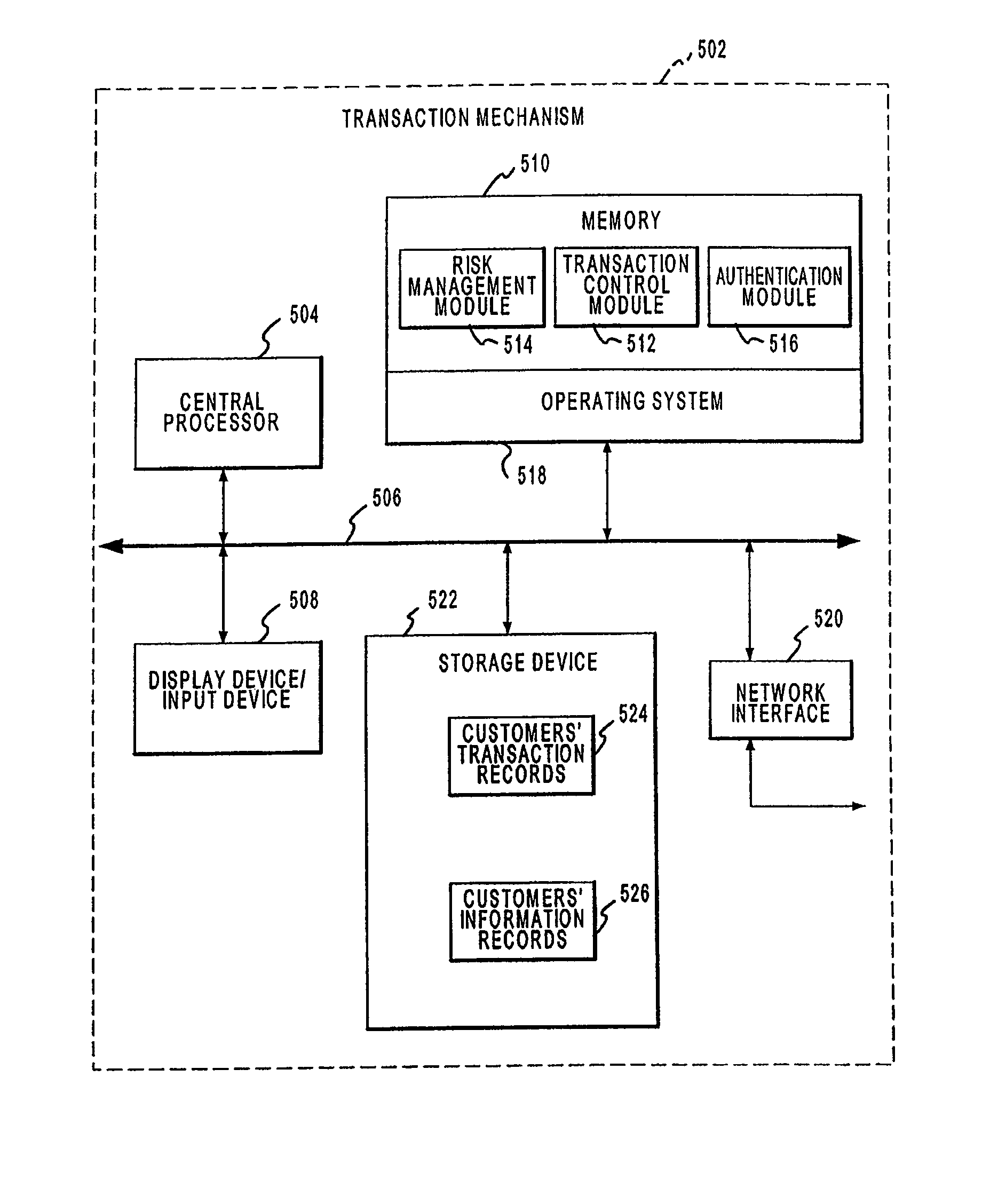
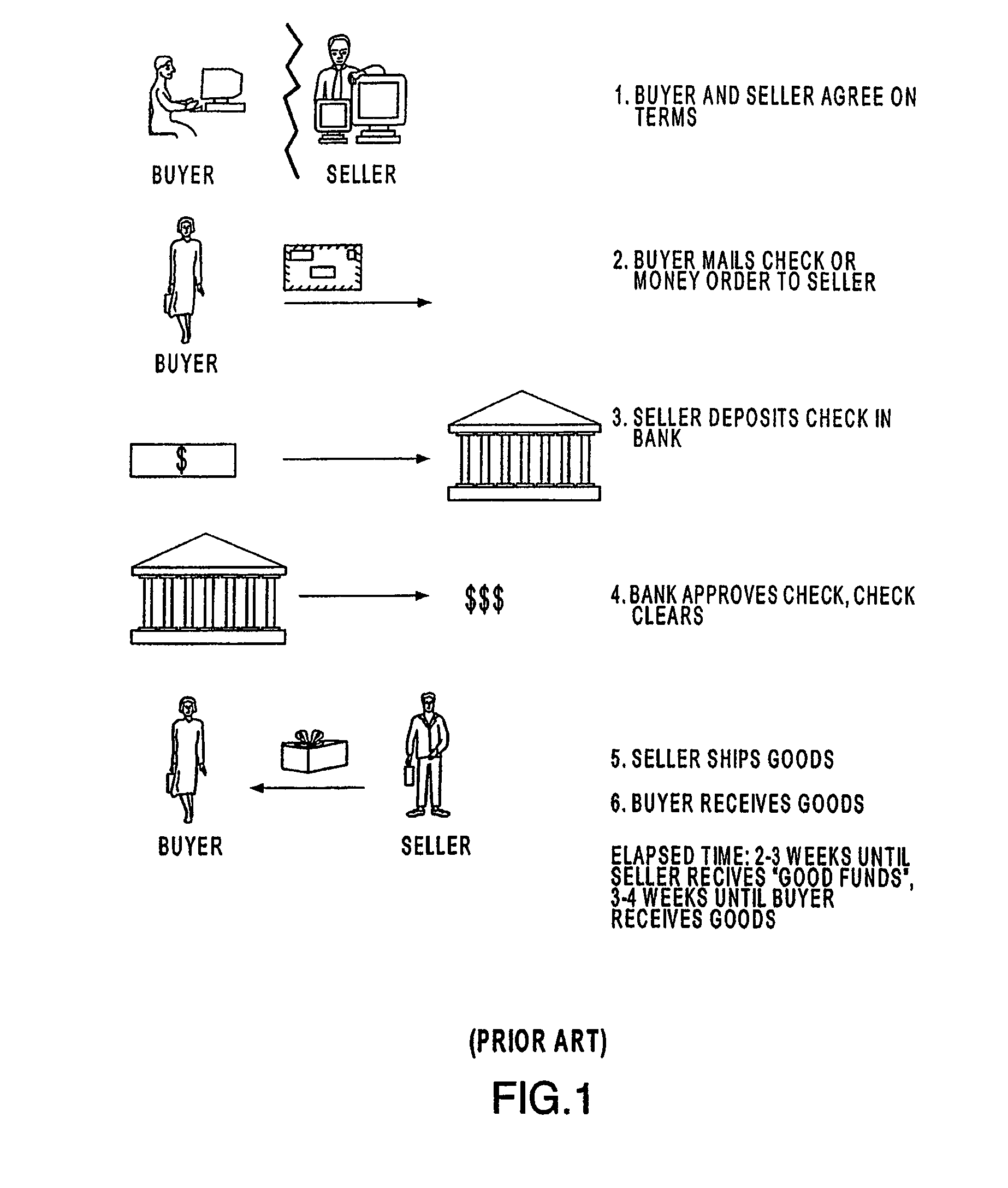
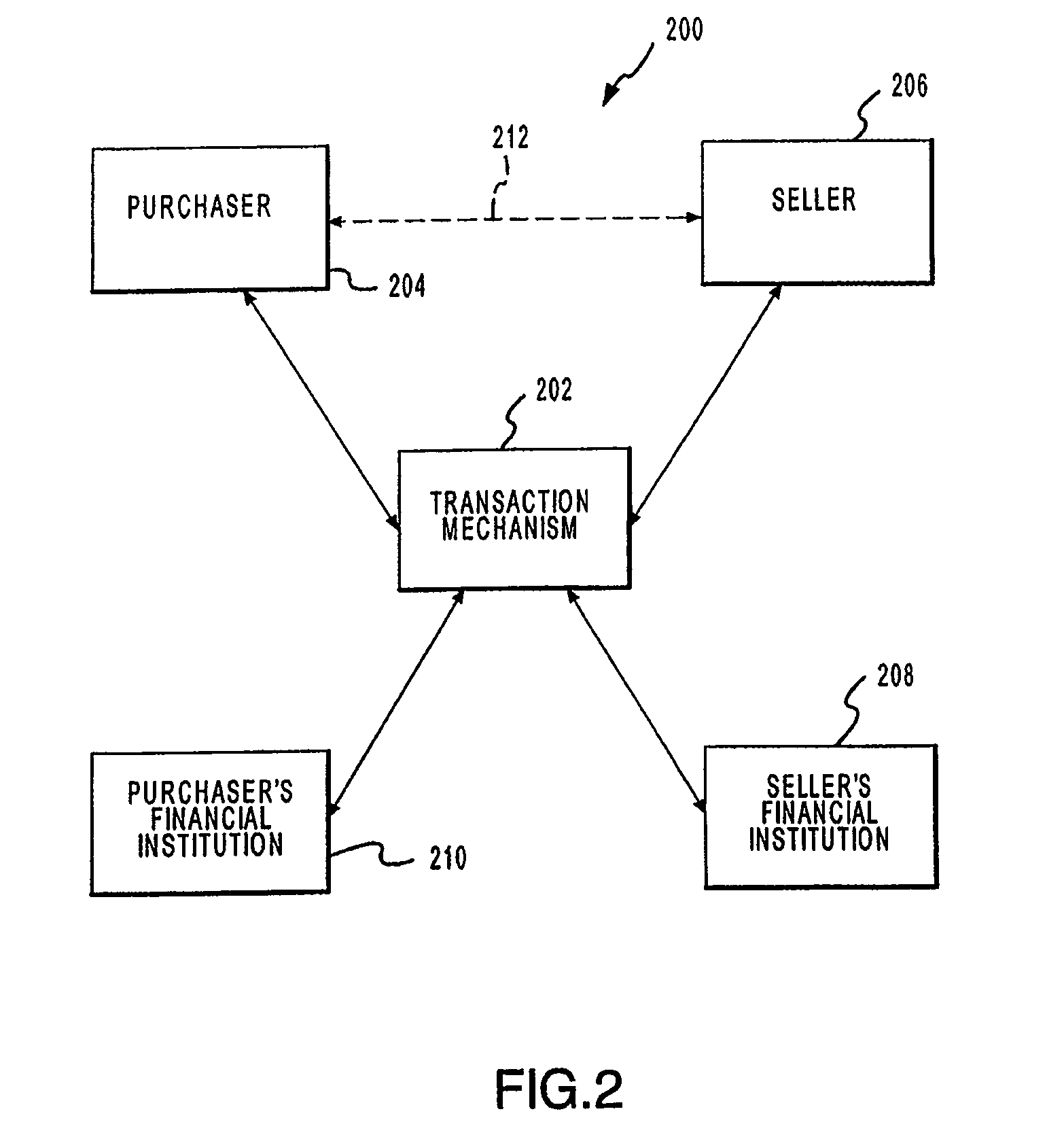
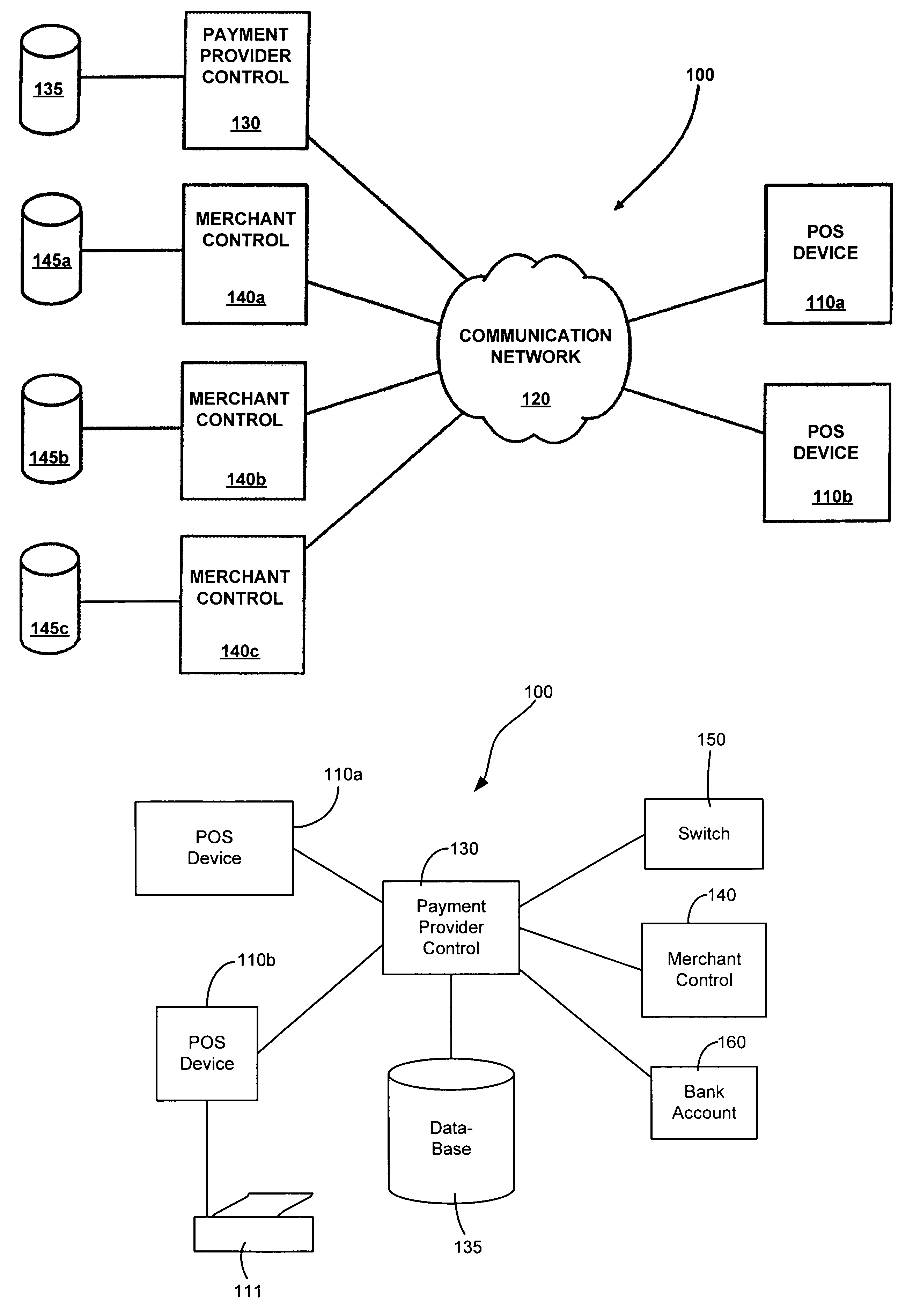
Patents
Literature
67 results about "Partial payment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Partial payment refers to the offering of a payment by check for less than the full amount claimed by the creditor. Such an offer for debt discharge by tender of a "payment-in-full" check is common practice. If the amount tendered is not grossly insufficient, the creditor must decide whether to accept the payment and forfeit the balance, or refuse and try to collect the full amount. Court rulings have treated the tender of such a check as the offer of an accord and satisfaction. If the creditor accepts, endorses, and receives payment from the check, he has accepted the contract, and so discharged the whole debt owed by the debtor.
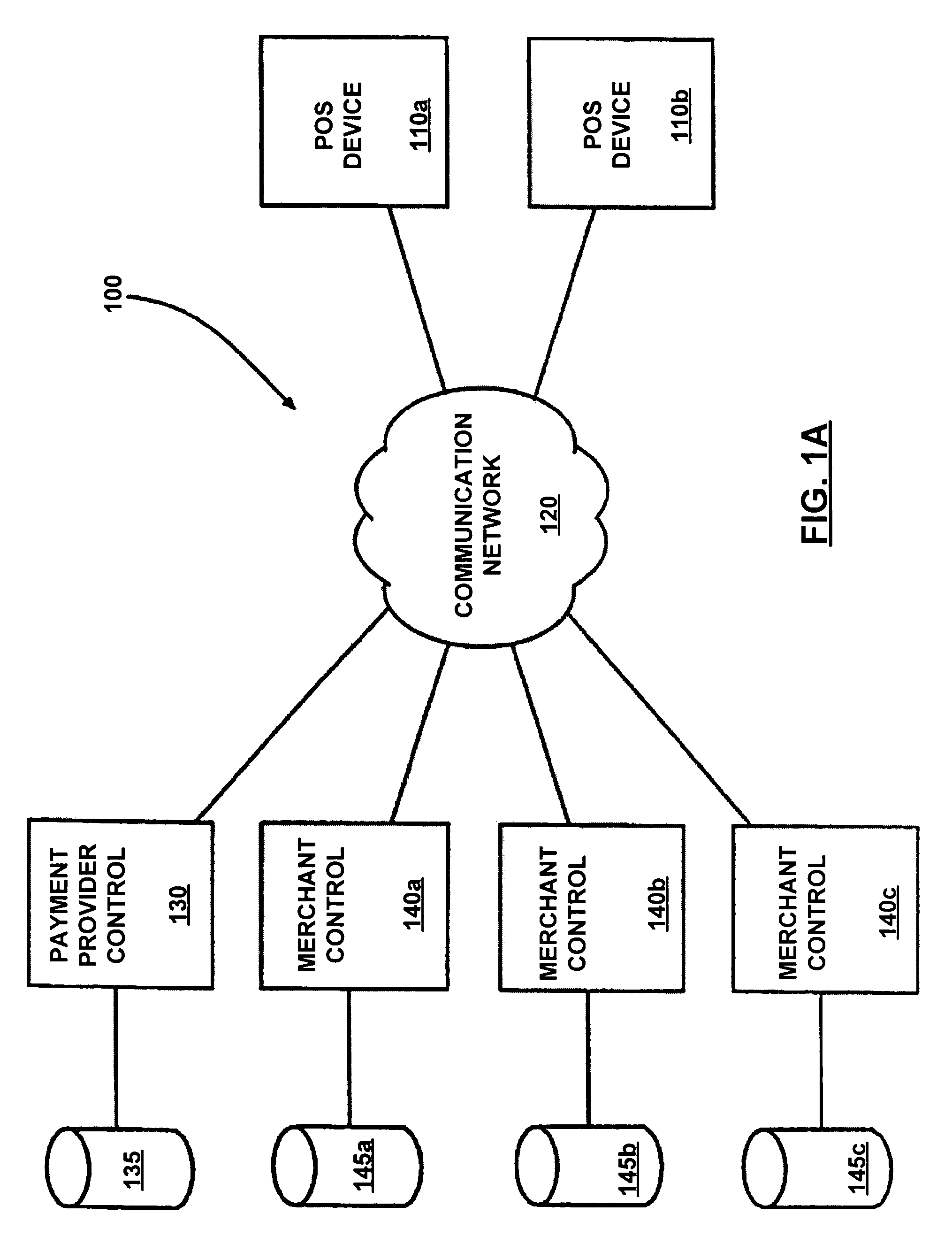
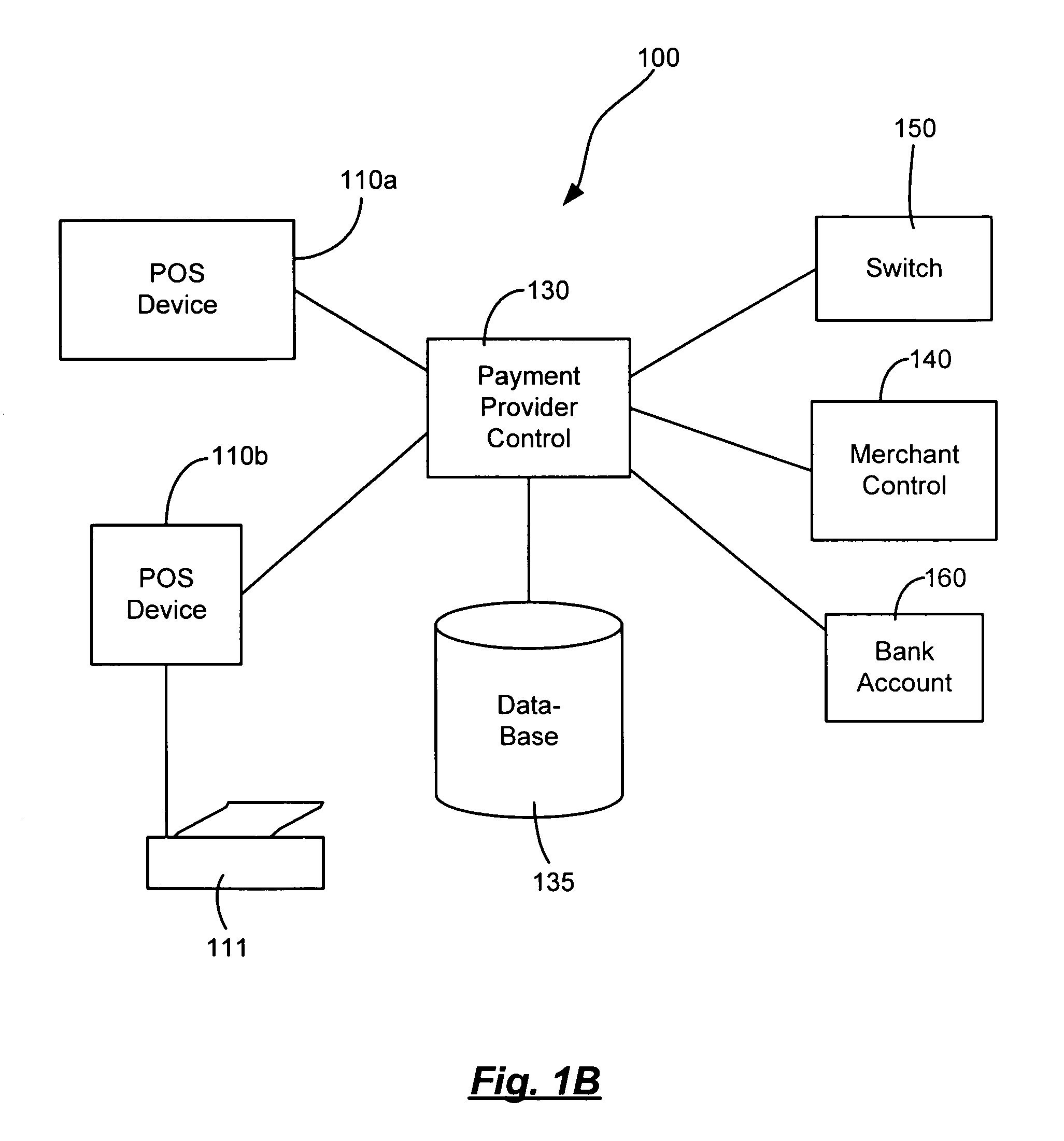
Bar or restaurant check-in and payment systems and methods of their operation
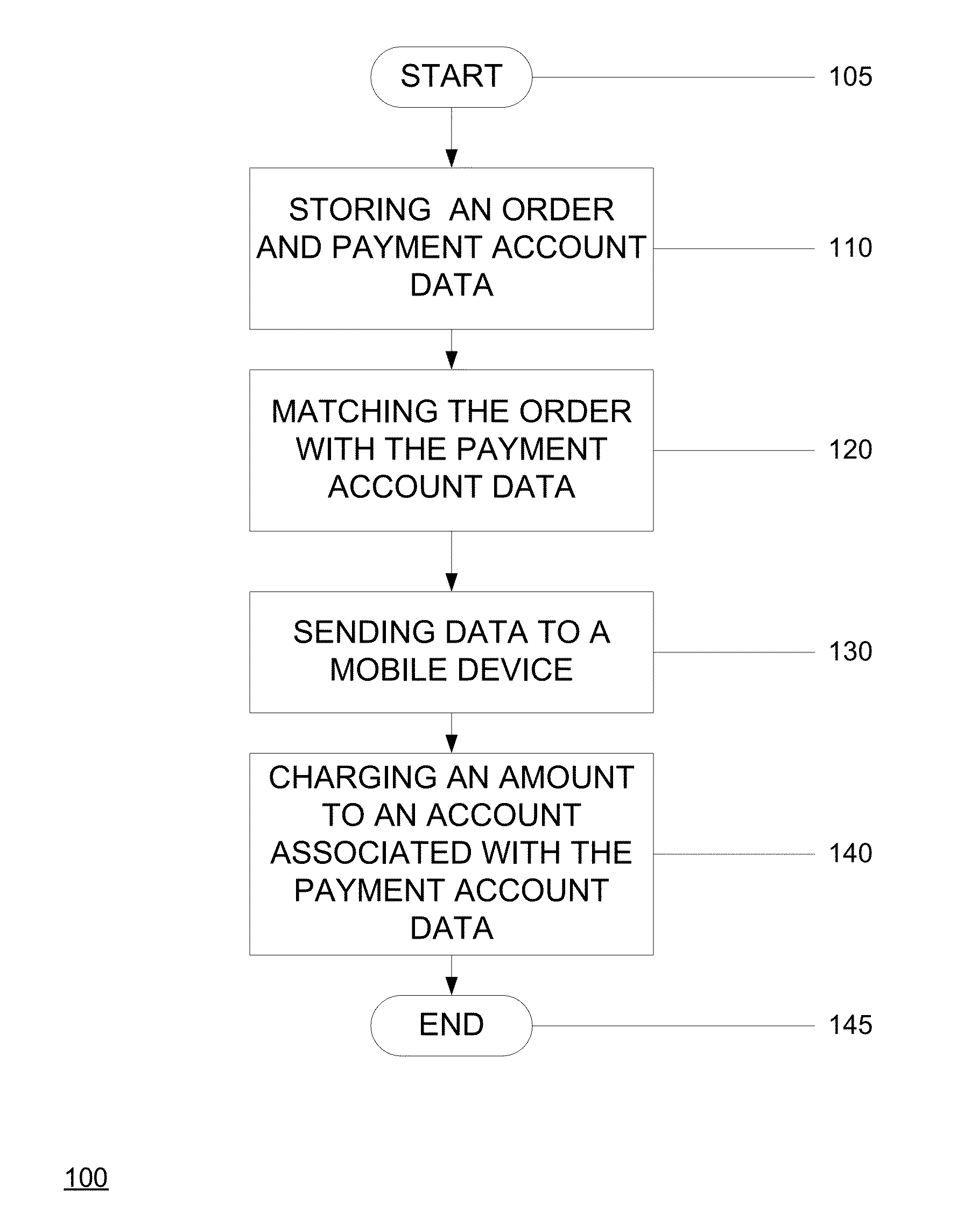
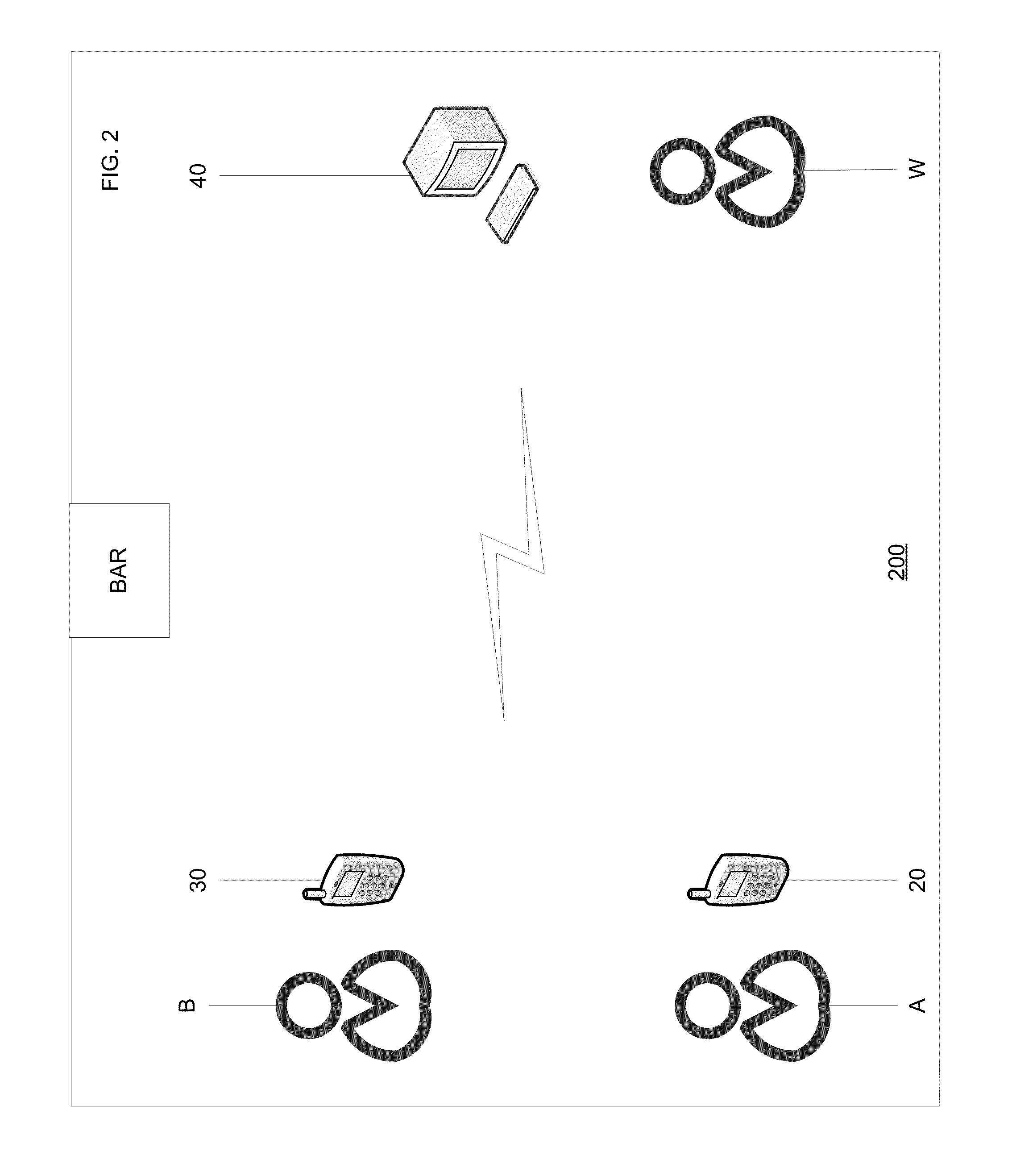
A method for allowing a customer to view and at least partially pay a bill incurred in a bar or a restaurant operating a POS system tracking the bill. The customer operates a mobile computing device running a mobile app communicating with the POS system. The bar or the restaurant has staff. The method includes receiving, via the POS system, check-in data in response to checking-in via the app and payment account data as a security in response to authorizing access to the payment account data via the app. The method includes receiving, via the staff, an order from the customer and associating, via the staff, the order with the payment account data in the POS system. The method includes displaying the bill in real-time via the app. The bill includes the order. The method includes receiving at least partial payment in response to such authorizing via the app.
