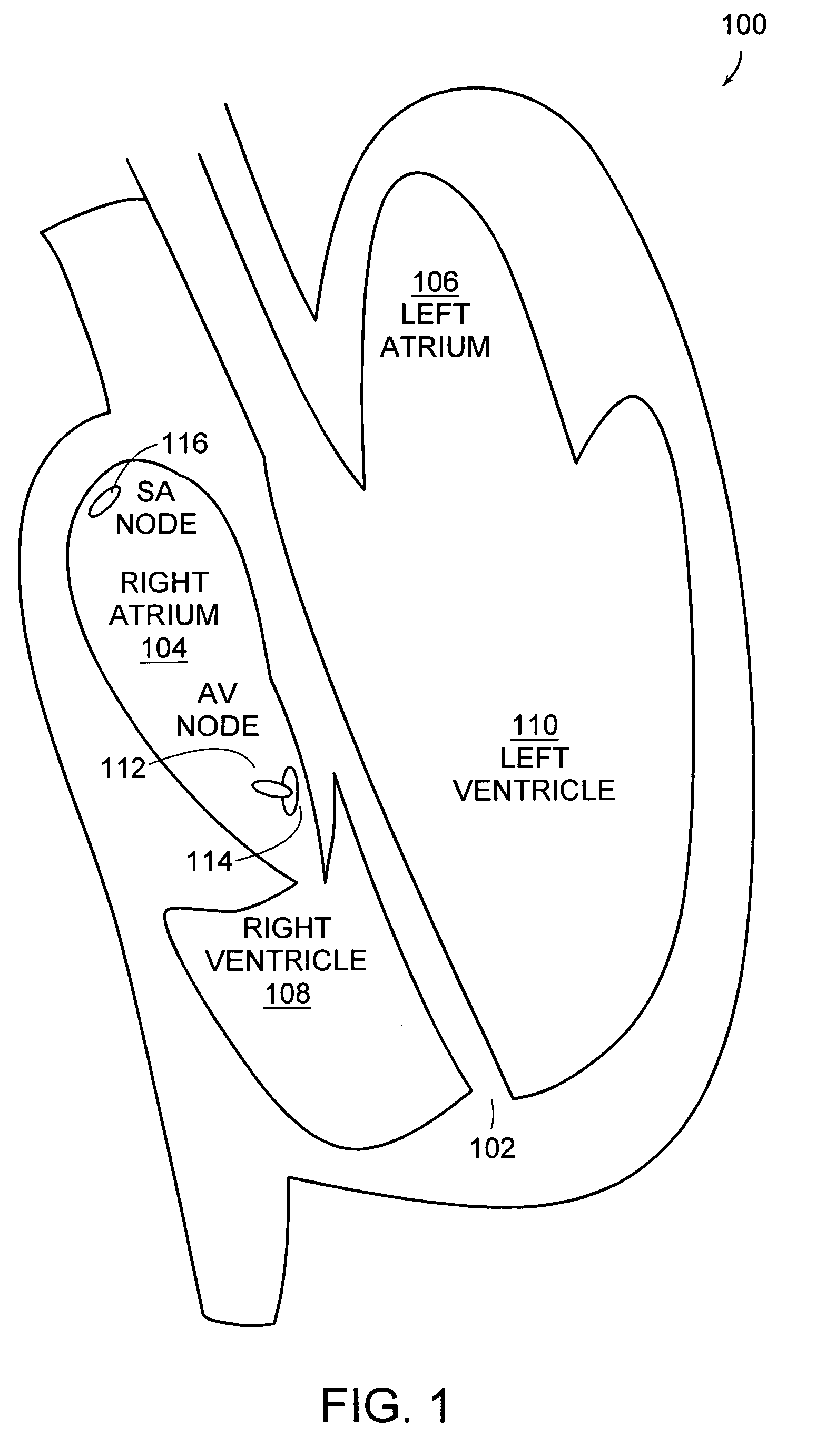
A pacemaker or implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) delivers energy to your heart muscle through wires called leads. A lead extraction is when one or more of those are removed.
MRI-safe implantable lead
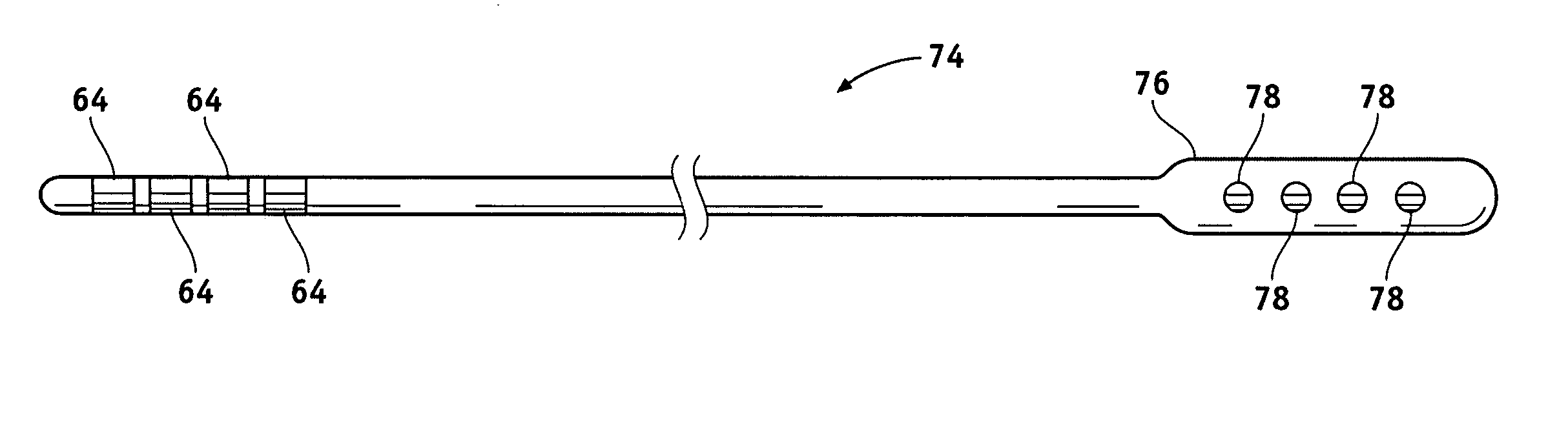
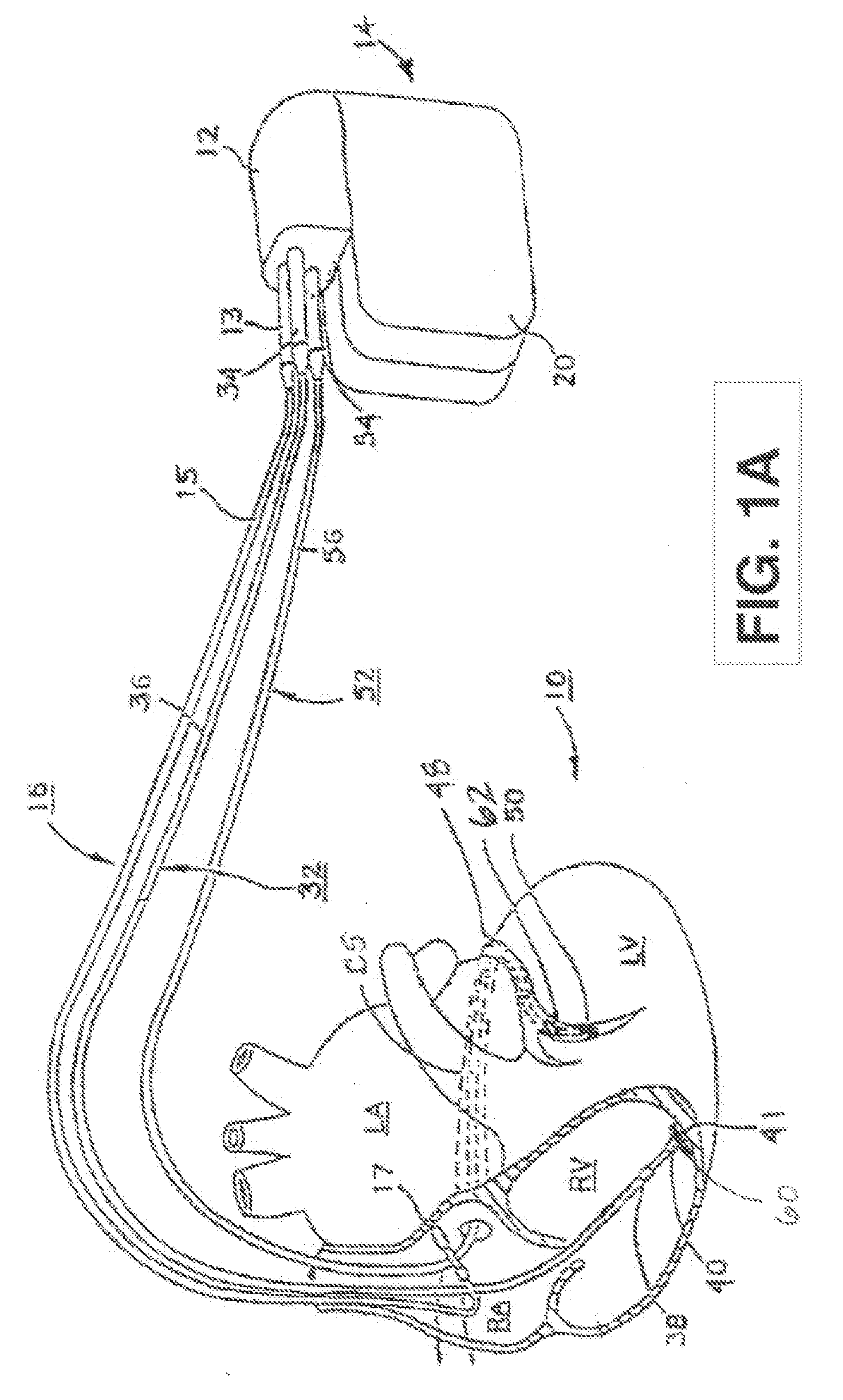
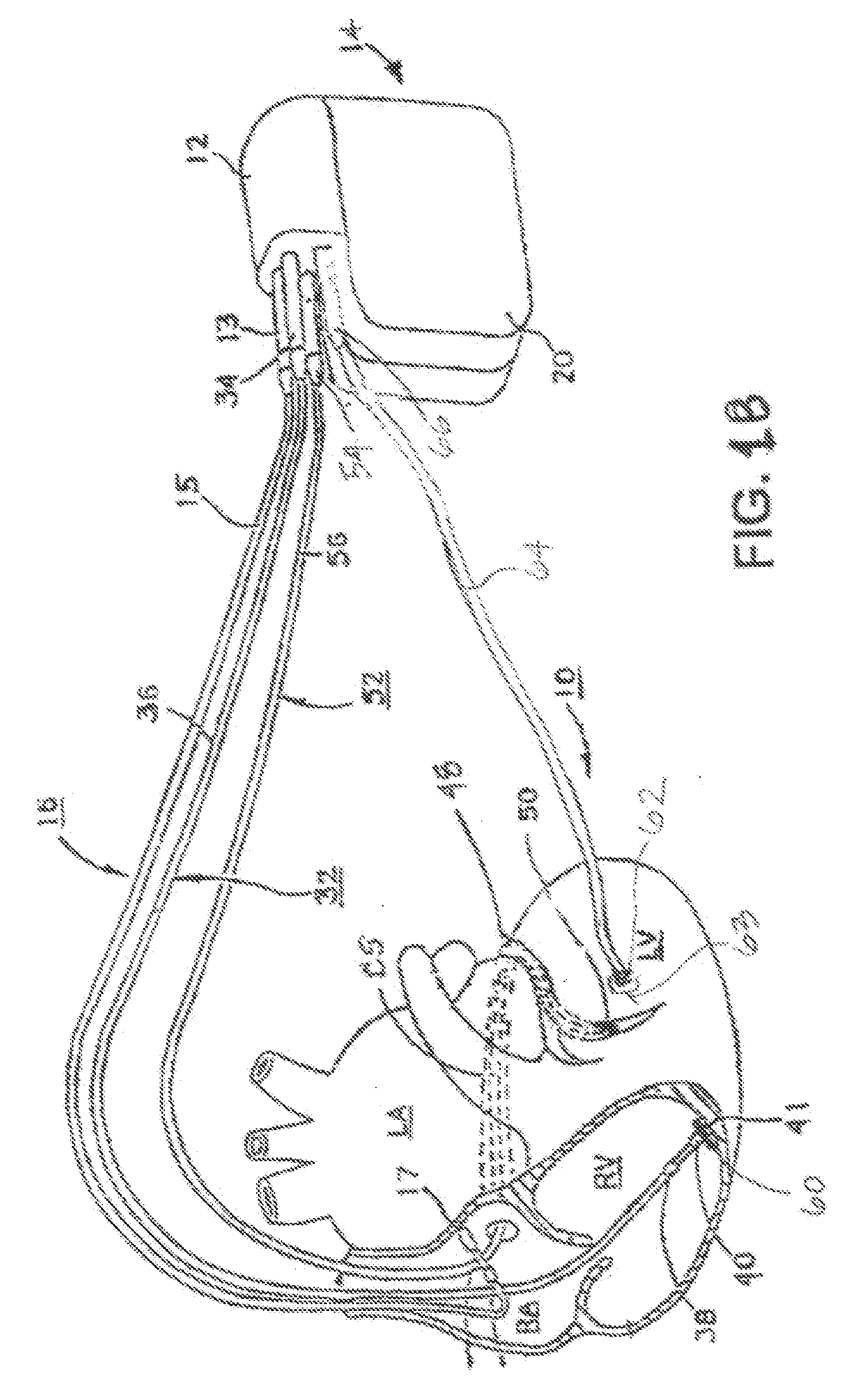
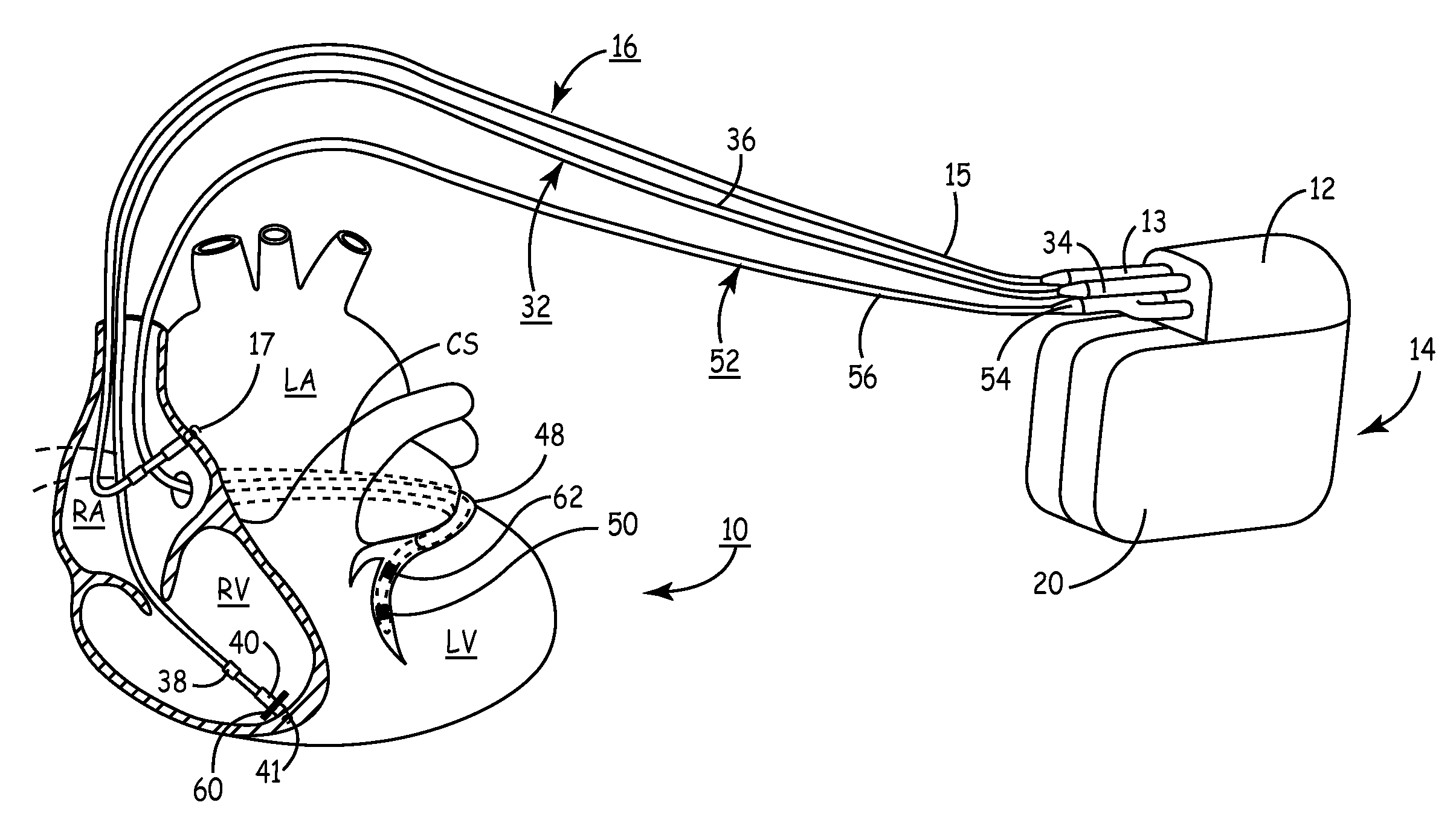
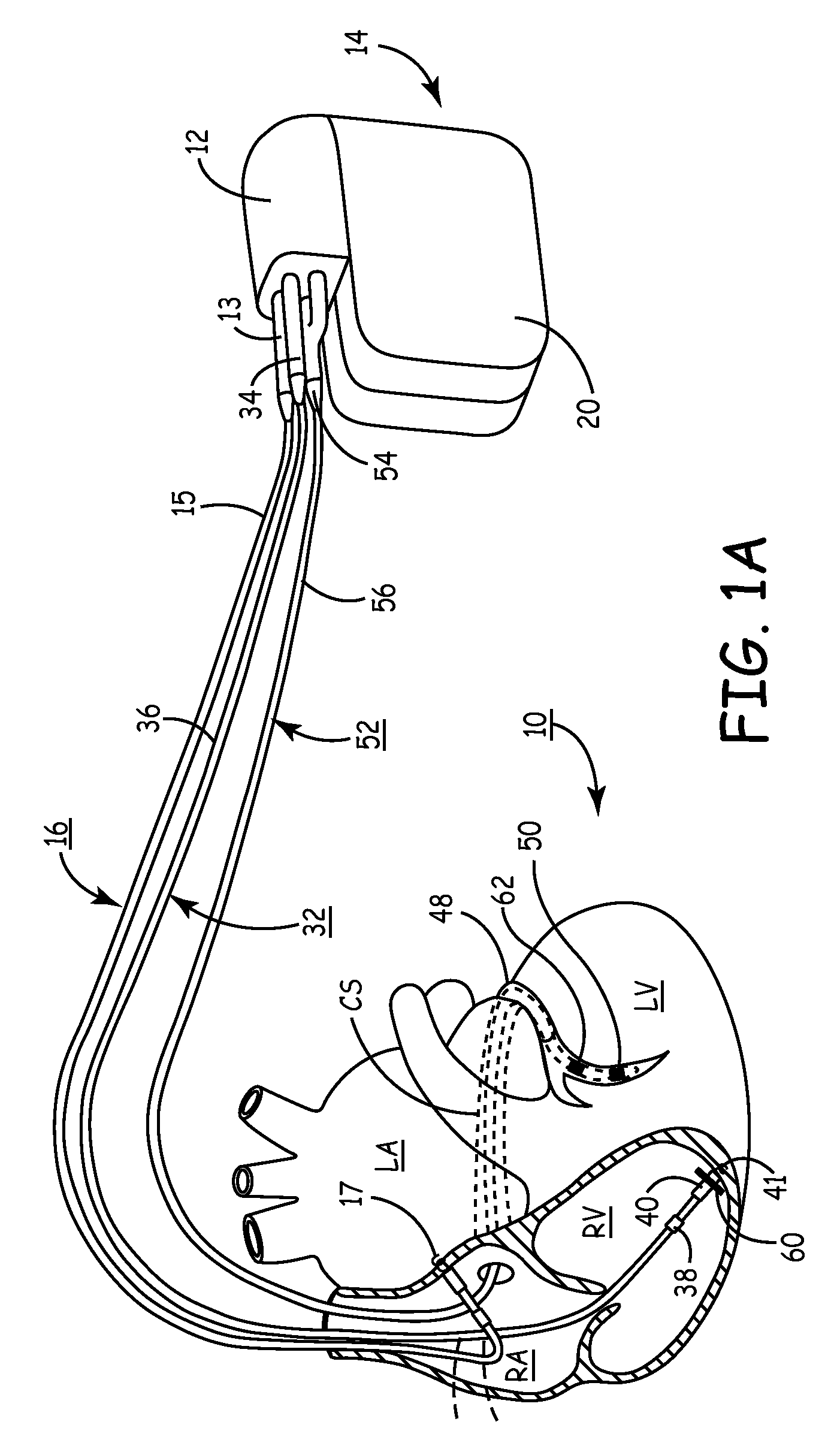
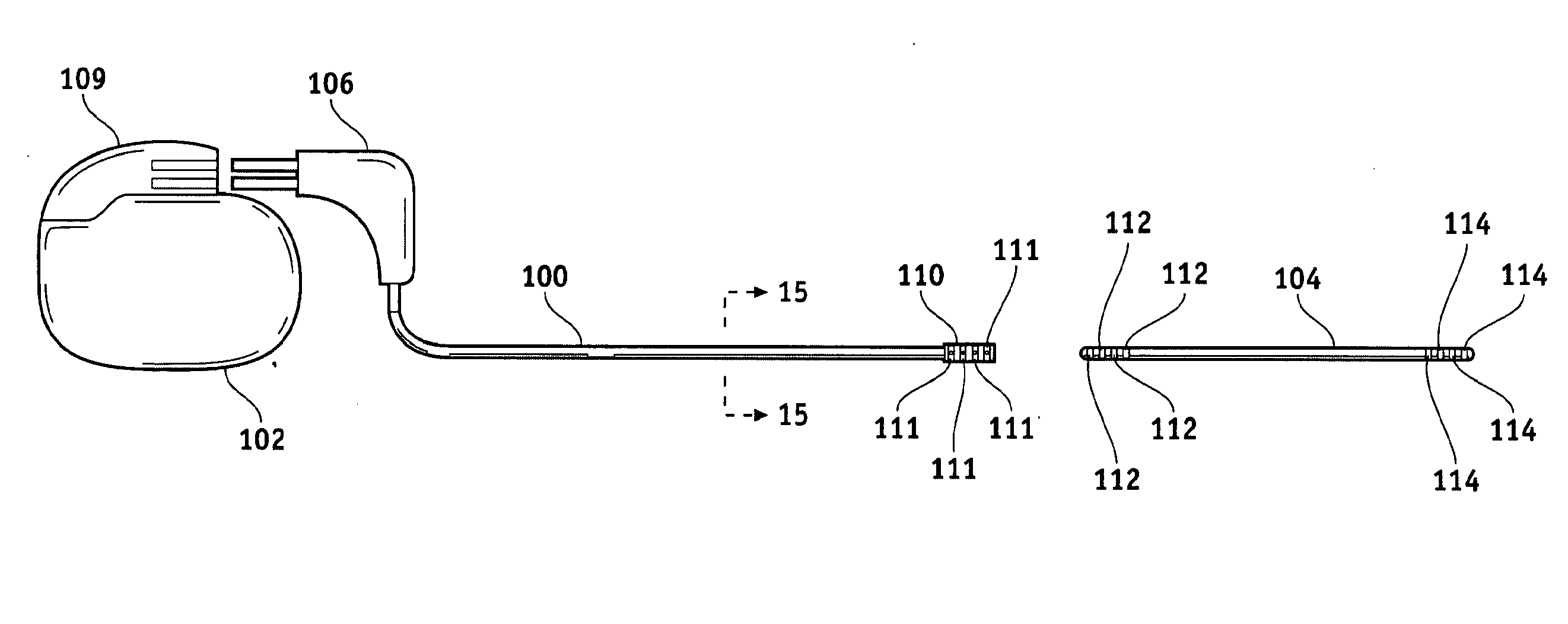
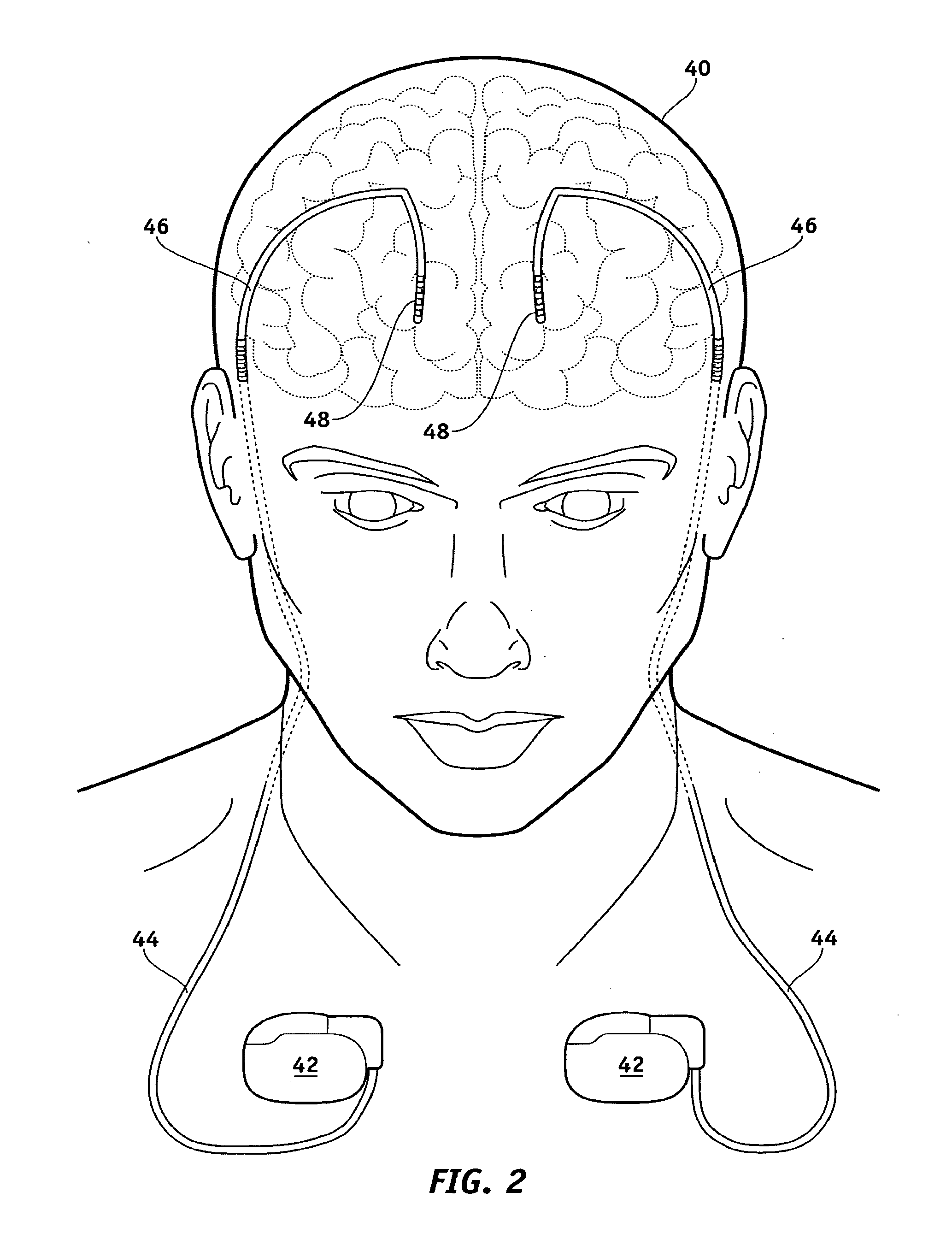
A stimulation lead is configured to be implanted into a patient's body and includes at least one distal stimulation electrode and at least one conductive filer electrically coupled to the distal stimulation electrode. A jacket is provided for housing the conductive filer and providing a path distributed along at least a portion of the length of the lead for conducting induced RF energy from the filer to the patient's body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Mechanical ventricular pacing capture detection for a post extrasystolic potentiation (PESP) pacing therapy using at least one lead-based accelerometer
InactiveUS20080234771A1Improve cardiac perfusionDecrease in cardiac performanceCatheterHeart stimulatorsPost extrasystolic potentiationAccelerometer
A system and method for monitoring at least one chamber of a heart (e.g., a left ventricular chamber) during delivery of extrasystolic stimulation to determine if the desired extra-systole (i.e., ventricular mechanical capture following refractory period expiration) occurs. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads such as epicardial, endocardial, and / or coronary sinus leads equipped with motion sensor(s). The device receives and processes acceleration sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of chamber capture resulting from one or more pacing stimulus delivered closely following expiration of the refractory period. A threshold optimization method optionally evaluates capture and at least one of: runs an iterative routine to establish or re-establish chamber capture for the PESP therapy, sets a logical flag relating to chamber capture status and stores parameter(s) relating to successful chamber capture for one or more subsequent cardiac cycles.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Mechanical Ventricular Pacing Non-Capture Detection for a Refractory Period Stimulation (RPS) Pacing Therapy Using at Least One Lead-Based Accelerometer
InactiveUS20080269825A1Increase contractilityIncrease perfusionElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerLeft ventricular size
A system and method for monitoring at least one chamber of a heart (e.g., a left ventricular chamber) during delivery of a refractory period stimulation (RPS) therapy to determine if the desired non-capture (i.e., lack of ventricular mechanical capture due to refractory period stimulation) occurs. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads such as epicardial, endocardial, and / or coronary sinus leads equipped with motion sensor(s). The device receives and processes acceleration sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of chamber capture due to pacing stimulus delivery, non-capture due to RPS therapy delivery, and / or contractile status based on the qualities of evoked response to pacing stimulation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Redundant pacing system with leaded and leadless pacing
InactiveUS20110276102A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesHeart defibrillatorsTransceiverControl signal
A pacing system includes a controller operable to provide control signals indicating desired pacing signals, a pulse generator connected to the controller and operable to receive the control signals and to generate the desired pacing signals based on the control signals, at least one lead electrically connected to the pulse generator and extending into a user's heart and operable to provide the pacing signals to the heart, at least one electrode positioned in the user's heart and electrically connected to the at least one lead, the at least one electrode in contact with the user's heart and operable to stimulate the heart based on the pacing signals; and a transceiver, in communication with the pulse generator and operable to selectively transmit the pacing signals to the electrode wirelessly. The transceiver is controlled by the controller to transmit the pacing signals when pacing signals are not received by the electrode from the at least one lead. The lead may include multiple leads held together in a sugar moiety as a unitary body for insertion into the heart. Once in the heart, the sugar moiety dissolves to allow the leads to separate for implantation at different points in the heart.
Owner:WINTHROP UNIV HOSPITAL
Method and apparatus for fixating a pacing lead of an implantable medical device
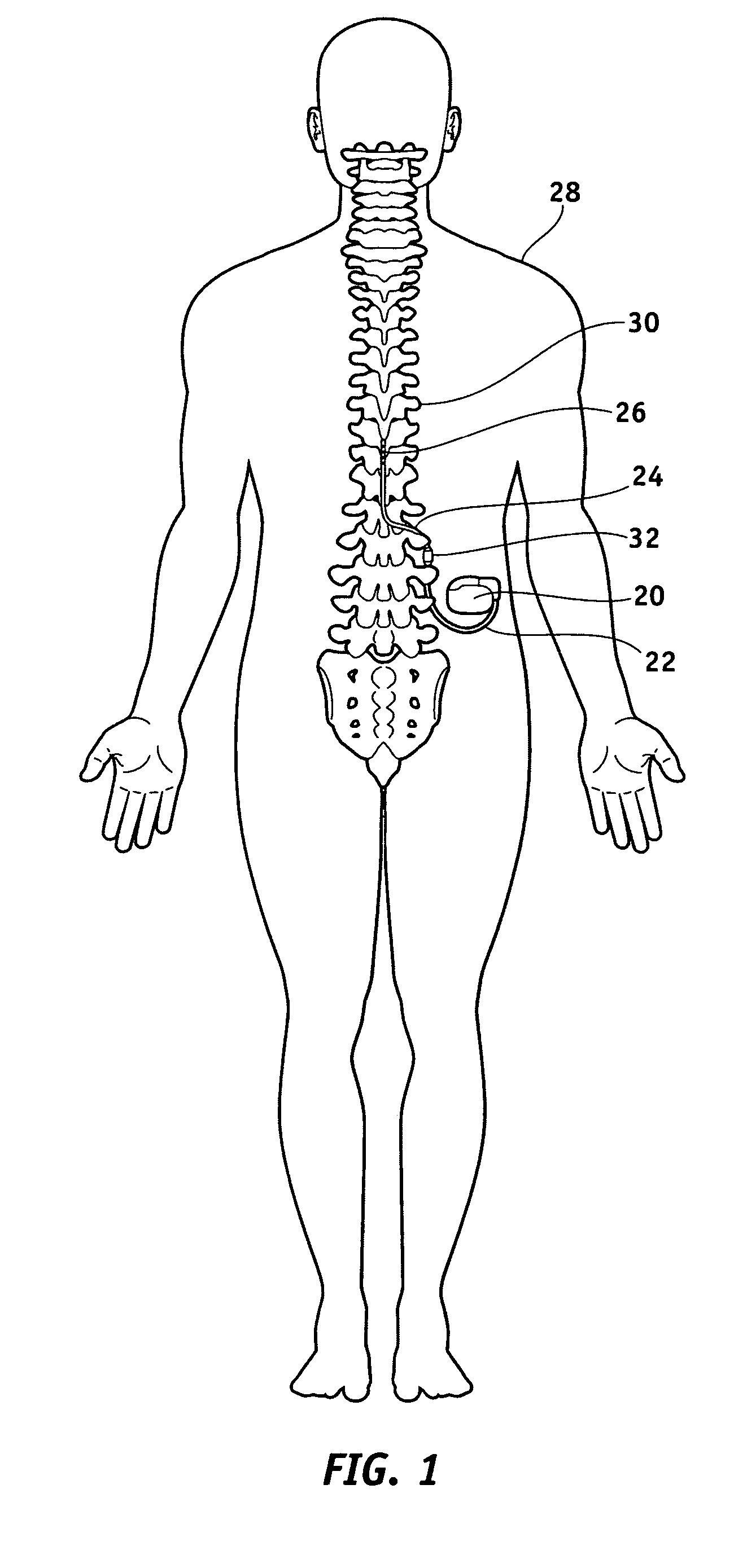
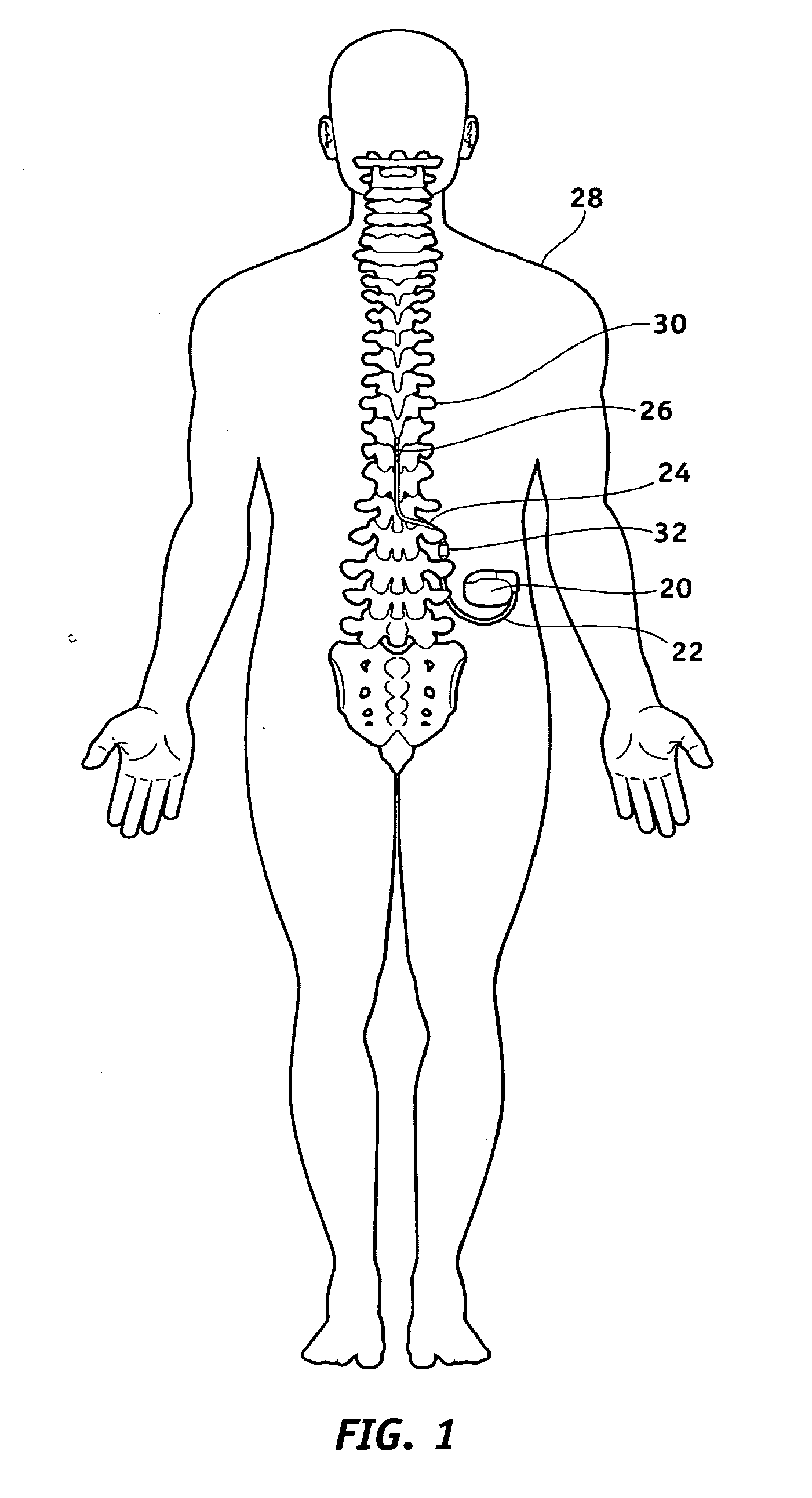
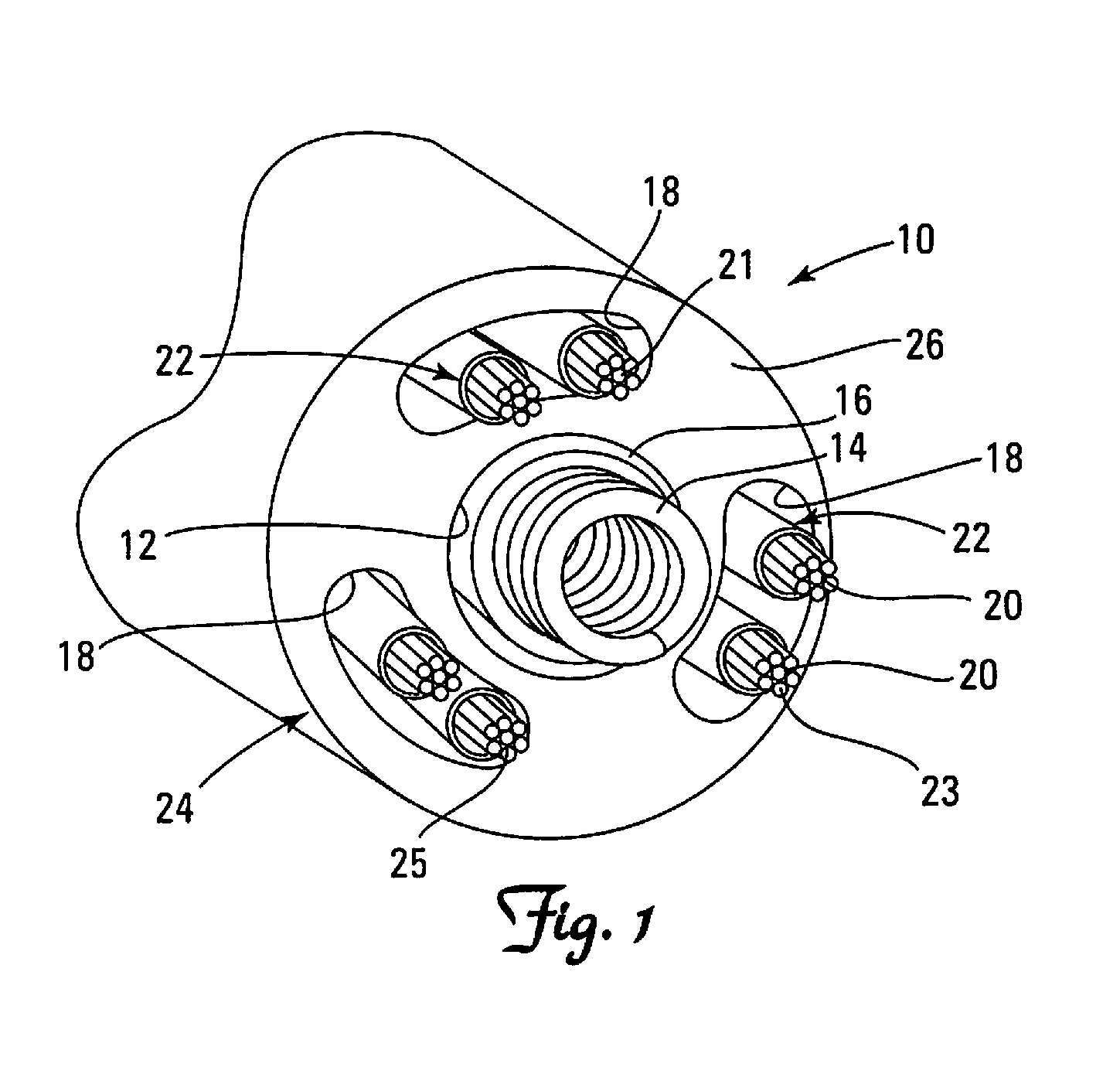
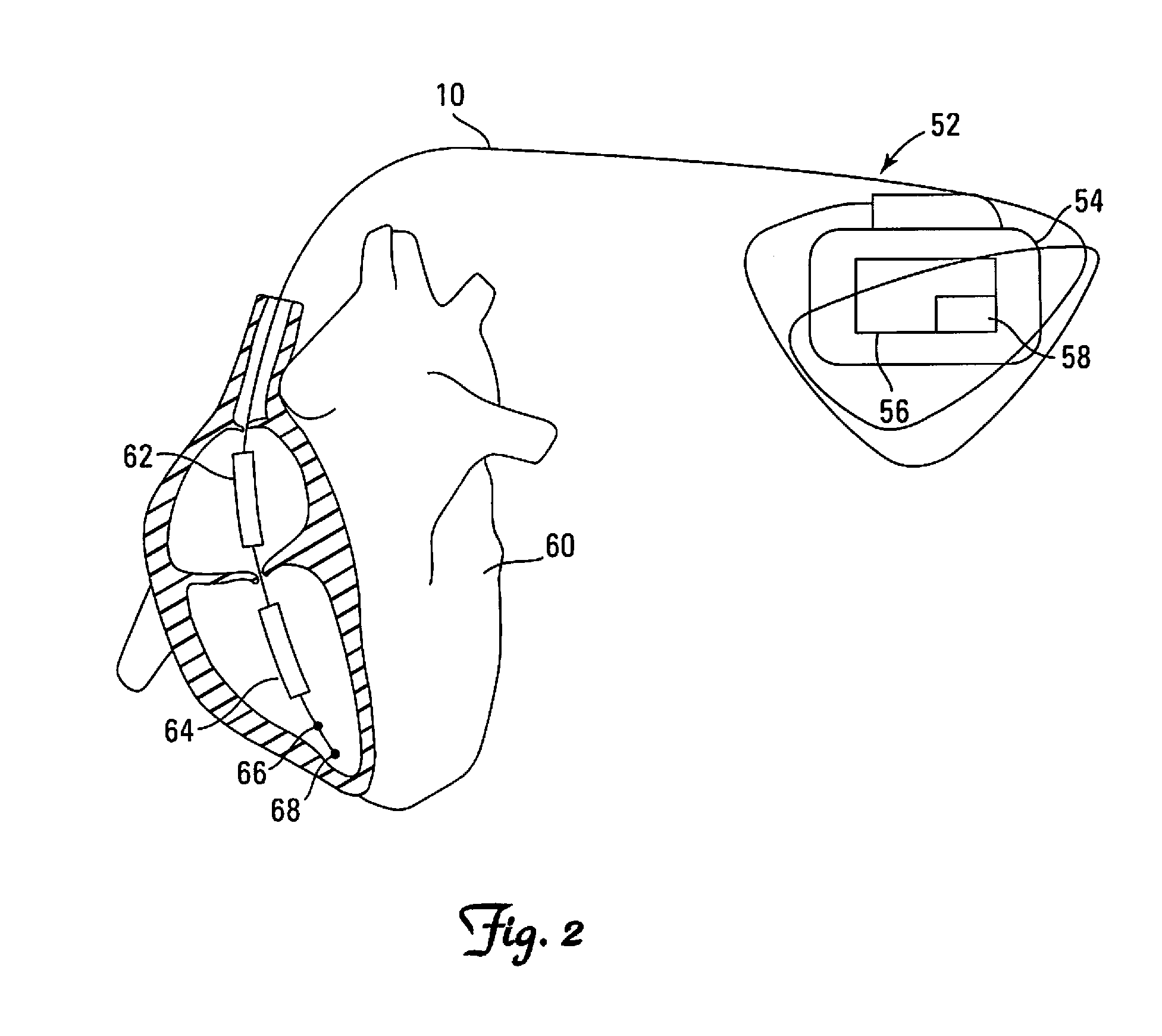
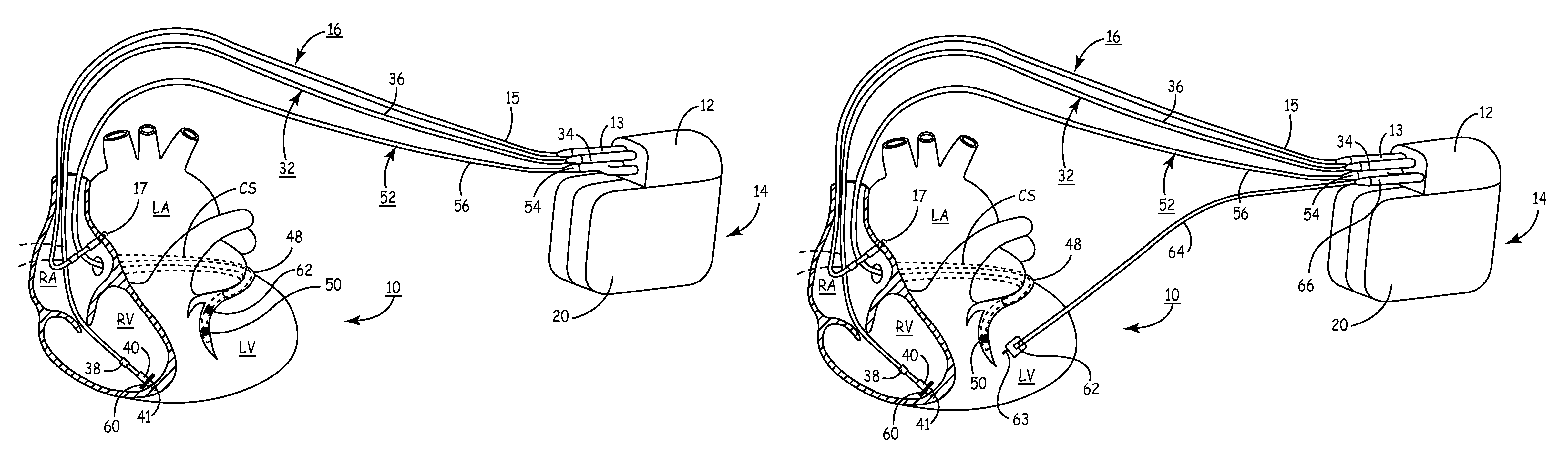
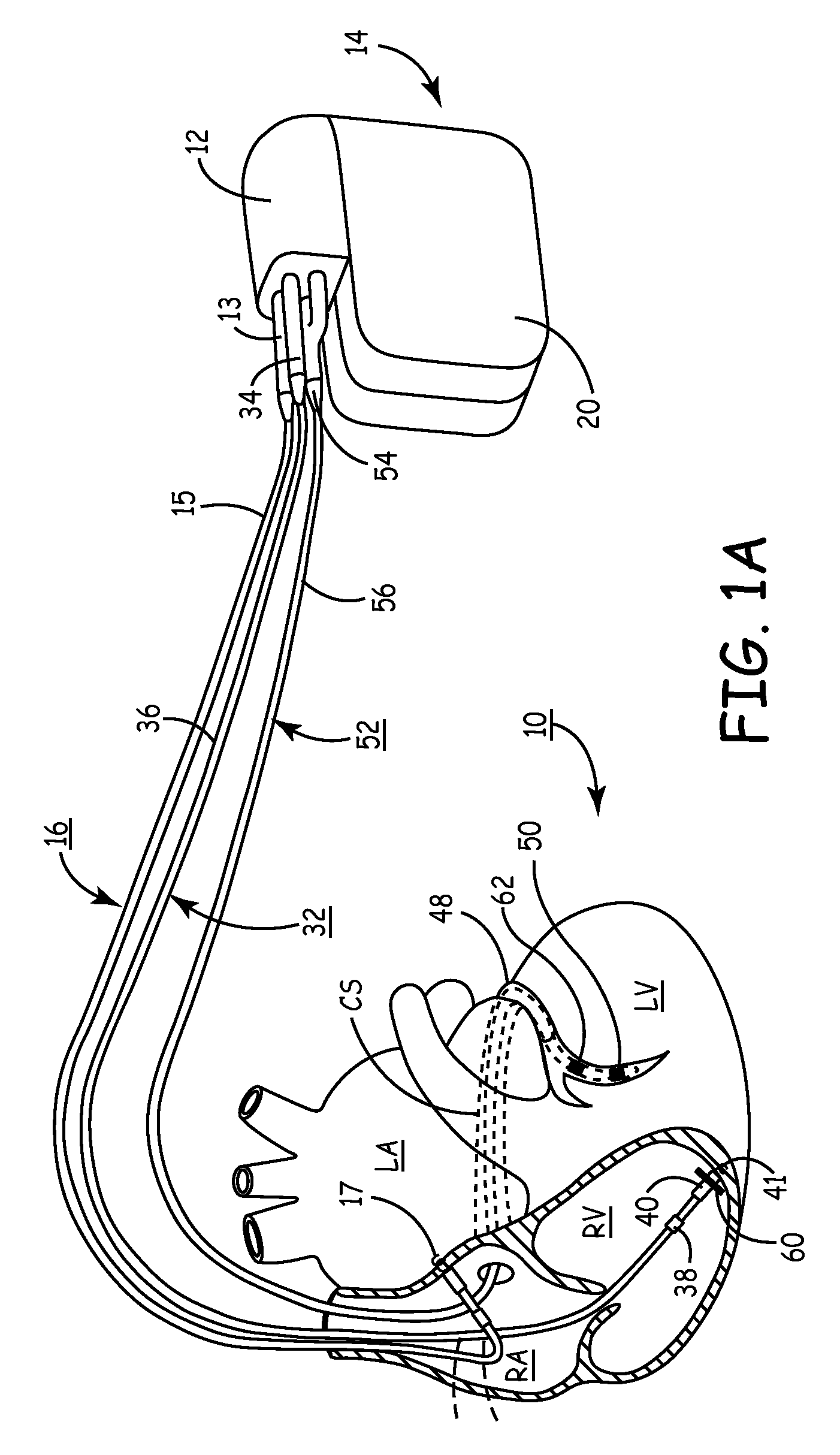
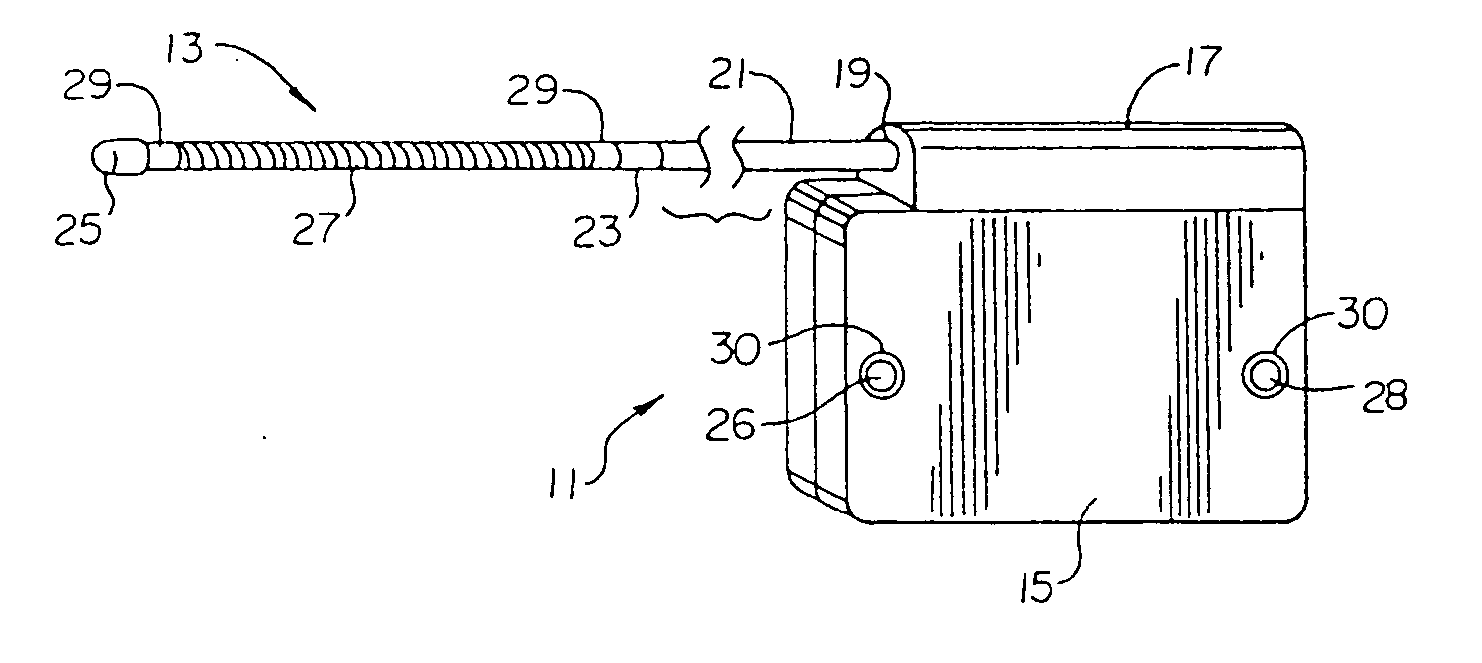
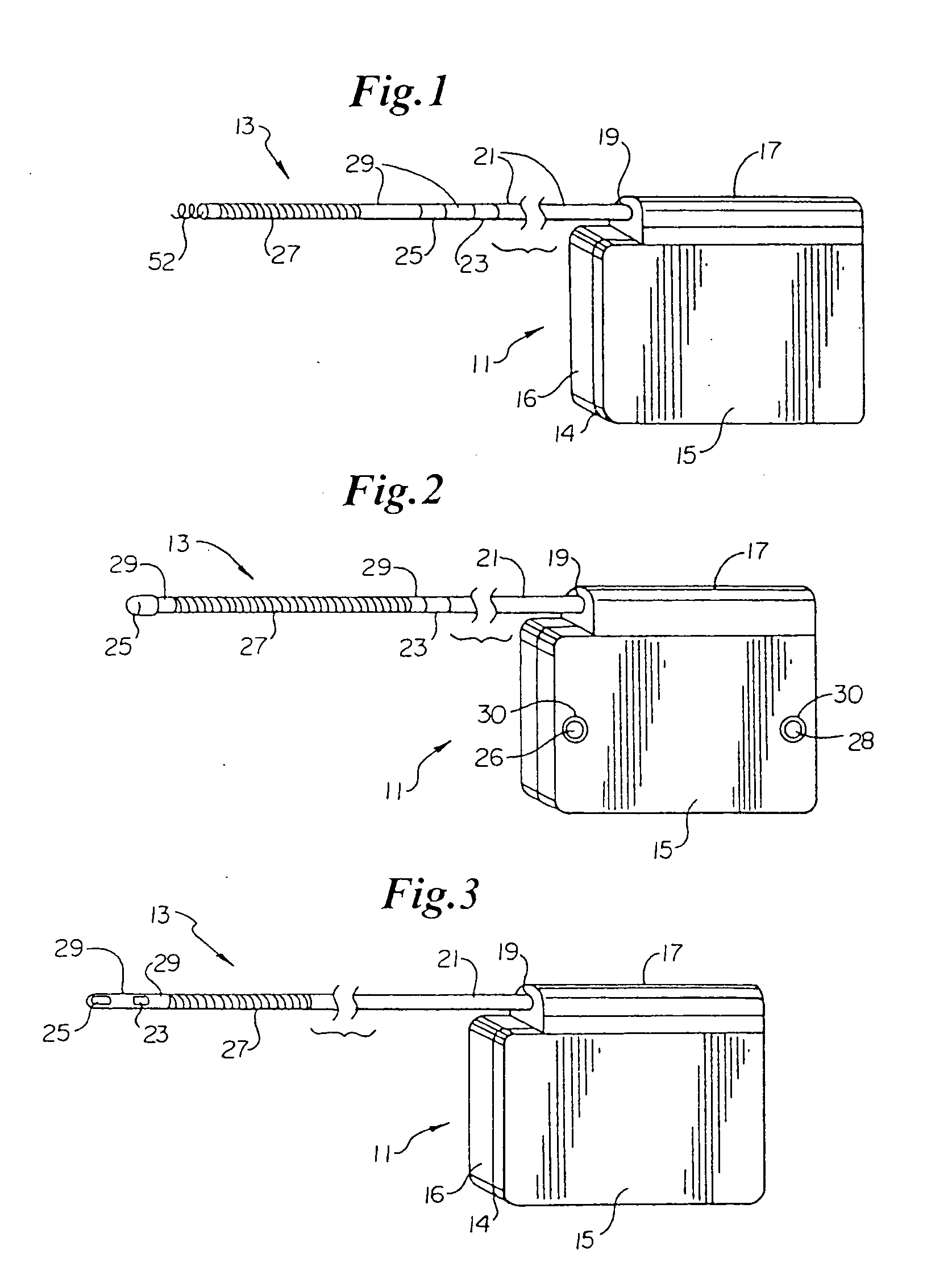
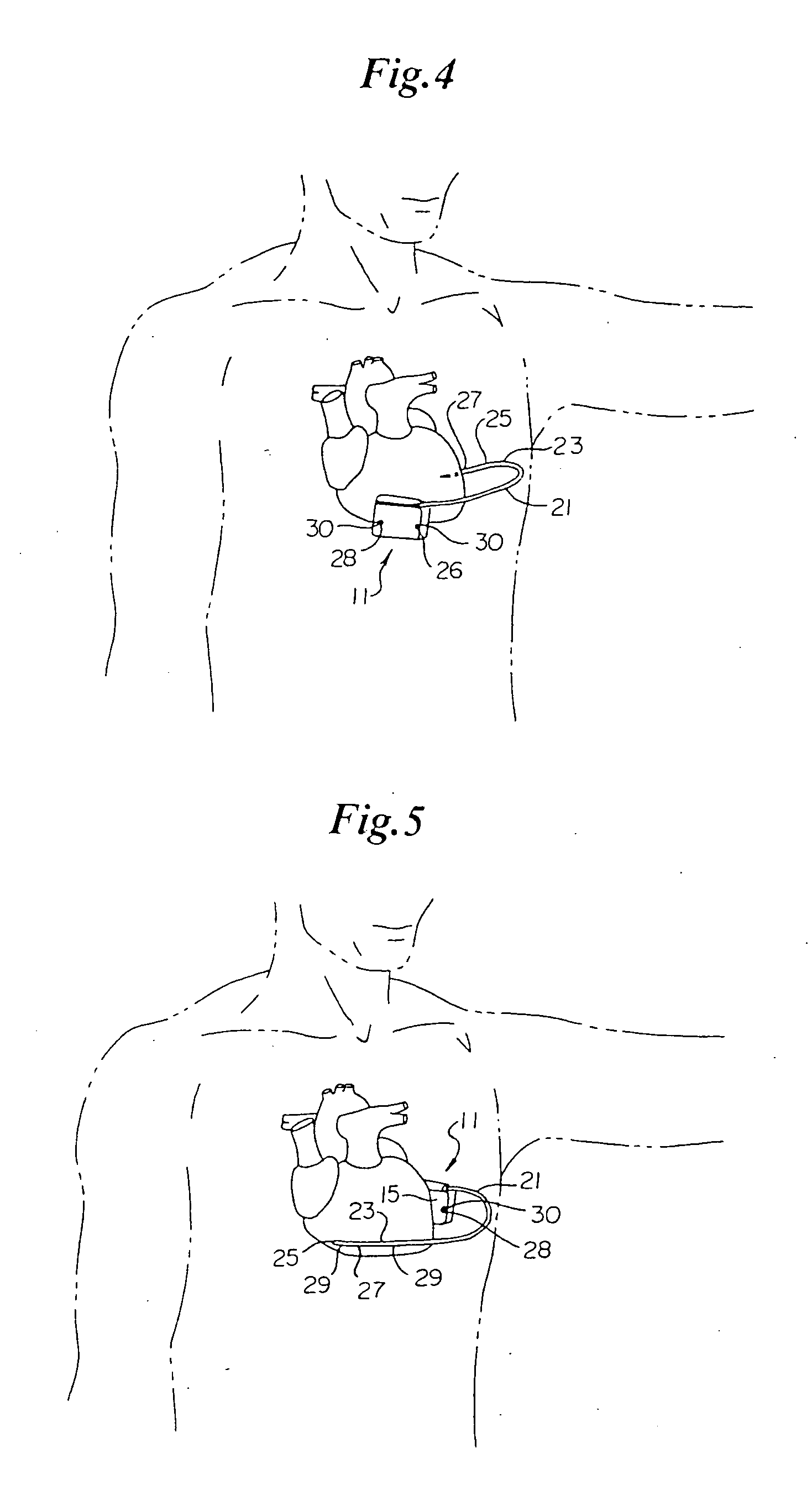
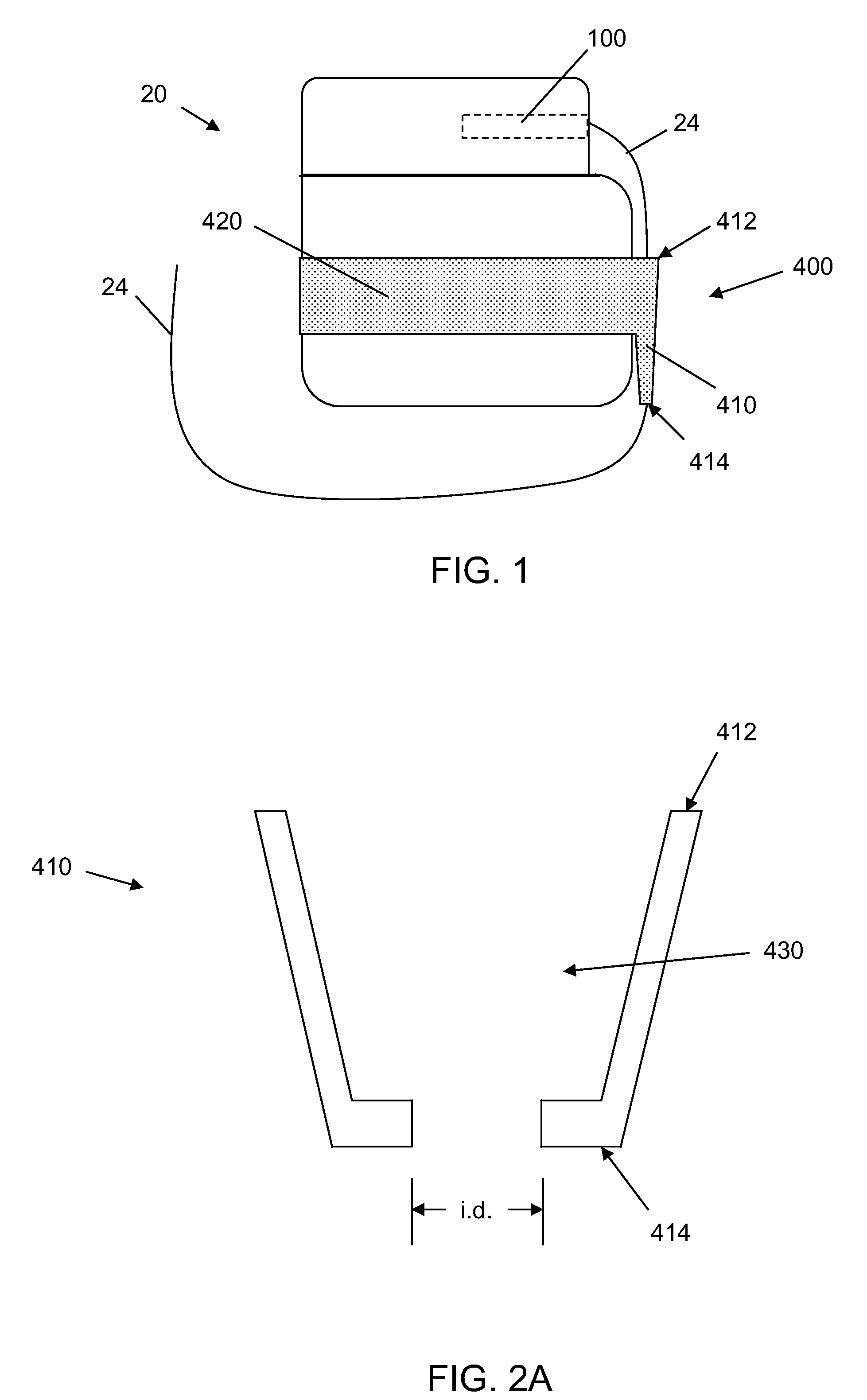
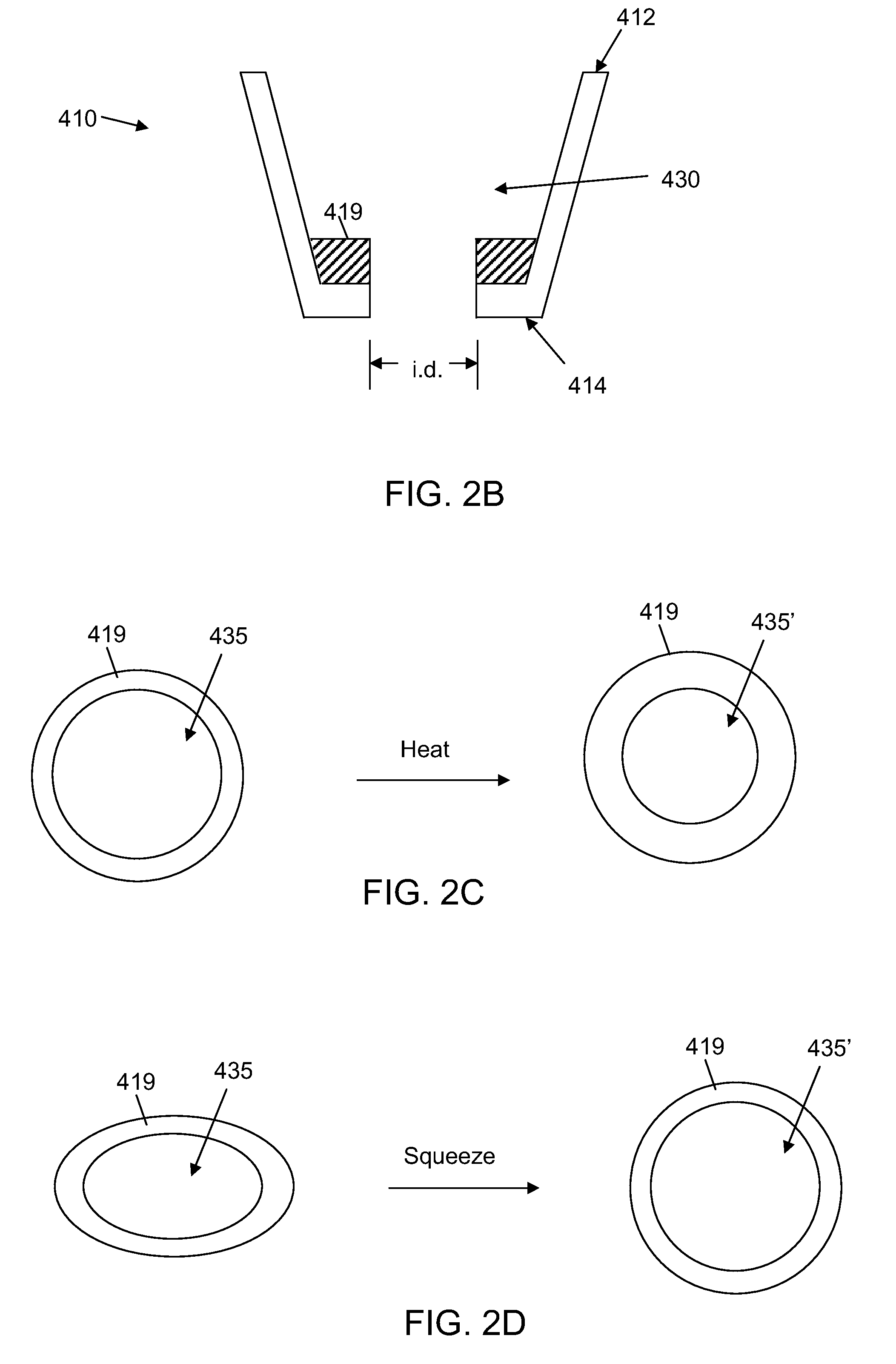
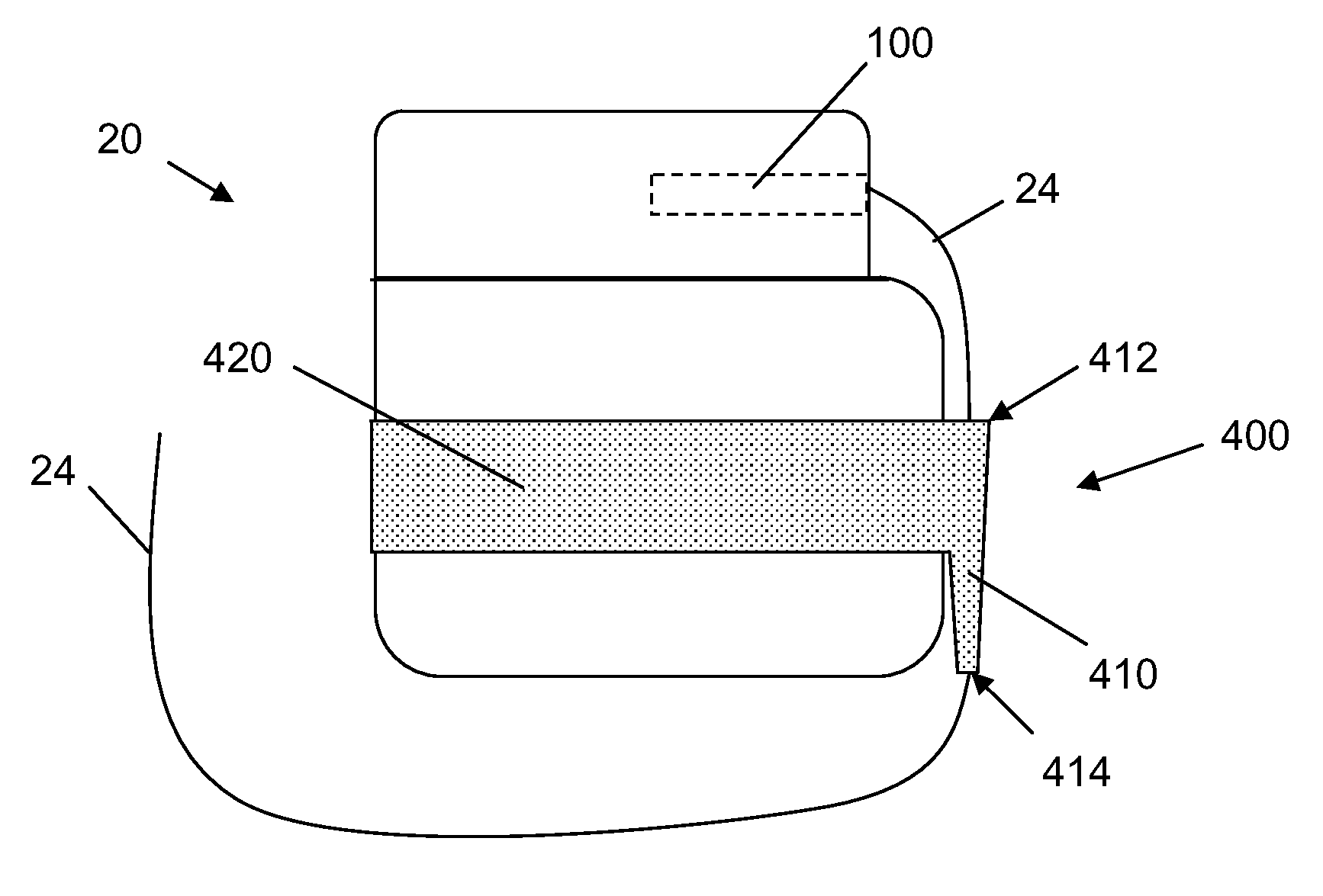
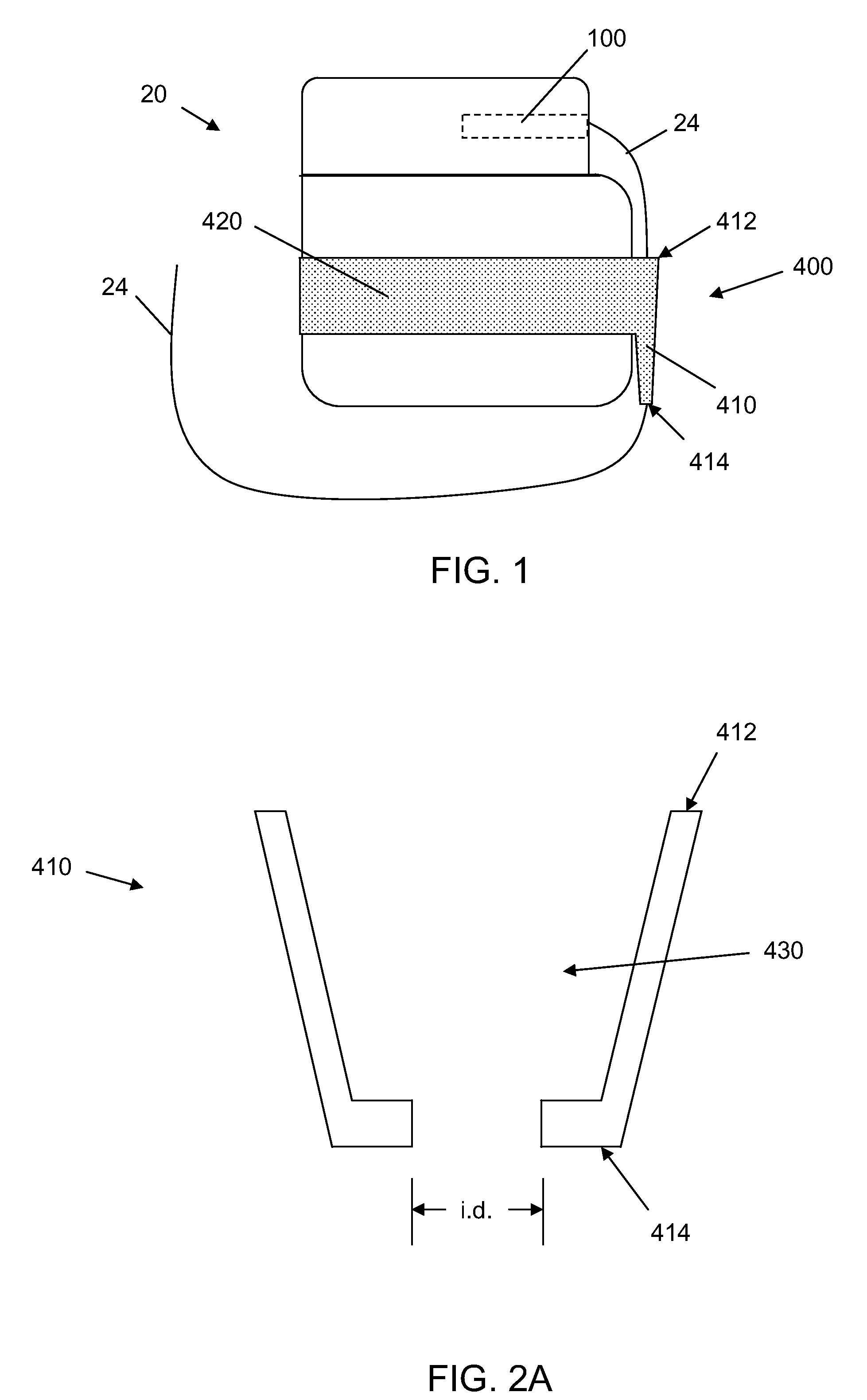
InactiveUS20030199961A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesIcd leadMedical device
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable medical electrical stimulation lead fixation method and apparatus