Owner:RM MERGER SUB II LLC
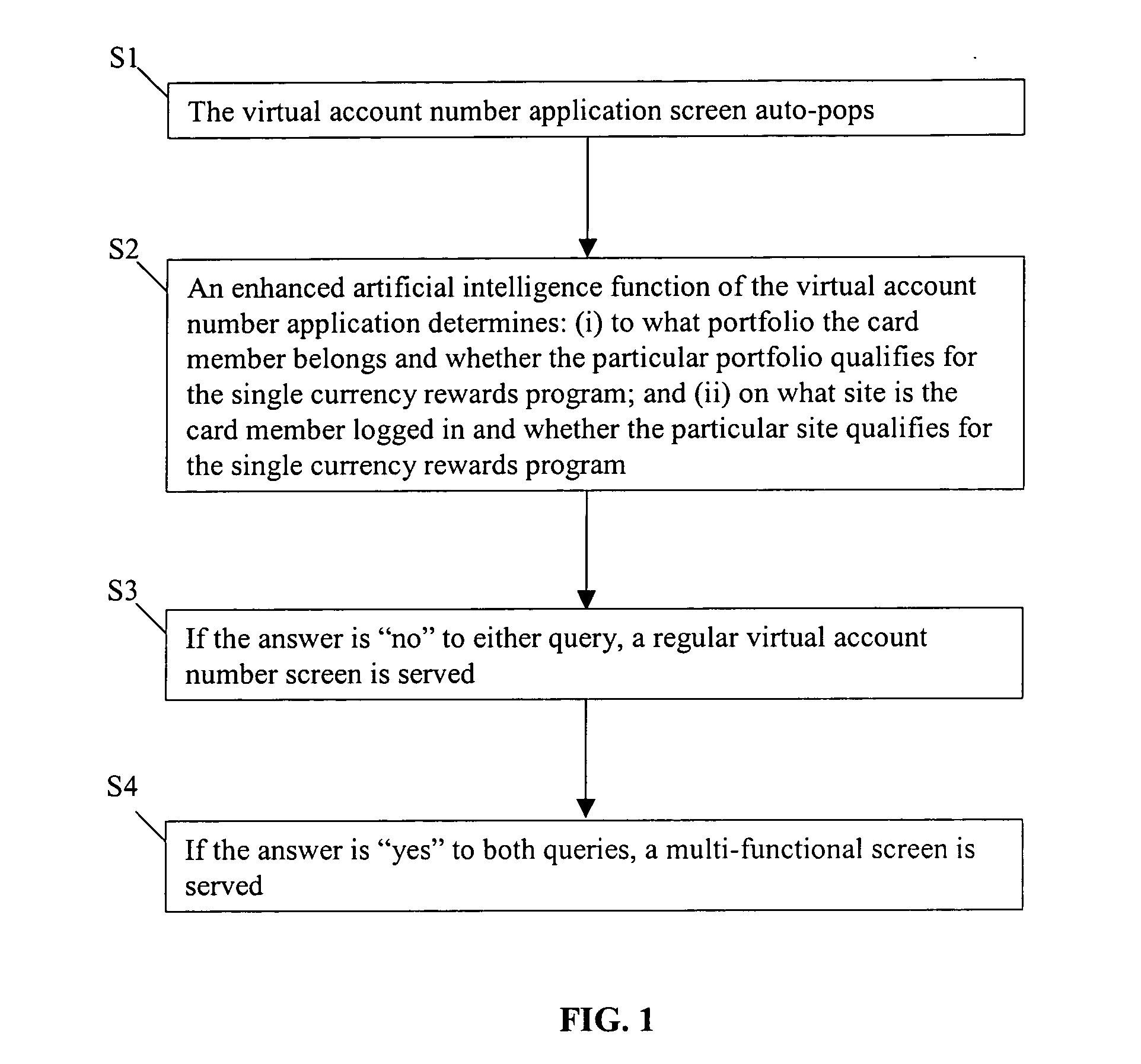
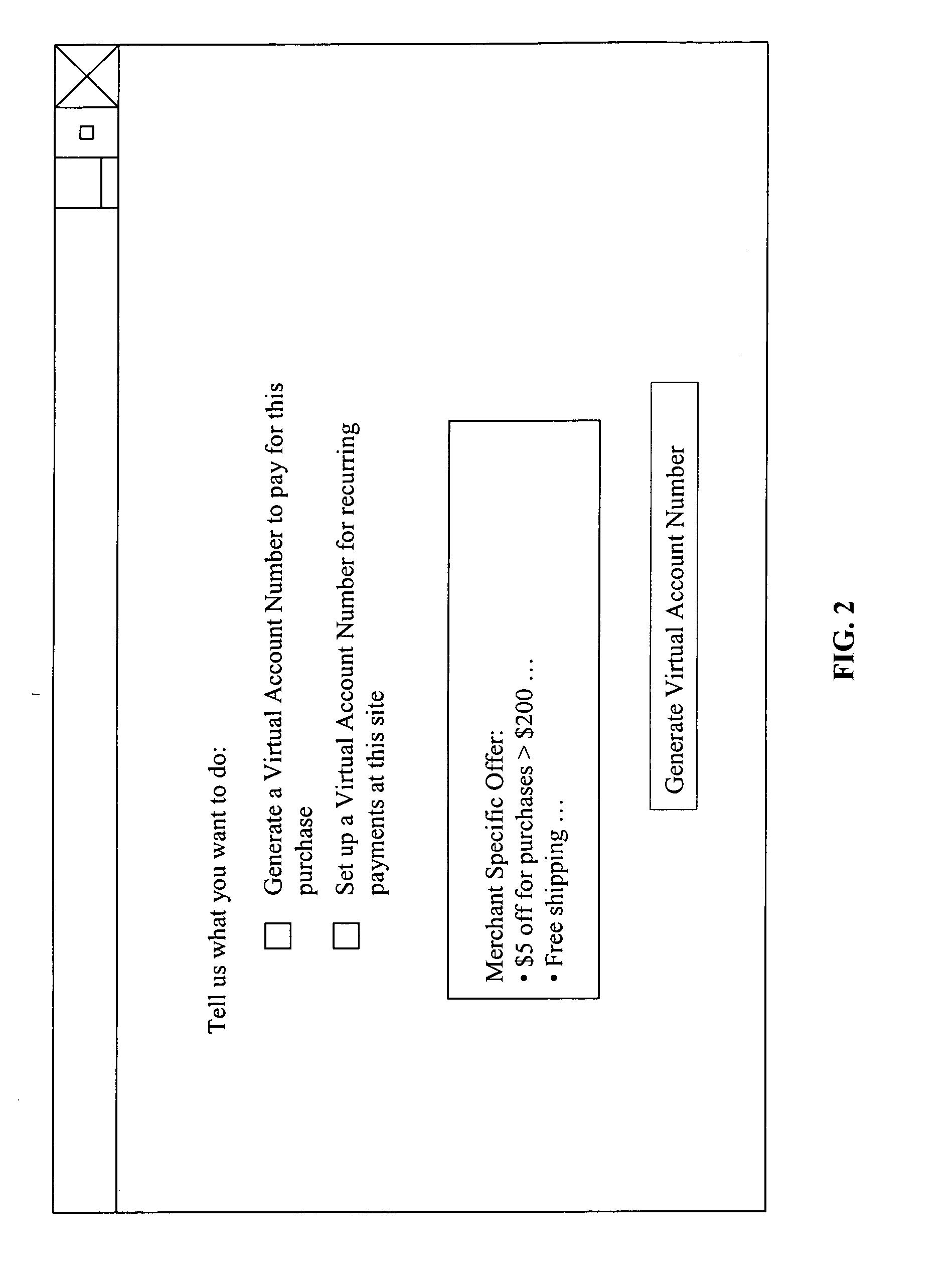
Methods and systems for integration of multiple rewards programs
InactiveUS20050251446A1Promote exchangeUse directlyBilling/invoicingPayment circuitsPayment transactionDatabase
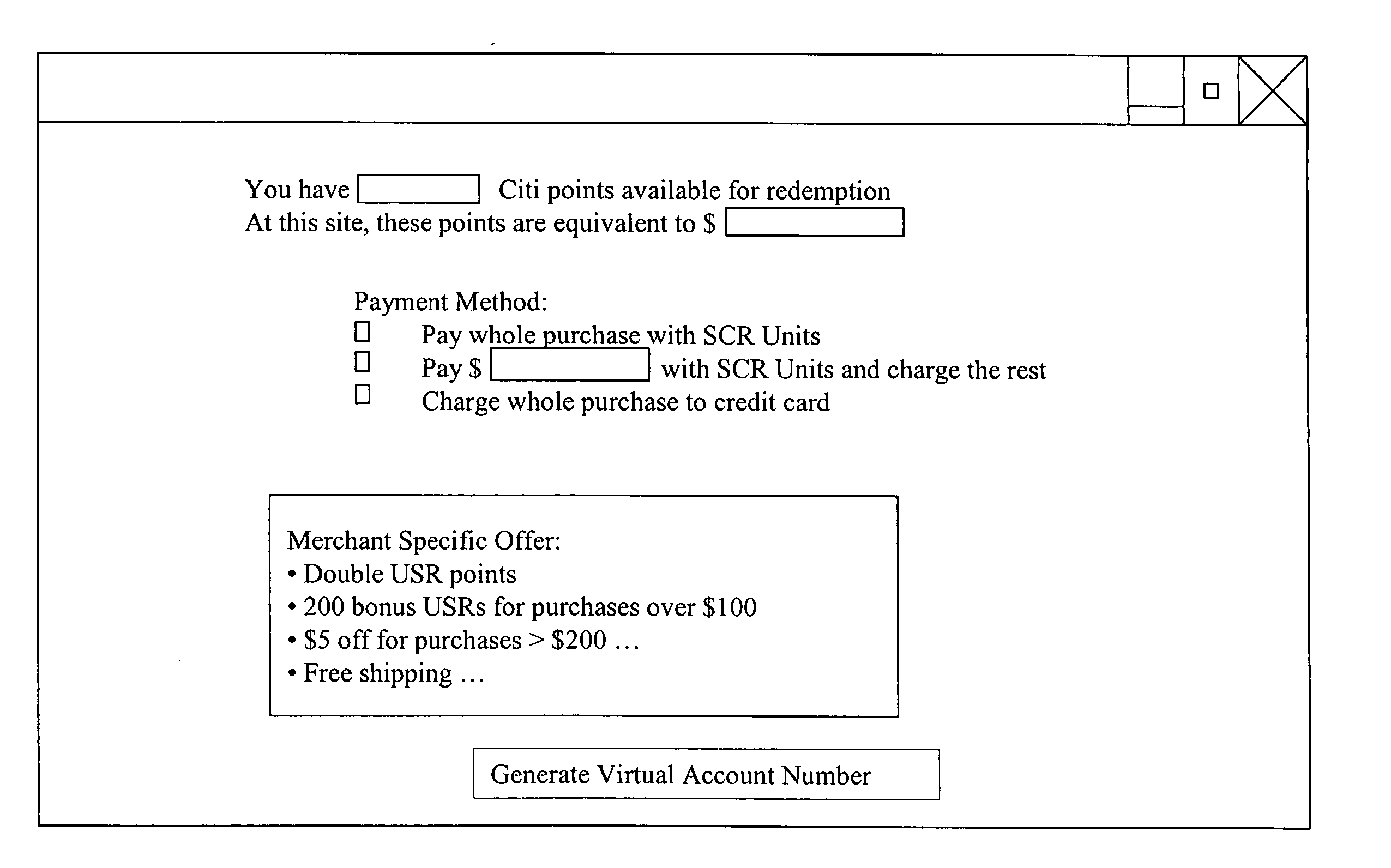
A method and system for consolidating loyalty rewards from multiple programs into a single currency which is managed in a single account allows a customer to utilize accumulated rewards for making full or partial payments at a point of sale with an online merchant. A payment transaction can represent the use of multiple accounts (i.e., reward currency, credit card, or debit card). When executing the transaction, the system conceals a customer's account information by generating a virtual account number (VAN). As such, the online merchant is not required to have any prior knowledge of the system and processes the transaction as a conventional credit card purchase.
Owner:CITICORP CREDIT SERVICES INC (USA)
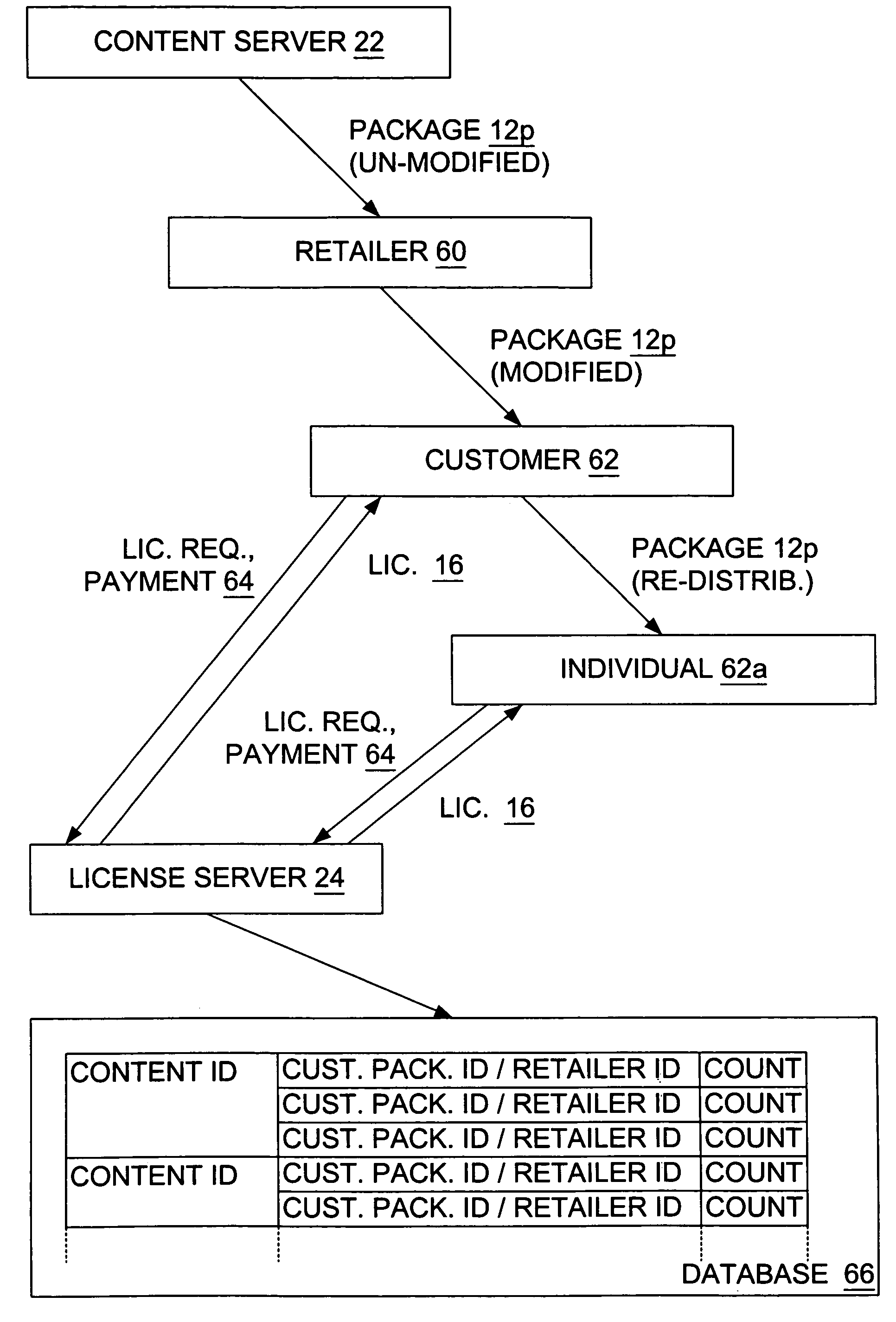
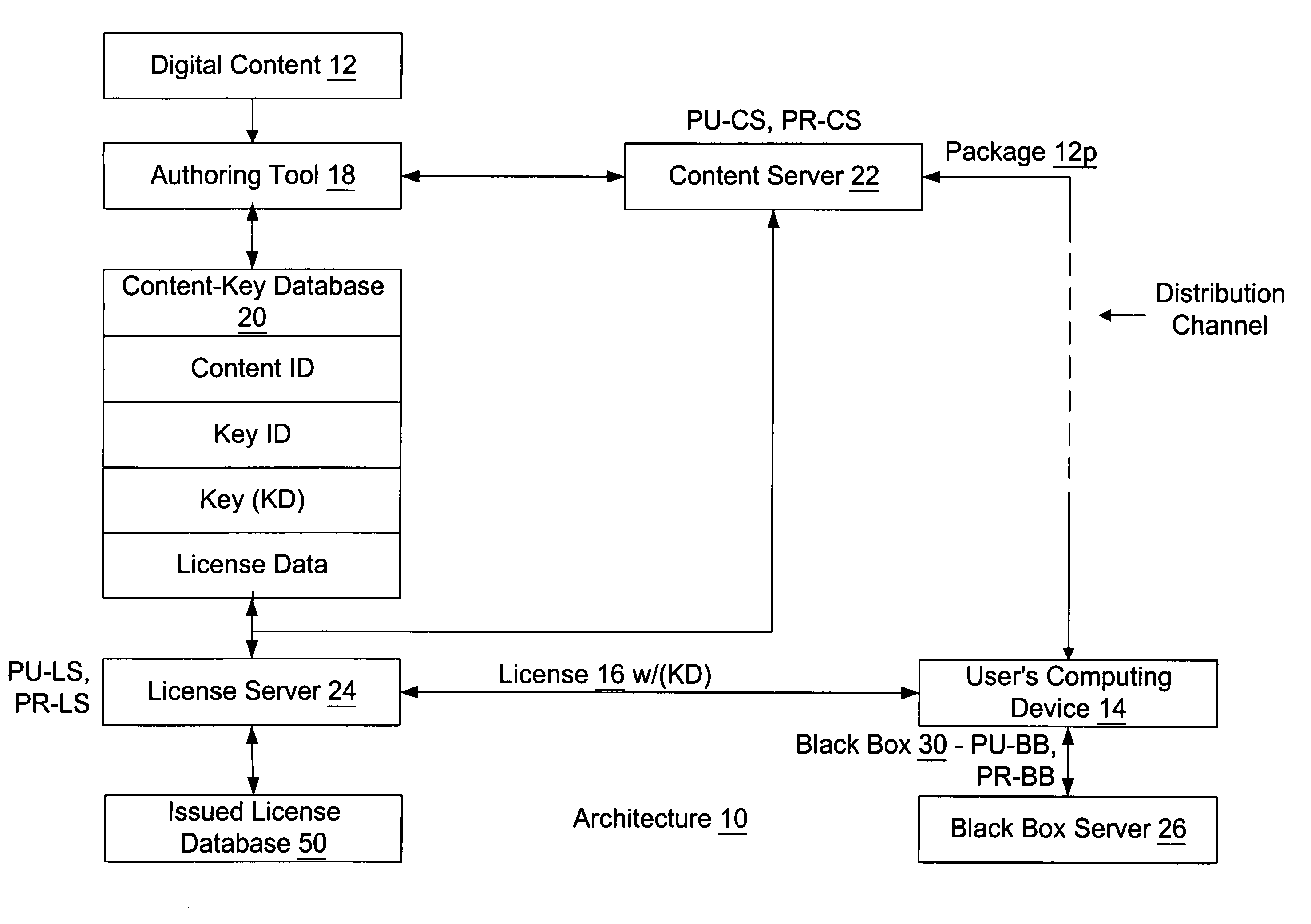
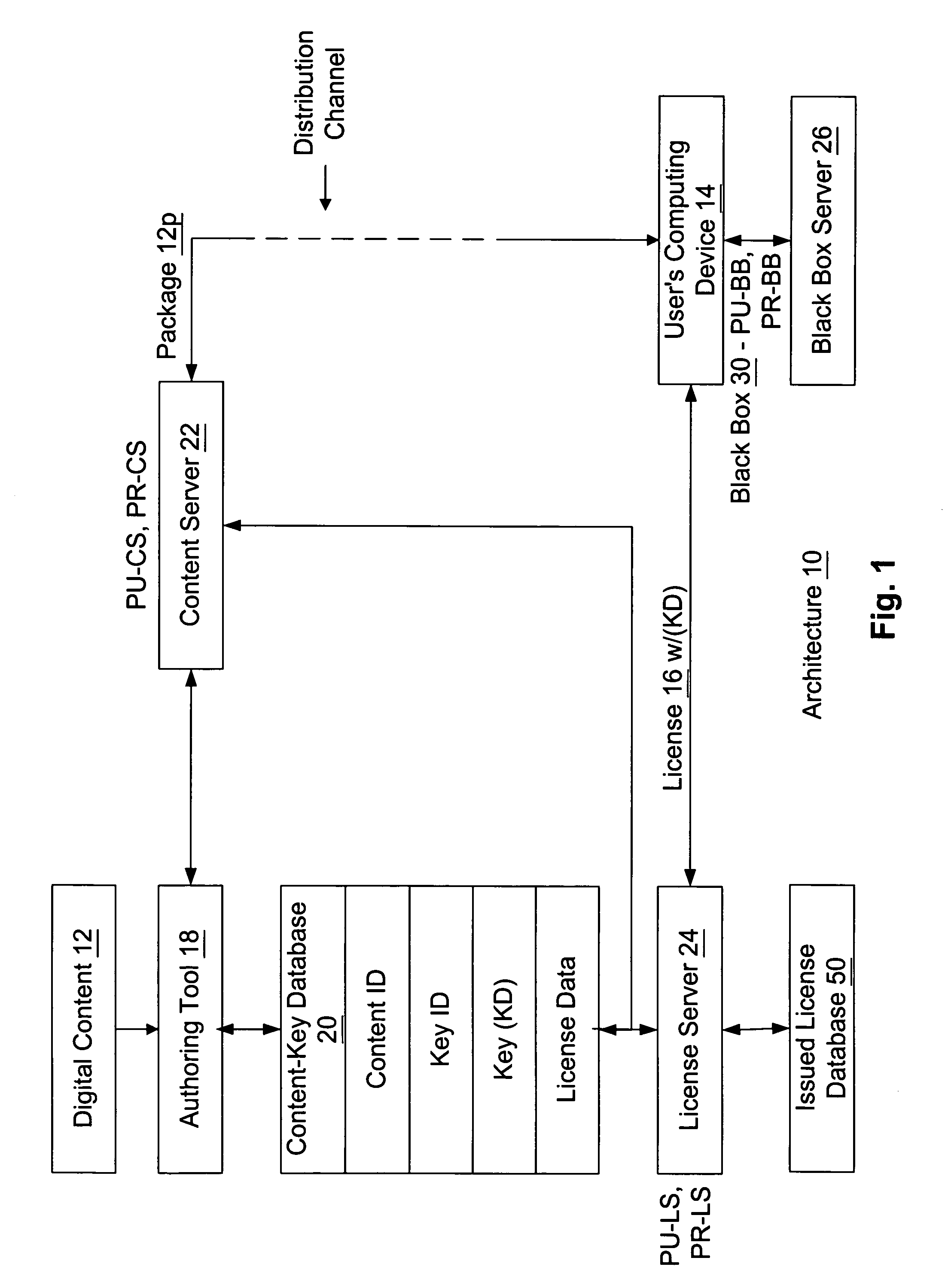
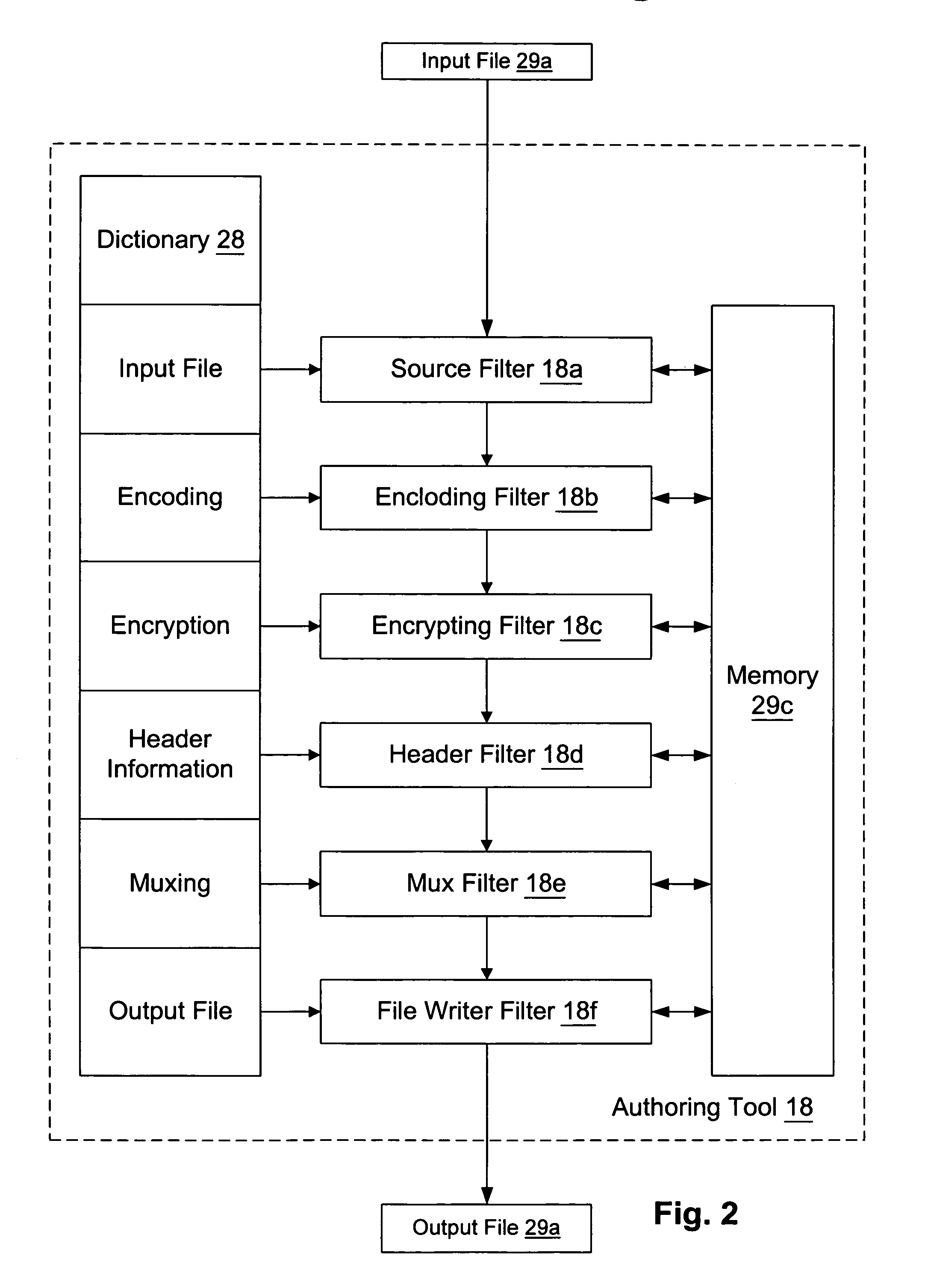
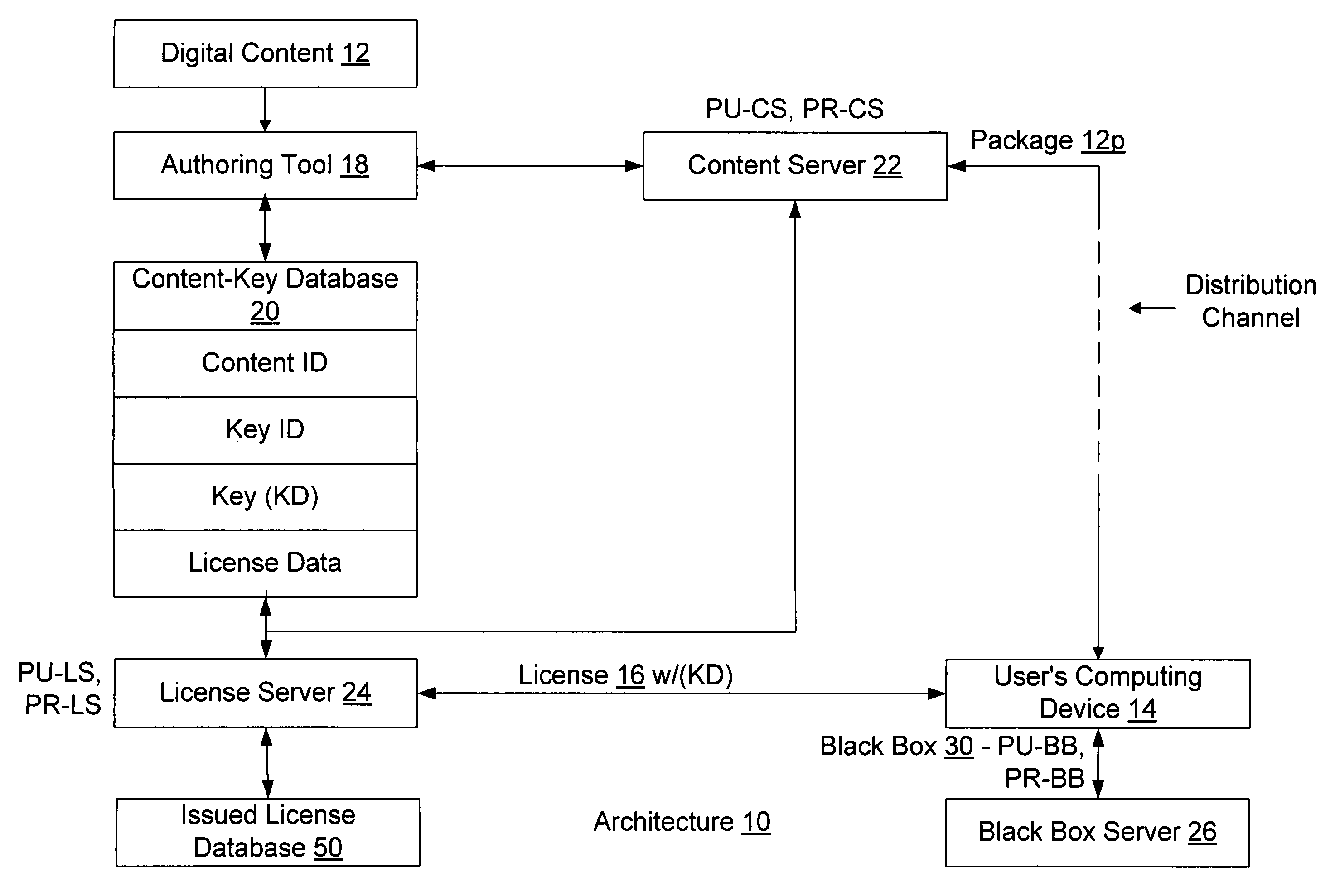
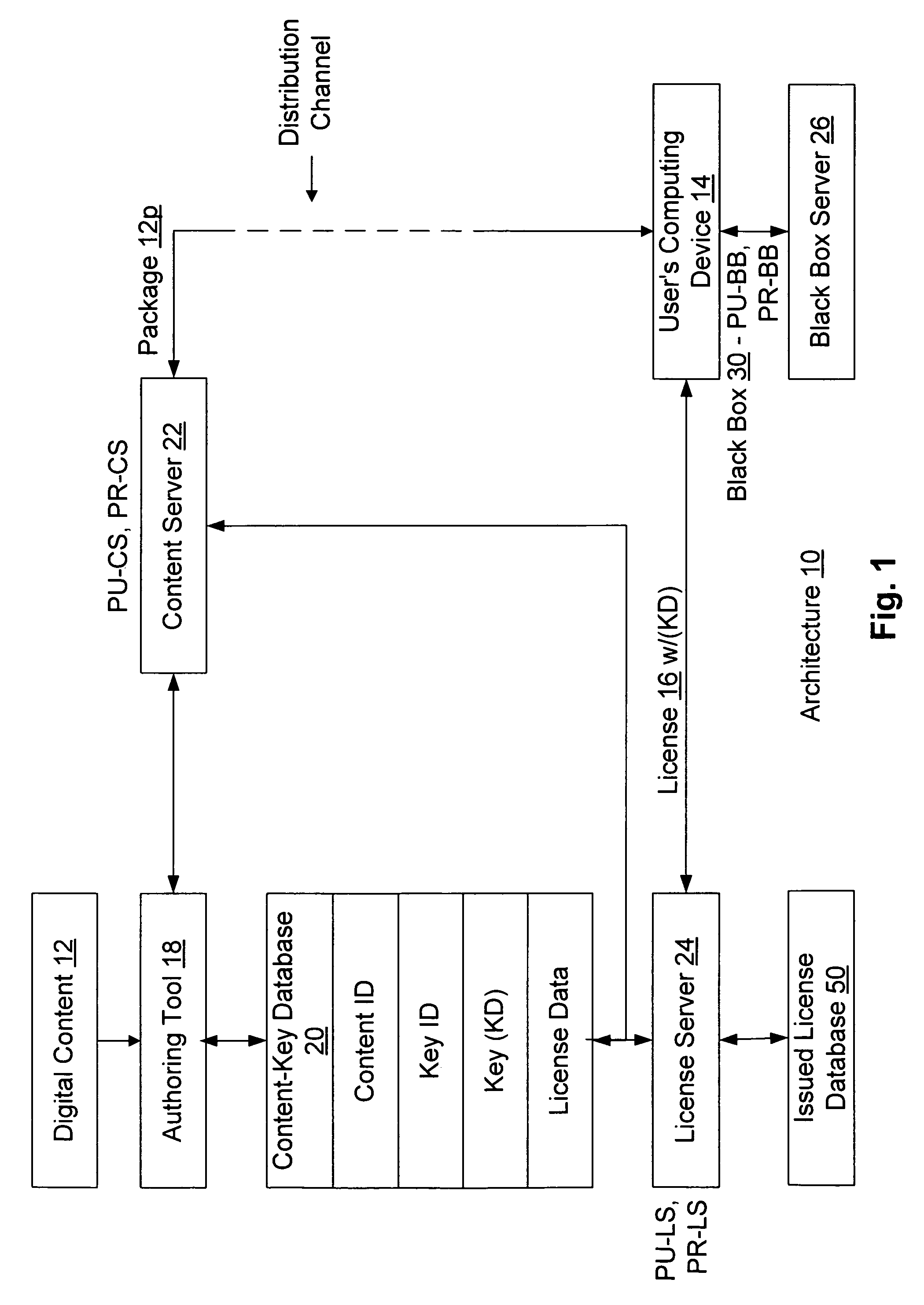
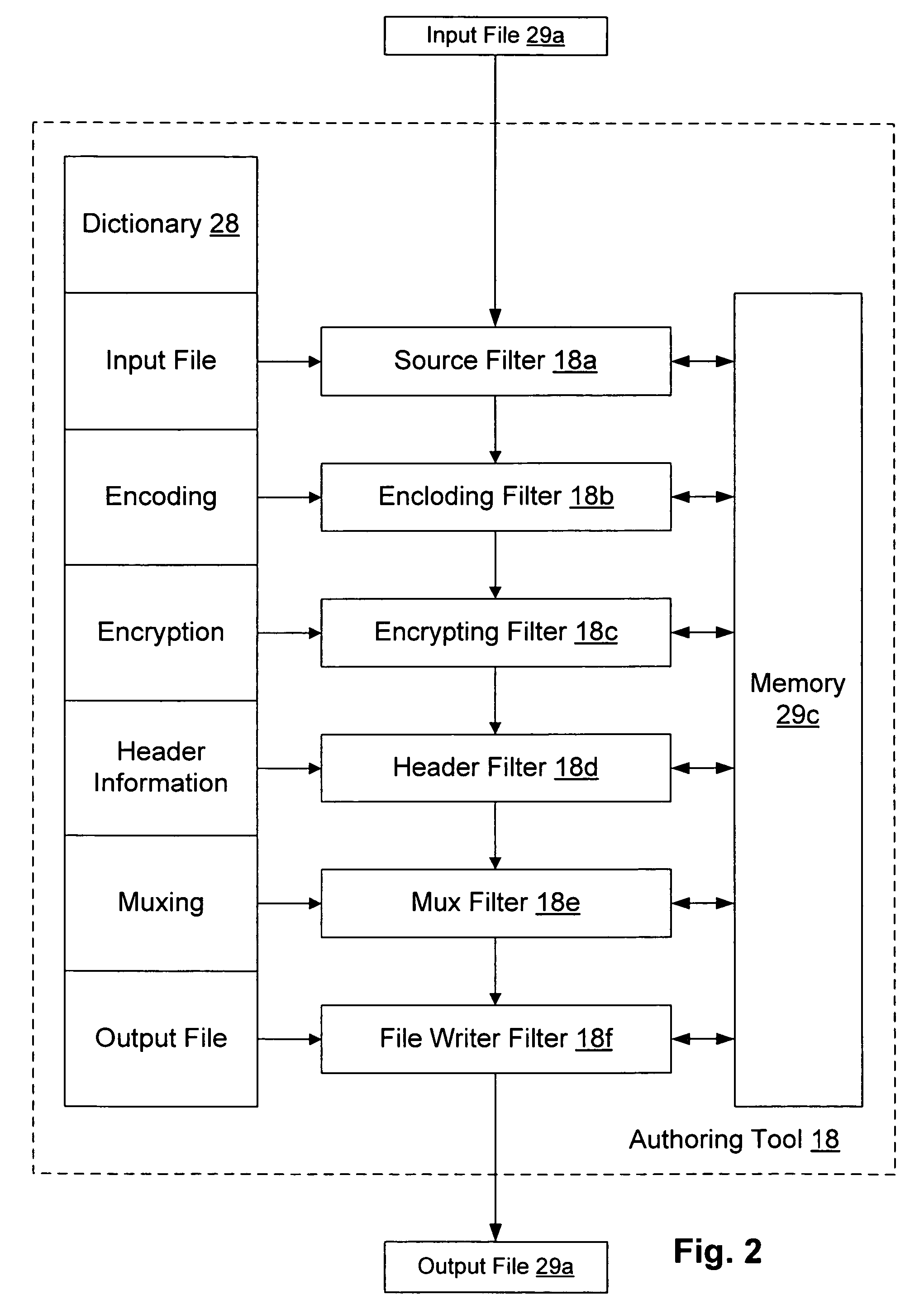
Retail transactions involving distributed and super-distributed digital content in a digital rights management (DRM) system
InactiveUS7149722B1Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationDigital contentDigital rights management
To distribute digital content from a retailer to a customer, the content as issued by a content provider is retrieved. The as issued content has license acquisition information for acquiring a corresponding license attached thereto, where the license acquisition information includes a site identifier identifying a site at which the customer may obtain a digital license corresponding to the content. The site identifier includes an additional information field attached thereto. The additional information field is modified to include retailer information identifying the retailer, and the content is delivered with the modified additional information field to the customer. Thus, a license request sent from the customer is addressed to the site identified by the site identifier in the license acquisition information and includes the modified additional information field attached thereto. The corresponding digital license is issued to the customer after receiving the license request at the site identified by the site identifier, and after payment is received at such site from the customer in connection with the license request. The retailer information from the license request is retrieved and the retailer is identified therefrom, and such identified retailer is credited for a portion of the payment received.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
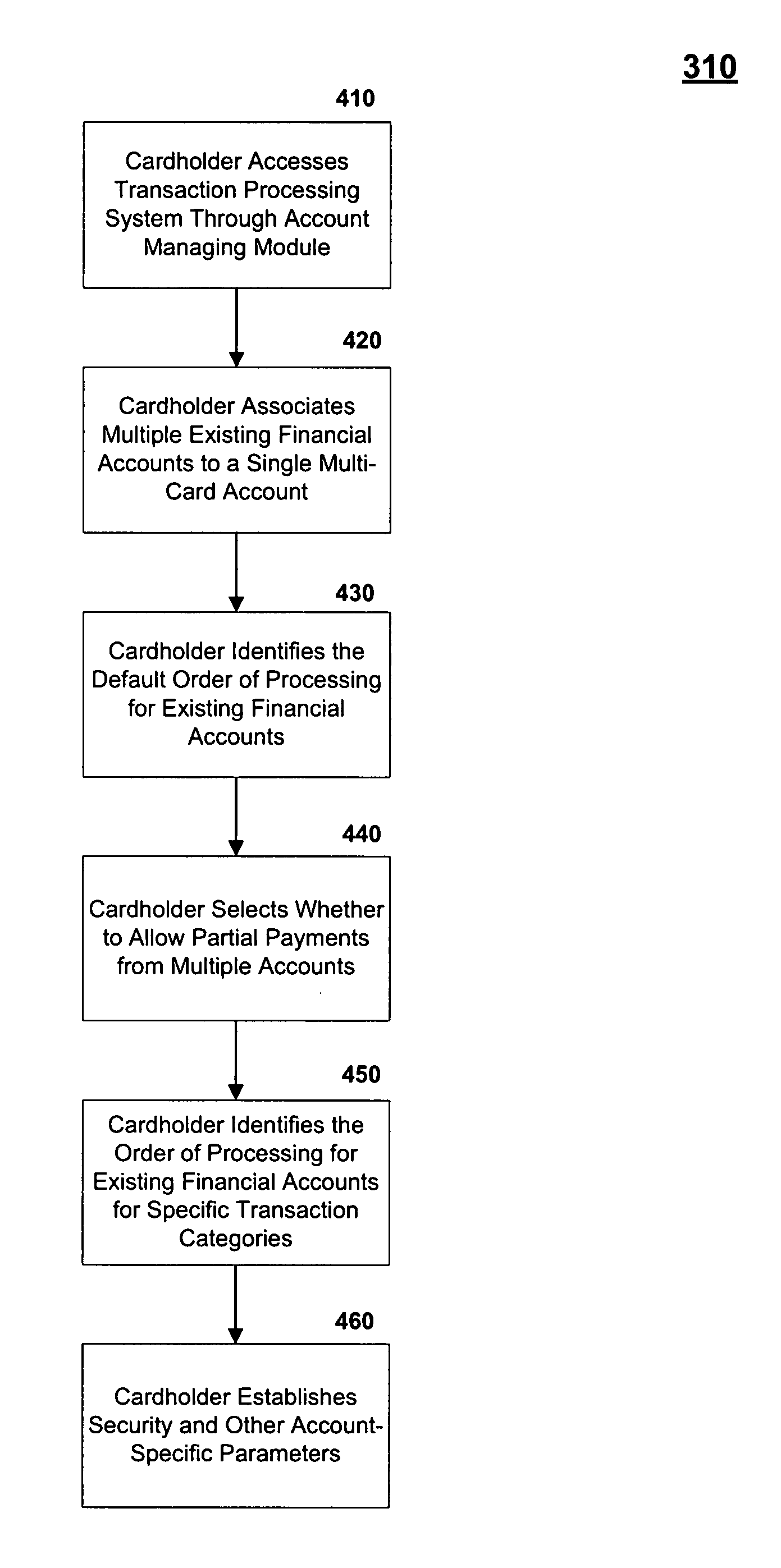
Method and system for processing financial transactions using multiple financial accounts
InactiveUS20080301041A1Minimizing chanceMinimize the numberFinanceCredit schemesFinancial transactionFinancial trading
Associating multiple existing financial accounts with a multi-card account. The single multi-card account may allow a cardholder to determine an order for processing a financial transaction among the multiple financial accounts. This ordering may be dependent on the type of financial transaction. Also, the cardholder may allows partial payments from multiple financial accounts, such that a single purchase could be allocated to multiple accounts associated with the multi-card account. These systems and methods minimize the number of cards a cardholder must carry, thus minimizing the chance of losing cards or otherwise having an unauthorized use of an account and also minimizing the chance of an embarrassing rejection of a transaction.
Owner:BRUK MARK EDWARD
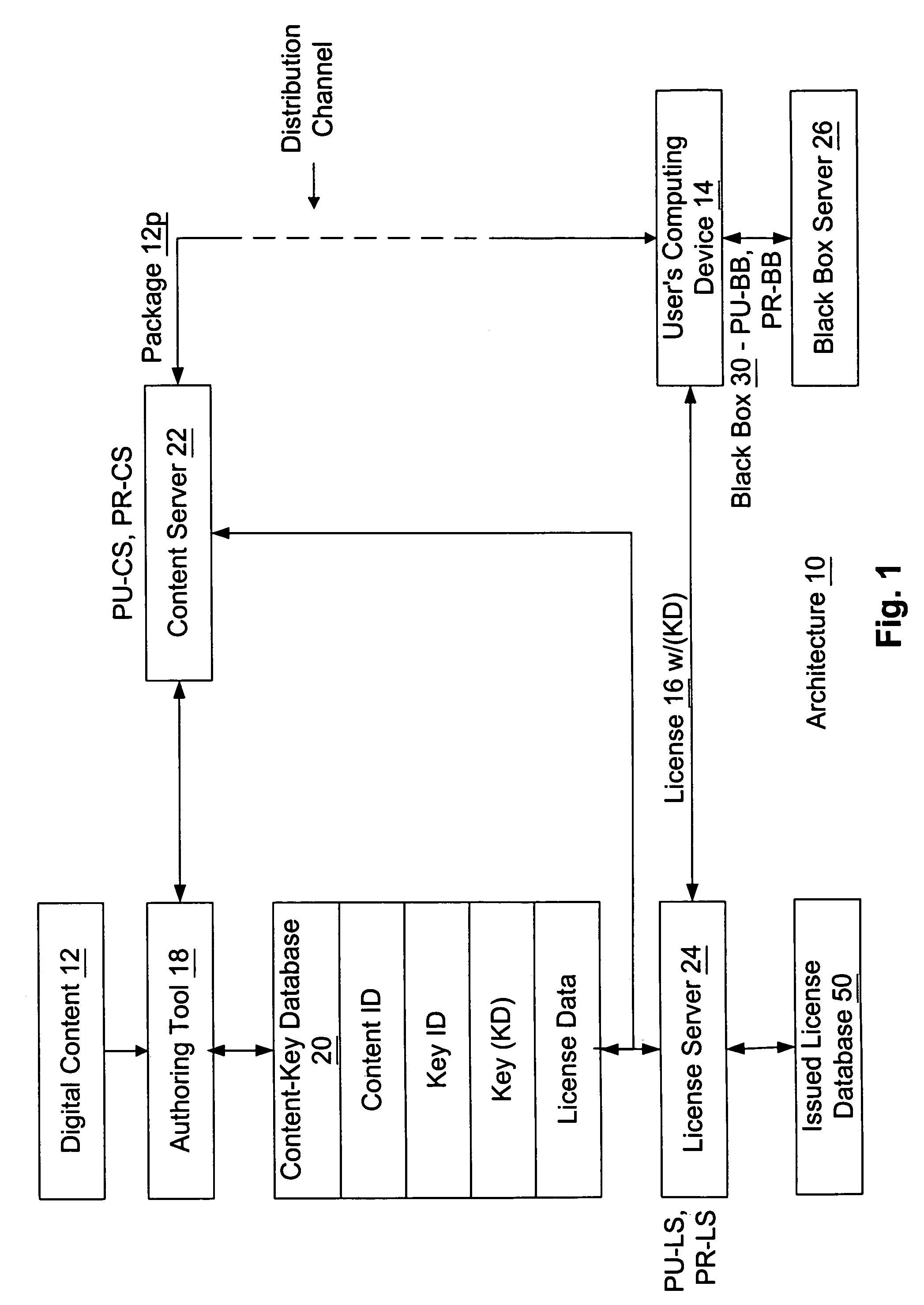
Retail transactions involving digital content in a digital rights management (DRM) system
InactiveUS7039615B1Easy to issuePublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital contentDigital rights management
A retailer facilitates issuance of a digital license from a licensor to a customer for a corresponding piece of digital content. The retailer receives payment for the license from the customer, where the payment is to be shared with the licensor in a pre-determined manner. The retailer also receives customer-based information from the customer. The retailer then composes an actual license request including the obtained customer-based information, and including retailer-based information identifying the retailer to the licensor and acknowledging to the licensor that the retailer owes a portion of the received payment to the licensor. Thereafter, the retailer forwards the actual license request to the licensor. The licensor notes based on the retailer-based information in the actual license request that the retailer identified thereby owes the licensor at least a portion of the forwarded payment. If an individual sends a license request directly to the licensor and thus fails to forward payment for the license to a retailer, the actual license request as composed by the individual fails to include the retailer-based information. Accordingly, the licensor refuses to issue a license as requested based on the lack of retailer-based information.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Bit currency: transactional trust tools