An implantable medical electrical lead for electrical stimulation of body tissue that includes at least one shape memory polymer portion that has a first configuration and a second configuration, wherein the second configuration is obtained upon exposure of the shape memory polymer portion to a transition stimulus, and wherein the second configuration of the modifiable portion exhibits a greater resistance to movement of the lead within the body tissue than does the first configuration; and at least one electrode configured to provide electrical stimulation of body tissue, wherein the lead has a proximal end and a distal end. Systems and kits as well as methods of utilizing the leads of the invention are also included.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Stimulation/sensing lead adapted for percutaneous insertion
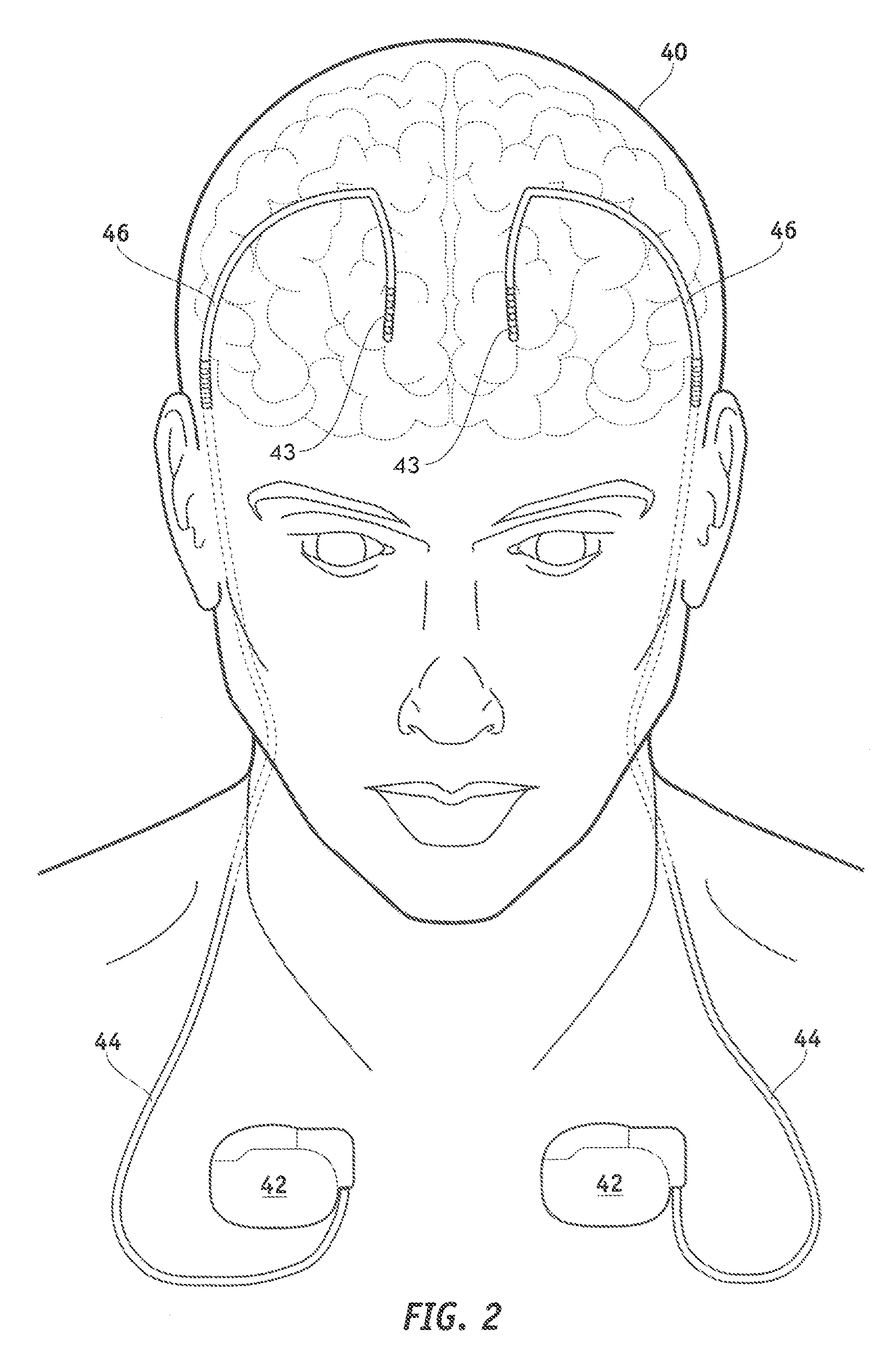
InactiveUS20050209667A1Increase flexibilityImprove maneuverabilitySpinal electrodesElectrocardiographyRadiologyIcd lead
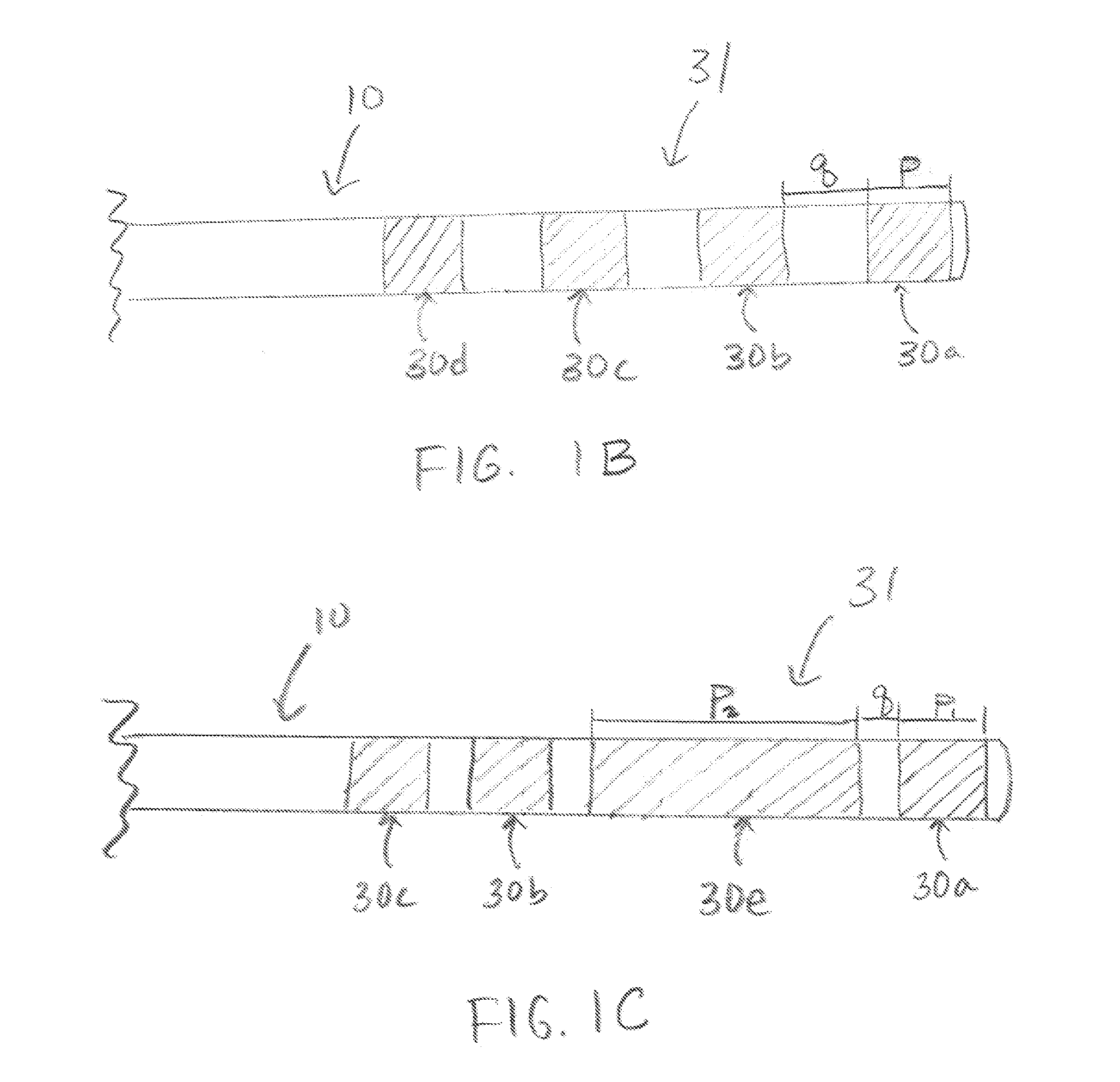
The present invention relates to a percutaneous insertion-capable lead, wherein insertion made through a percutaneous insertion structure. For one embodiment of such lead, the electrode-supporting stimulation portion of the lead includes at least one waisted region, relative to a transverse dimension of the lead, to facilitate lead steerability.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Arrangement and Method for Evaluating Operational Effectiveness of Implantable Medical Electrode Leads for Different Lead Placements
InactiveUS20080249375A1Improved and simplifiedElevated PSAElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalOperational effectiveness
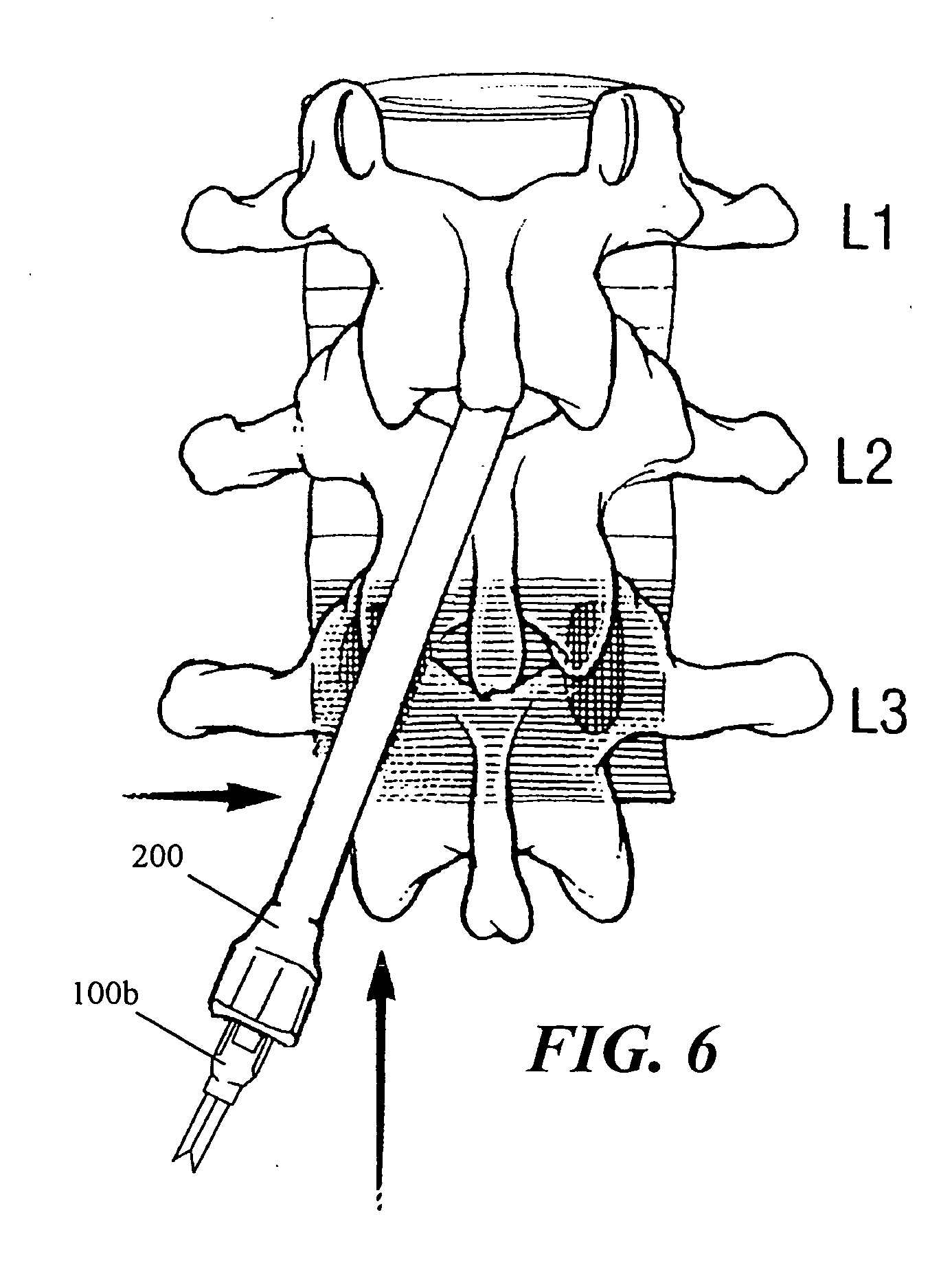
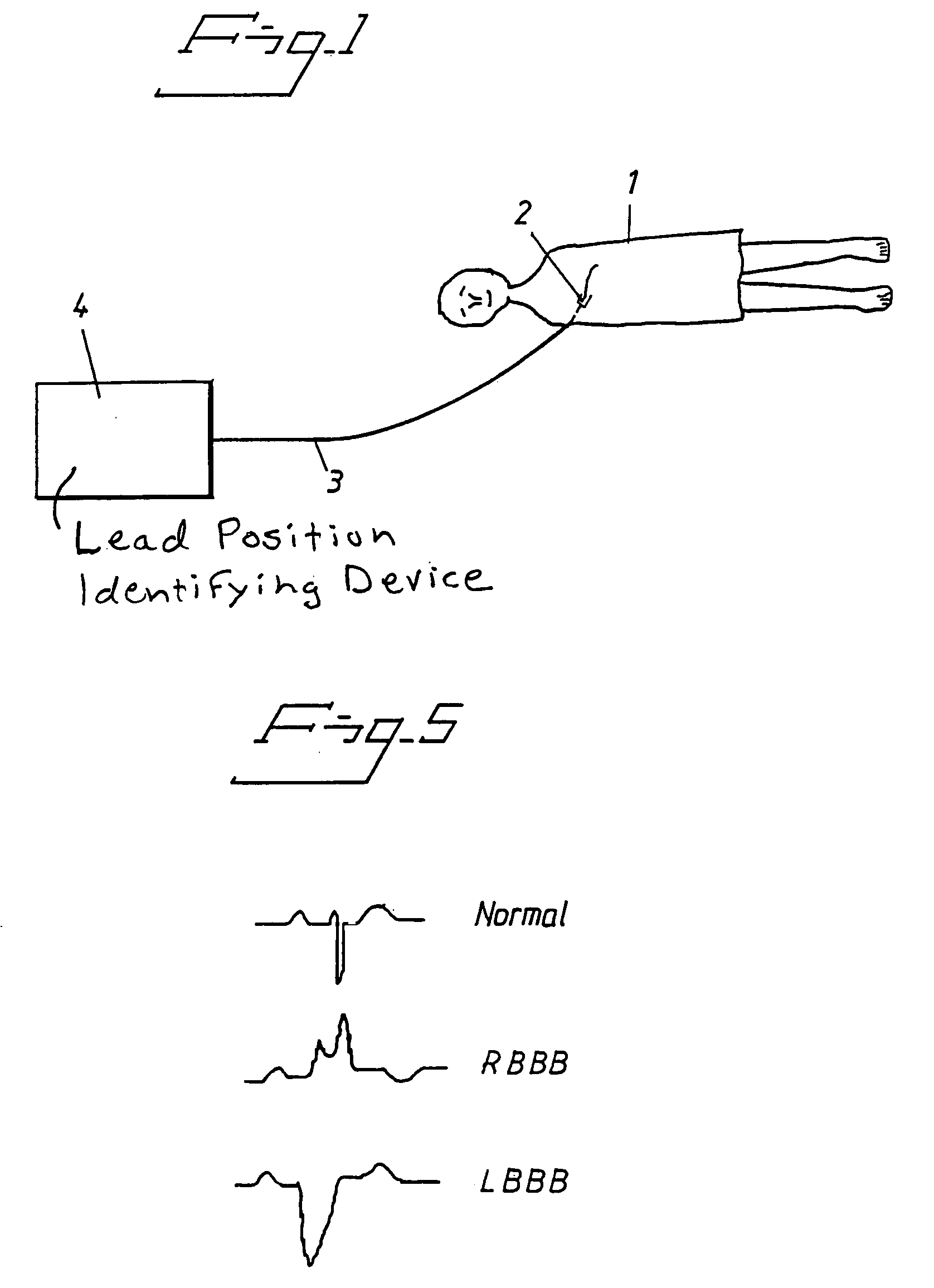
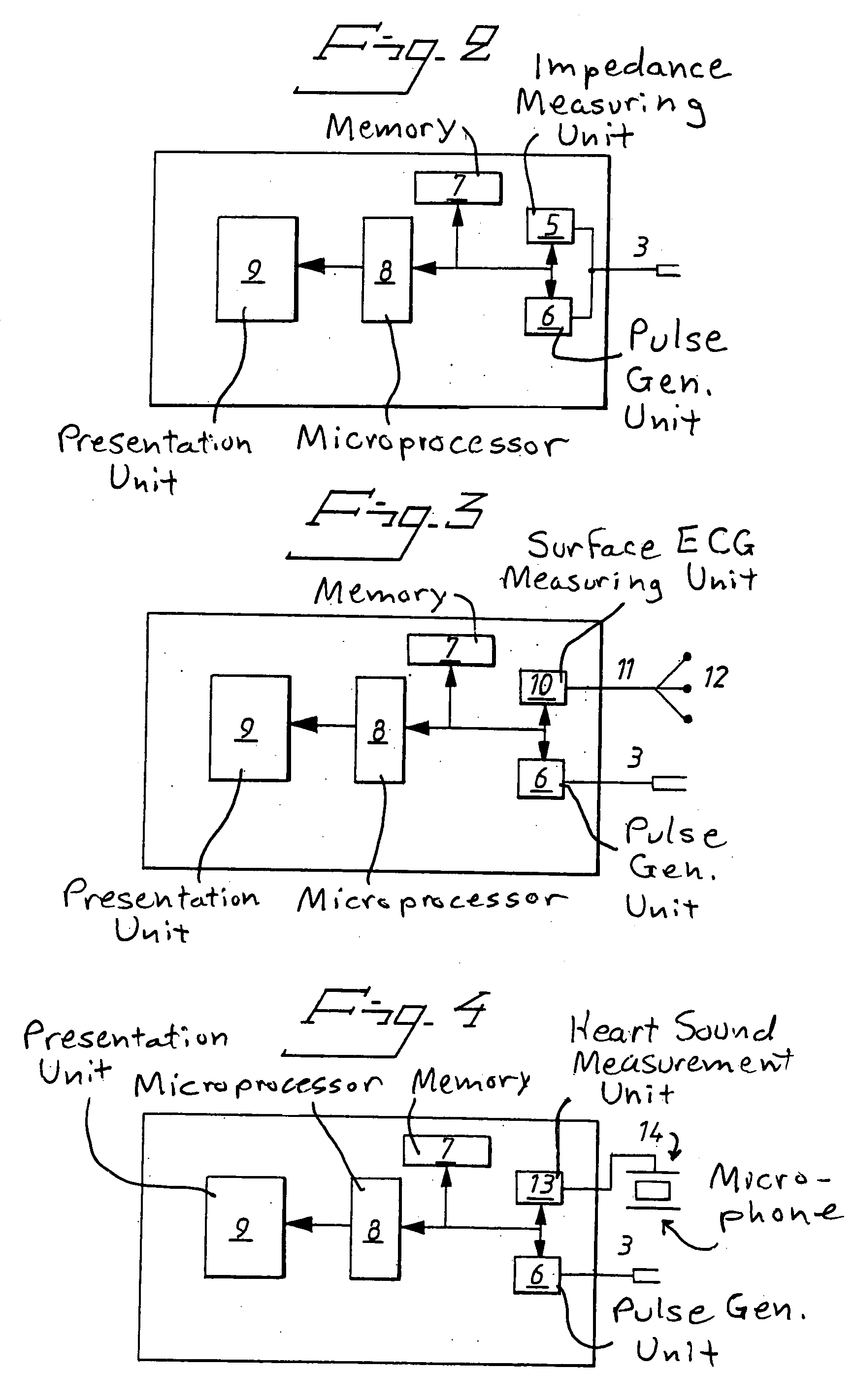
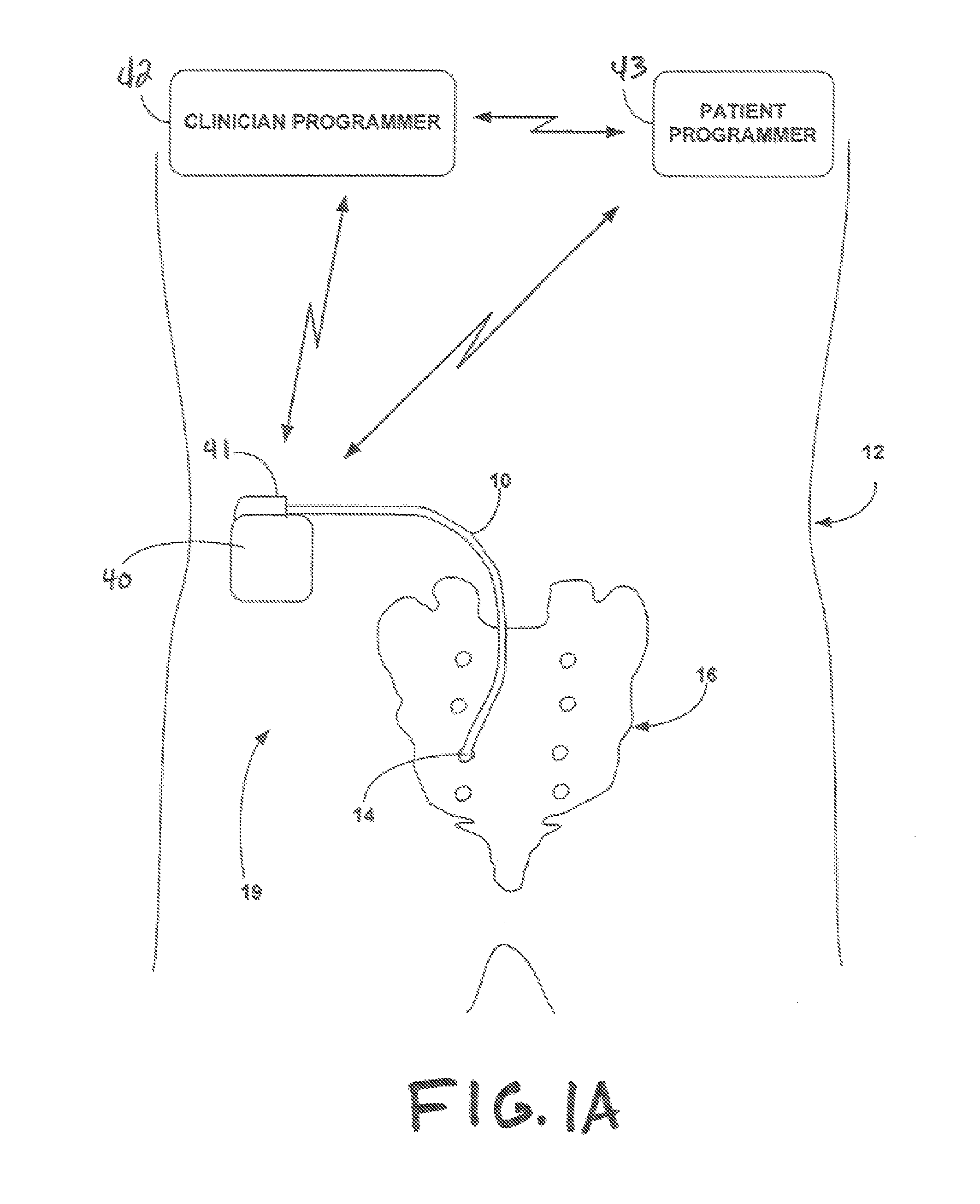
In a method and an arrangement for evaluating operational effectiveness of an implantable medical device for different lead placements associated with the medical device, a measuring unit records signals that are characteristic of cardiac activity at respectively different lead positions, and these signals are stored. A processor accesses the stored signals and, from the stored signals, determines a measure of cardiac activity at each of the lead positions. The recorded signals may be intracardiac ECG signals, surface ECG signals, heart sound signals obtained from a microphone, or impedance signals. The lead position at which the best hemodynamic behavior of the heart is identified from the analysis of the stored signals, and is determined as being the optimum site for placement of the electrode leads.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Implantable Medical Electrical Stimulation Lead Fixation Method and Apparatus
An implantable medical electrical lead for electrical stimulation of body tissue that includes at least one electrode; a lead body; and at least one modifiable portion wherein the at least one modifiable portion can exist in both a deflated configuration and an inflated configuration, and wherein the inflated configuration exhibits a greater resistance to movement of the lead within the body tissue than does the deflated configuration. Kits, systems, and methods of using the leads are also included.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
MRI-safe implantable lead
A stimulation lead to be implanted into a patient's body includes at least one distal stimulation electrode and at least one conductive filer electrically coupled to the distal stimulation electrode. A jacket houses the conductive filer and provides a path distributed along at least a portion of the length of the lead for conducting induced RF energy from the filer to the patient's body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Lead Electrode for Use in an MRI-Safe Implantable Medical Device
A neurostimulation lead is configured to be implanted into a patient's body and has at least one distal electrode. The lead comprises at least one conductive filer electrically coupled to the distal electrode, a jacket for housing the conductive filer and a shield surrounding at least a portion of the filer for reducing electromagnetic coupling to the filer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
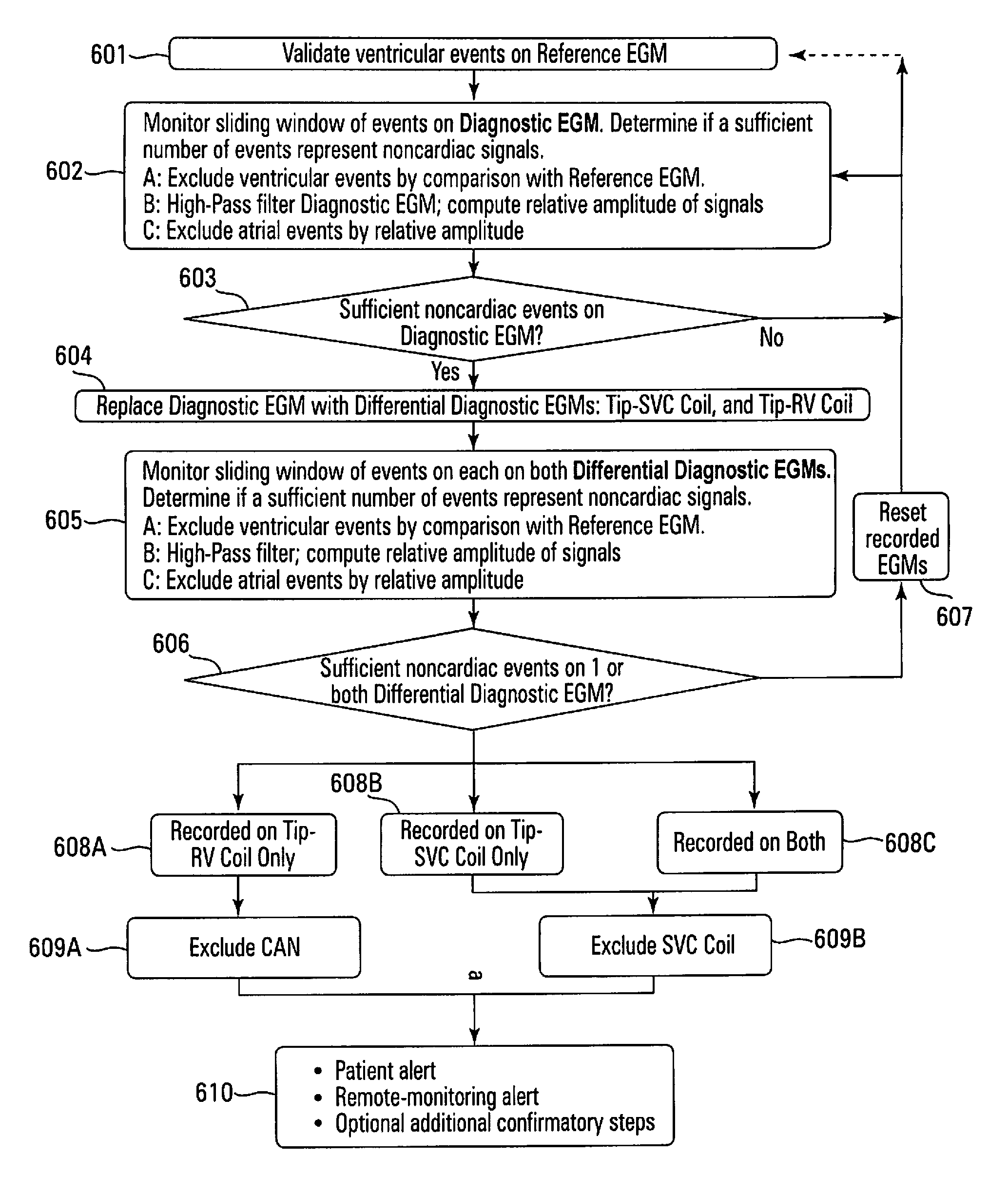
Detection of implantable lead failures by differential EGM analysis
ActiveUS9486624B2High sensitivityStrong specificityHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesIcd leadEngineering
A method and system for the diagnosis of anomalies in a lead attached to an implantable medical device, such as an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), including an insulation breach resulting in a short circuit of the high-voltage shock pulse. Determination that the defibrillation pathway is shorted may be made by initial analysis of a Reference EGM and Diagnostic EGM and subsequent analysis of Differential Diagnostic EGMs. Upon determining if a specific defibrillation pathway is shorted, the nonessential defibrillation electrode of that pathway may be excluded from the defibrillation circuit, delivering defibrillation current only between functioning defibrillation electrodes. Alternatively, the ICD system can confirm the presence of a lead anomaly with one or more alternative diagnostic approaches. Patient and remote-monitoring alerts may be initiated.
Owner:LAMBDA NU TECH
Implantable lead connector
An implantable lead connector configured for long term implantation and to electrically interconnect multiple medical devices and to channel electrical signals between said interconnected devices and a target organ, comprising: a first port adapted to receive a first signal suitable to stimulate a target tissue, a second port adapted to receive a second signal suitable to stimulate a target tissue, and a third port configured to connect to a target organ, wherein at least one of said first and second ports is configured to connect to a signal generator not integrated with said connector.
Owner:IMPULSE DYNAMICS NV
Detection of Implantable Lead Failures by Differential EGM Analysis