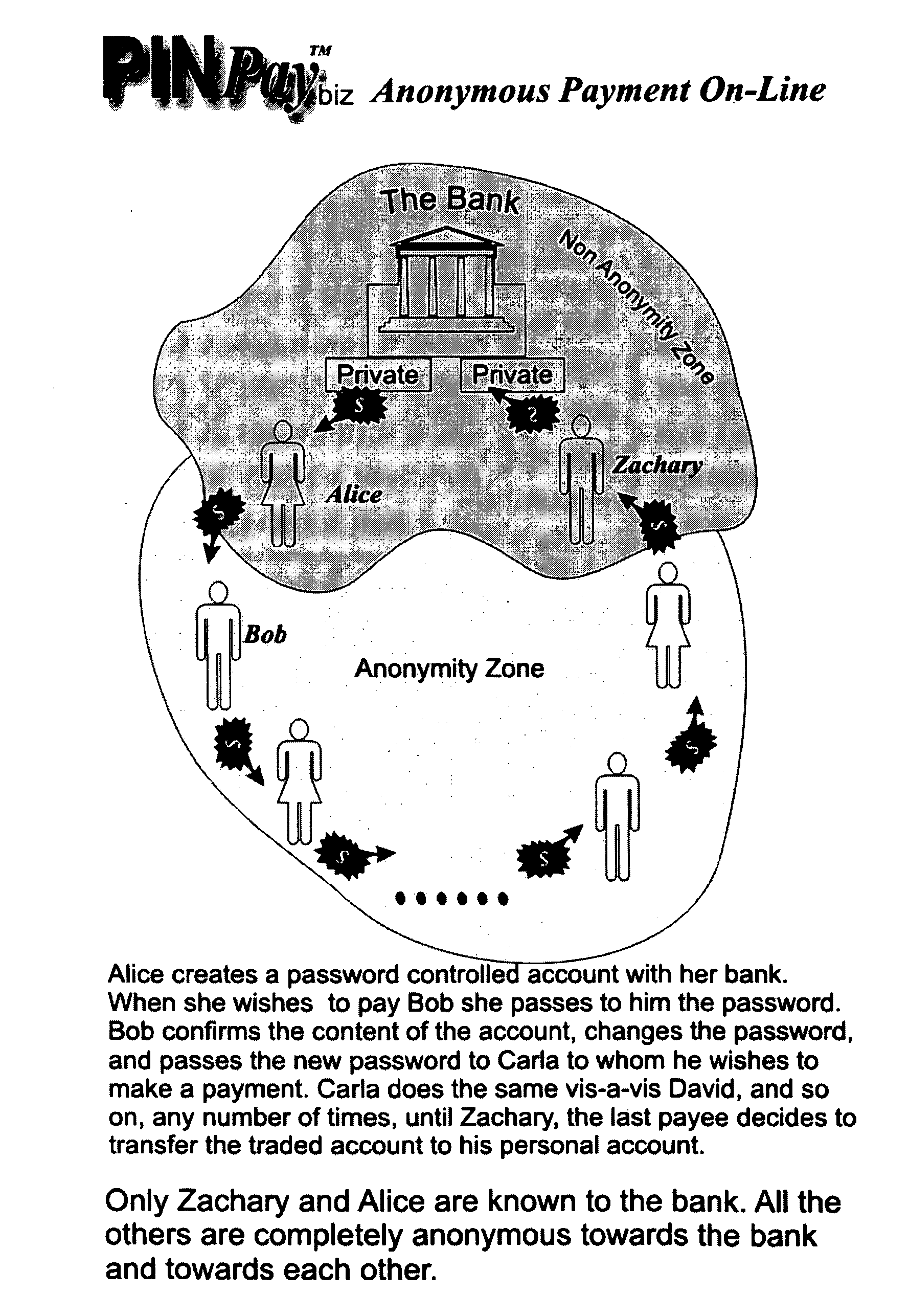
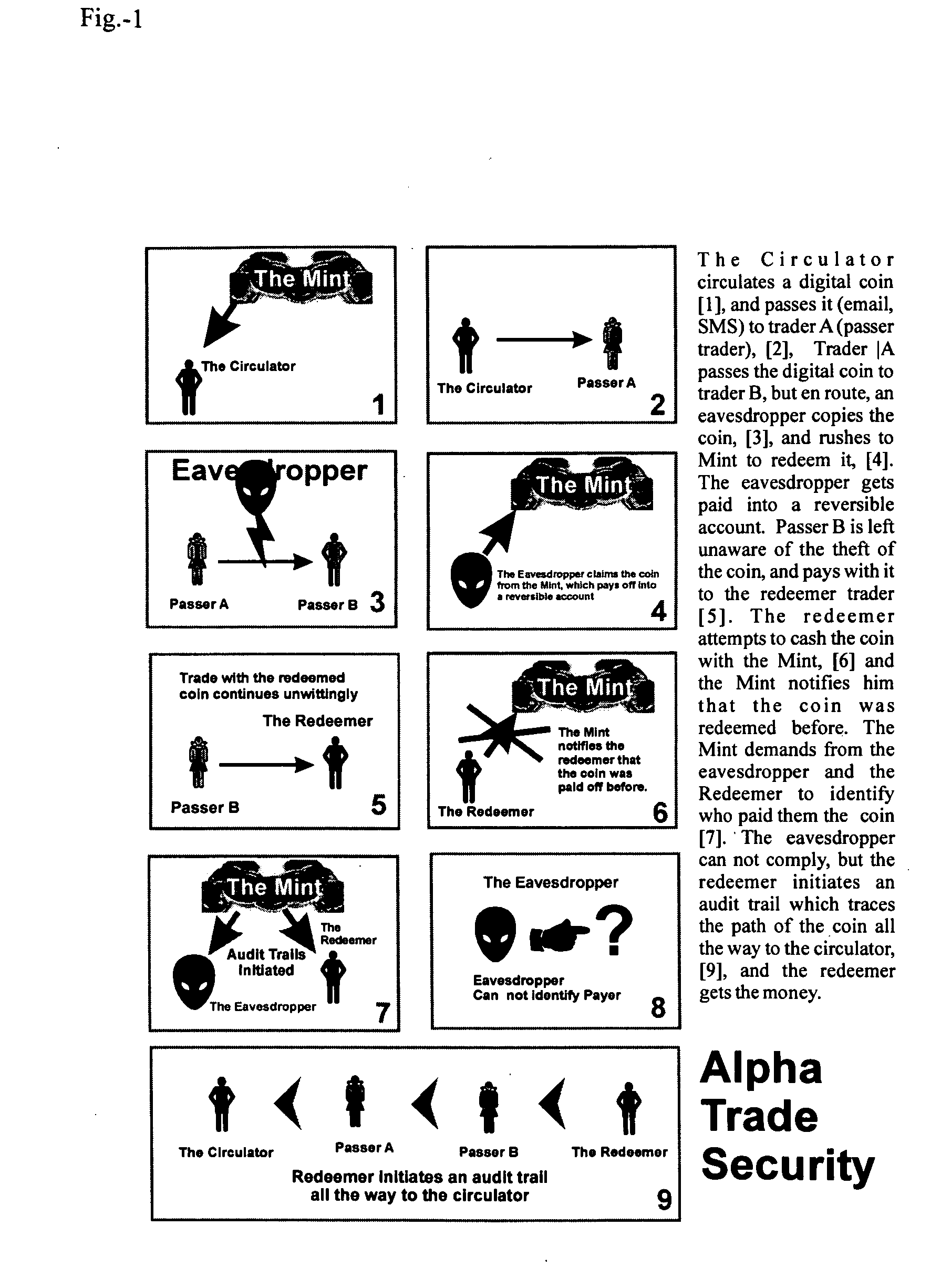
ActiveUS20080262969A1Gives riseConvenient transactionFinanceCryptography processingThird partyDigital file
Bit-currency Transactional Trust Tools (T3) is a set of tools and procedures based on expressing value through a bit string where the size of the string (bit count) reflects its value, and the identity of the bits is used to distinguish one such digital coin from the other, and for enabling an authentication hierarchy that alleviates the bottleneck of having a single source coin authentication for all transactions in coins issued (minted) by that mint; also enabling an instant split of a coin by simply splitting off a portion of the string of the coin, such that the bit count of the split-off string reflects its value. Each coin is comprised of that body string as described above, and a header that contains information regarding coin identifier, payment conditions, and suchlike. Such bit currency can be carried around everywhere bits are handled, and may be encrypted as necessary. Two online strangers could transact and make a payment by using the PINprivate procedure where by the strangers create a temporary secret which is sufficient for the payee to access the online location with the payment, and empty it before any third party can steal it; the temporary secret is based on the payer pre-calculating several computational tasks allowing the payee to randomly choose a task to compute, and communicating the identity of the chosen task (the temporary secret) by sending back the result, the task being a one-way function, it's unfeasible for any third party to find the secret before computing all the presented tasks. The bit currency can be exchanged between software applets carrying out rules of exchange and thereby allowing peer-to-peer networks to work more efficiently, and also allow for peer-to-peer distribution of digital goods to be carried out while honoring the digital rights of the digital file owner, so doing by allowing the mint to cut a portion of the payment digitally paid by the receiving node and allocate such cut to the digital rights owner.
Owner:SAMID GIDEON
Enhanced Electronic Data and Metadata Interchange System and Process for Electronic Billing and Payment System
A Software As A System (SAAS)-based system is disclosed herein for sending bills and payments in conjunction with a third-party accounting system. The system deploys a downloadable program interface to configure the third-party accounting system and then send and receive data between the two systems. The transmitted bills may contain an electronic signature, a line item billing, and / or other transaction-specific meta data, and, based on cash flow needs and outstanding bills, some or all customers may be offered a very substantial time-limited discount for immediate payment. Also, customers may use the line-item billing feature to withhold partial payments for specific issues attributed to specific items. Alternatively, a communication module between SAAS units (CSU) may be deployed to configure the third-party accounting system and then send and receive data between the two systems.
Owner:BILL COM LLC
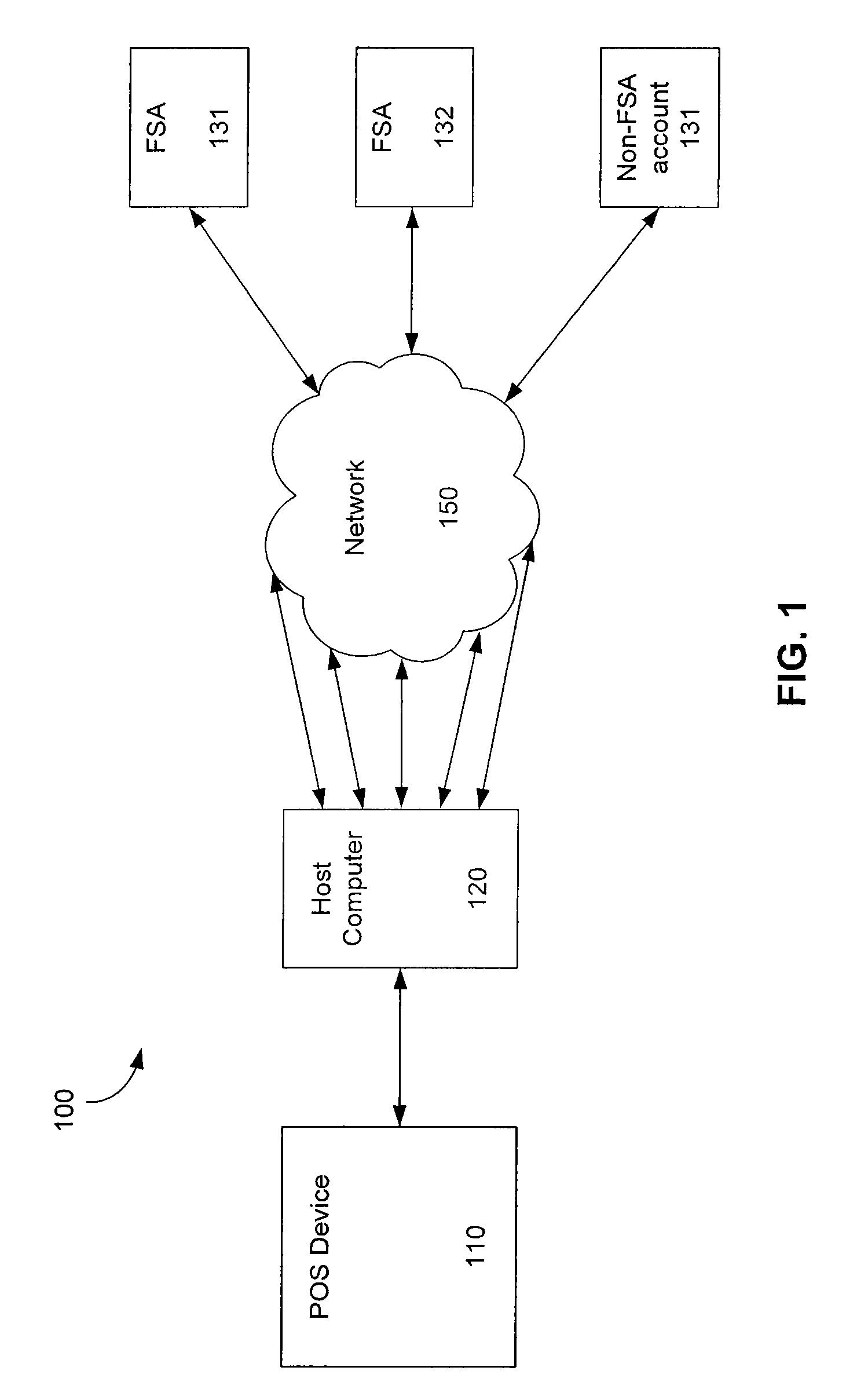
Airline ticket payment and reservation system and methods
InactiveUS7117183B2Ticket-issuing apparatusDigital data processing detailsComputerized systemFinancial transaction
A method for accepting payments from a consumer for a travel ticket from a travel company comprises receiving at a point of sale device a transaction request that includes a transaction identifier that identifies a travel arrangement made with the travel company and a payment amount. The payment amount and the transaction identifier is transmitted to a host computer system for validation. Also, a validation from the host computer system is received indicating that the transaction requested has been validated. A payment is received from the consumer, and at least a portion of the payment is electronically transmitted to the travel company.
Owner:THE WESTERN UNION CO
Allocating partial payment of a transaction amount using an allocation rule
InactiveUS8458086B2Increase purchase intentionConvenient transactionFinancePayment architectureDatabaseTransaction account
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Staged transactions systems and methods
InactiveUS7184989B2Credit registering devices actuationDiscounts/incentivesTime limitFinancial transaction
Systems and methods for accepting payments for goods and services provided by a merchant. In one embodiment, a method for accepting payments from a consumer for a good or service provided by a merchant comprises receiving a transaction request from the merchant, receiving a payment from the consumer, associating the payment with the transaction request, and sending at least a portion of the payment to the merchant. In this manner, the merchant stages the transaction, and the consumer completes the transaction by making the payment. An optional time limit feature also may be used, and the transaction may be staged by the consumer, or others.