ActiveUS20140371831A1High sensitivityStrong specificityInternal electrodesExternal electrodesIcd leadEngineering
A method and system for the diagnosis of anomalies in a lead attached to an implantable medical device, such as an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), including an insulation breach resulting in a short circuit of the high-voltage shock pulse. Determination that the defibrillation pathway is shorted may be made by initial analysis of a Reference EGM and Diagnostic EGM and subsequent analysis of Differential Diagnostic EGMs. Upon determining if a specific defibrillation pathway is shorted, the nonessential defibrillation electrode of that pathway may be excluded from the defibrillation circuit, delivering defibrillation current only between functioning defibrillation electrodes. Alternatively, the ICD system can confirm the presence of a lead anomaly with one or more alternative diagnostic approaches. Patient and remote-monitoring alerts may be initiated.
Owner:LAMBDA NU TECH
Mechanical ventricular pacing non-capture detection for a refractory period stimulation (RPS) pacing therapy using at least one lead-based accelerometer
InactiveUS7787942B2Increase contractilityIncrease perfusionElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerLeft ventricular size
A system and method for monitoring at least one chamber of a heart (e.g., a left ventricular chamber) during delivery of a refractory period stimulation (RPS) therapy to determine if the desired non-capture (i.e., lack of ventricular mechanical capture due to refractory period stimulation) occurs. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads such as epicardial, endocardial, and / or coronary sinus leads equipped with motion sensor(s). The device receives and processes acceleration sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of chamber capture due to pacing stimulus delivery, non-capture due to RPS therapy delivery, and / or contractile status based on the qualities of evoked response to pacing stimulation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
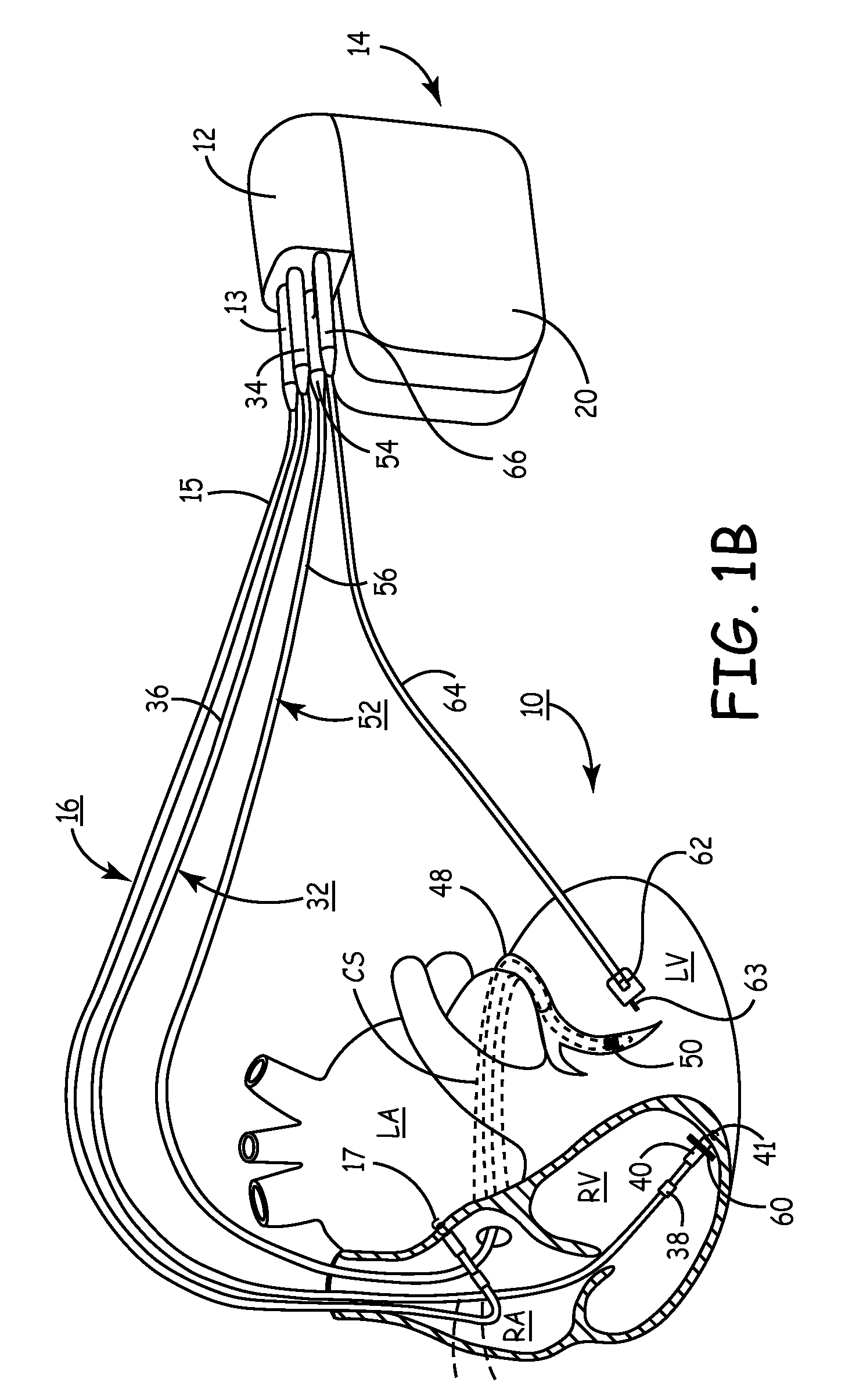
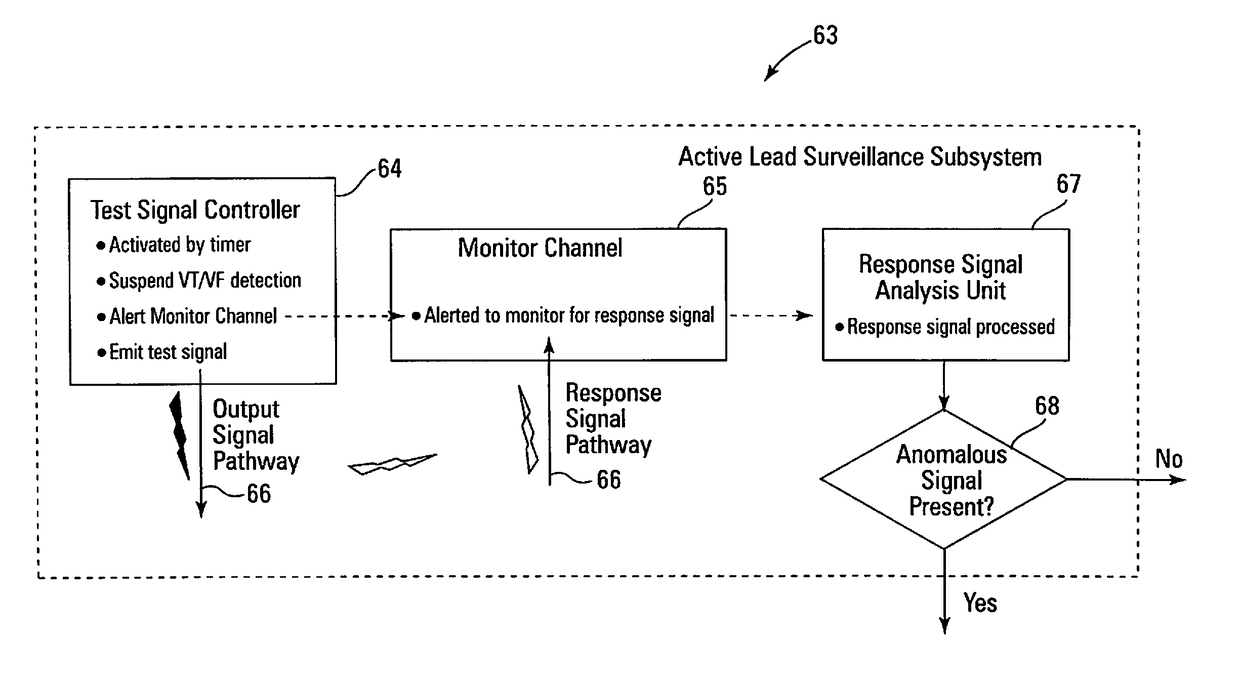
Active surveillance of implanted medical leads for lead integrity
ActiveUS9636500B2Potential for detectionMinimize signalingHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesSignal onIcd lead
Active surveillance of potential lead anomalies in implanted medical leads utilizes test signal(s) delivered through an output current pathway and induced signals monitored via an independent monitor current pathway to detect for any reactions to the test signals in the induced signals. Various specific responses can be initiated if a potential insulation breach or anomaly in the implanted medical lead is identified due to detection of a “positive” test result in the induced signals on the monitor current pathway in reaction to a test signal applied to the output current pathway.
Owner:LAMBDA NU TECH
Implantable medical electrical stimulation lead fixation method and apparatus
The invention includes an implantable medical electrical lead for electrical stimulation of body tissue that includes at least one electrode; a lead body; and at least one modifiable portion that is coaxial with the lead body, wherein the at least one modifiable portion can exist in both a first configuration and a second configuration, wherein the second configuration exhibits a greater resistance to movement of the lead within the body tissue than does the first configuration, and wherein the first configuration is exhibited when an external force is applied to the outer surface of the modifiable portion. Kits, systems and methods of implanting are also included in the invention.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
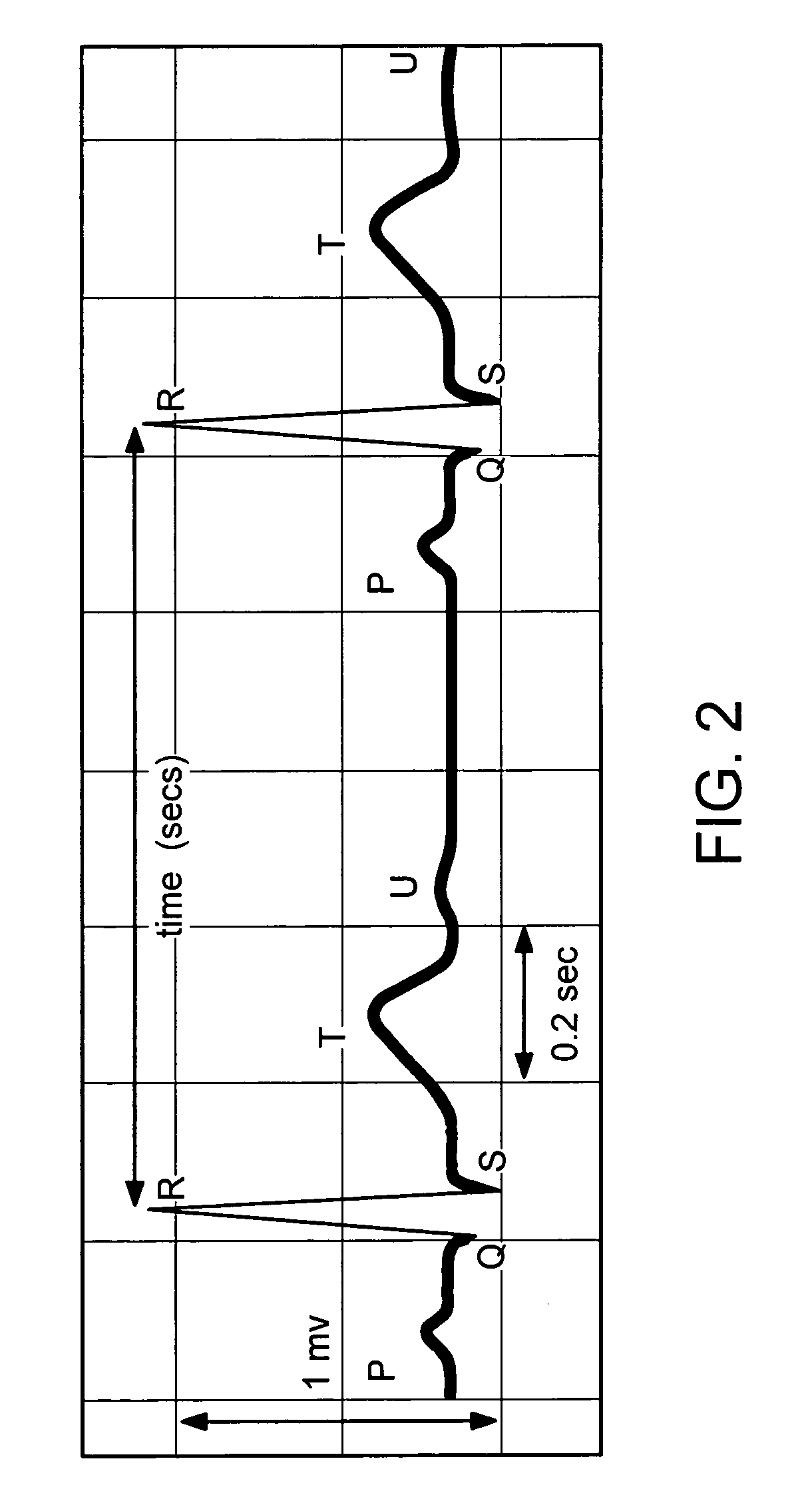
Method and system for detecting premature ventricular contraction from a surface electrocardiogram
InactiveUS7751876B2Reduce skin irritationElectrocardiographySensorsSmall form factorVentricular contraction
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Implantable medical electrical stimulation lead fixation method and apparatus
The invention includes a implantable medical electrical lead for electrical stimulation of body tissue that includes at least one electrode; a lead body; and at least one modifiable portion, wherein the at least one modifiable portion has a first configuration and a second configuration, wherein the first configuration exists when axial tension is exerted on the at least one modifiable portion, and wherein the second configuration exhibits a greater resistance to movement of the lead within the body tissue than does the first configuration. Kits, and systems and methods of using the lead are also included.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable Lead
ActiveUS20180133464A1Easy to compressImprove the immunityTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesAxial displacementIcd lead
Implantable lead having an electrode body with a free end and an inner part axially movable or rotatably movable with respect to it and an end on which means of fixation are extendable out of the free end by axially displacing the inner part, the inner periphery of the electrode body having an elastically deformable, peripheral, ring or ring segment-shaped, sealing / resistance element fixed to it. The outer periphery of the inner part having a section whose diameter changes (decreases) in the axial direction; this section passes the sealing / resistance element when the inner part is axially displaced. The inner periphery of the electrode body having a section whose diameter changes (decreases) in the axial direction; this section placed so that the sealing / resistance element passes this section when the inner part is axially displaced, the sealing / resistance element increasingly deformed during axial displacement of the inner part and counteracting movement thereof.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator employing a telescoping lead
One embodiment of the present invention provides an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib within a patient, the implantable cardioverter-defibrillator including a housing including a first electrode; a telescoping lead assembly including a second electrode, wherein the telescoping lead assembly is electrically and mechanically coupled to the housing; and an electrical circuit located within and electrically coupled to the housing.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
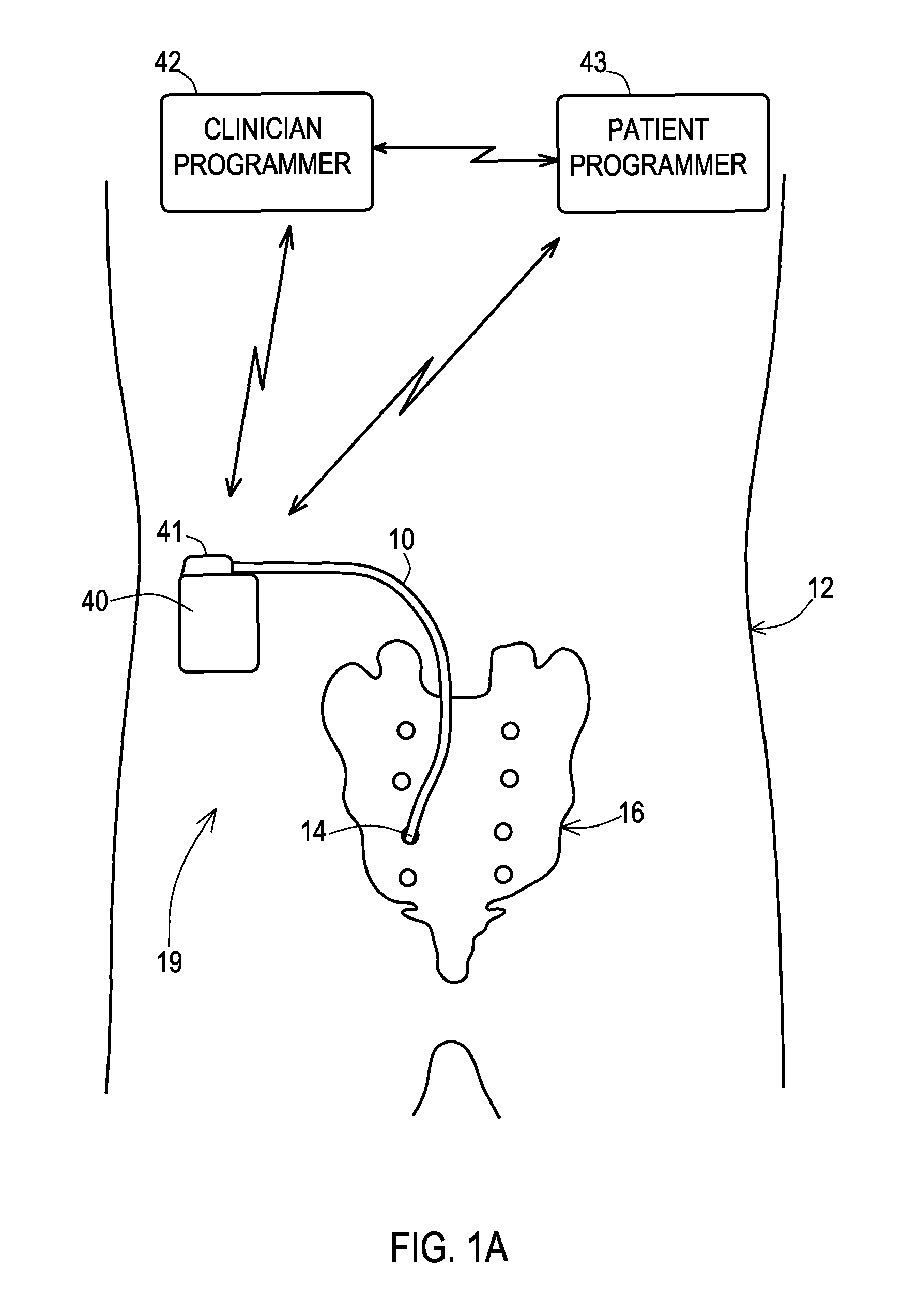
Implantable lead management
ActiveUS8209016B2Small sizeImprove life performanceCoupling device detailsInternal electrodesIcd leadMedical device
An apparatus for managing a lead of an implantable medical device includes a lead retention element and a fixation element. The lead retention element has a proximal end, a distal end, and a lumen extending from the proximal end to the distal end. The lumen is configured to slidably receive the lead. The fixation element is configured to fix the lead retention element relative to the implantable medical device in an orientation orthogonal to a lead receptacle of the device such that the proximal end of the lead retention element is closer to an opening of the lead receptacle than the distal end of the retention element. The distal end of the lead retention element is configured to firmly engage the lead to resist proximal sliding of the lead in the lumen of the retention element once the lead has been moved distally through the lumen.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable lead management
ActiveUS20100241205A1Small sizeImprove life performanceCoupling device detailsInternal electrodesIcd leadMedical device
An apparatus for managing a lead of an implantable medical device includes a lead retention element and a fixation element. The lead retention element has a proximal end, a distal end, and a lumen extending from the proximal end to the distal end. The lumen is configured to slidably receive the lead. The fixation element is configured to fix the lead retention element relative to the implantable medical device in an orientation orthogonal to a lead receptacle of the device such that the proximal end of the lead retention element is closer to an opening of the lead receptacle than the distal end of the retention element. The distal end of the lead retention element is configured to firmly engage the lead to resist proximal sliding of the lead in the lumen of the retention element once the lead has been moved distally through the lumen.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
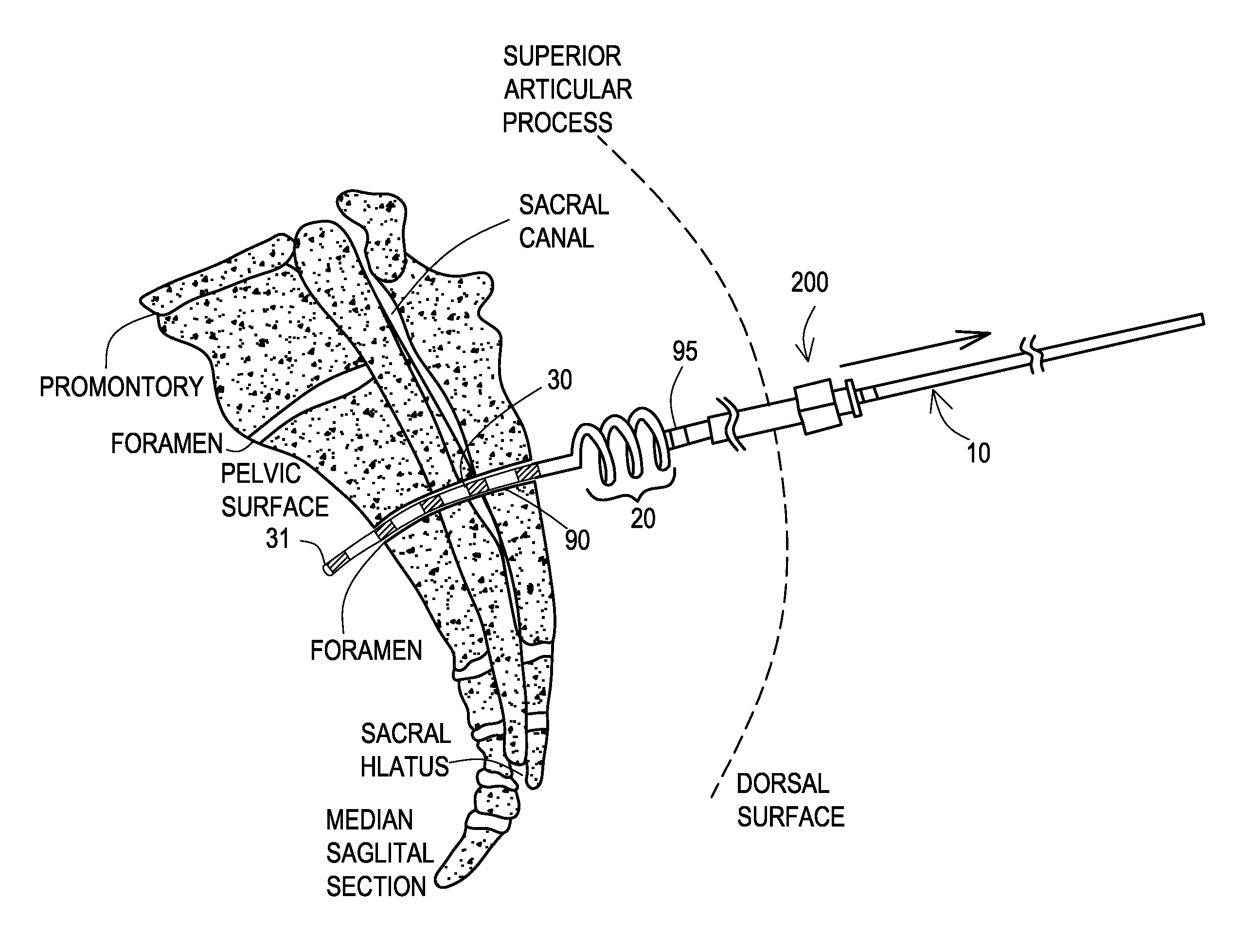
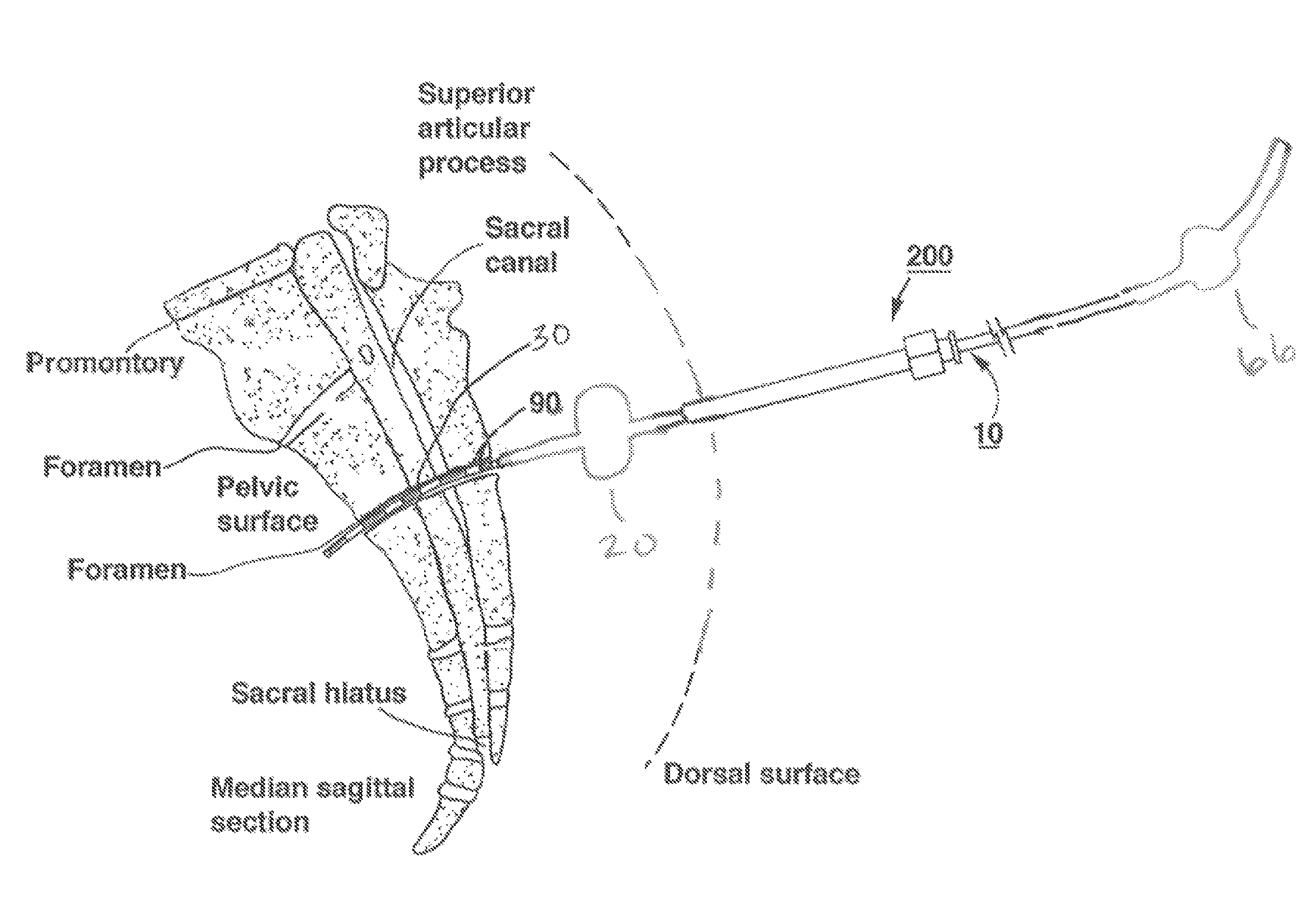
System and method for implantation of lead and electrodes to the endopelvic portion of the pelvic nerves and connection cable for electrode with direction marker
InactiveUS20170043156A1Prevention of decubitus ulcerMinimize decubitus ulcerSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesPelvic nervePERITONEOSCOPE
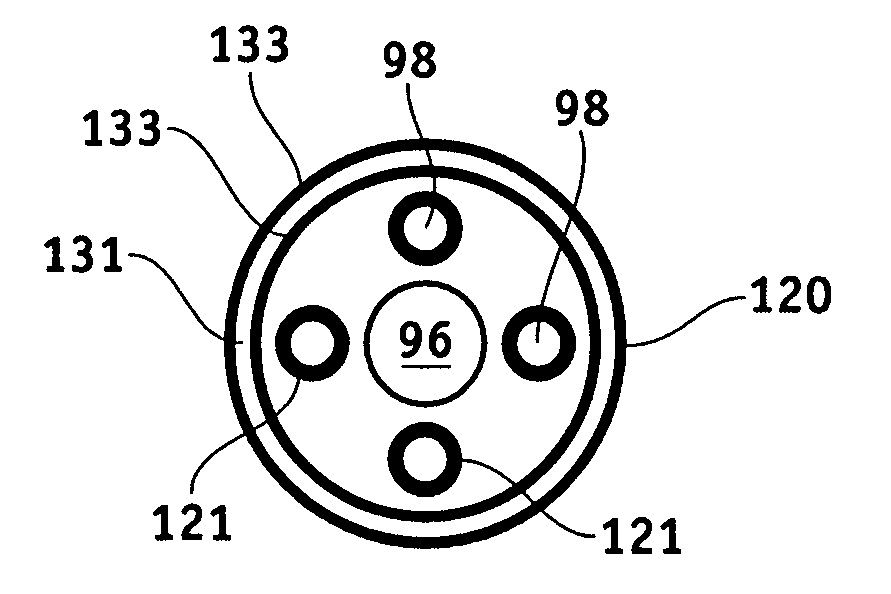
A collector electrode assembly which can be implanted by laparoscopy through the abdominal wall into the small pelvis of the human body includes a collector electrode for neurostimulation of nerves; a connection cable having an outer surface, said collector electrode being arranged at one end of said connection cable and comprising several outer segment electrodes which can be contacted individually and / or in groups and which are arranged axially one after another in the direction of the longitudinal extent of the collector electrode, wherein an insulating section is arranged axially between in each case two adjacent outer segment electrodes and permits electrical insulation of respective two adjacent outer segment electrodes; radially expandable fixing structures positioned on the collector electrode and radially expandable from a withdrawn position to a radially expanded position for fixing the collector electrode in place at said nerves; a visually perceptible direction marker on the outer surface of the connection cable, at least in a cable section which is spaced apart from axial ends of the connection cable and has an axial extent of at least 10 cm and / or at least 15% of total length of the connection cable, said direction marker indicating orientation of the connection cable to an operator using the assembly, and wherein the direction marker is designed and arranged in such a way that the identification of the orientation of the connection cable is possible at any desired axial section of the cable section having a maximum axial extent of 2 cm.