Owner:THE WESTERN UNION CO
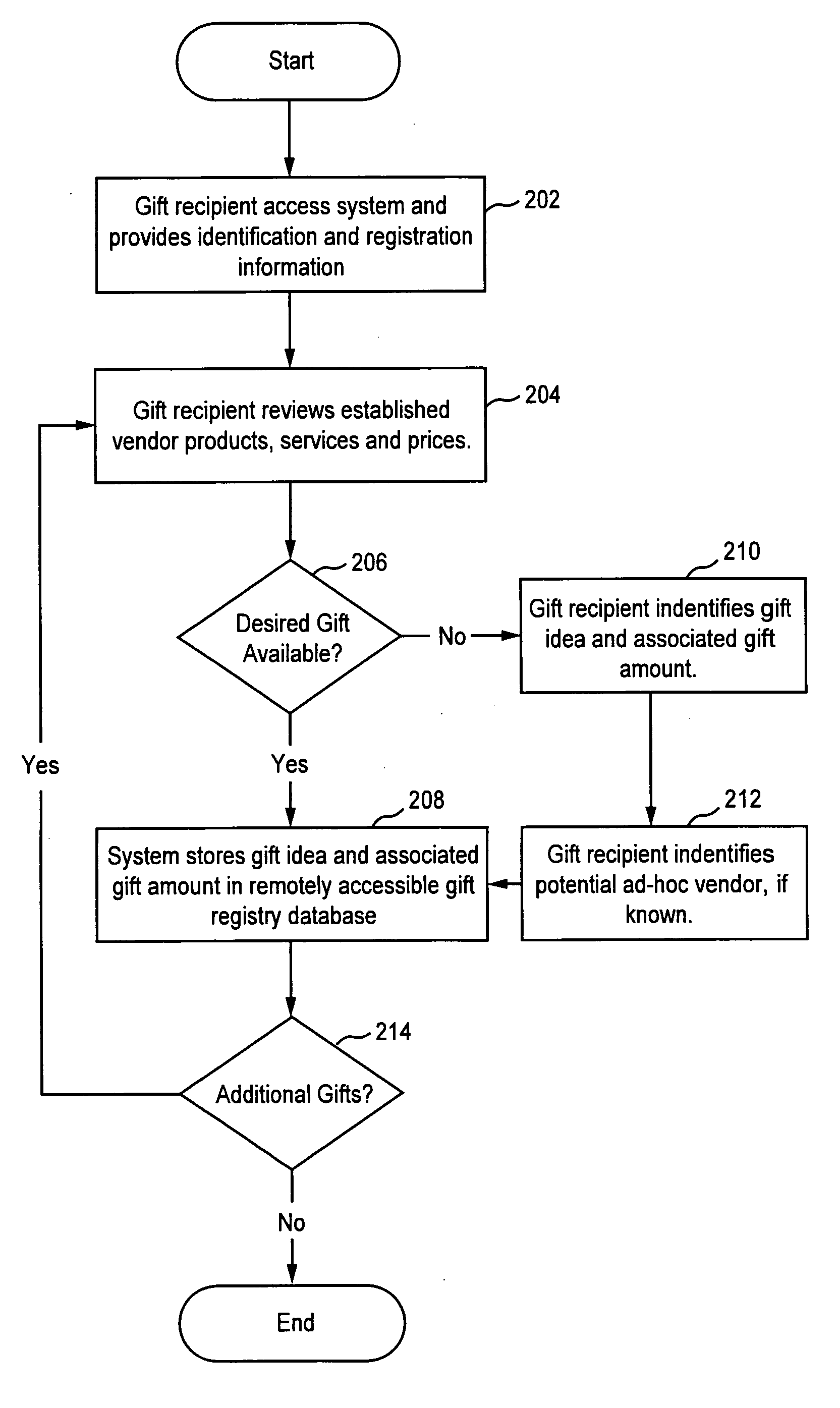
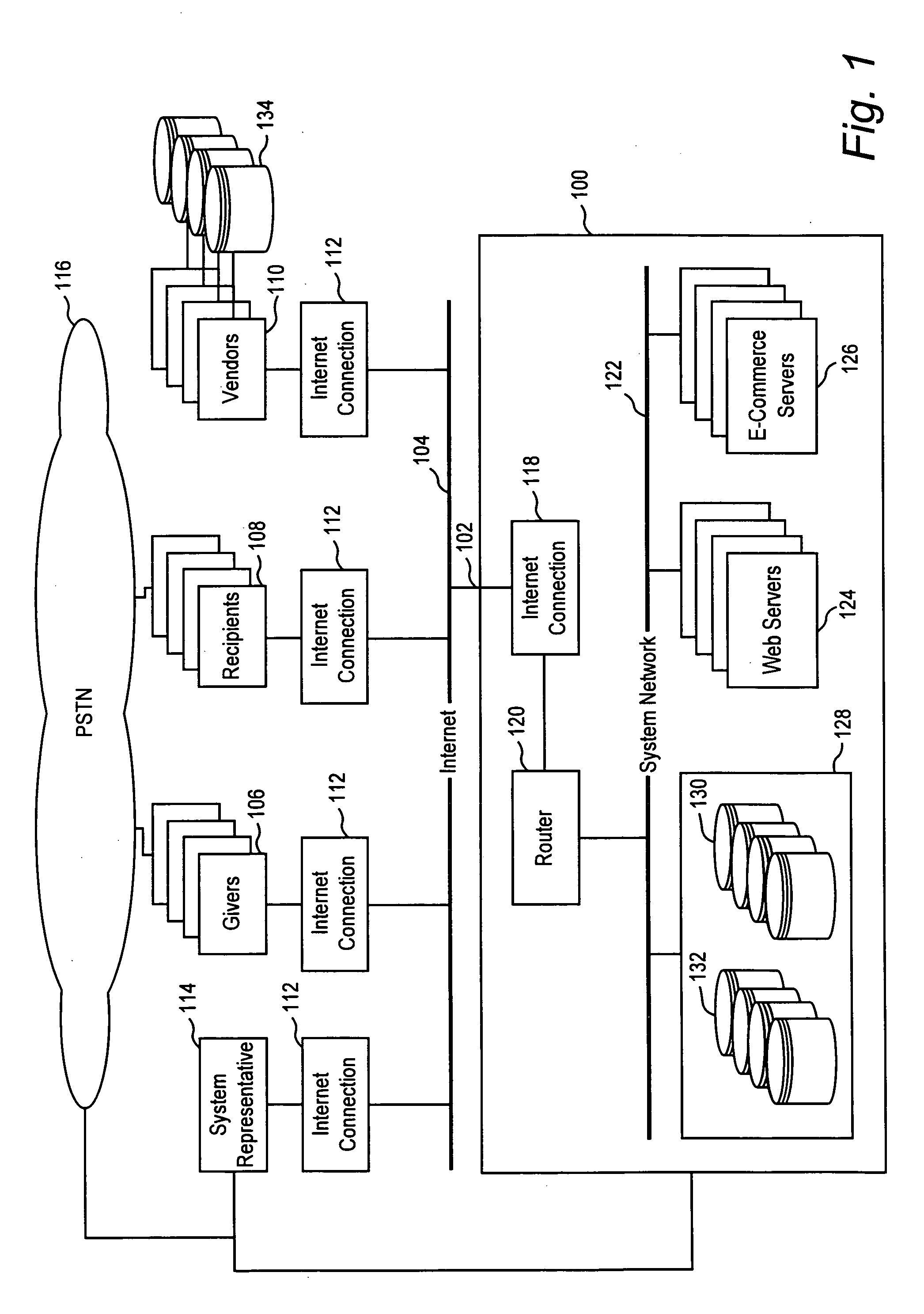
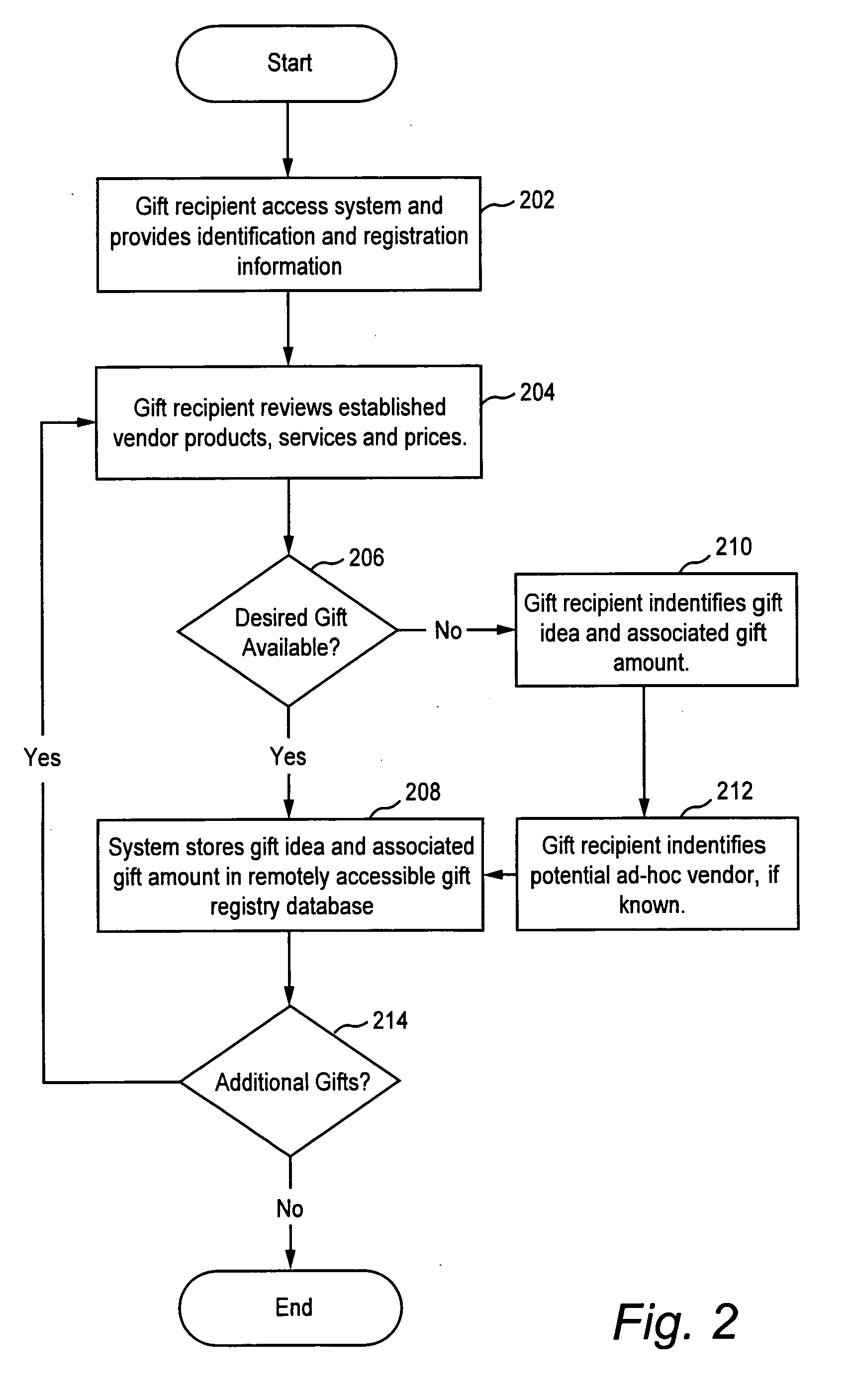
Method and system for universal gift registry
A gift registry providing a partial payment option for gift givers and a mandatory and contingent gift substitution for gift recipients. The gift recipient registers any type of gift idea from any store or establishment, for any occasion with an associated gift amount in the registry. The registrant is able to name their own gift price by selecting a gift amount not necessarily the same as the retail cost of the gift idea. The gift recipient also indicates whether they will accept a contingent substitute of gift or cash if the system is unable to provide the gift idea at the gift amount. The recipient can also select mandatory substitution of gift or cash. The difference between mandatory and contingent substitution is that mandatory substitution automatically occurs while contingent substitution occurs if and only if the selected gift is unavailable at the specified gift amount or could not be delivered in time. In effect, mandatory substitution for cash allows the registrant to arrange for automatic gift return and receipt of a cash gift. Gift givers are able to review gift ideas and associated gift amounts and select them. A gift giver is also able to select a gift idea and make a partial contribution toward purchase of the gift idea. This allows higher cost gifts to be purchased by multiple gift givers and thereby provides recipients and givers with greater flexibility in their gift selection. When a mandatory or contingent substitution for cash is provided, the system includes incentives, such as coupons. The coupons or incentives are independently profitable and help to offset the cost of managing the mandatory and contingent substitutions.
Owner:THE KNOT
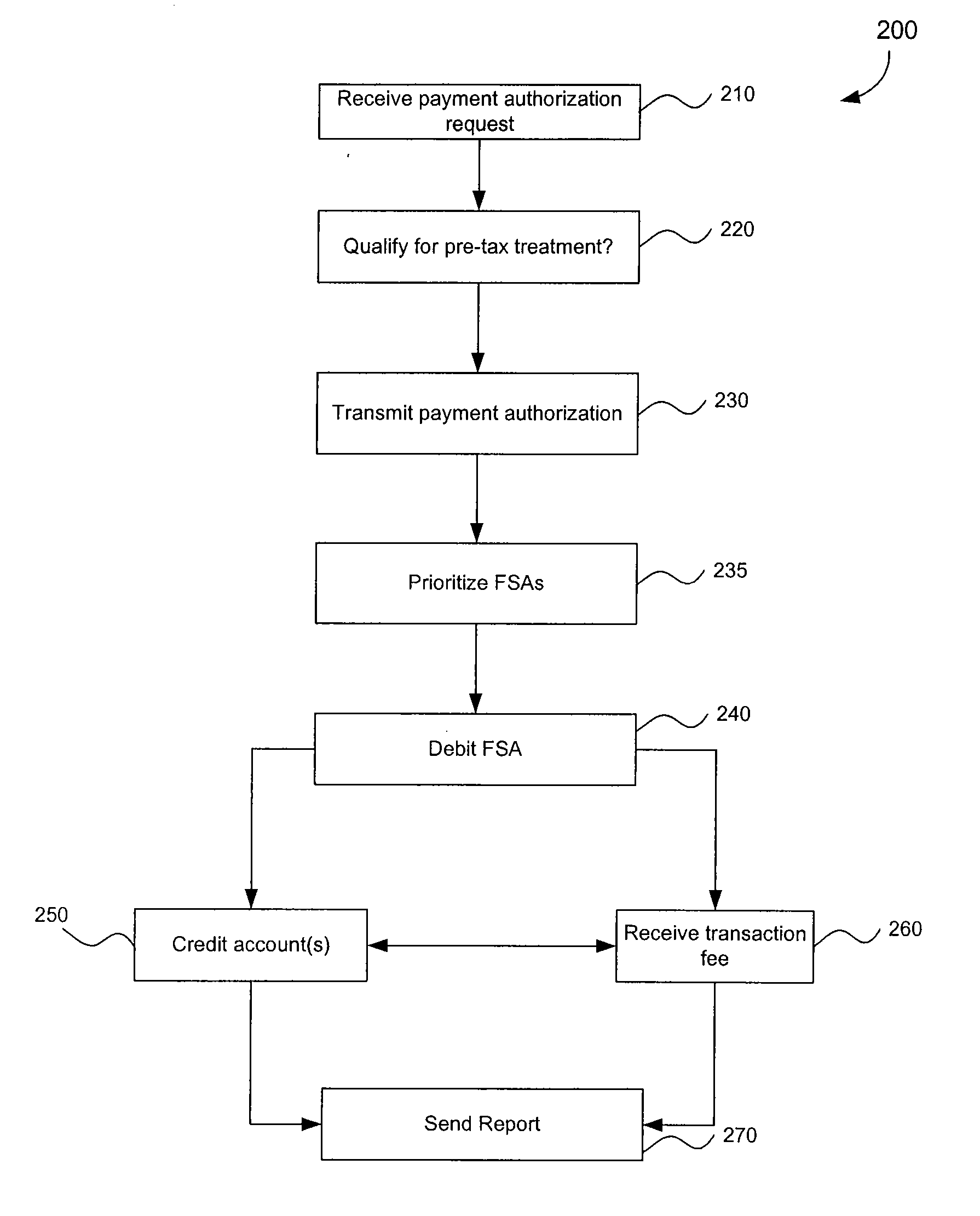
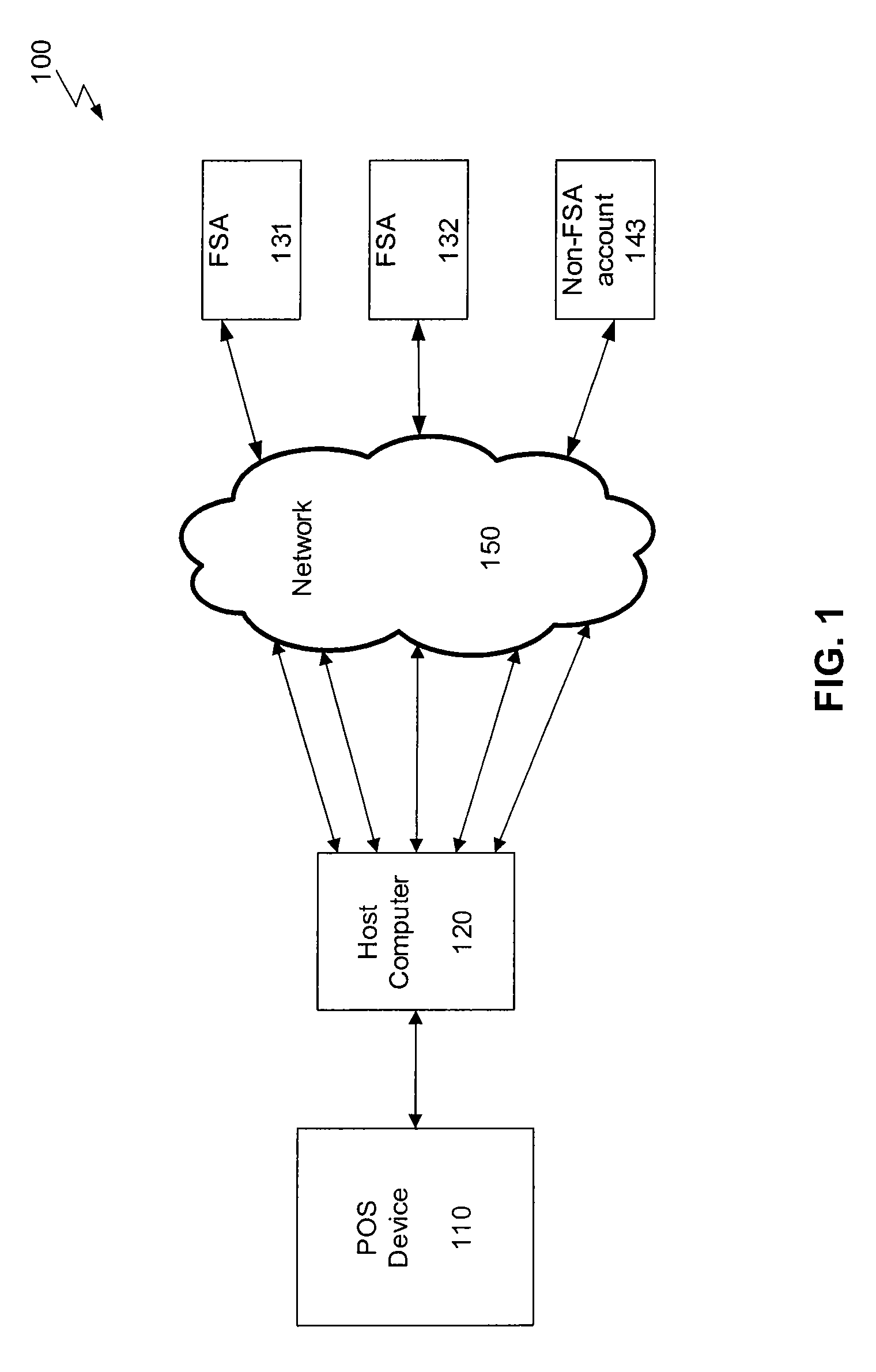
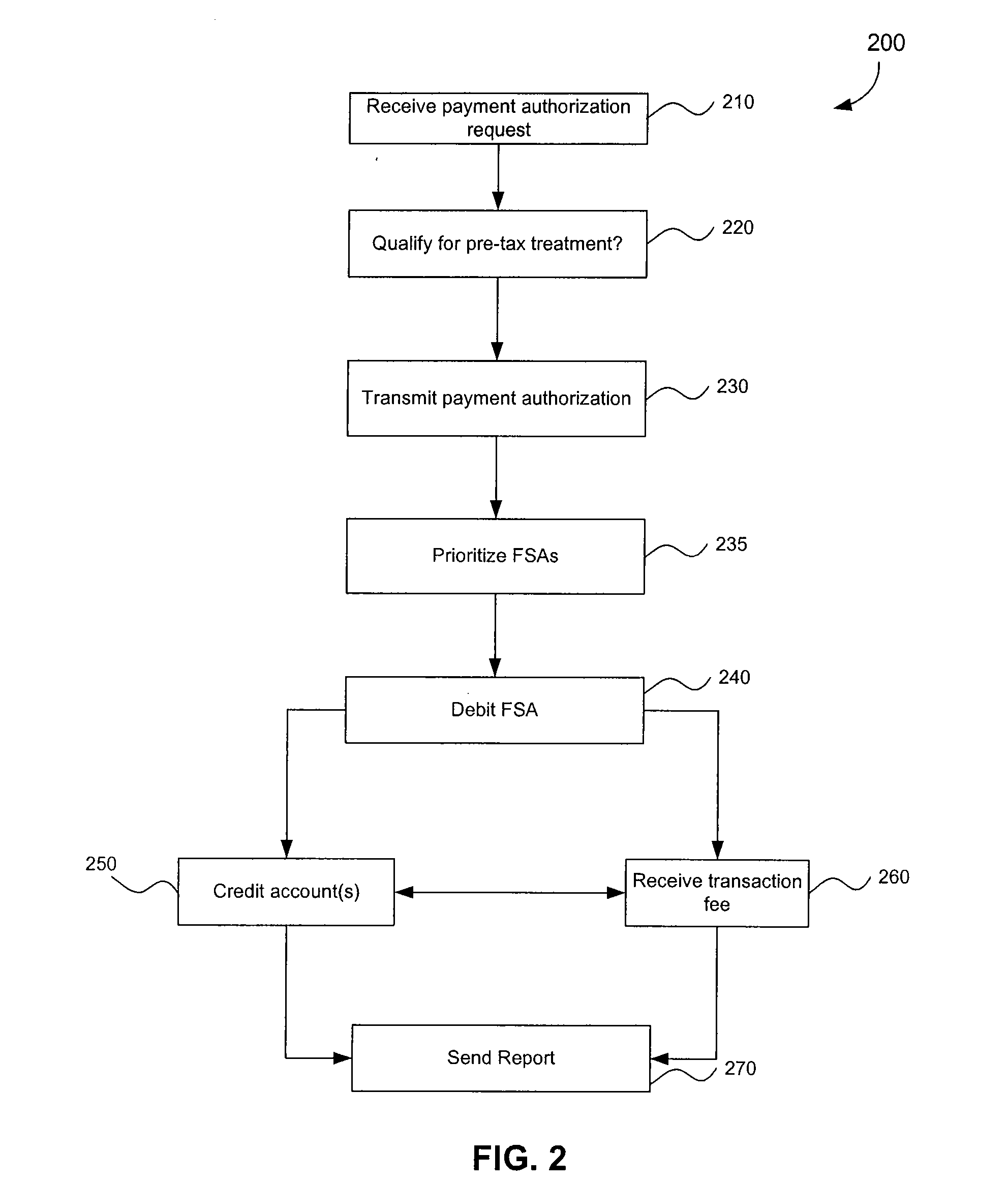
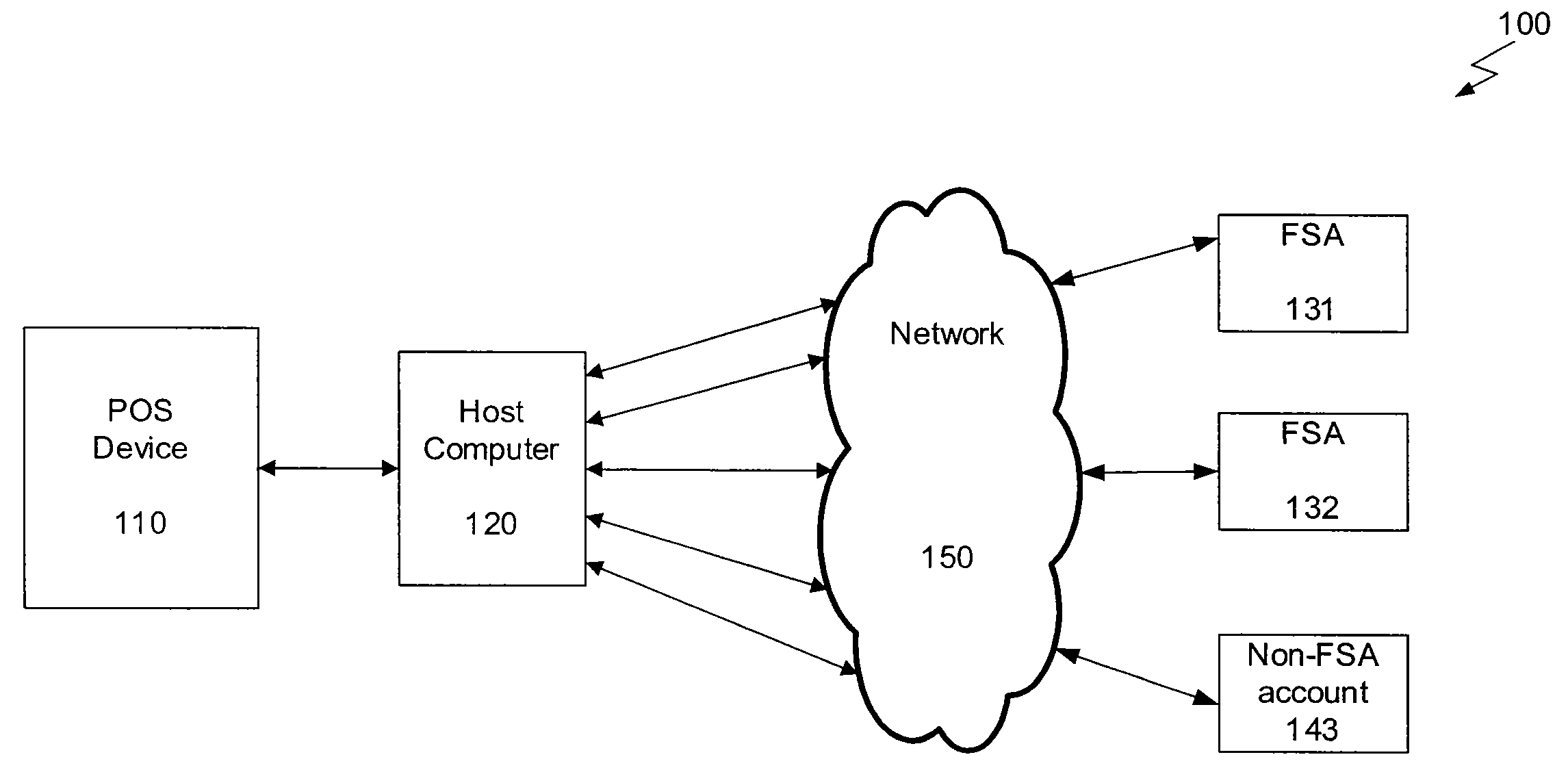
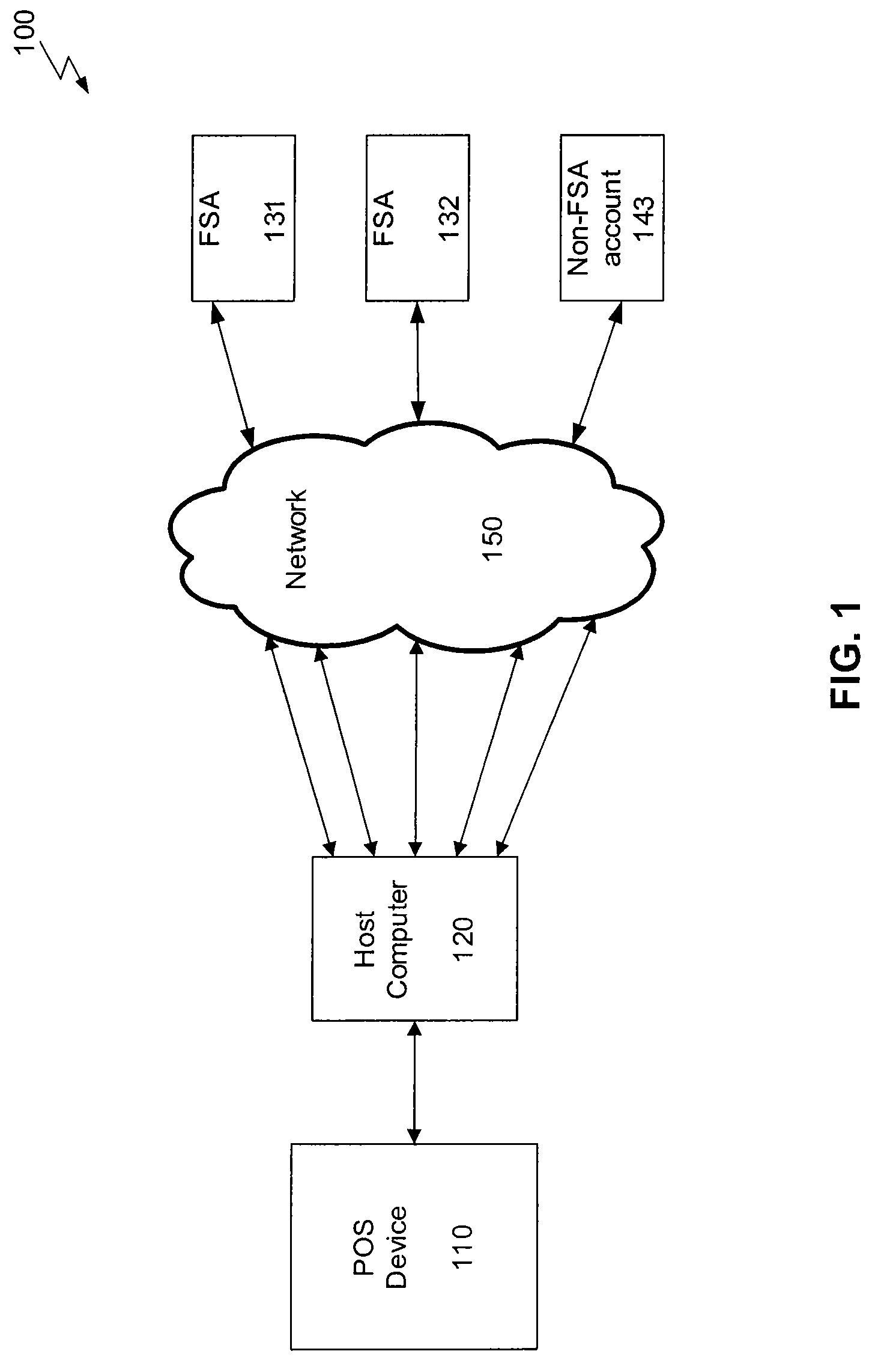
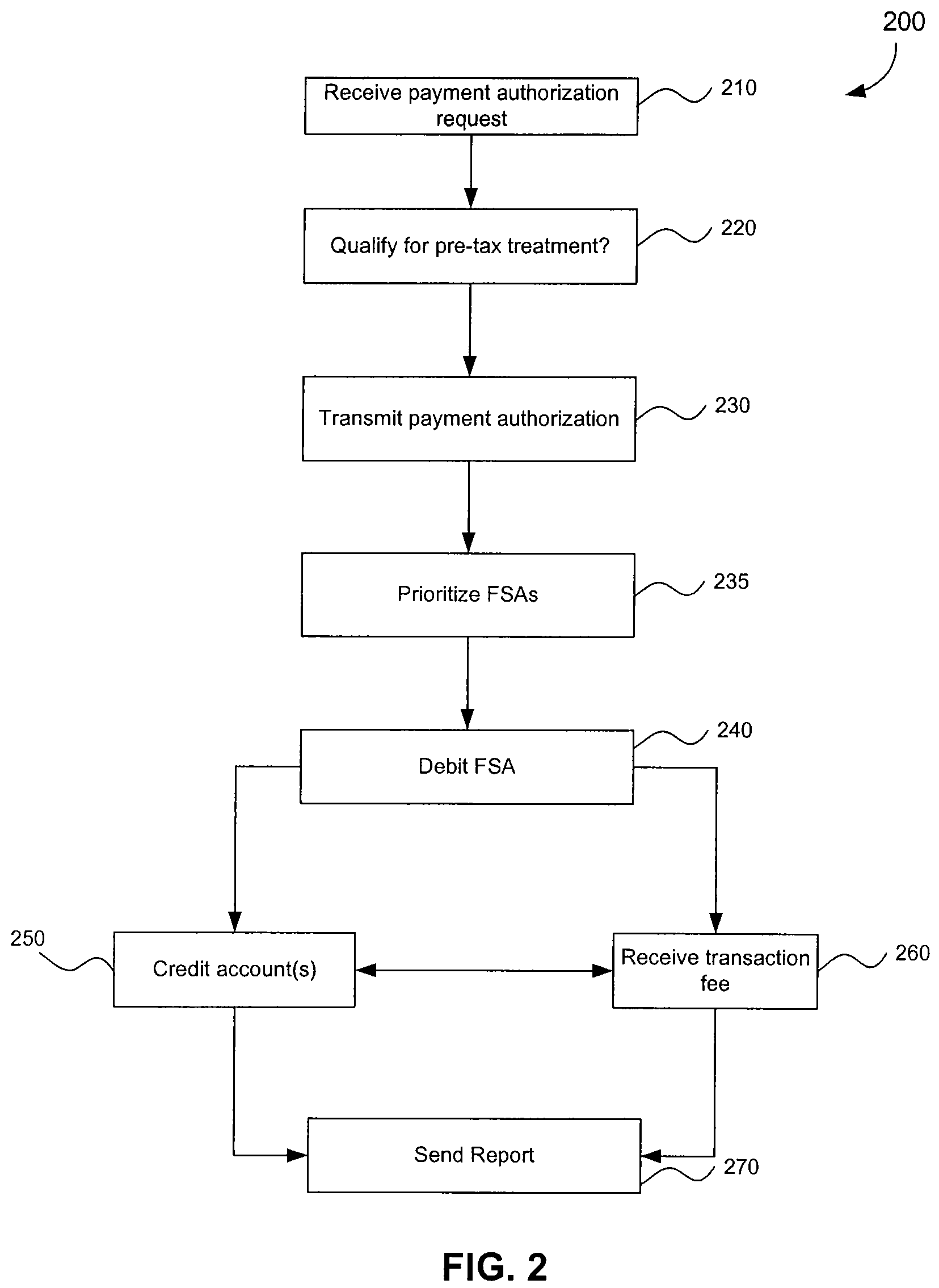
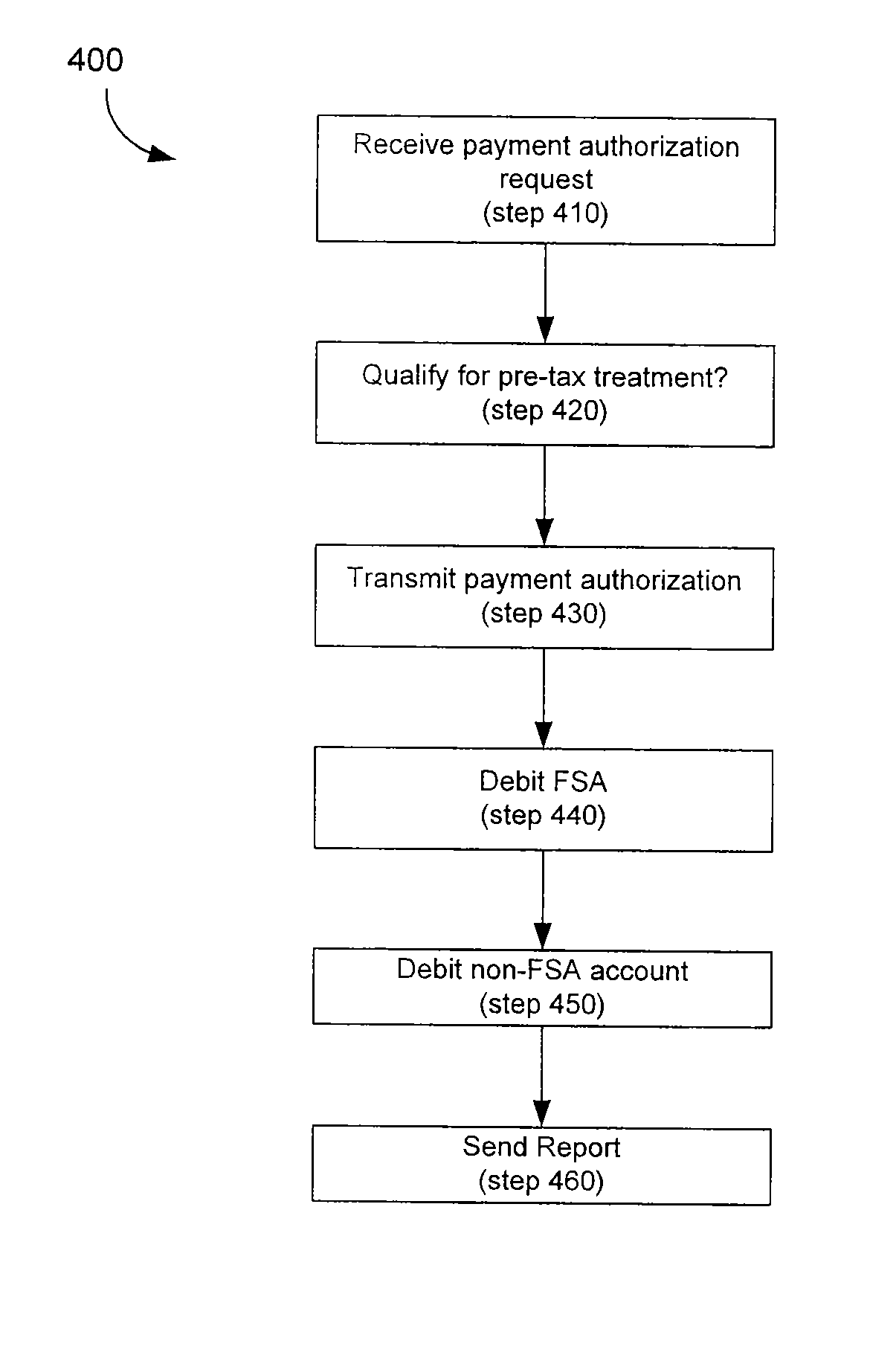
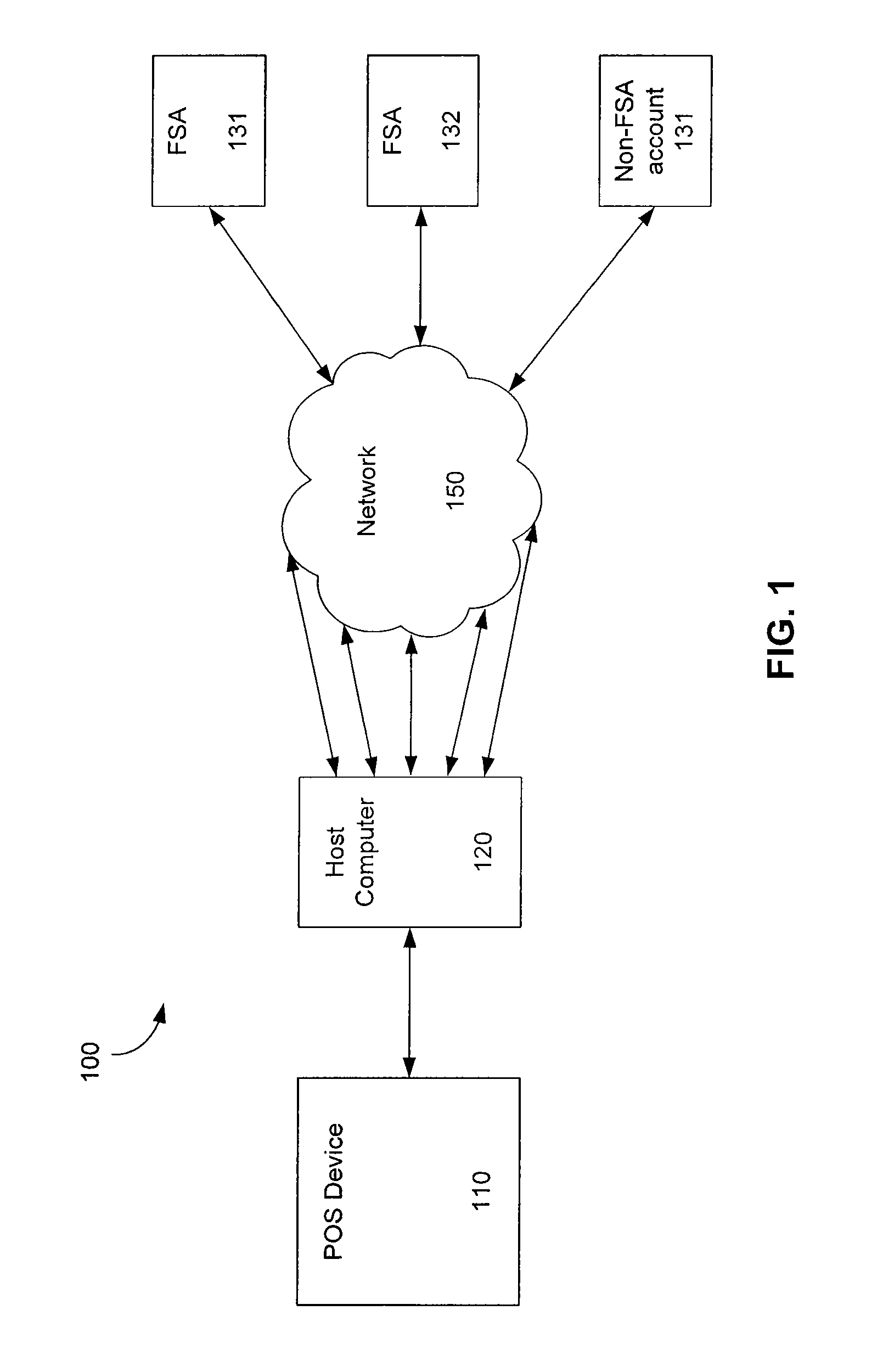
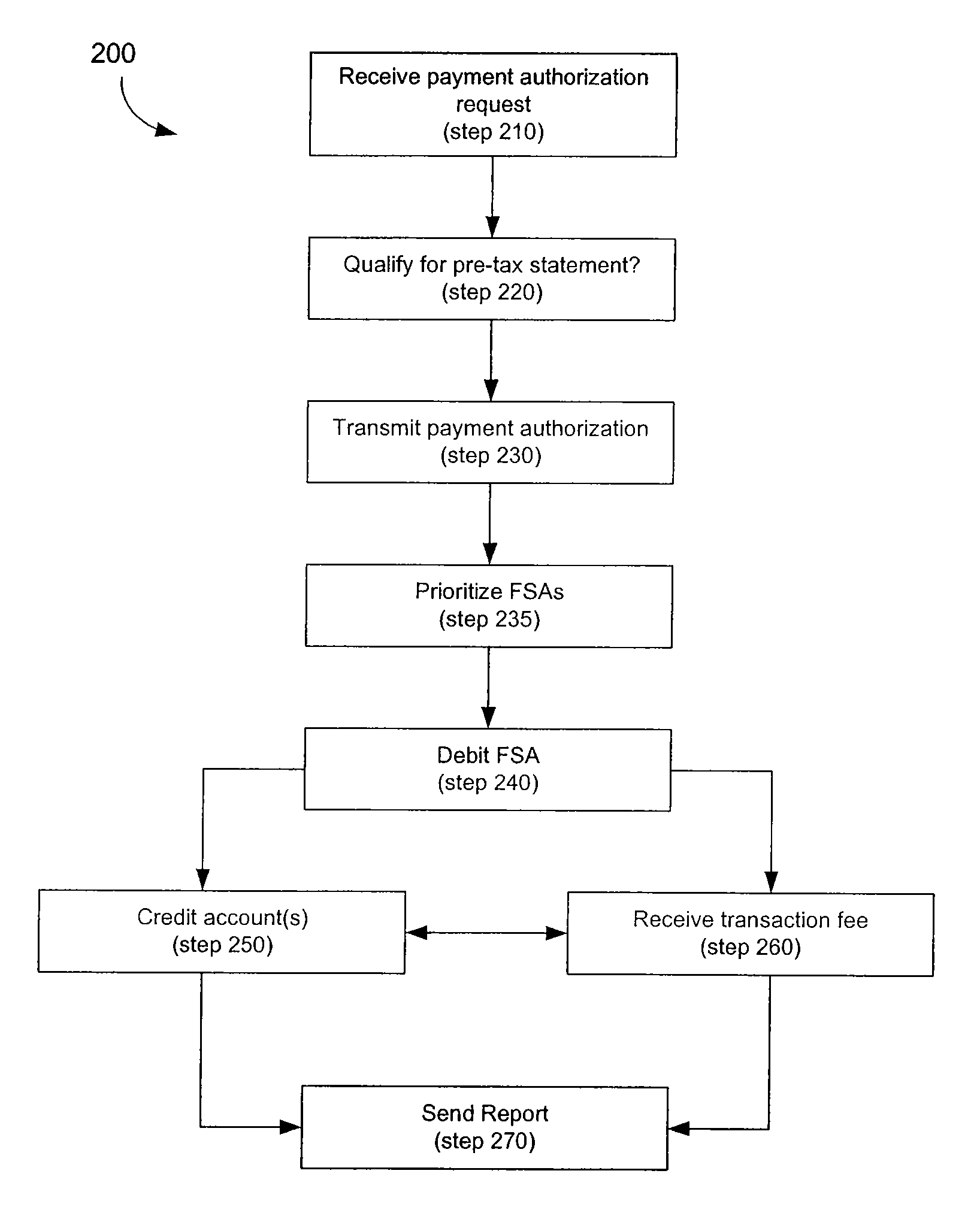
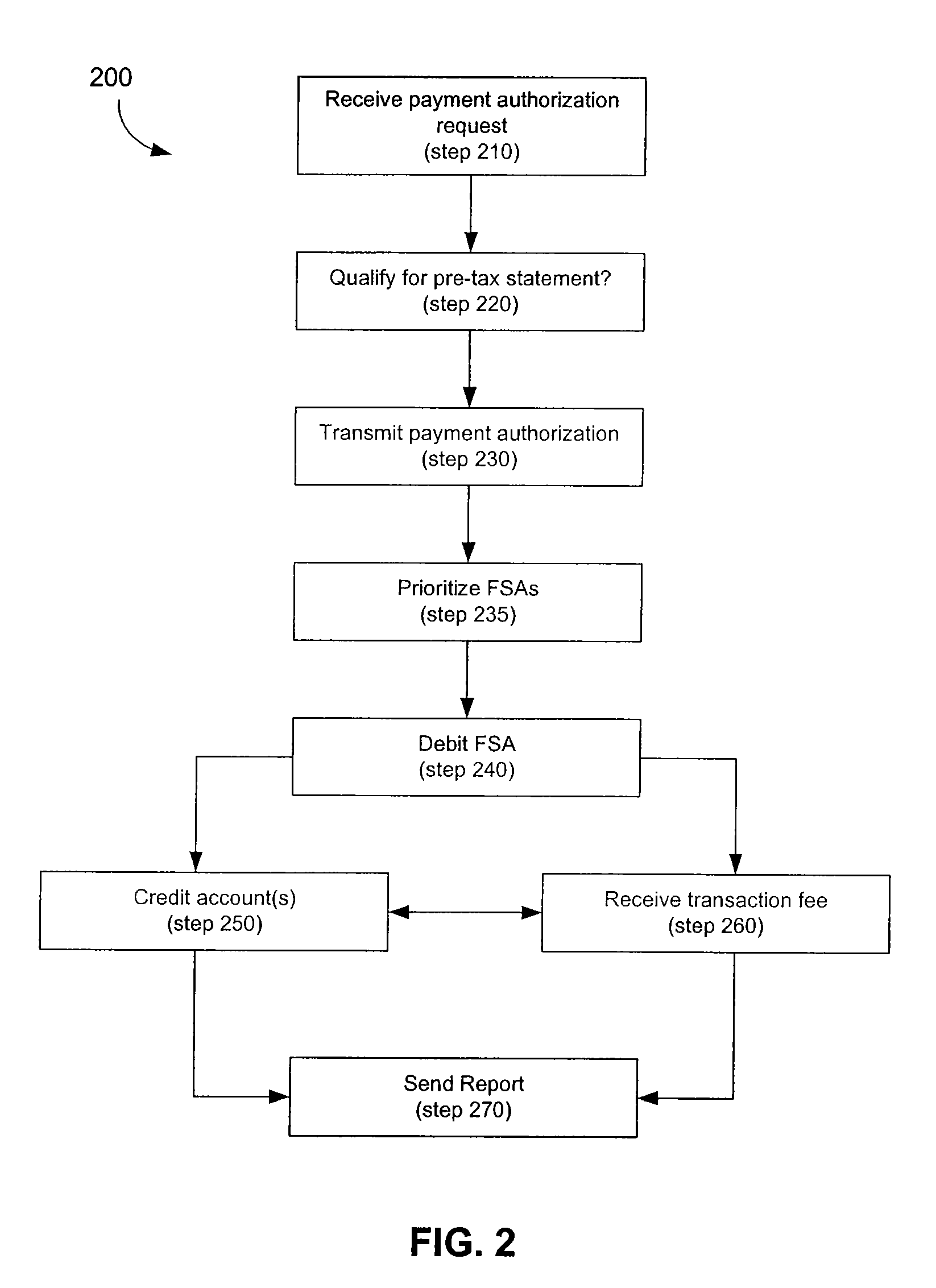
Linking Transaction Cards With Spending Accounts