Owner:POSSOVER MARC
Implantable medical electrical stimulation lead fixation method and apparatus
An implantable medical electrical lead for electrical stimulation of body tissue that includes at least one electrode; a lead body; and at least one modifiable portion wherein the at least one modifiable portion can exist in both a deflated configuration and an inflated configuration, and wherein the inflated configuration exhibits a greater resistance to movement of the lead within the body tissue than does the deflated configuration. Kits, systems, and methods of using the leads are also included.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
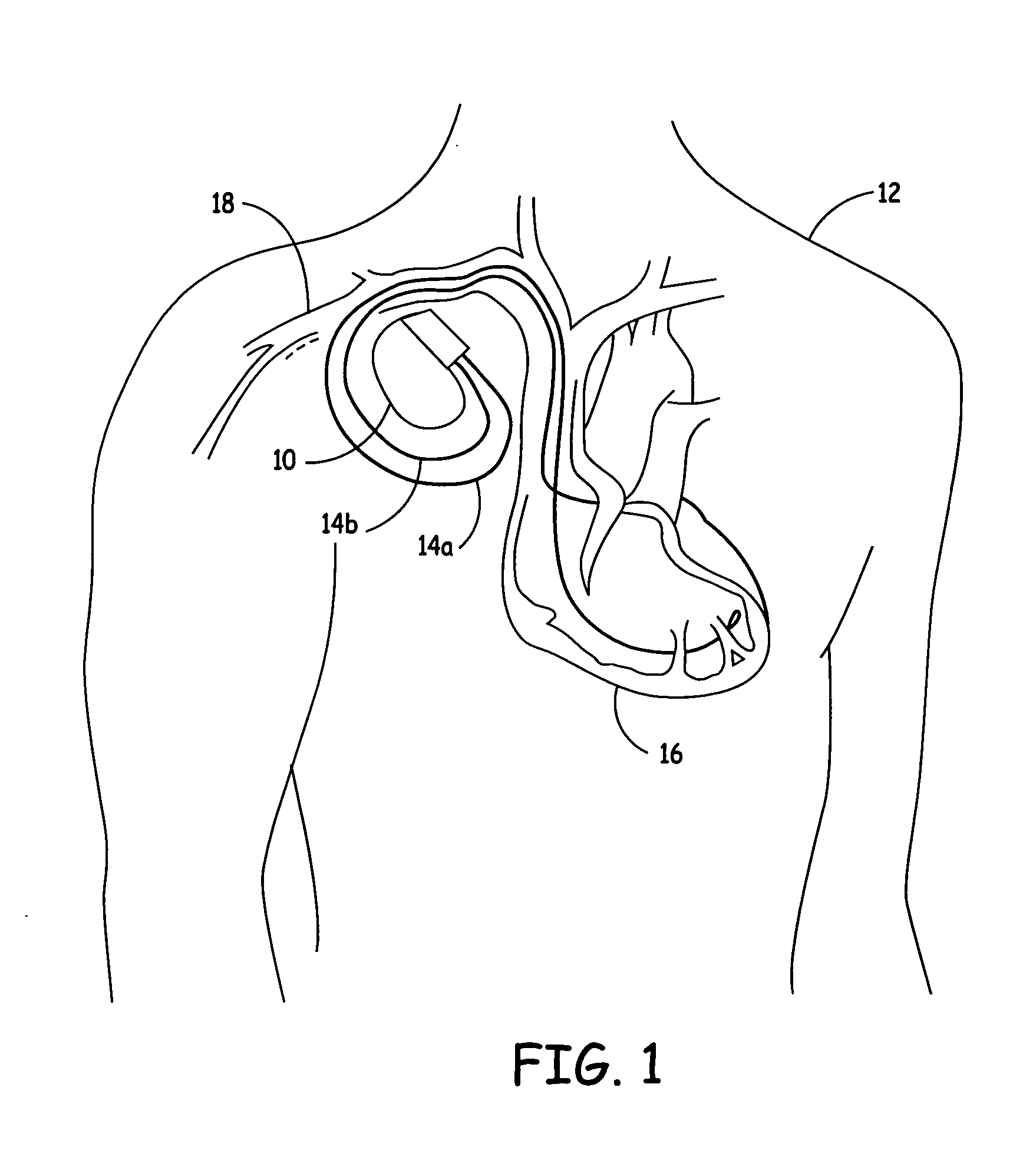
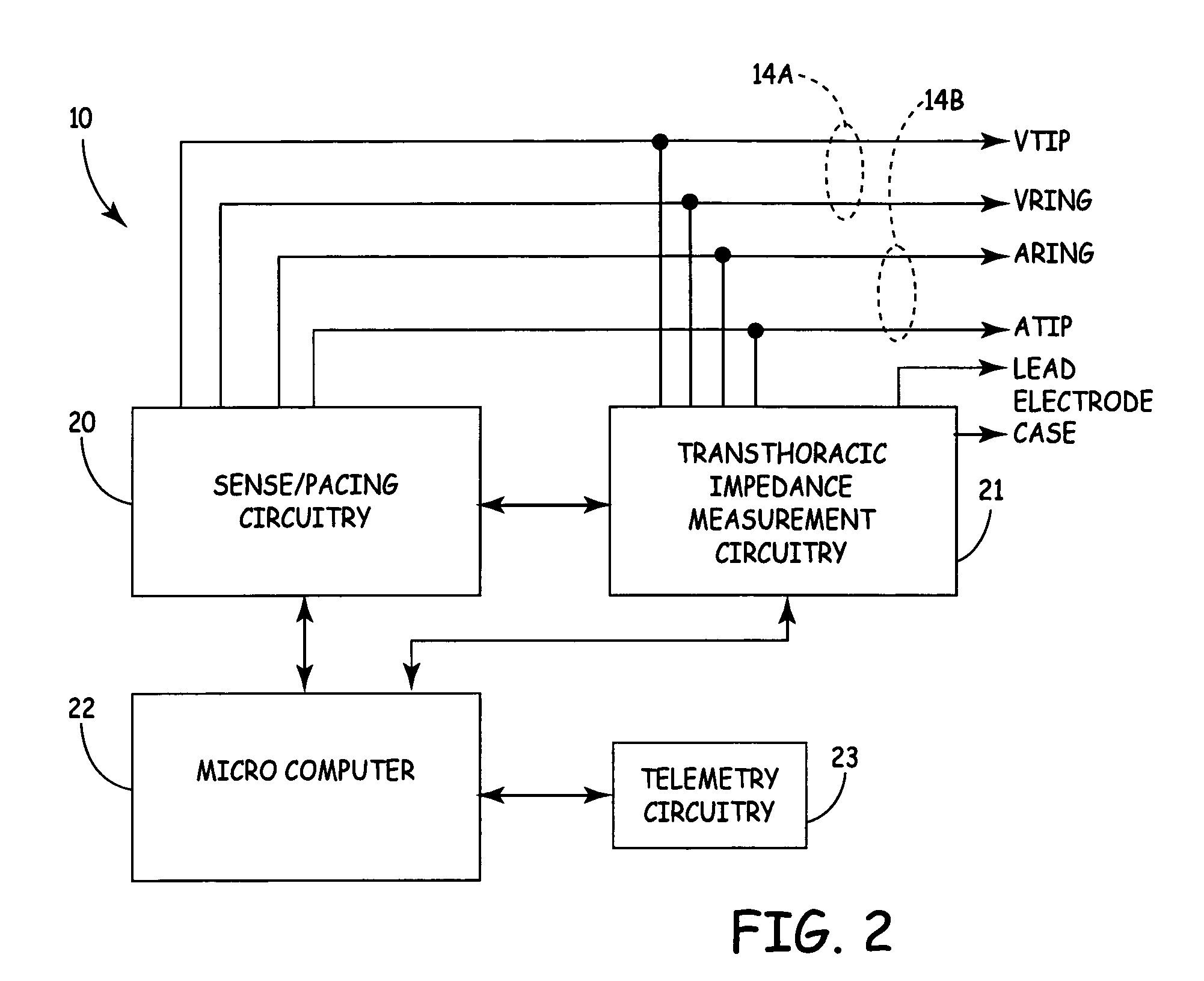
Lead-carried proximal electrode for quadripolar transthoracic impedance monitoring
ActiveUS20070179544A1Reduce complexityLow costHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringProximateIcd lead
An implantable medical device (IMD) provides quadripolar transthoracic impedance measurement capability by forming at least one of the two electrodes associated with the canister of the device on a lead proximate the canister.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
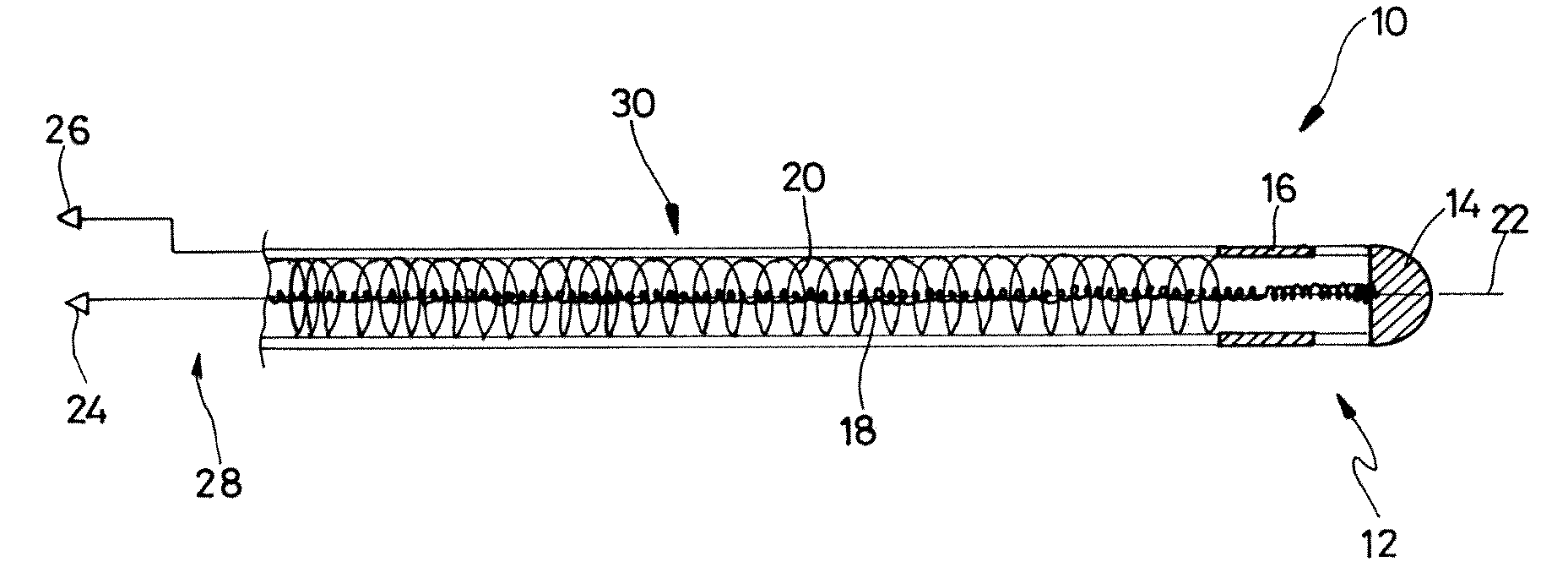
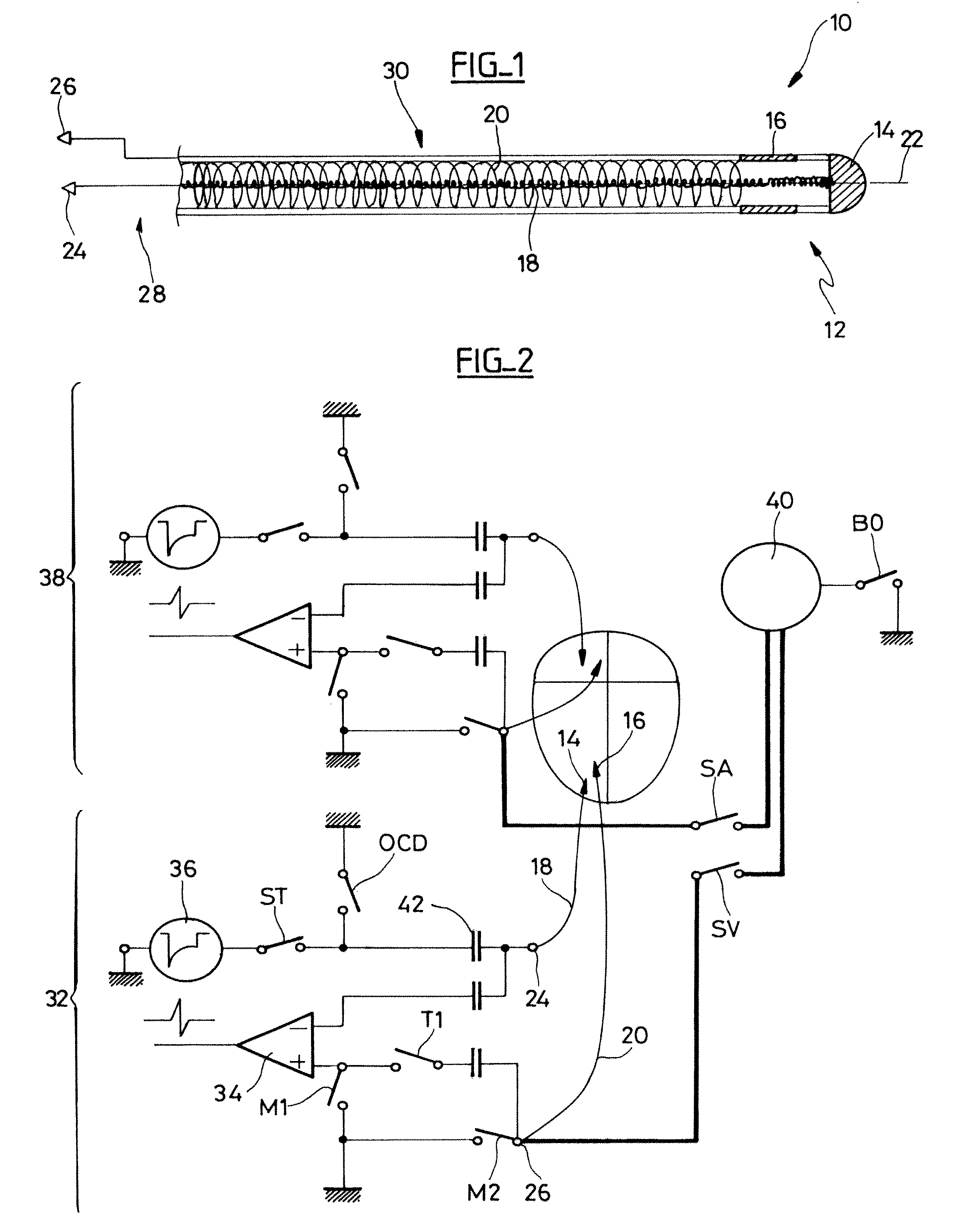
Implantable cardiac prosthesis generator having protection from an MRI examination
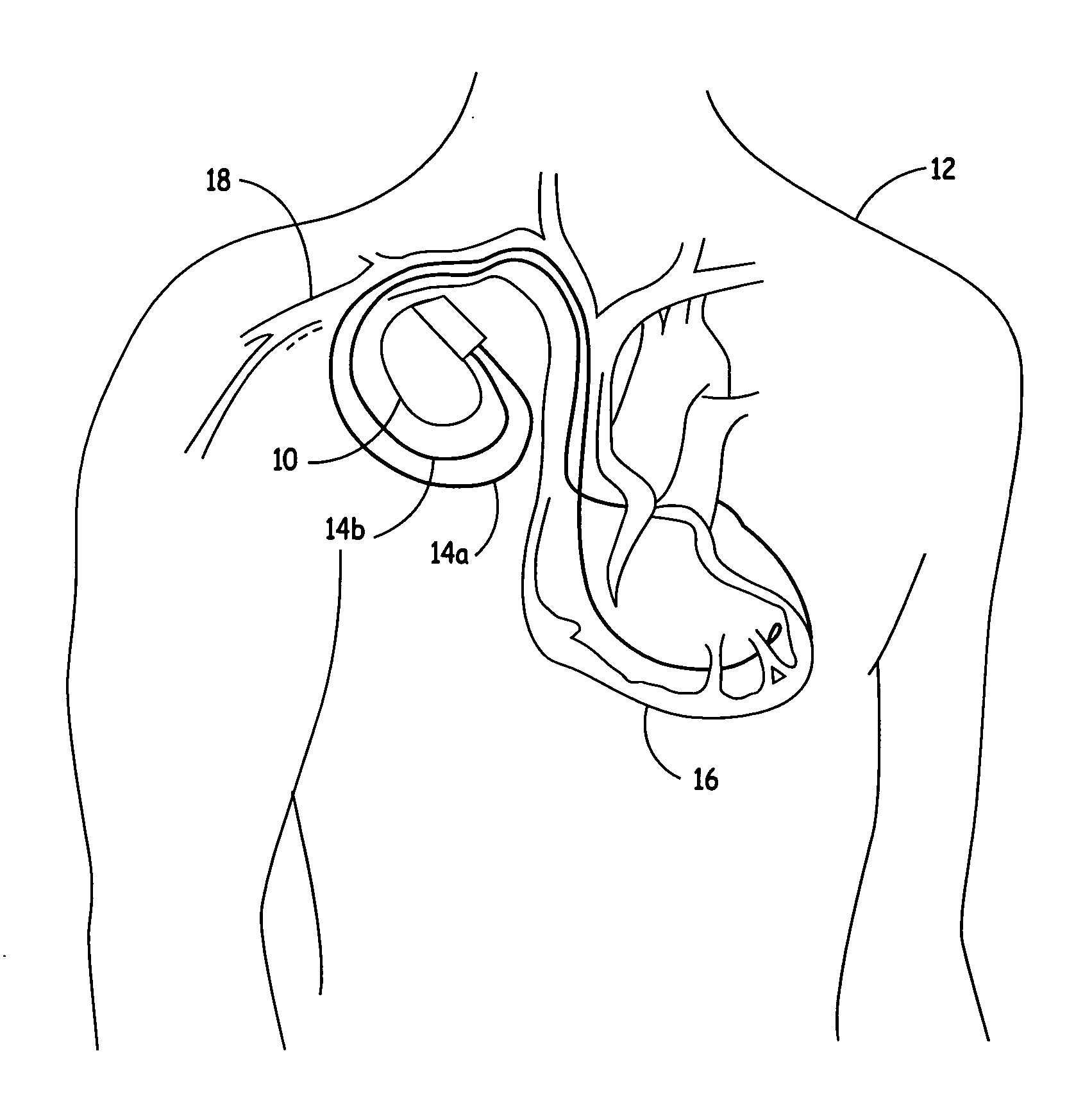
A generator for an implantable cardiac prosthesis, having a safekeeping mode of operation during an exposure to a magnetic field. The generator is connected to a lead including a first conductor (18) connected to a distal electrode (14), and a second conductor (20) connected to a proximal electrode (16). The generator to which the lead is connected includes a switch that temporarily switches to the potential of the metal housing of the generator (i.e., the ground potential) a first terminal connection (26) coupled to the external conductor (20) of the lead, and connects to the electronic circuit of detection / stimulation a second terminal connection (24) coupled to the internal conductor (18) of the lead. The first conductor temporarily acts as a shield for the second conductor for the duration of an MRI examination ensuring protection against the deleterious effects of exposure of the lead to the magnetic field generated by the MRI apparatus, notably heating of the electrodes due to induced currents in the conductors.