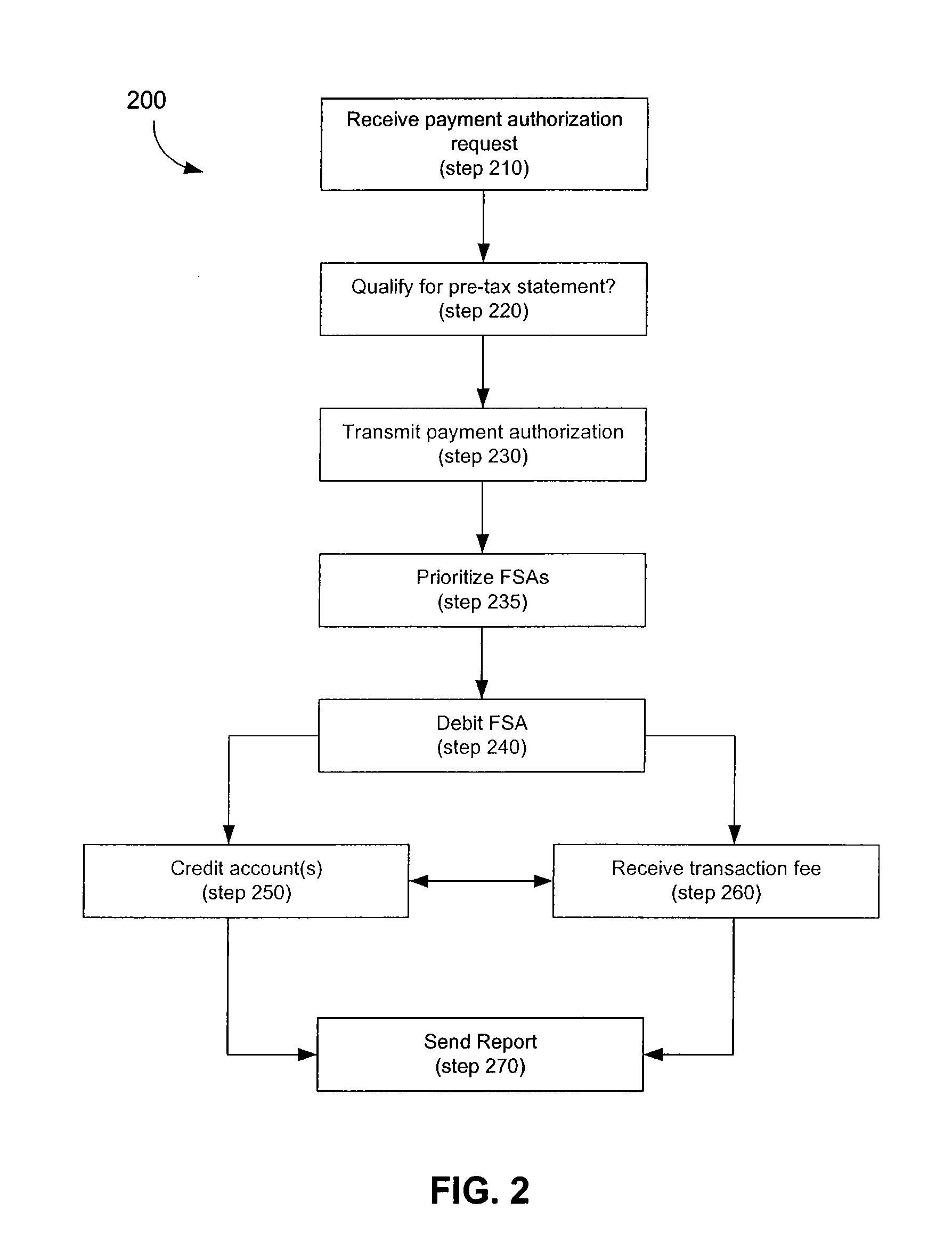
A computer-implemented system and method to facilitate a purchase utilizing a flexible spending account, comprising the steps of: receiving, at a host computer, a request for payment authorization for an item; determining whether the item qualifies for pre-tax treatment; and when the item qualifies for pre-tax treatment: determining at least partial payment authorization for the item, transmitting the at least partial payment authorization for the item to a point of sale device; causing the flexible spending account to be debited for at least a portion of the purchasing amount of the item based on the payment authorization; and debiting a non-flexible spending account for an item not qualifying for pre-tax treatment.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Linking transaction cards with spending accounts
A computer-implemented system and method to facilitate a purchase utilizing a flexible spending account, comprising the steps of: receiving, at a host computer, a request for payment authorization for an item; determining whether the item qualifies for pre-tax treatment; and when the item qualifies for pre-tax treatment: determining at least partial payment authorization for the item, transmitting the at least partial payment authorization for the item to a point of sale device; causing the flexible spending account to be debited for at least a portion of the purchasing amount of the item based on the payment authorization; and debiting a non-flexible spending account for an item not qualifying for pre-tax treatment.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
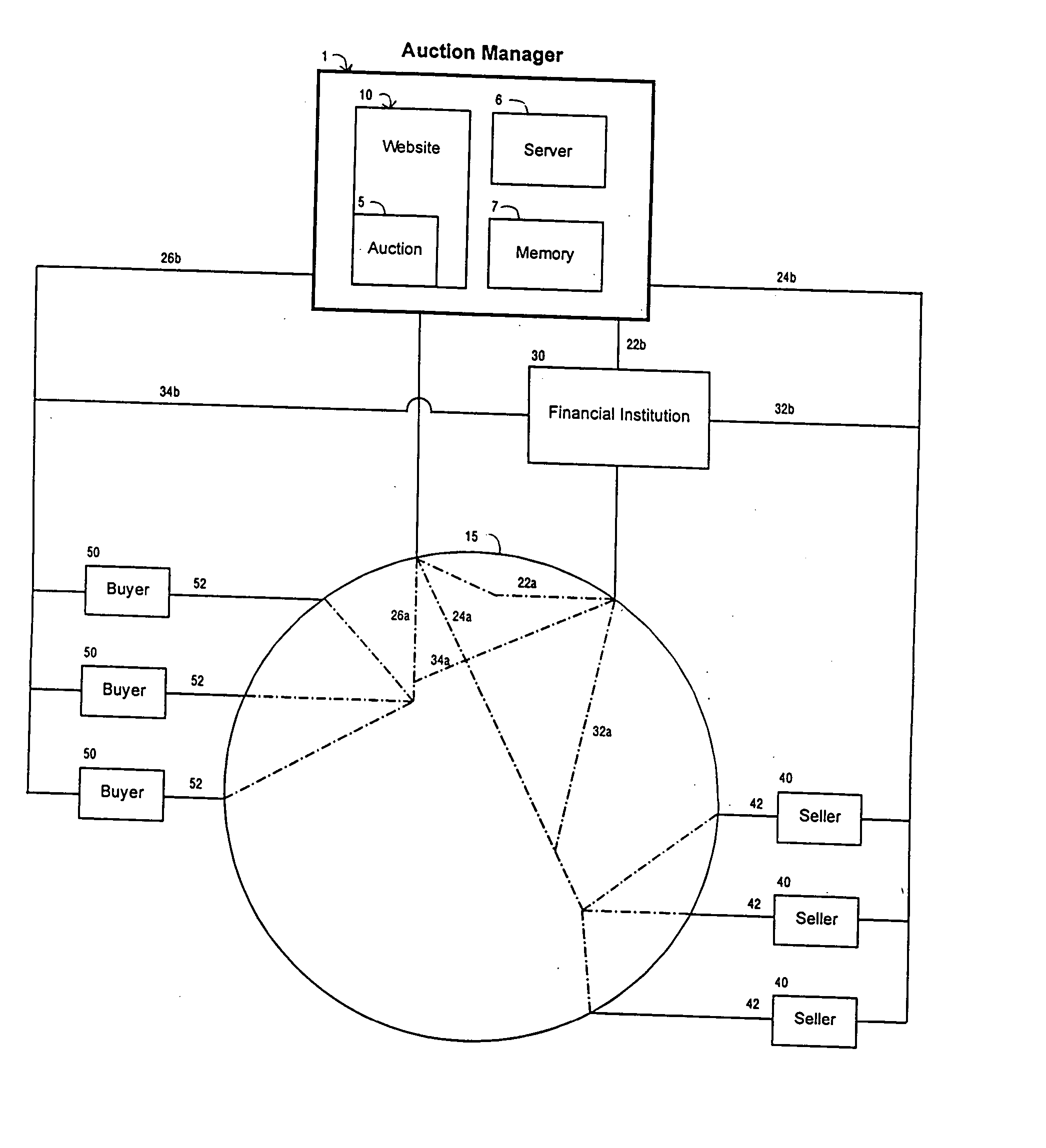
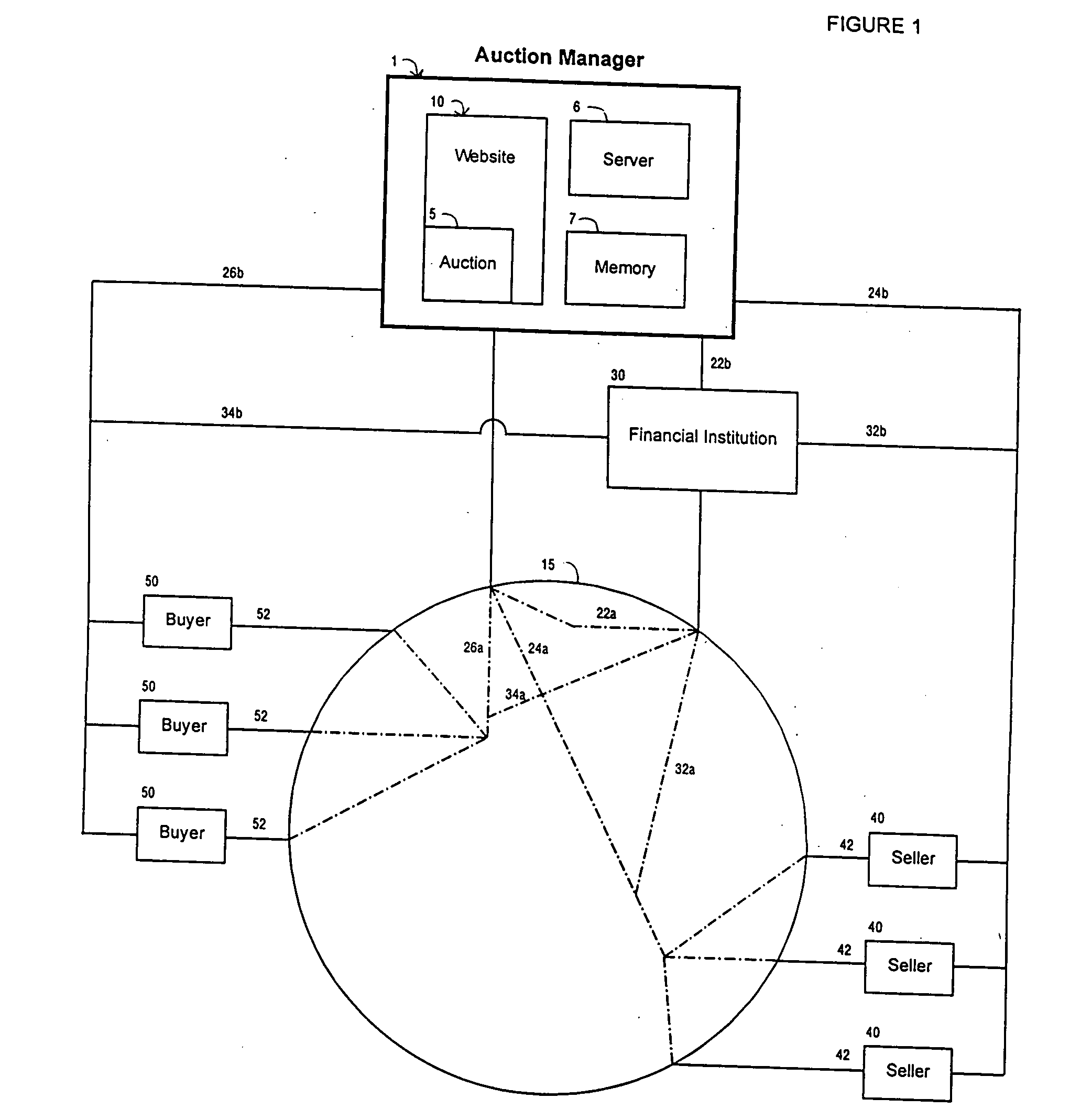
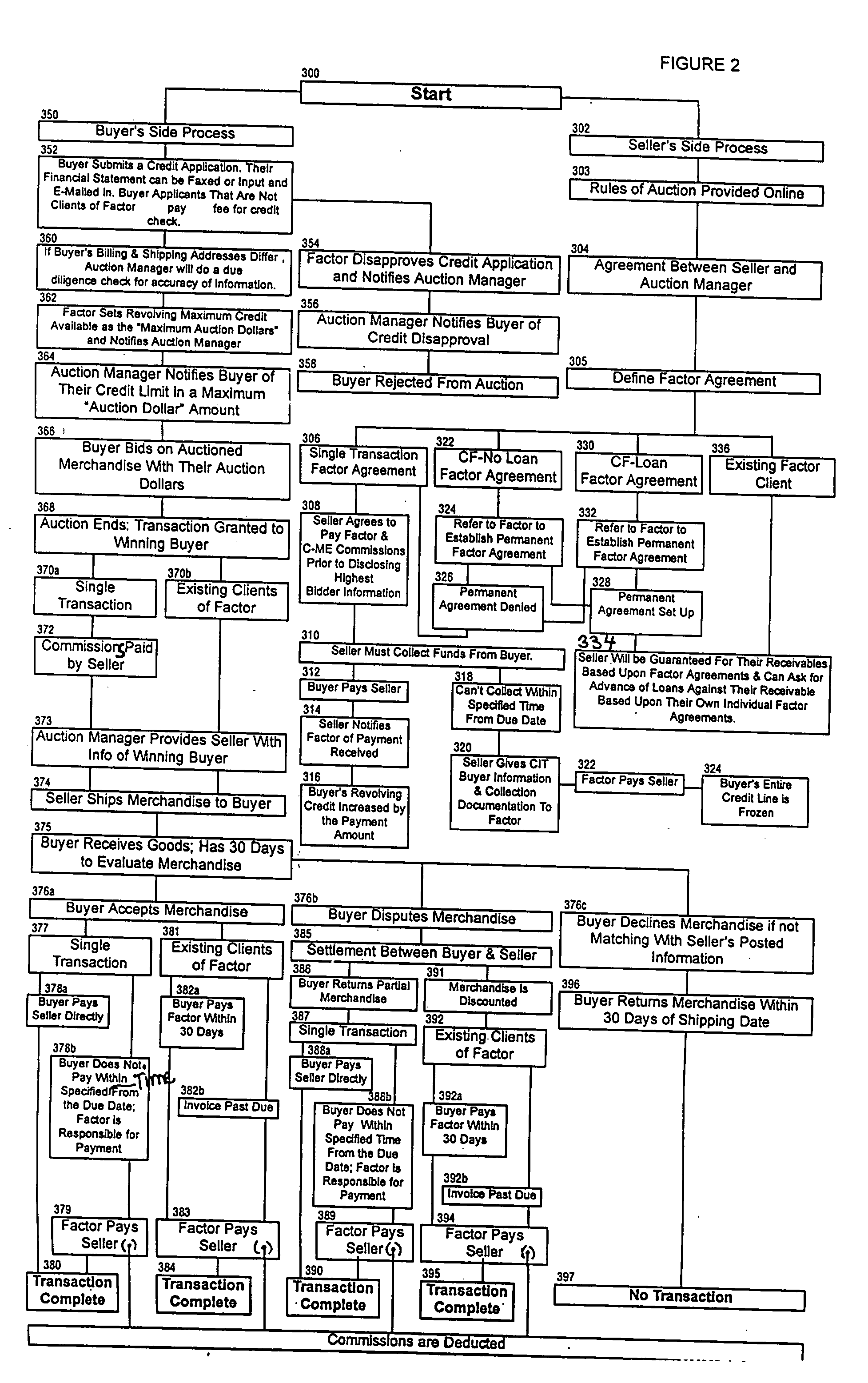
Auction with methods and mechanisms to avoid fraud
An auction with methods and mechanisms to avoid fraud are described. One fraud avoidance aspect involves the use of a financial institution, such as a factoring entity. The financial institution guarantees at least a partial payment of the amount owed by the winning buyer to the seller in case the winning buyer does not pay. Another fraud avoidance aspect provides the winning buyer with a period of time to inspect the goods or services purchased at the auction before having to pay for them.
Owner:YUAN FR S
Payment Programs For Healthcare Plans
The invention is a computer-implemented method and system to facilitate a purchase utilizing a tax-advantaged account. A request for payment for an item is received from a requester. A determination is made whether the item qualifies for pre-tax treatment. If the item qualifies for pre-tax treatment at least a partial payment amount for the item is determined. The tax-advantaged account is debited for at least a portion of the purchasing amount of the item based on the payment authorization; and the at least partial payment amount for the item is transmitted to an account of the requestor.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Staged transactions systems and methods
ActiveUS20070016526A1Credit registering devices actuationDiscounts/incentivesTime limitFinancial transaction
Systems and methods for accepting payments for goods and services provided by a merchant. In one embodiment, a method for accepting payments from a consumer for a good or service provided by a merchant comprises receiving a transaction request from the merchant, receiving a payment from the consumer, associating the payment with the transaction request, and sending at least a portion of the payment to the merchant. In this manner, the merchant stages the transaction, and the consumer completes the transaction by making the payment. An optional time limit feature also may be used, and the transaction may be staged by the consumer, or others.
Owner:THE WESTERN UNION CO
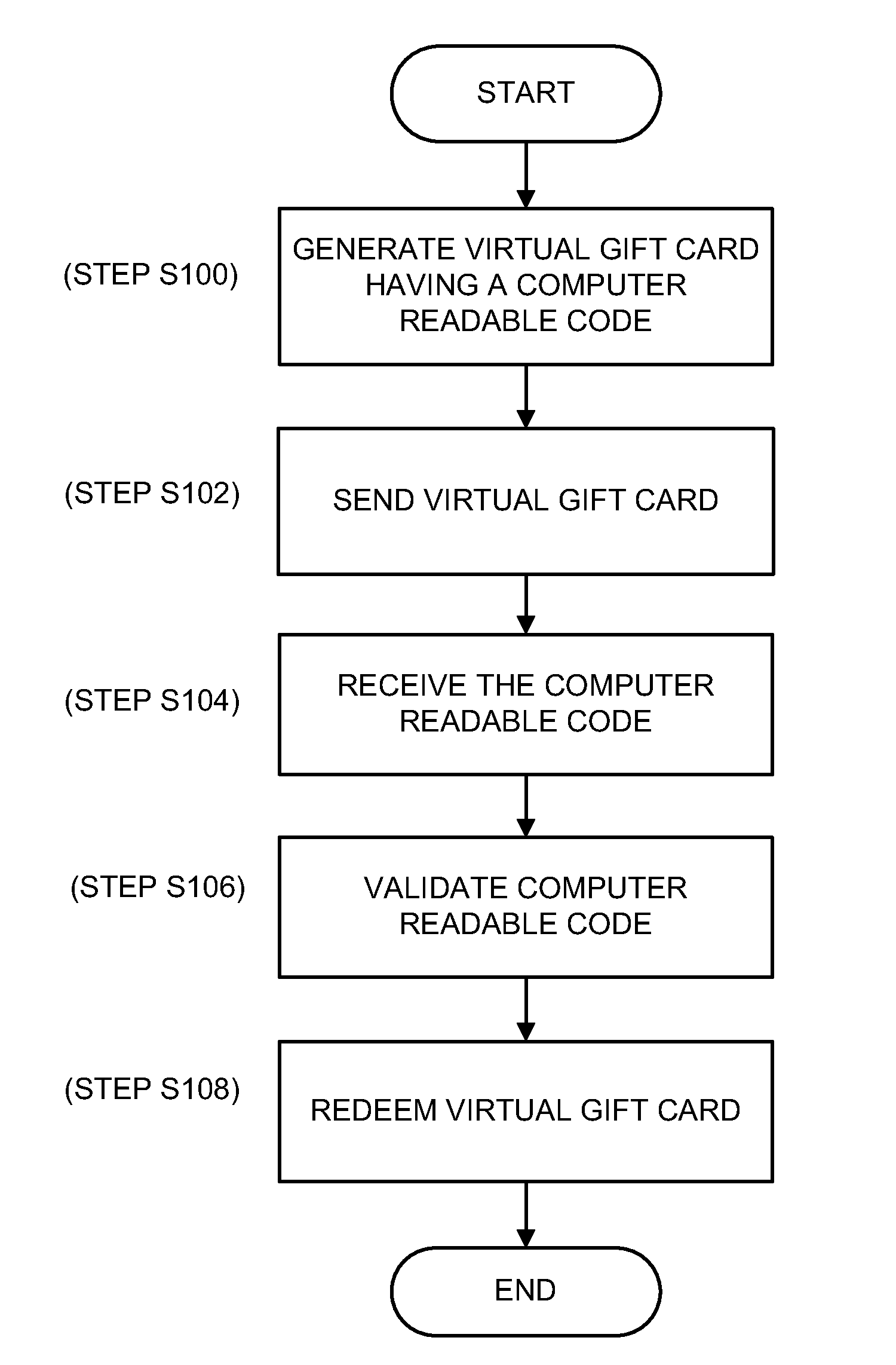
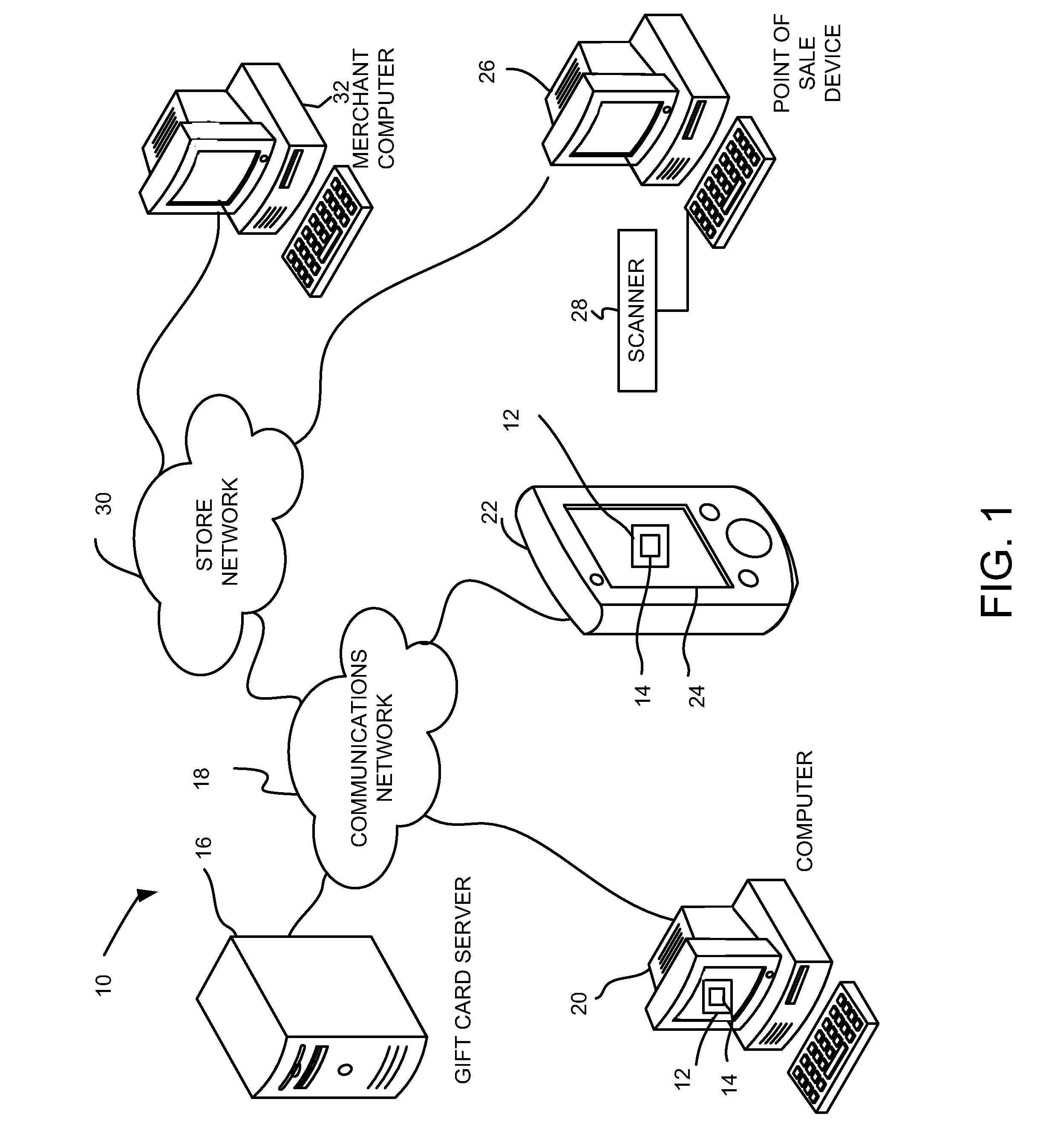
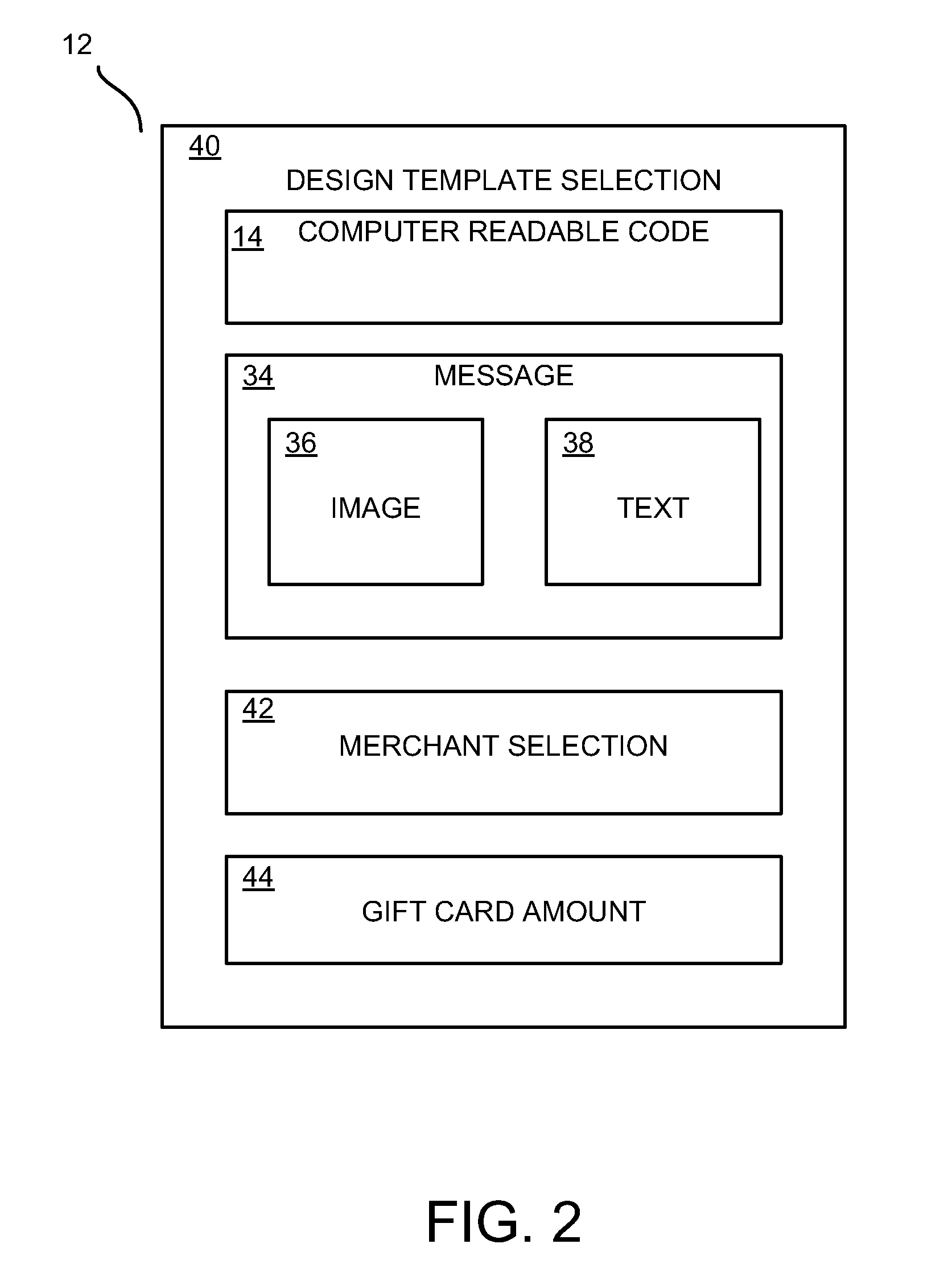
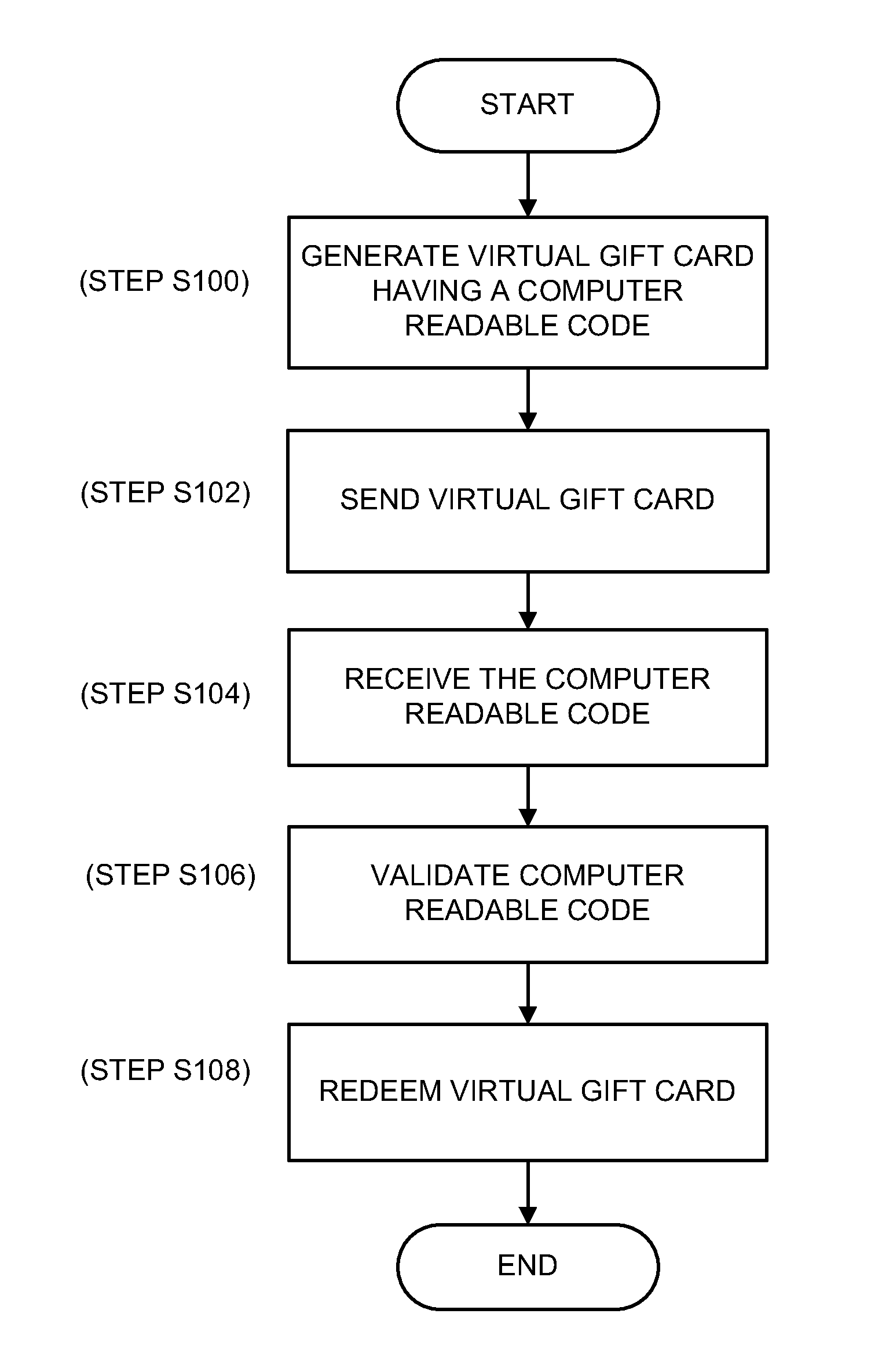
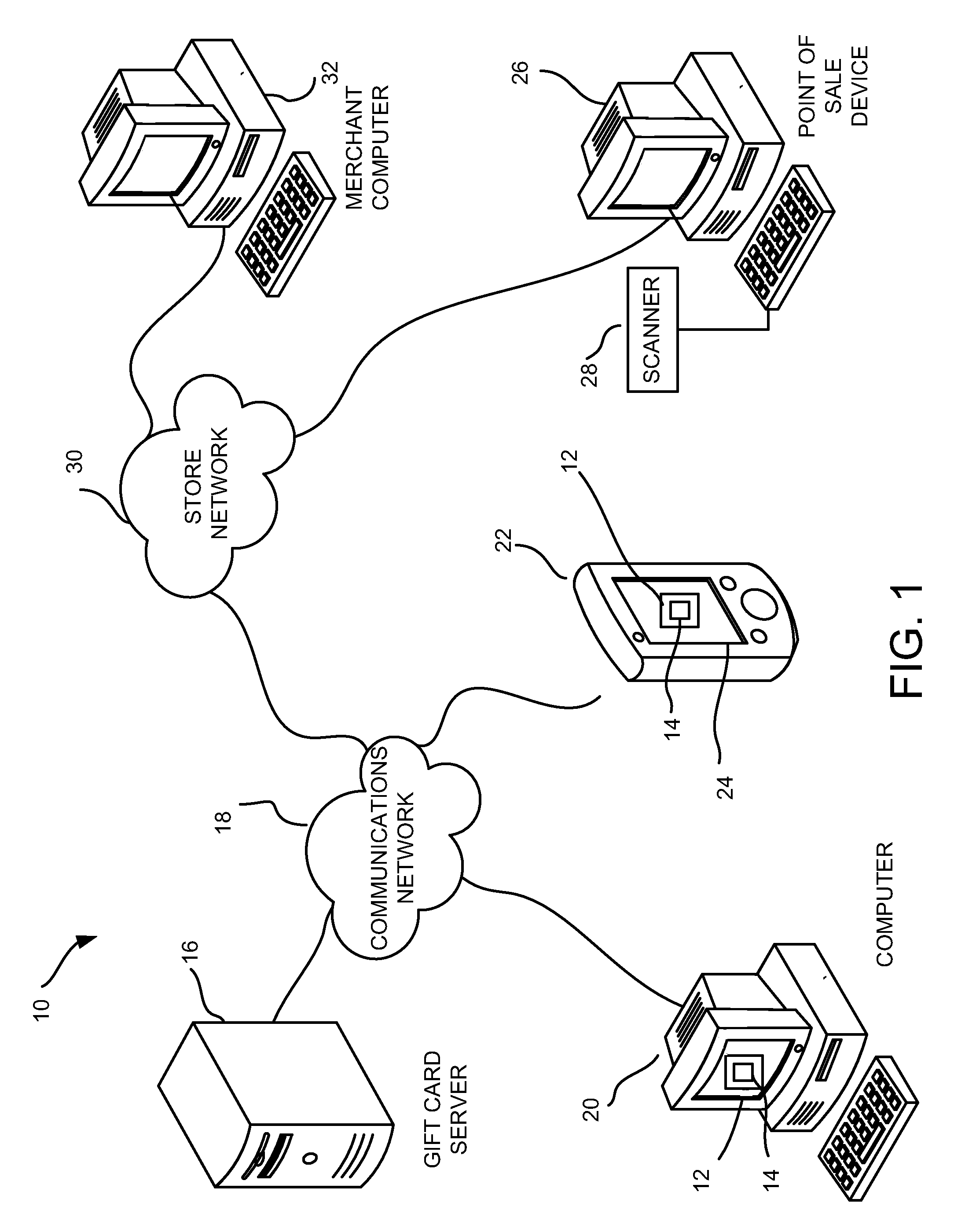
Method and system for electronic merchant gift card creation and redemption
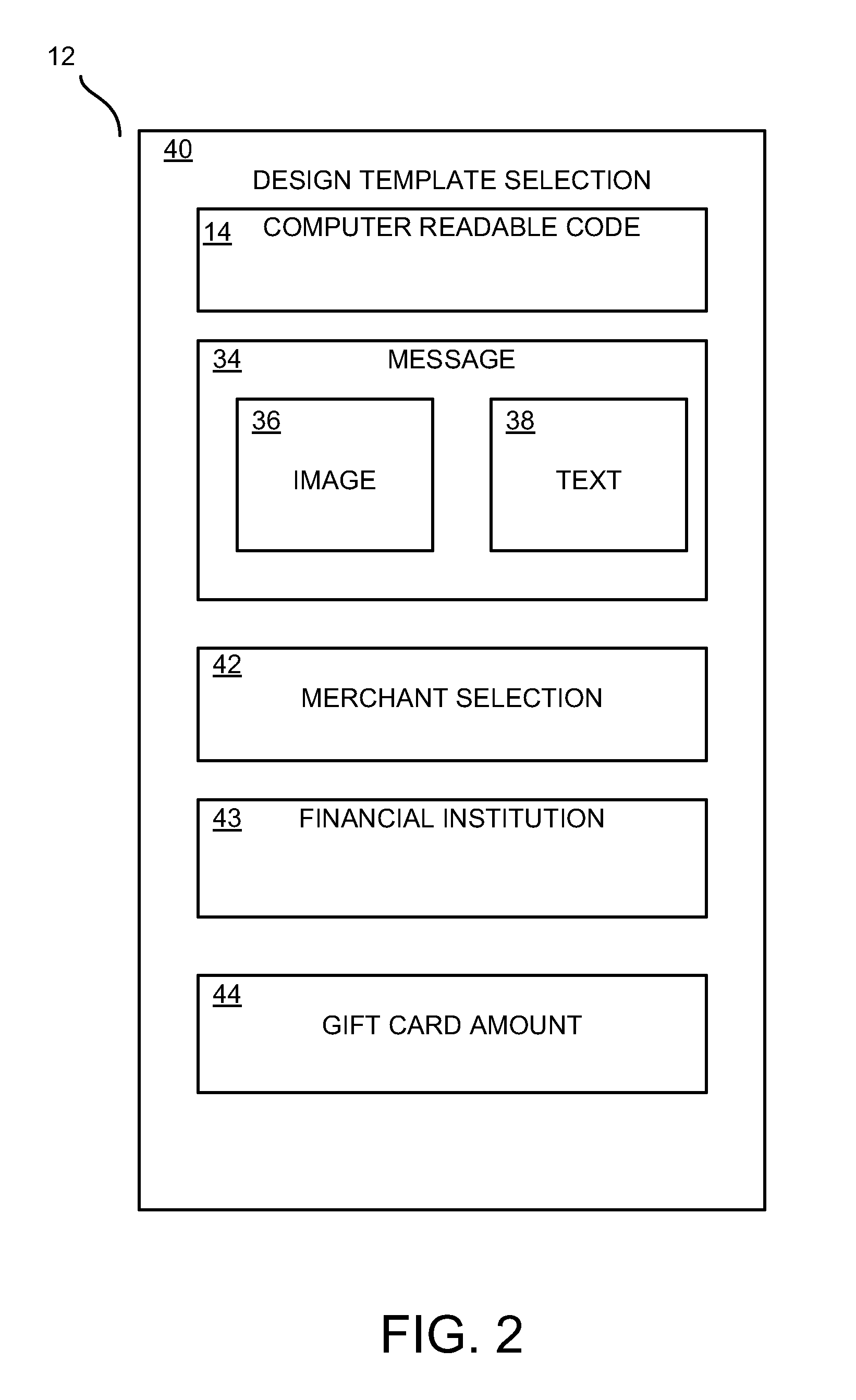
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, system and a point of sale device for generating and redeeming a virtual gift card. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a virtual gift card is generated. The virtual gift card includes a computer readable code that corresponds to a gift card amount. The virtual gift card is sent to a recipient. The computer readable code is received from a wireless mobile device at a point of sale. The gift card amount is applied as at least partial payment for a purchase.