Owner:SORIN CRM
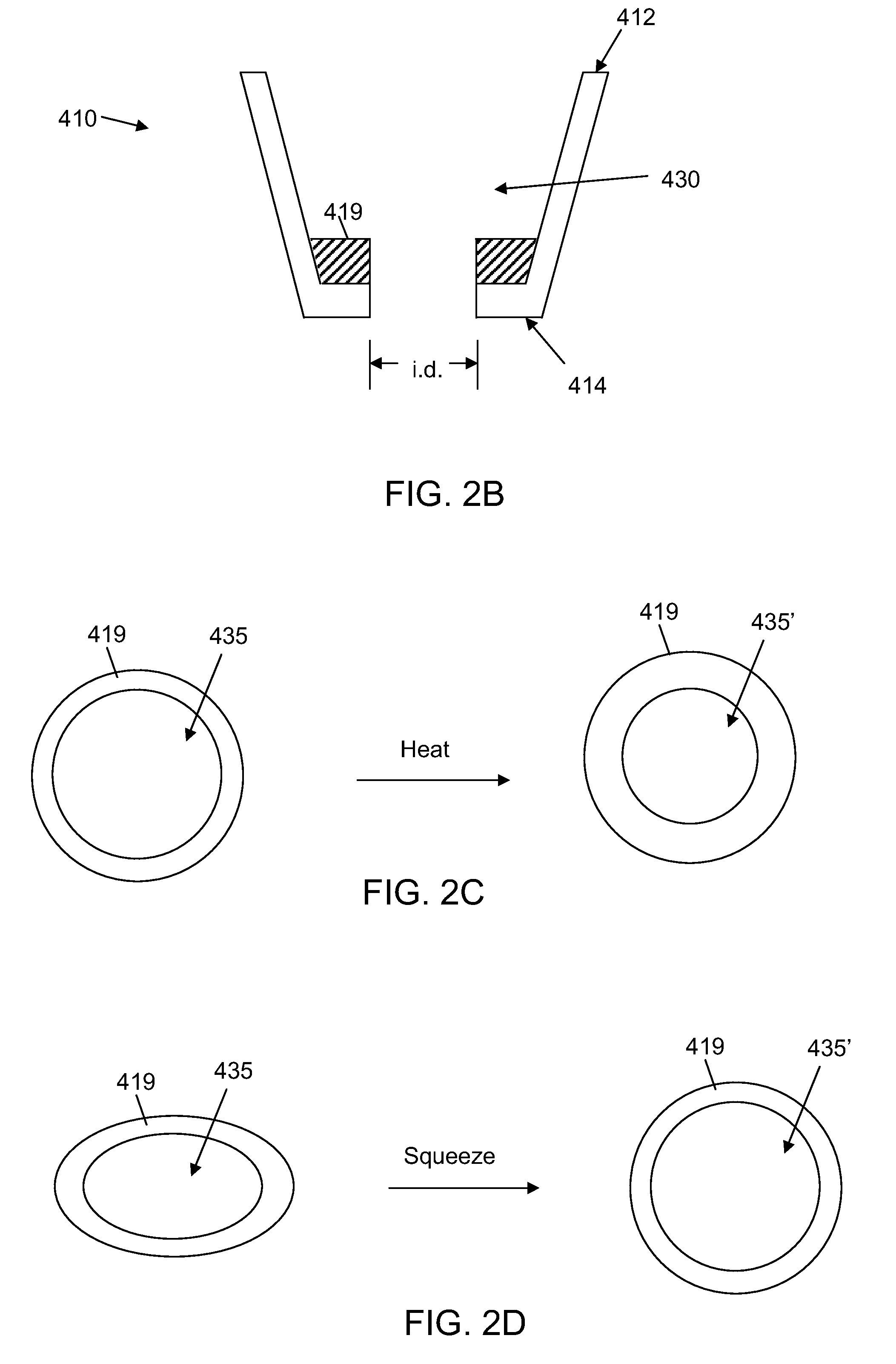
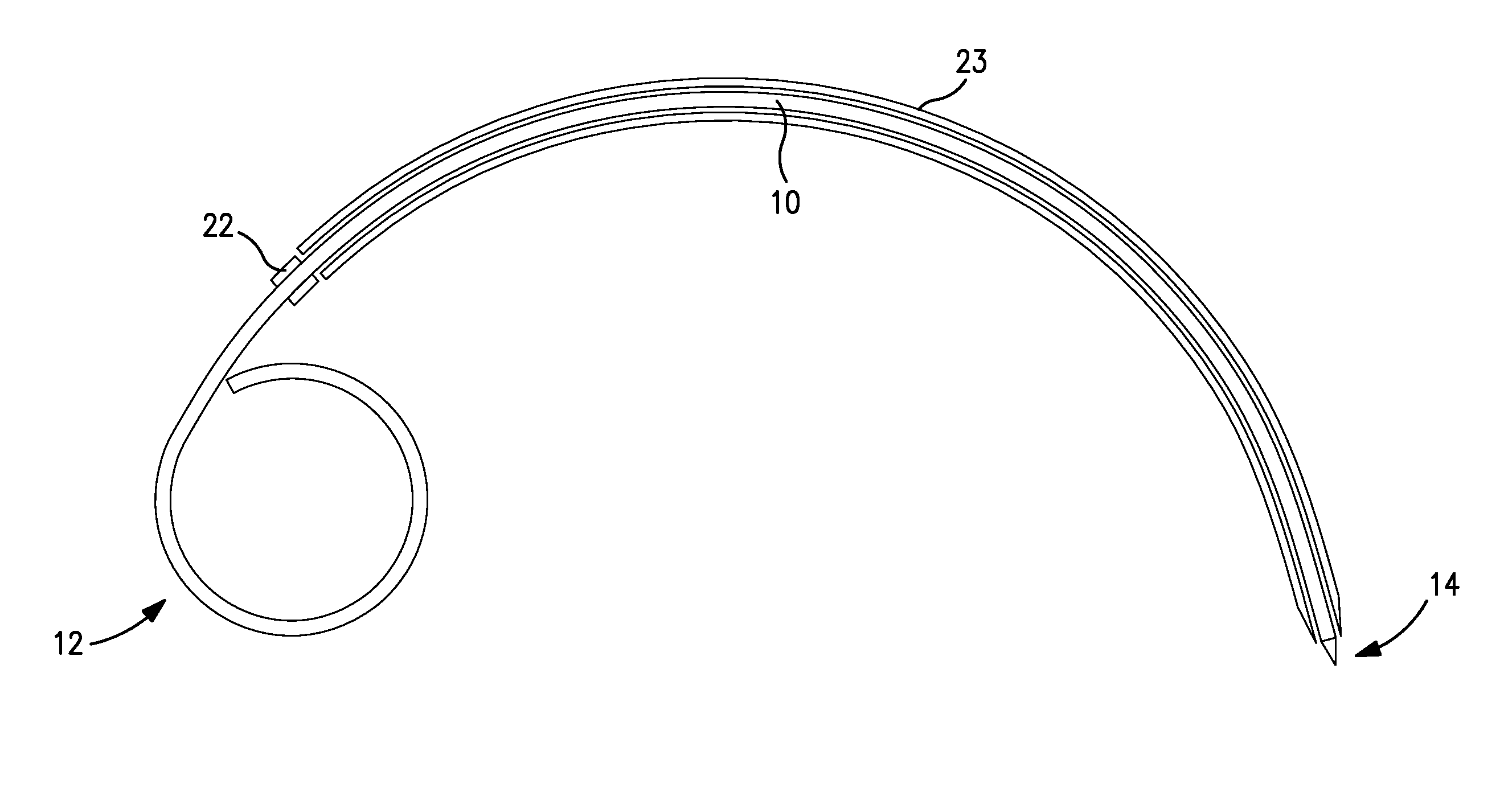
Subcutaneous implantable lead
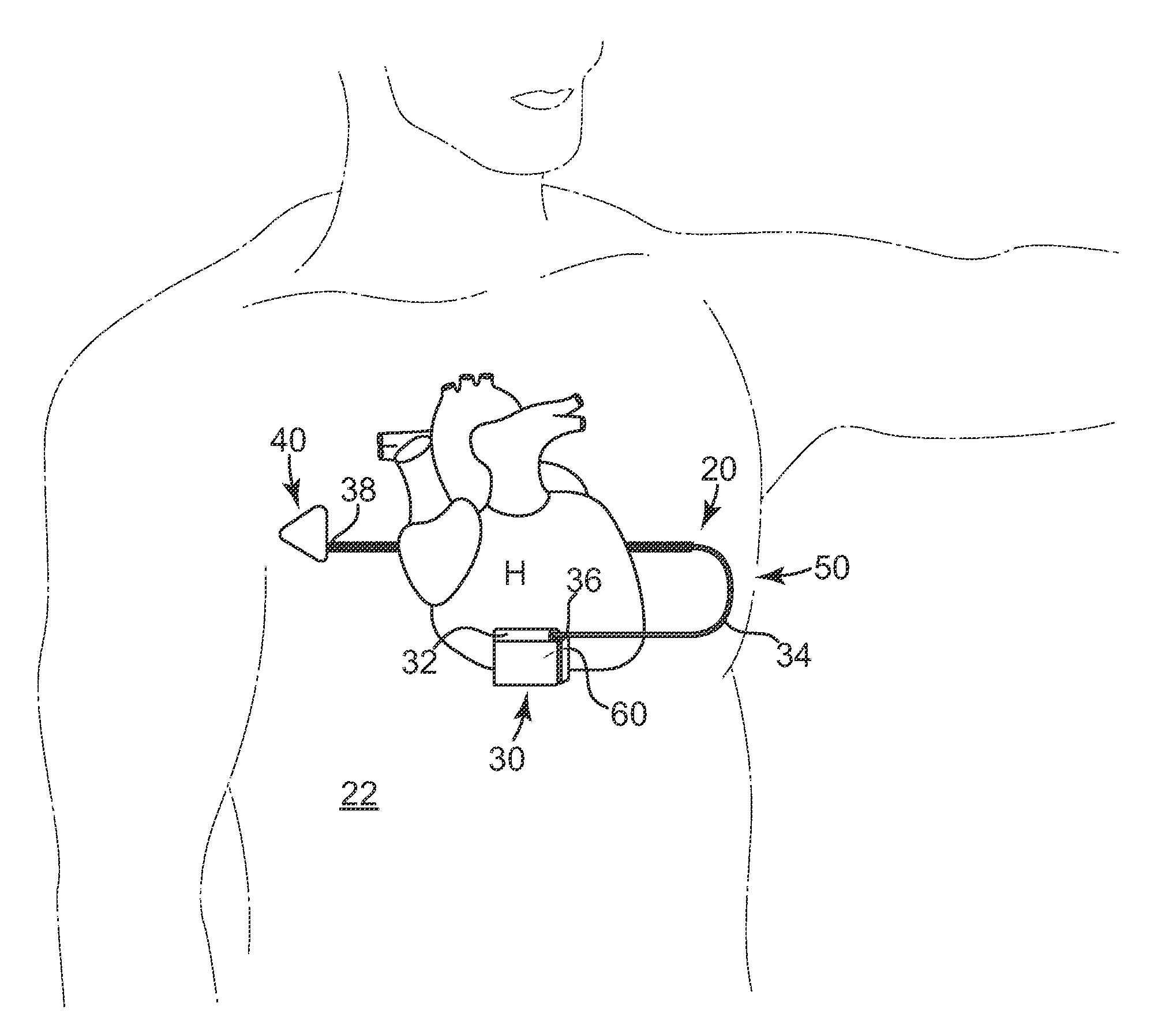
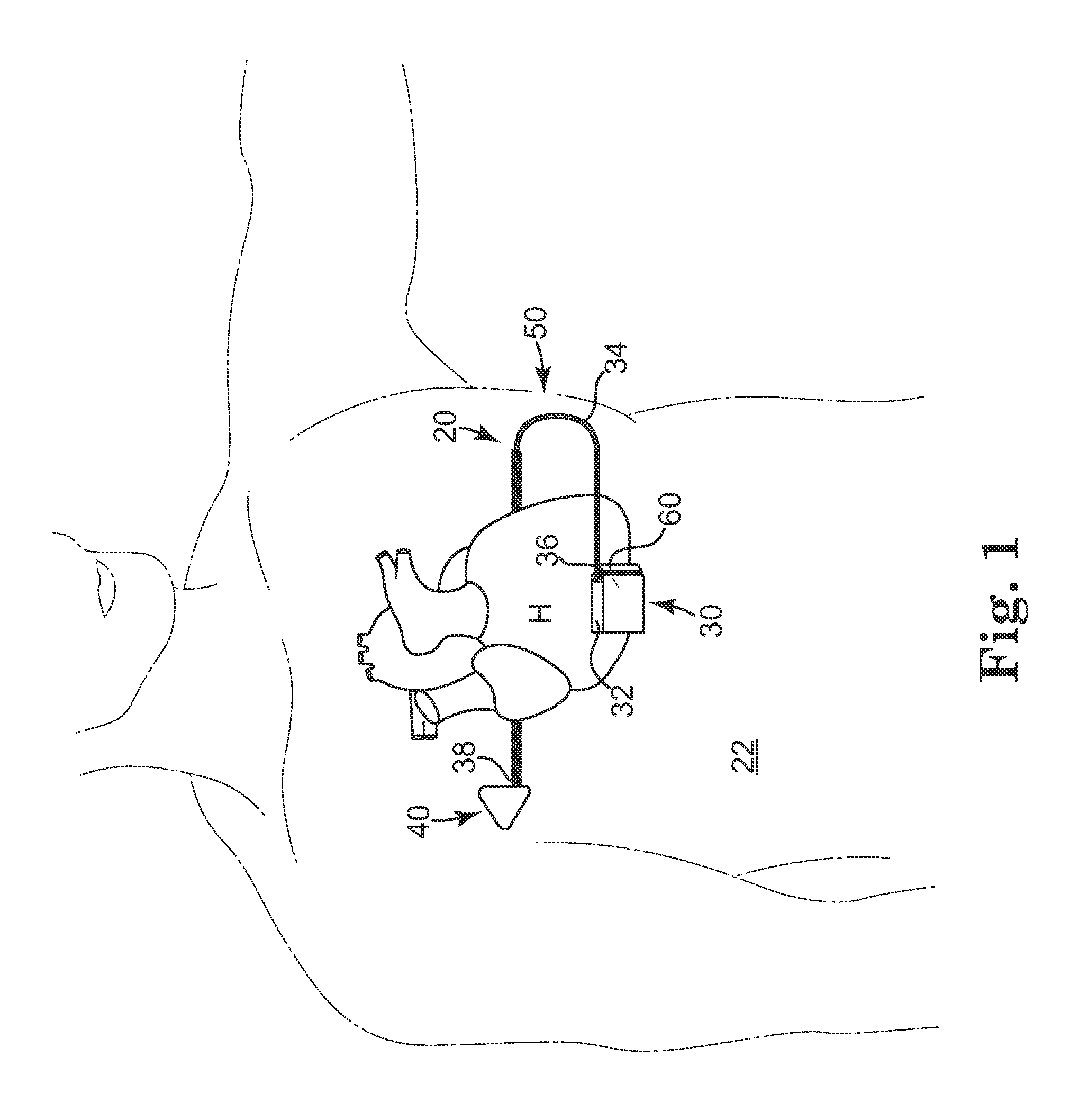
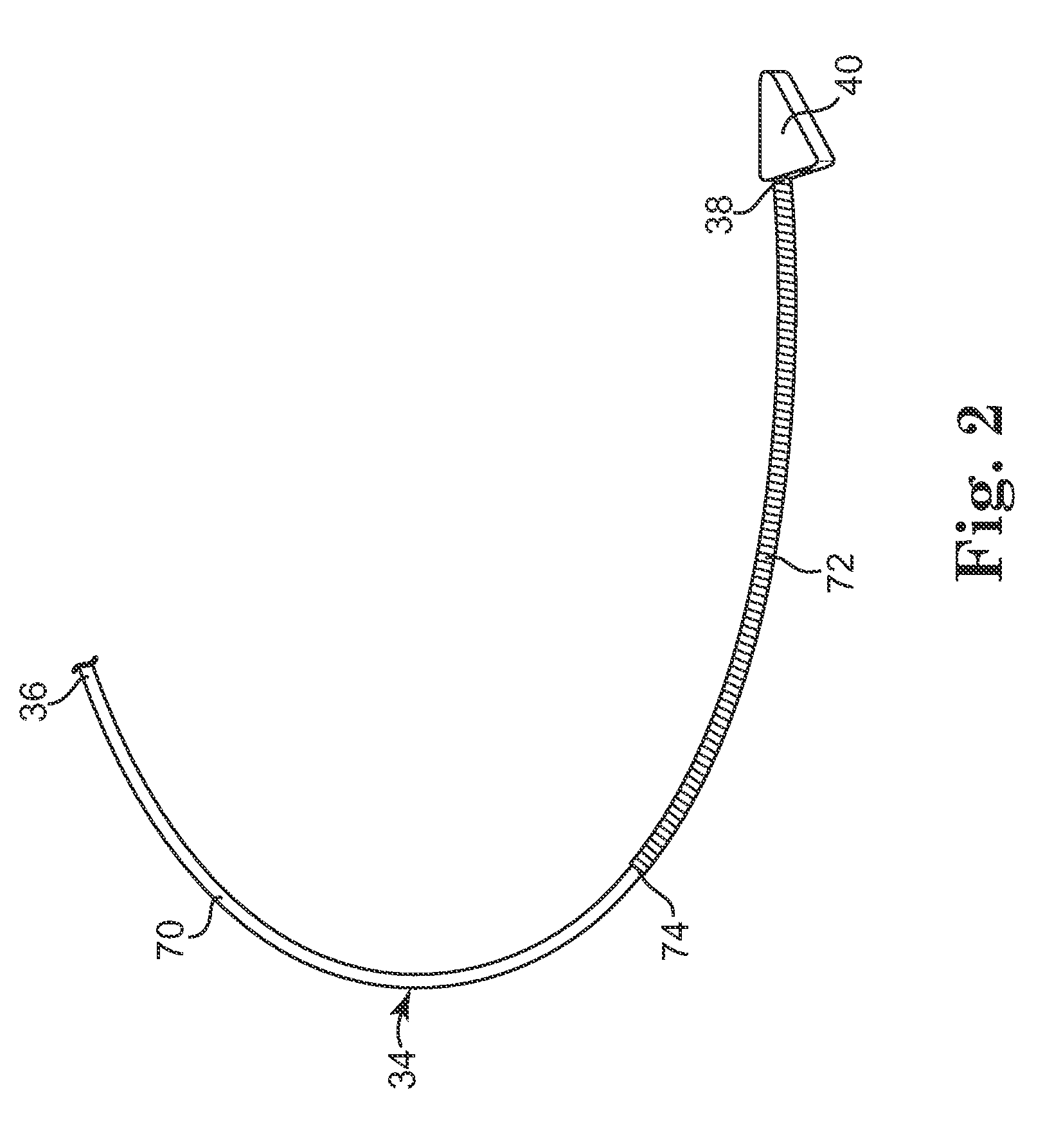
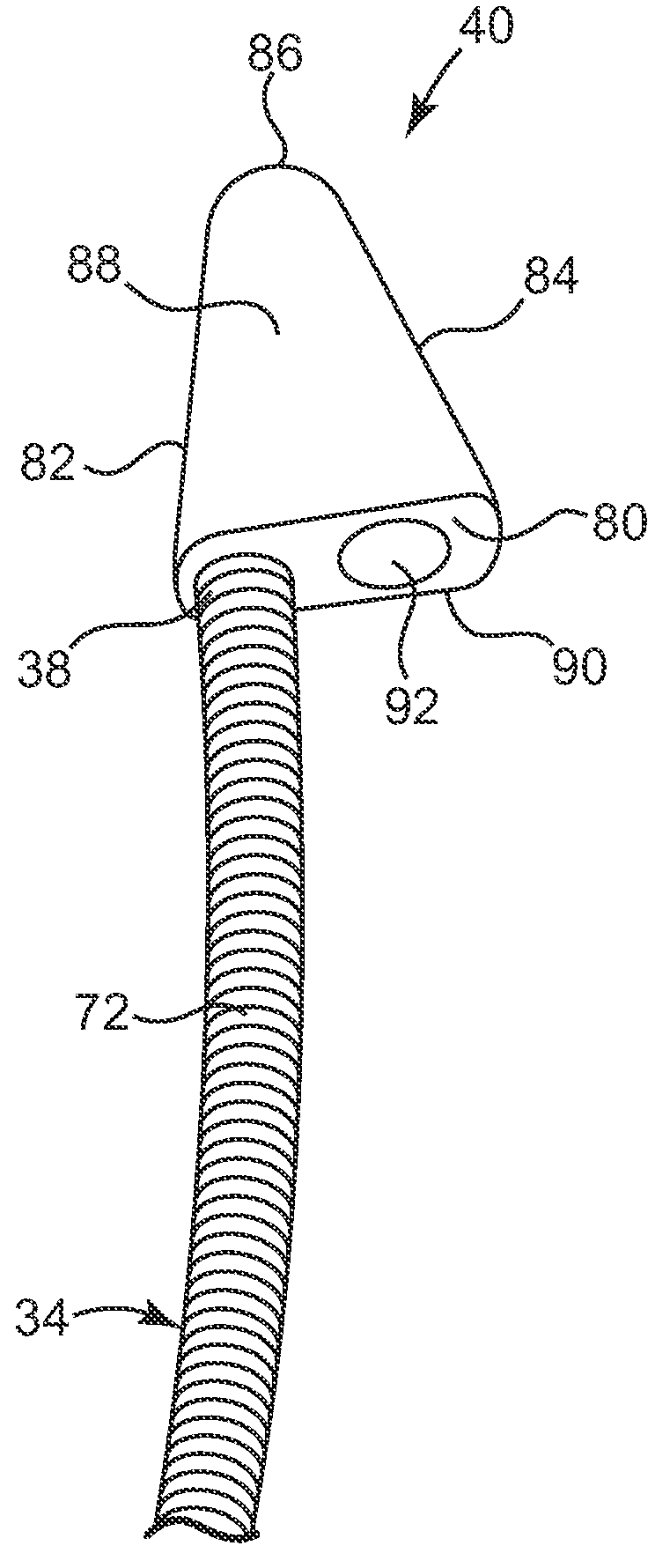
A subcutaneous implantable device is provided that includes a defibrillation electrode disposed along a portion of a lead, and a lead tip connected to the lead. The lead tip includes a trailing end coupled to a distal end of the lead, and first and second non-parallel sides extending from the trailing end that converge to a leading end that is configured to wedge between tissue layers as the lead is advanced subcutaneously.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Subcutaneous implantable lead
A subcutaneous implantable device is provided that includes a defibrillation electrode disposed along a portion of a lead, and a lead tip connected to the lead. The lead tip includes a trailing end coupled to a distal end of the lead, and first and second non-parallel sides extending from the trailing end that converge to a leading end that is configured to wedge between tissue layers as the lead is advanced subcutaneously.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
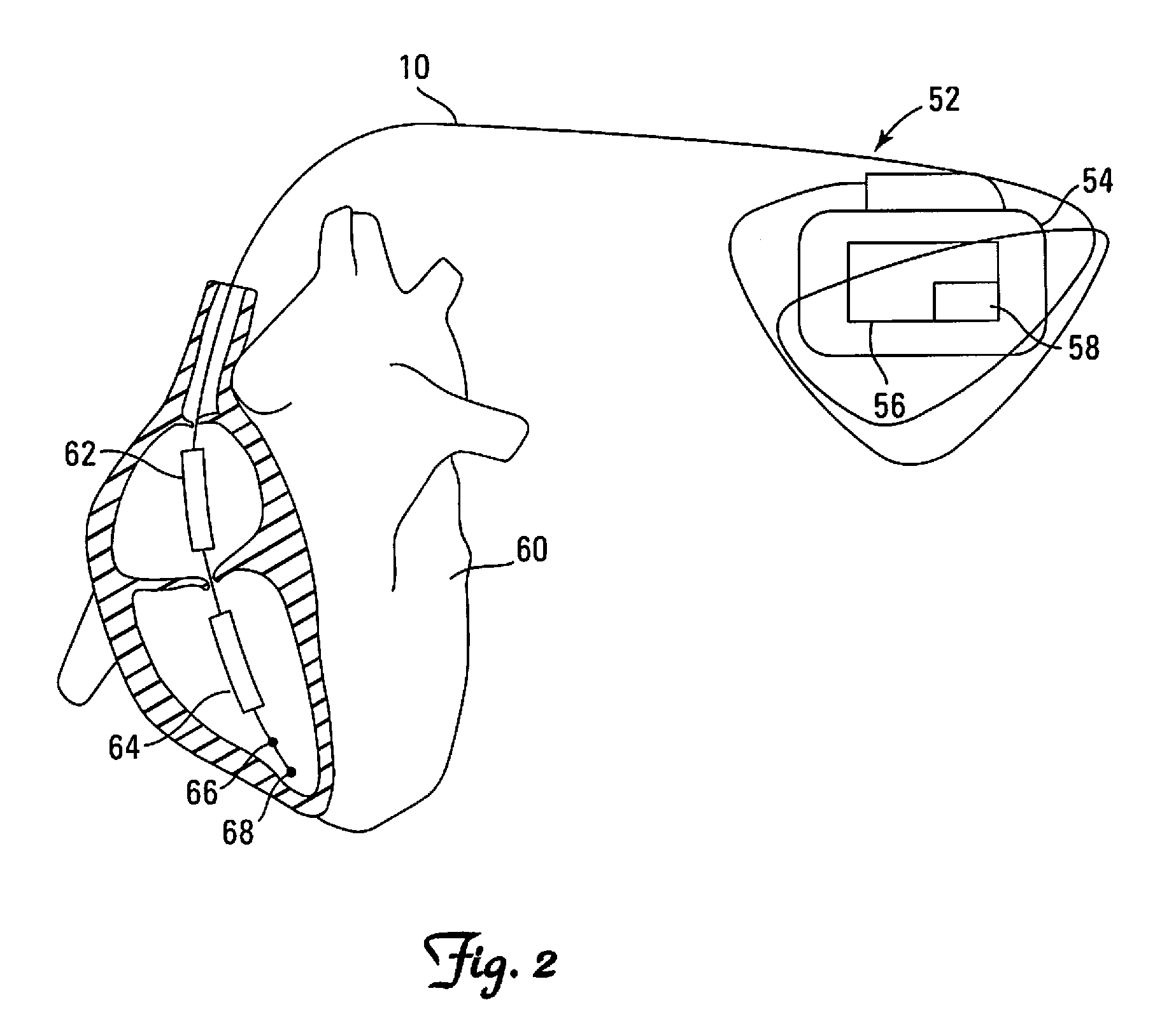
Implantable sensor lead
ActiveUS20090253993A1ElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesIcd leadCardiac activity
In an implantable sensor lead for sensing mechanical cardiac activity of a heart, as well as a sensing method and a cardiac stimulator embodying such a sensor lead, multiple cardiac activity sensing elements are distributed along a portion of a length of the lead body of the implantable lead. The sensing elements sense or detect mechanical cardiac activity and respectively emit electrical signals corresponding to the detected mechanical cardiac activity. The delivery of cardiac stimulation pulses can be controlled dependent on an analysis of the detected mechanical cardiac activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com