Owner:ARIEL INVENTIONS
Retail transactions involving digital content in a digital rights management (DRM) system
InactiveUS7925591B2Easy to issueBuying/selling/leasing transactionsProgram/content distribution protectionDigital contentDigital rights management
A retailer facilitates issuance of a digital license from a licensor to a customer for a corresponding piece of digital content. The retailer receives payment for the license from the customer, where the payment is to be shared with the licensor in a pre-determined manner. The retailer also receives customer-based information from the customer. The retailer then composes an actual license request including the obtained customer-based information, and including retailer-based information identifying the retailer to the licensor and acknowledging to the licensor that the retailer owes a portion of the received payment to the licensor. Thereafter, the retailer forwards the actual license request to the licensor. The licensor notes based on the retailer-based information in the actual license request that the retailer identified thereby owes the licensor at least a portion of the forwarded payment. If an individual sends a license request directly to the licensor and thus fails to forward payment for the license to a retailer, the actual license request as composed by the individual fails to include the retailer-based information. Accordingly, the licensor refuses to issue a license as requested based on the lack of retailer-based information.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
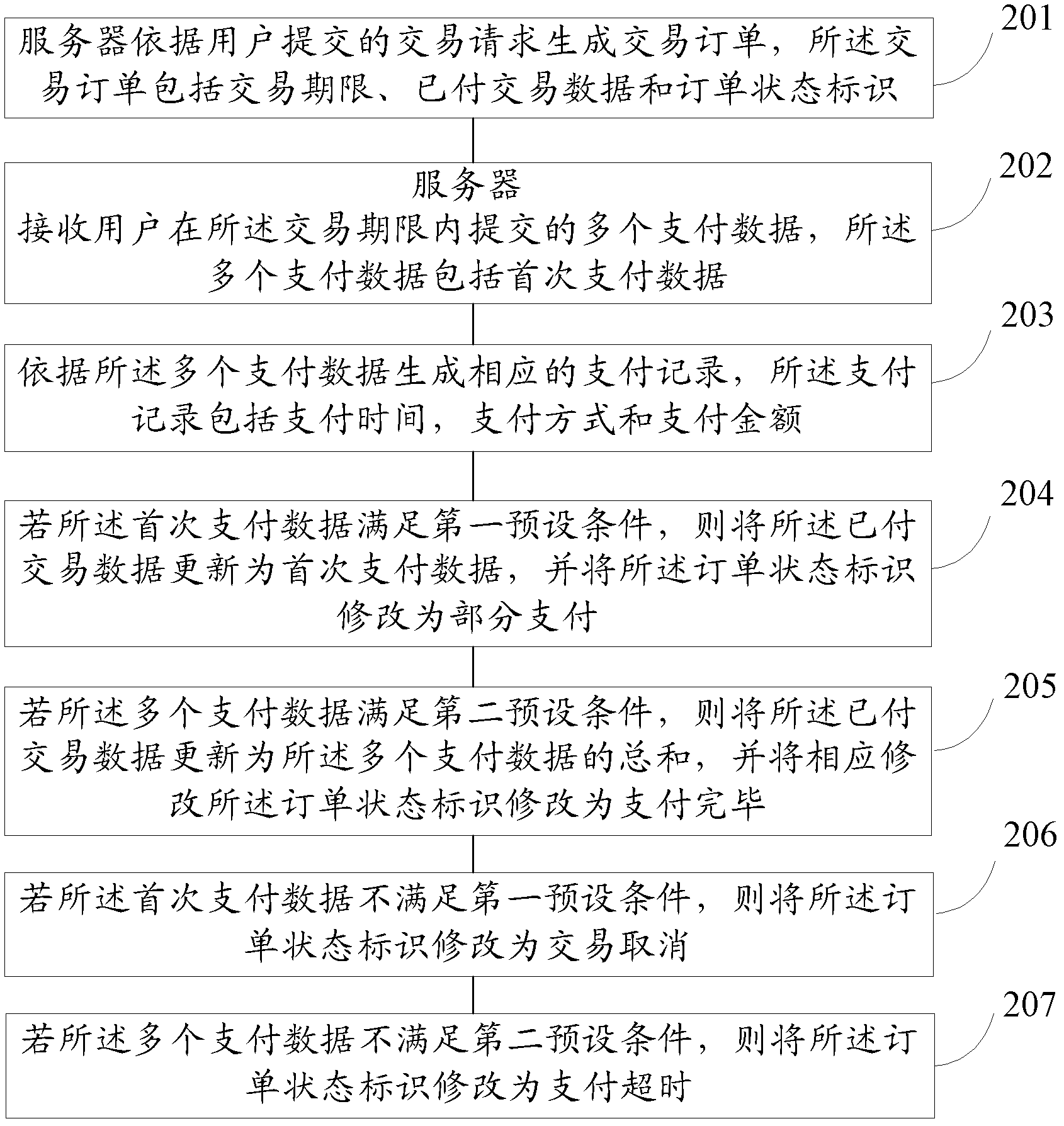
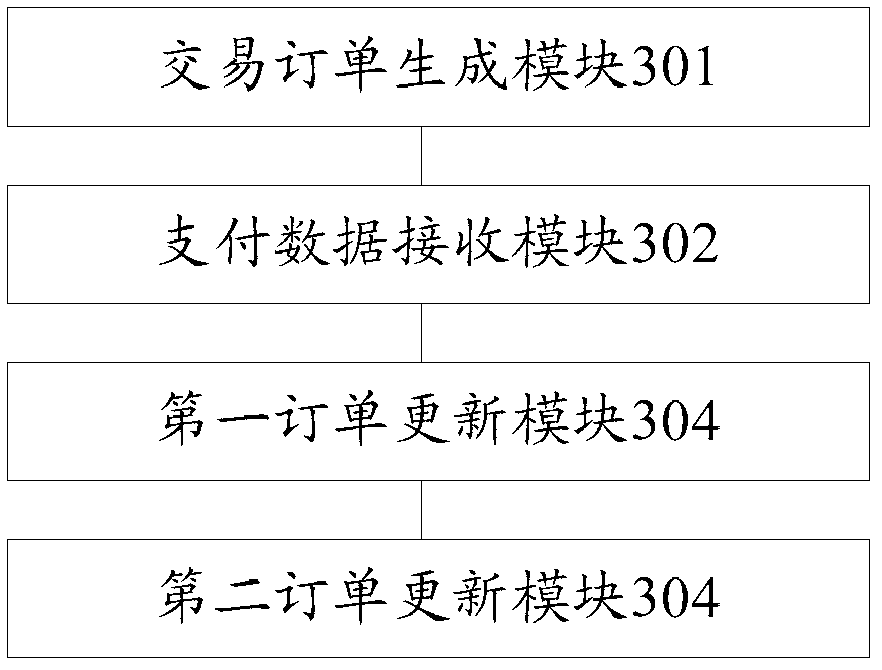
Trade information processing method and device
InactiveCN103106575AReduce complexityReduce access burdenPayment architectureCommerceInformation processingTransaction data
The invention provides a trade information processing method and a device. The trade information processing method includes the steps that a server generates a trade order according to a trade request submitted by a user. The trade order comprises a trade deadline, paid trade data and an order status identification; the server receives a plurality of paying data submitted by the user in the trade deadline. The plurality of paying data comprise first-time paying data; if the first-time paying data meet a first presupposed condition, the paid trade data are updated as the first-time paying data, and the order status identification is modified as partial payment; if the plurality of paying data meet a second presupposed condition, the paid trade data are updated as the sum of the plurality of paying data, and the order status identification is modified as payment completed. The trade information processing method can enable a user to obtain goods through payment for many times on the condition that the user can not complete one-off payment for the goods, reduces complexity of operations of the user, and reduces access burden of the server and occupancy of network bandwidth.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Spending Account Systems and Methods
A computer-implemented method and system to facilitate a purchase utilizing a tax-advantaged account. A request to charge the tax-advantaged account for an item is received at a host computer. A determination is made whether the item qualifies for pre-tax treatment. If the item qualifies for pre-tax treatment then at least partial payment authorization for the item is determined, and the tax-advantaged account is debited for at least a portion of the purchasing amount of the item based on the payment authorization. If the item does not qualify for pre-tax treatment, then a non-tax advantaged account is debited for an item not qualifying for pre-tax treatment.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC +1
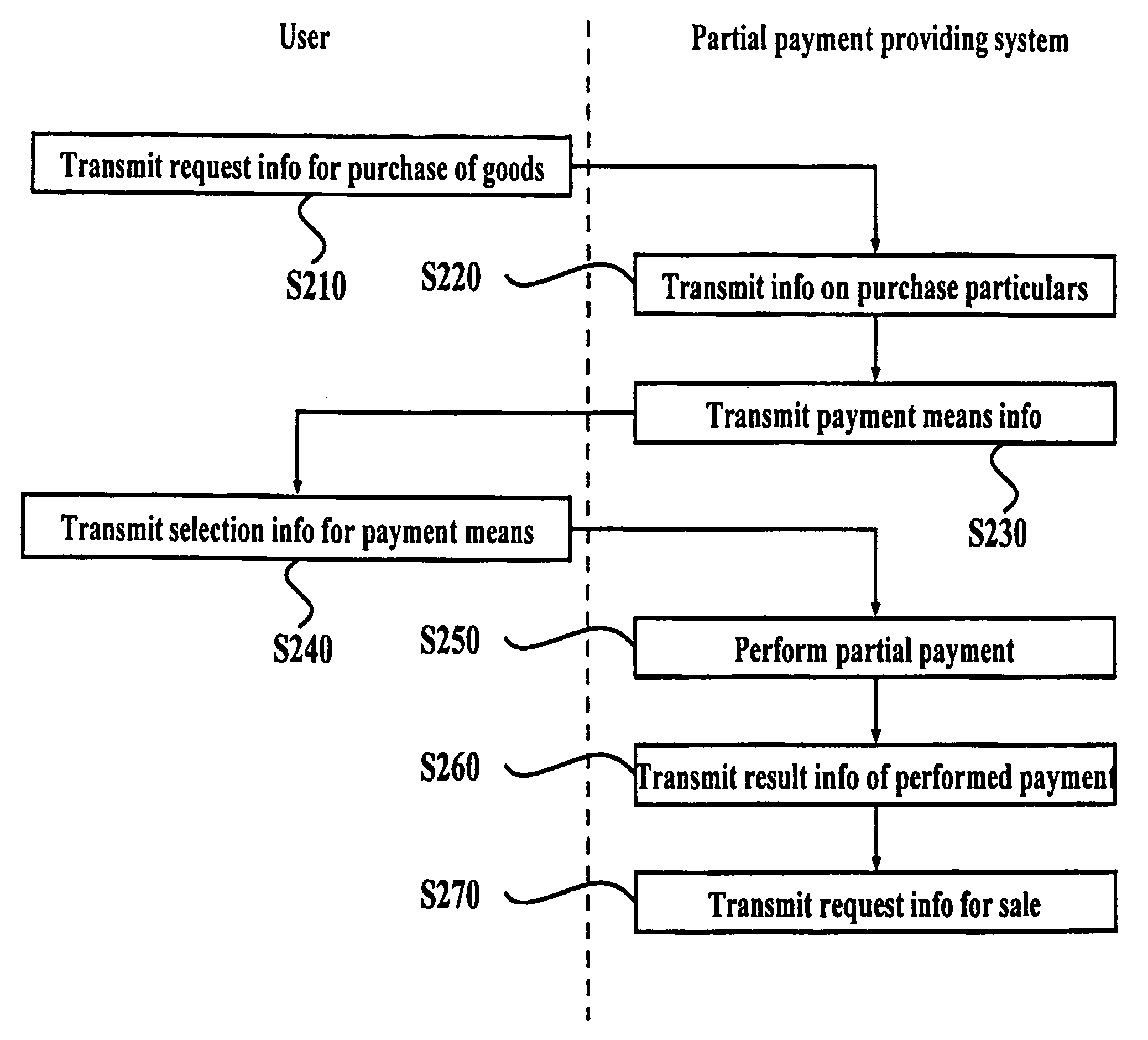
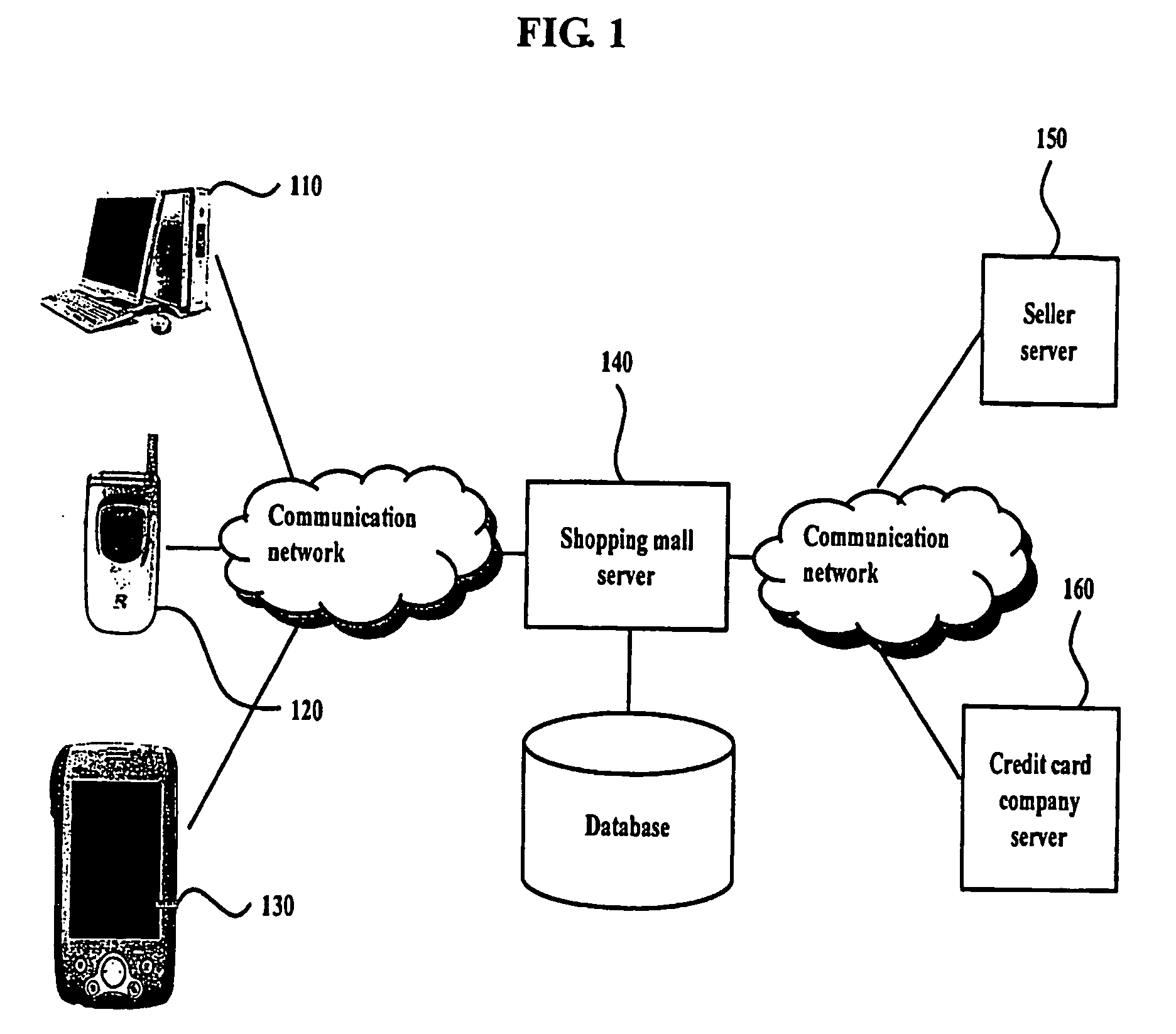
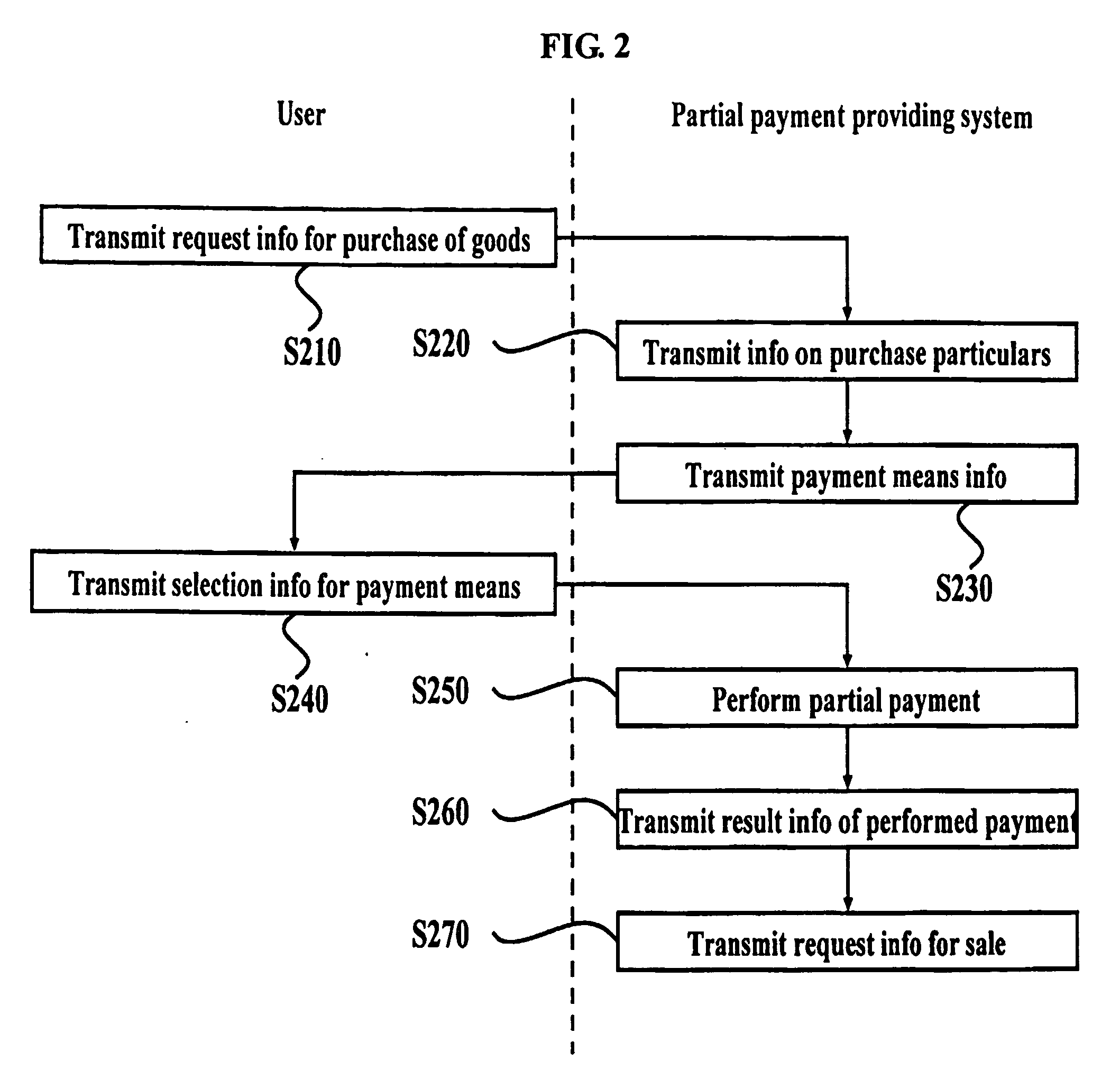
System and method for providing partial payment in the electronic commerce
The present invention relates to a method and system for providing a partial payment in the electronic commerce via the Internet. More particularly, the present invention relates to the present invention relates to a method and system which can more simplify procedures of payment when a user makes a payment with a plurality of payment means or when the user cancels a payment partially, changes a payment means, or changes goods.
Owner:NHN BUSINESS PLATFORM CORP
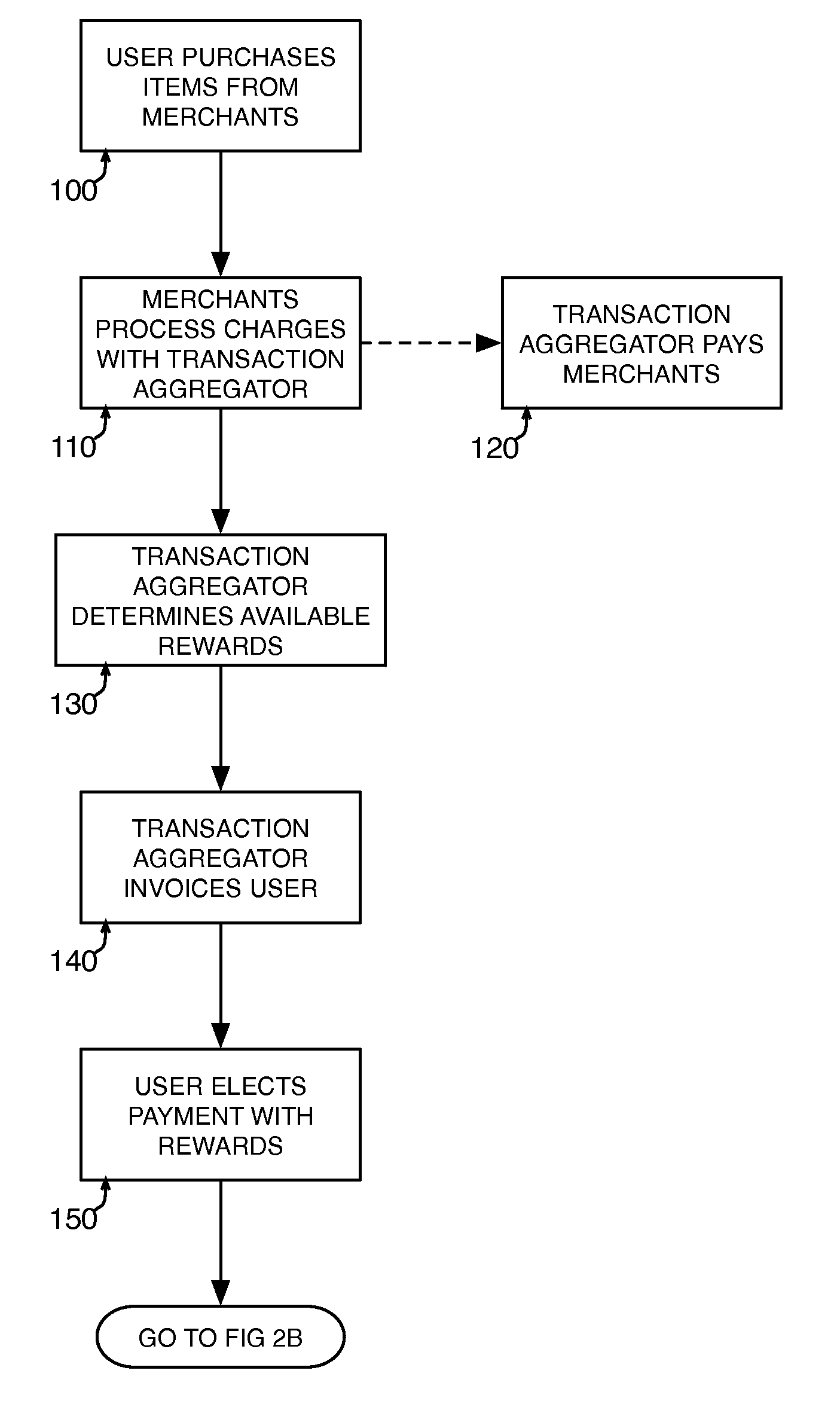
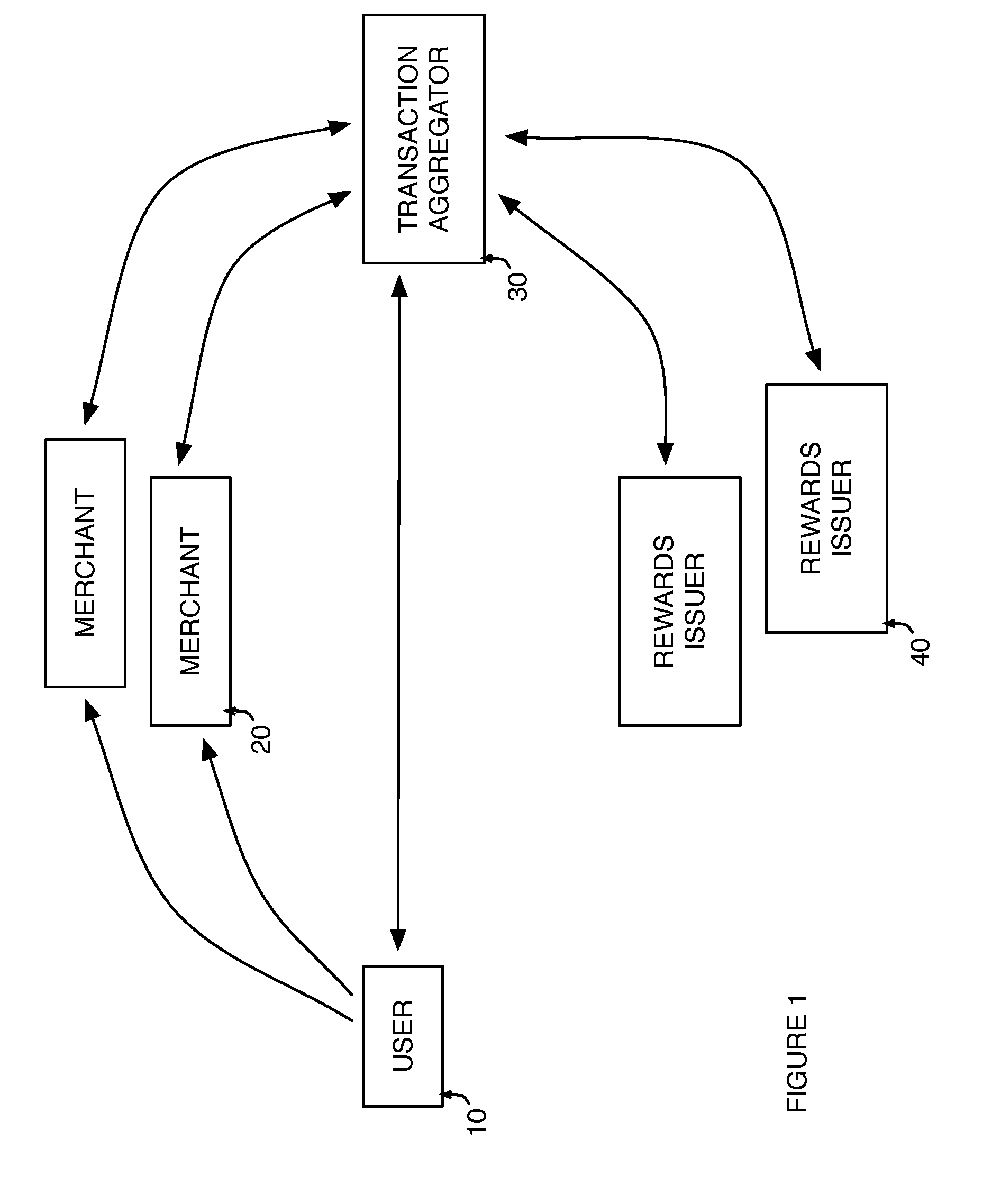
Method and system for redeeming rewards in payment of a transaction account
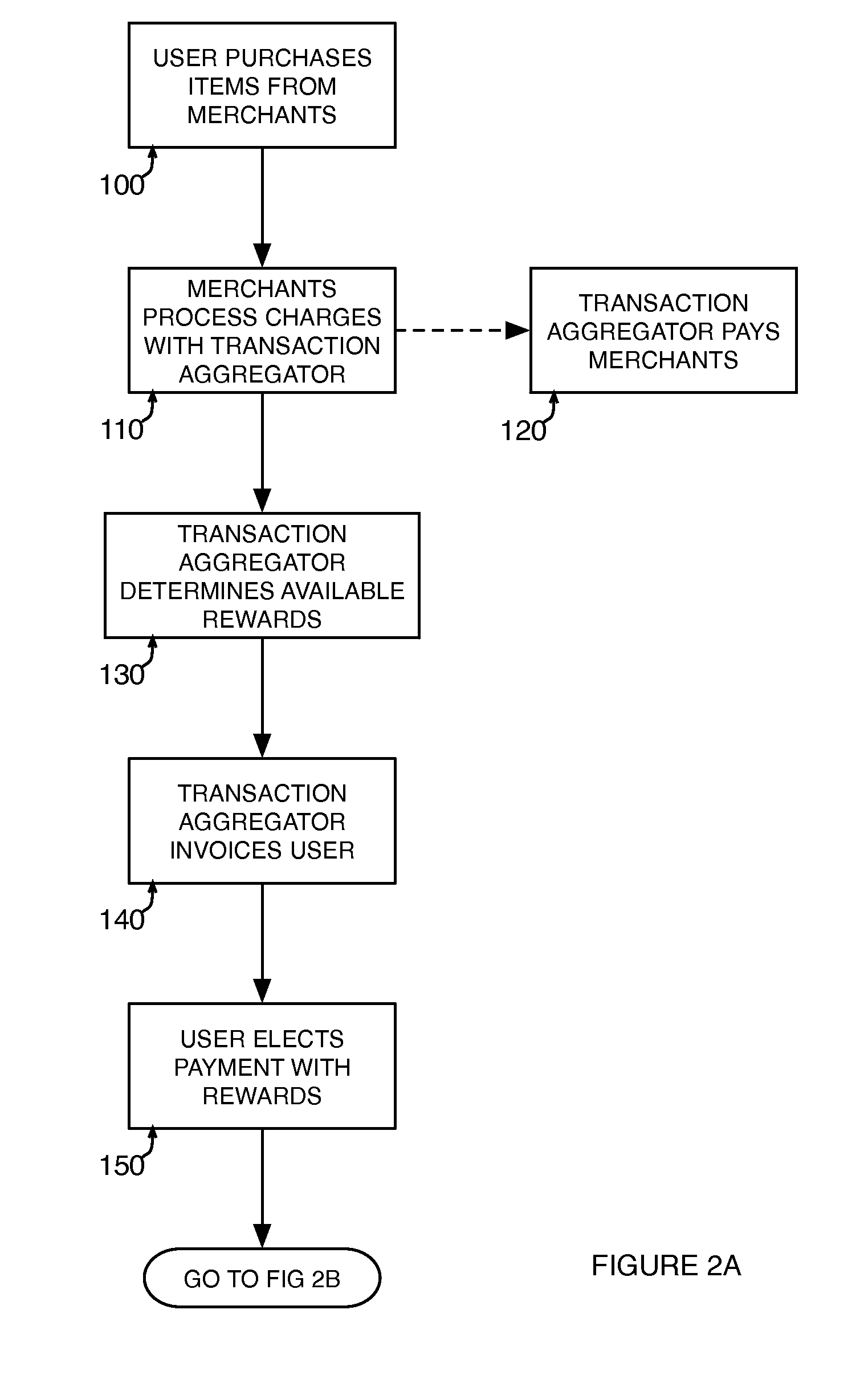
A transaction aggregator aggregates a plurality of transaction account charges for a user transaction account. The transaction charges are received from merchants for acquisitions made by a user. The user is offered an option to make at least a partial payment to the user transaction account by redeeming rewards from at least one user reward account associated with a rewards issuer. A reward redemption instruction is received from the user, the reward redemption instruction designating the redemption of rewards from at least one user reward account. The user reward account(s) designated by the user is caused to redeem the rewards by decreasing the rewards in the user reward account and conveying corresponding consideration to the transaction aggregator. A credit is provided on the user transaction account for an amount corresponding to the value of the rewards decreased in the user reward account(s).
Owner:SIGNATURE SYST
Methods and systems for coordinating pooled financial transactions
ActiveUS20080005019A1Simplify poolingFinancePayment architectureFinancial transactionFinancial trading
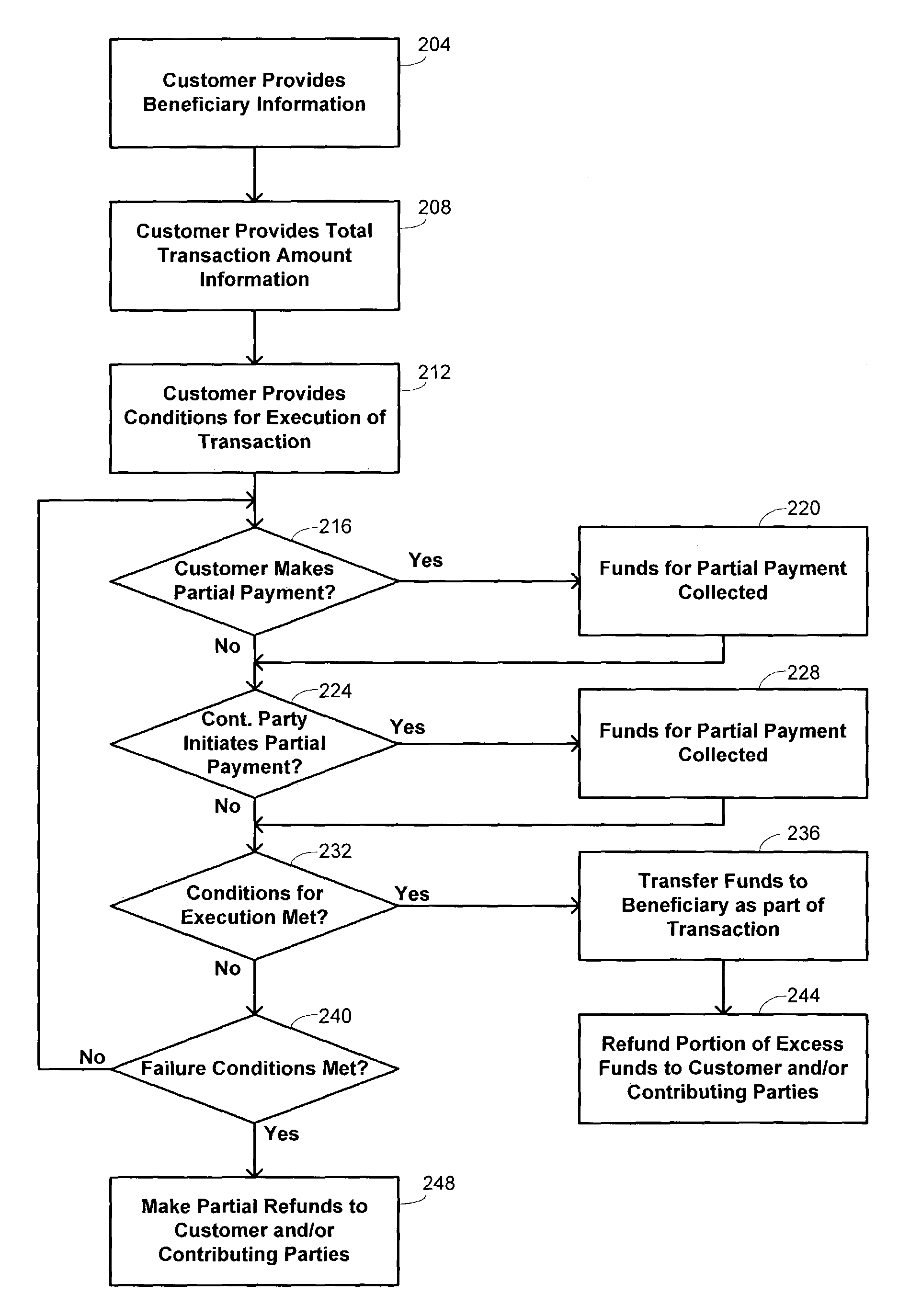
Methods and systems are provided for processing a financial transaction. A set of conditions is received that define circumstances for execution of the financial transaction. Funds are collected for each of a plurality of partial payments prior to satisfaction of the set of conditions, with at least two of the partial payments being collected from different persons. The collected funds are accumulated for support of the financial transaction until satisfaction or failure of the set of conditions.
Owner:PAYMAP
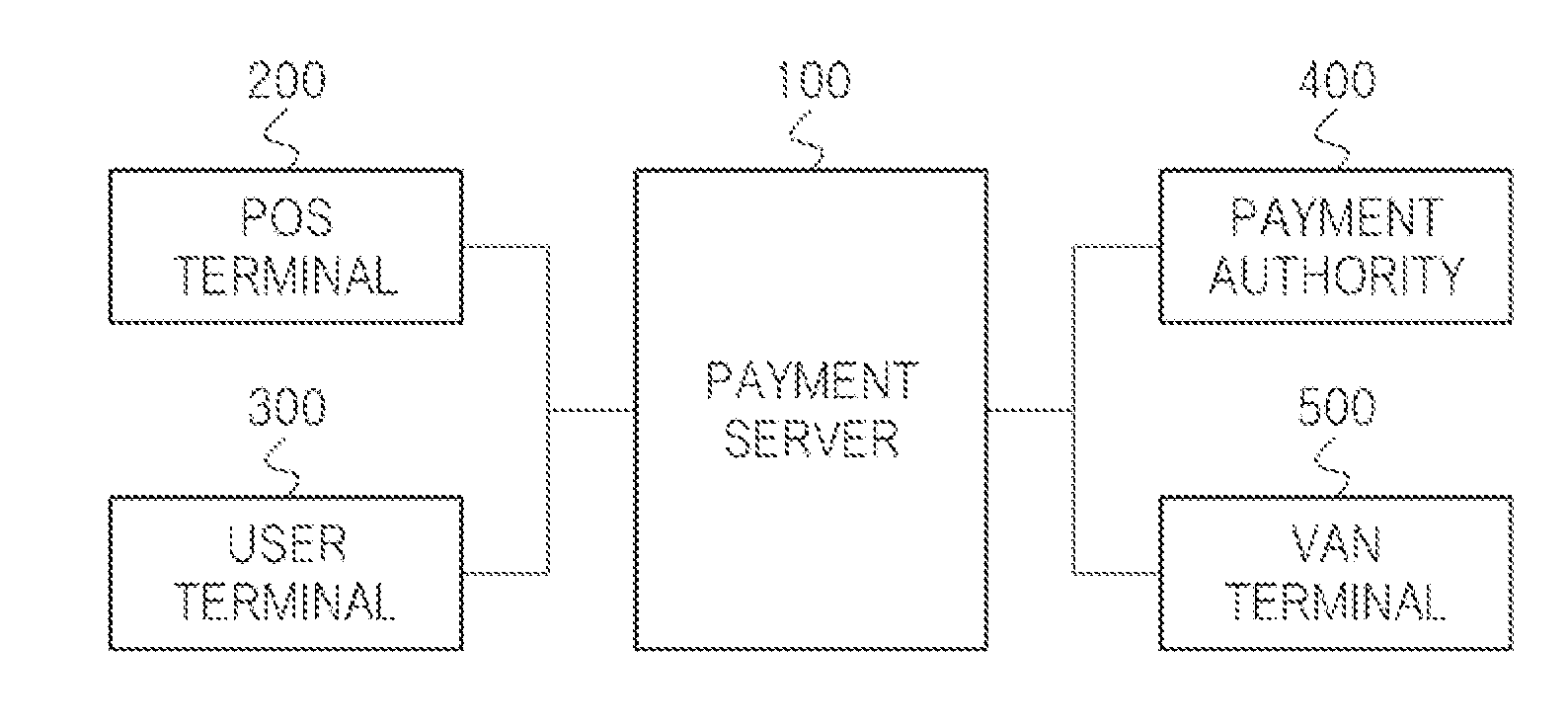
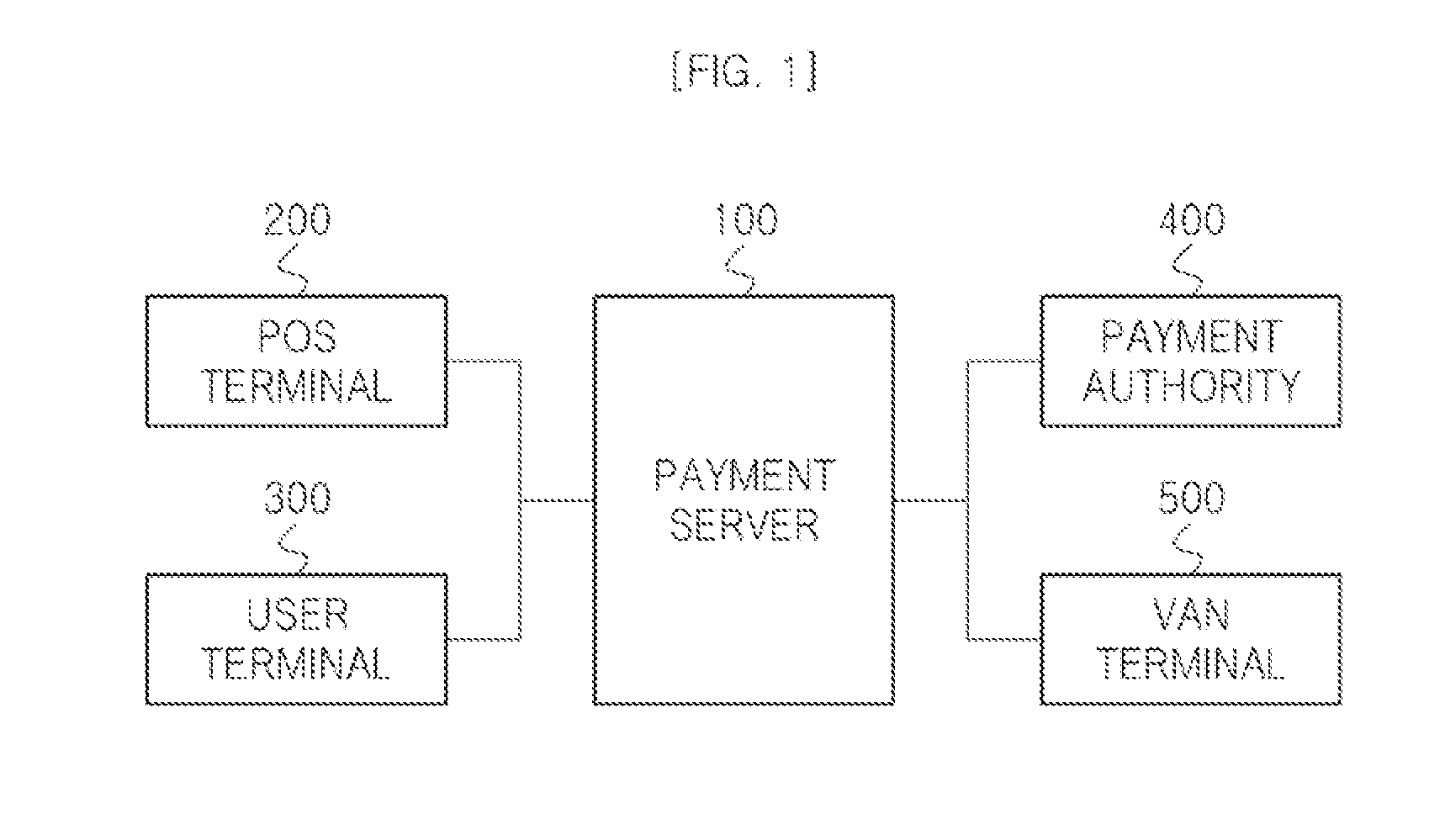
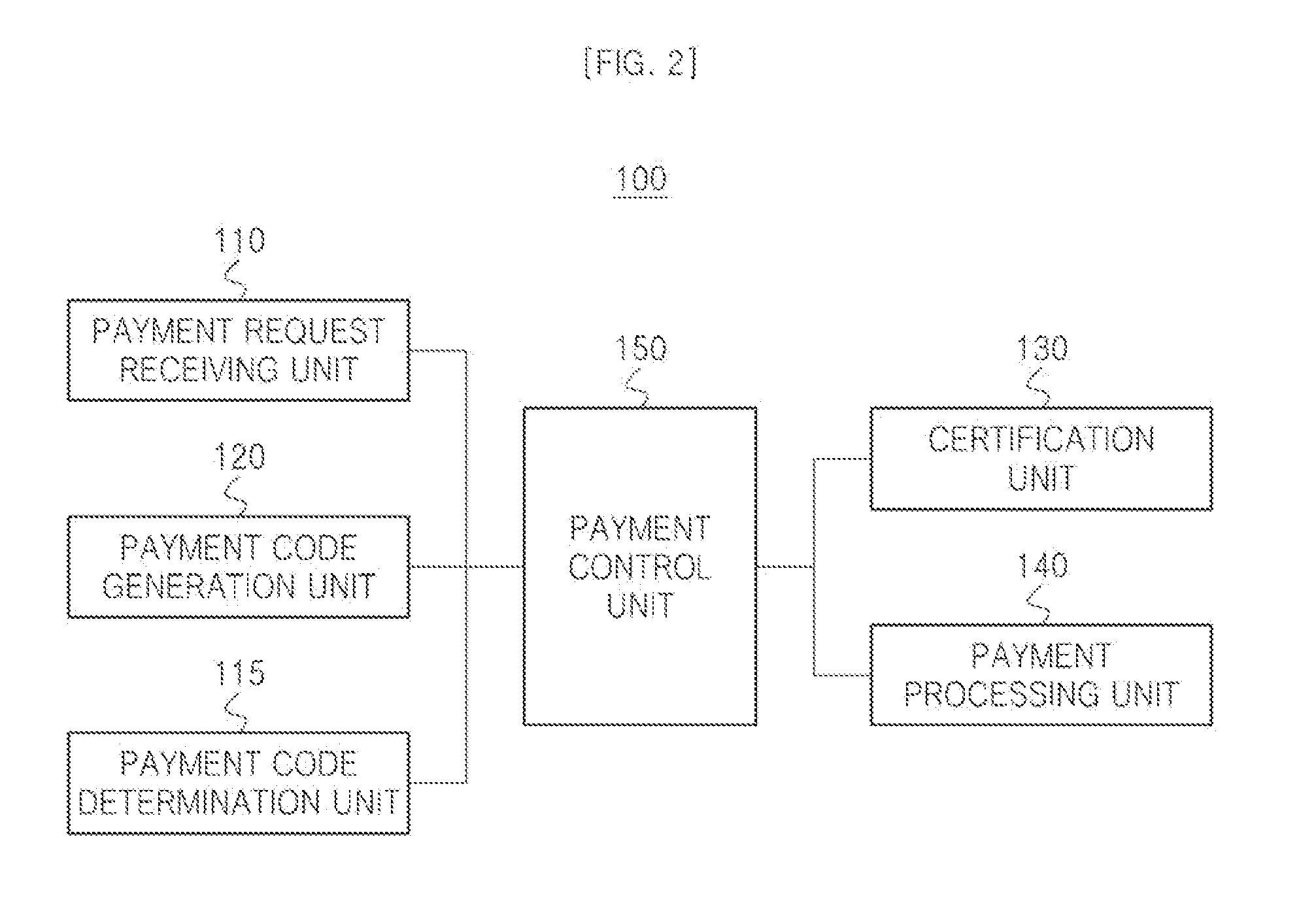
Payment method, payment server performing the same and payment system performing the same
ActiveUS20140081784A1Improved user authenticationEnhanced authenticationHand manipulated computer devicesFinancePayment systemOperating system
A payment server that includes a payment request receiving unit configured to receive a payment request code including a first partial payment code, and a payment code determination unit configured to determine a second partial payment code based on the received payment request code. The payment server also includes a payment code generation unit configured to generate a payment code based on the first and second partial payment codes, the payment code being payable by a user.
Owner:LG CNS
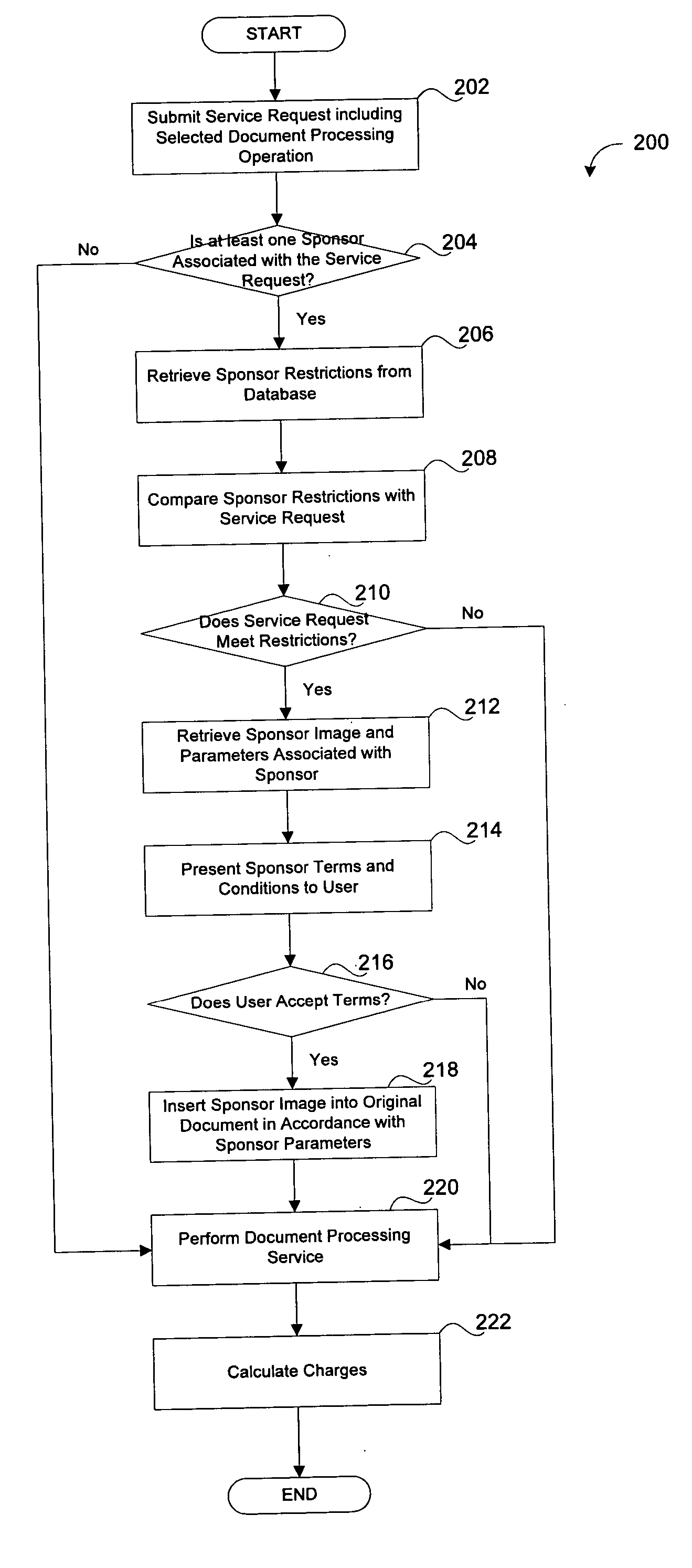
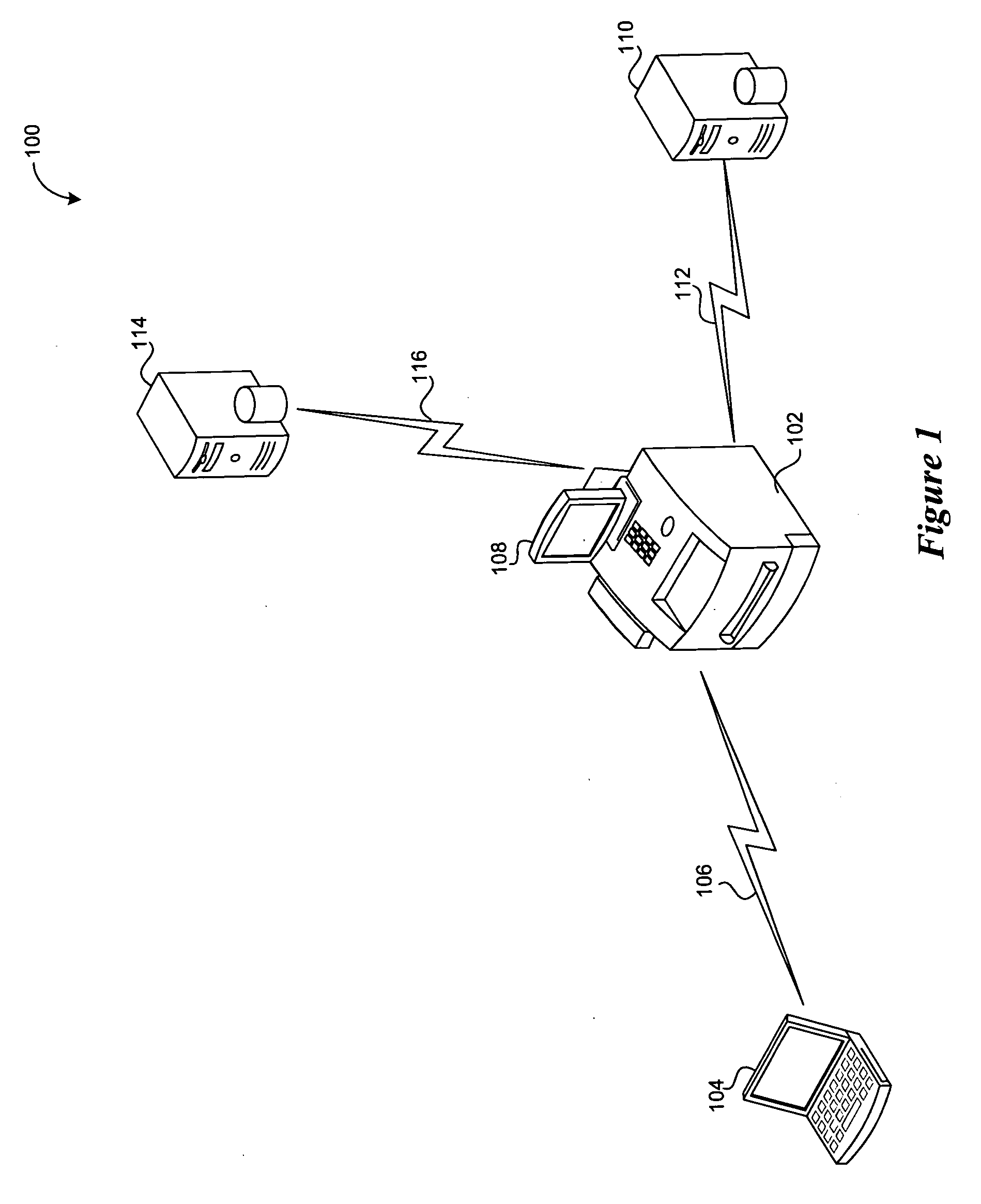
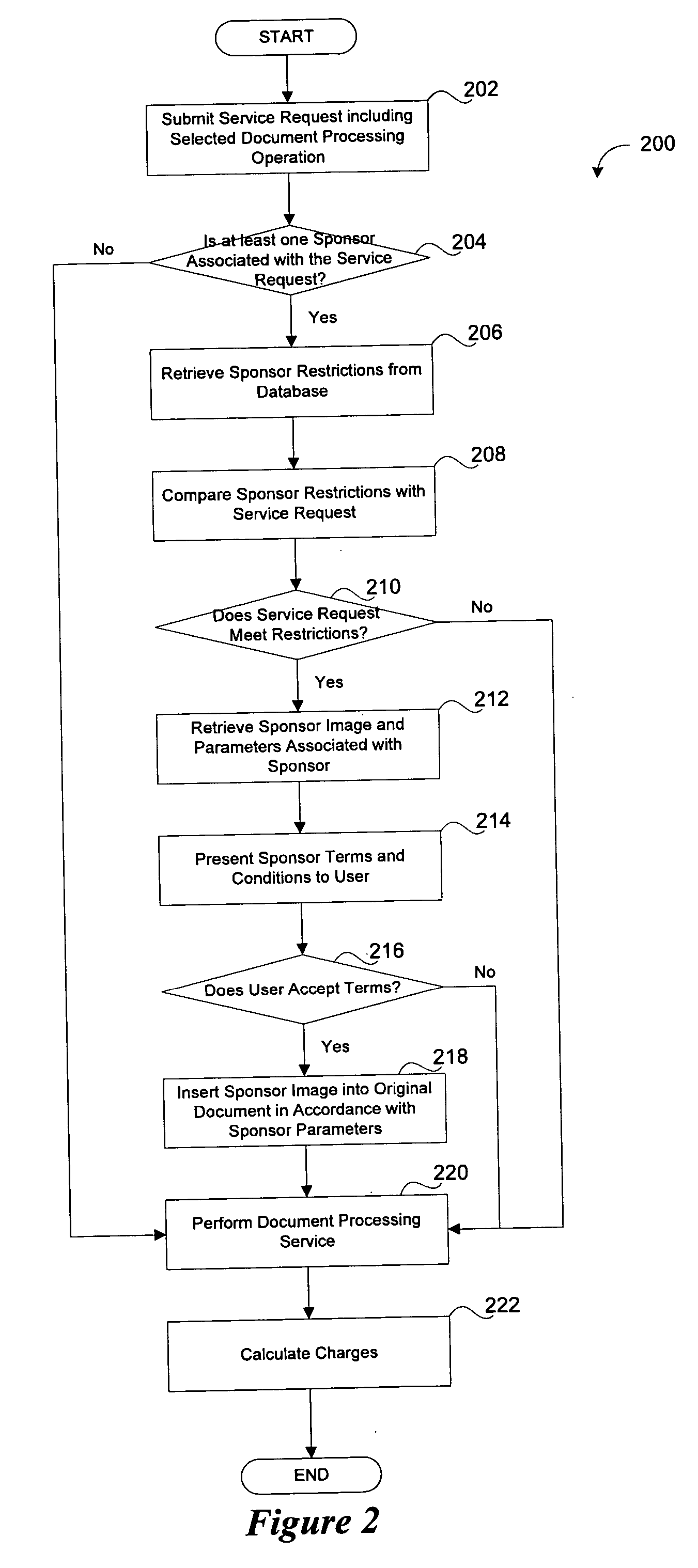
System and method for sponsored document processing services
A method and system for enabling the sponsorship of document processing services. A document processing service request is submitted by an associated user. At least one sponsor, associated with the document processing service request is then identified and communicated to the user. Terms and conditions regarding the sponsorship of the request are then presented to the user for acceptance. The terms and conditions include restrictions on the number of pages, size and color, as well as the placement of an advertisement on the output. The advertisement is in the form of a banner, watermark or reverse-side image. Once accepted, the advertisement is inserted into the request and the selected operation is performed. The fees associated with the request are then calculated and charged to the sponsor. When only partial payment is authorized by the sponsor, the user is charged for the remaining fees.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
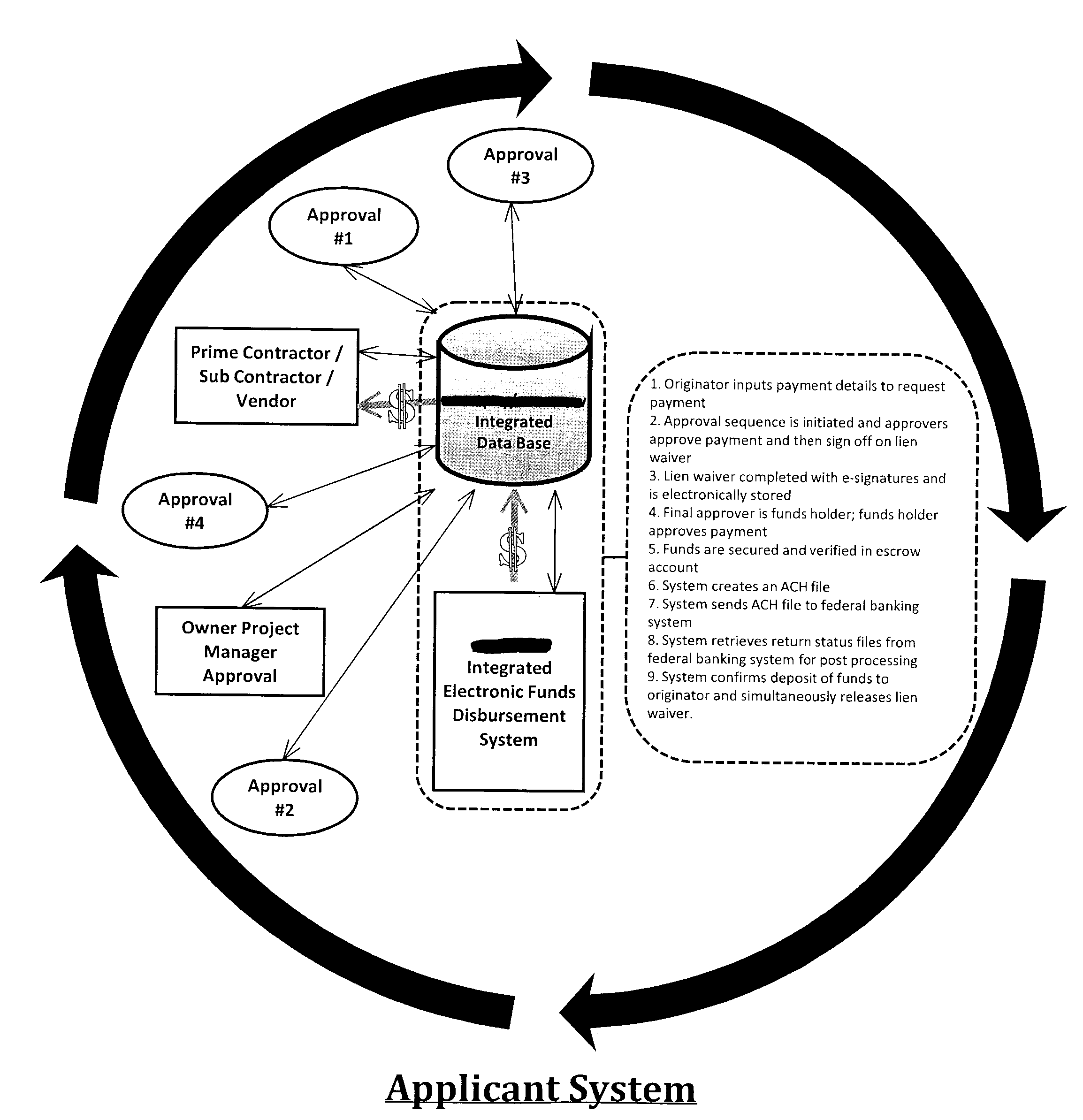
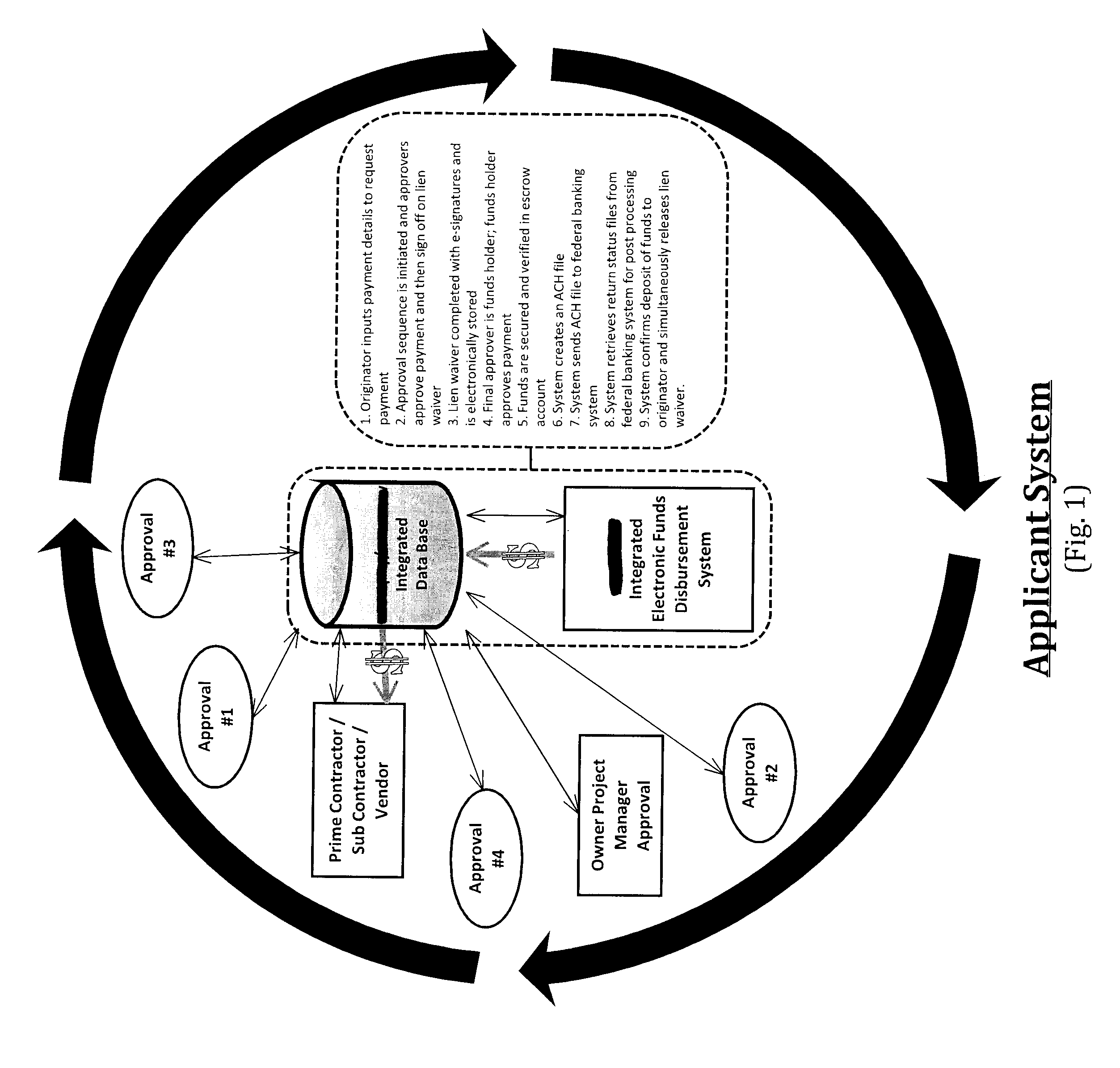
Pay Request System
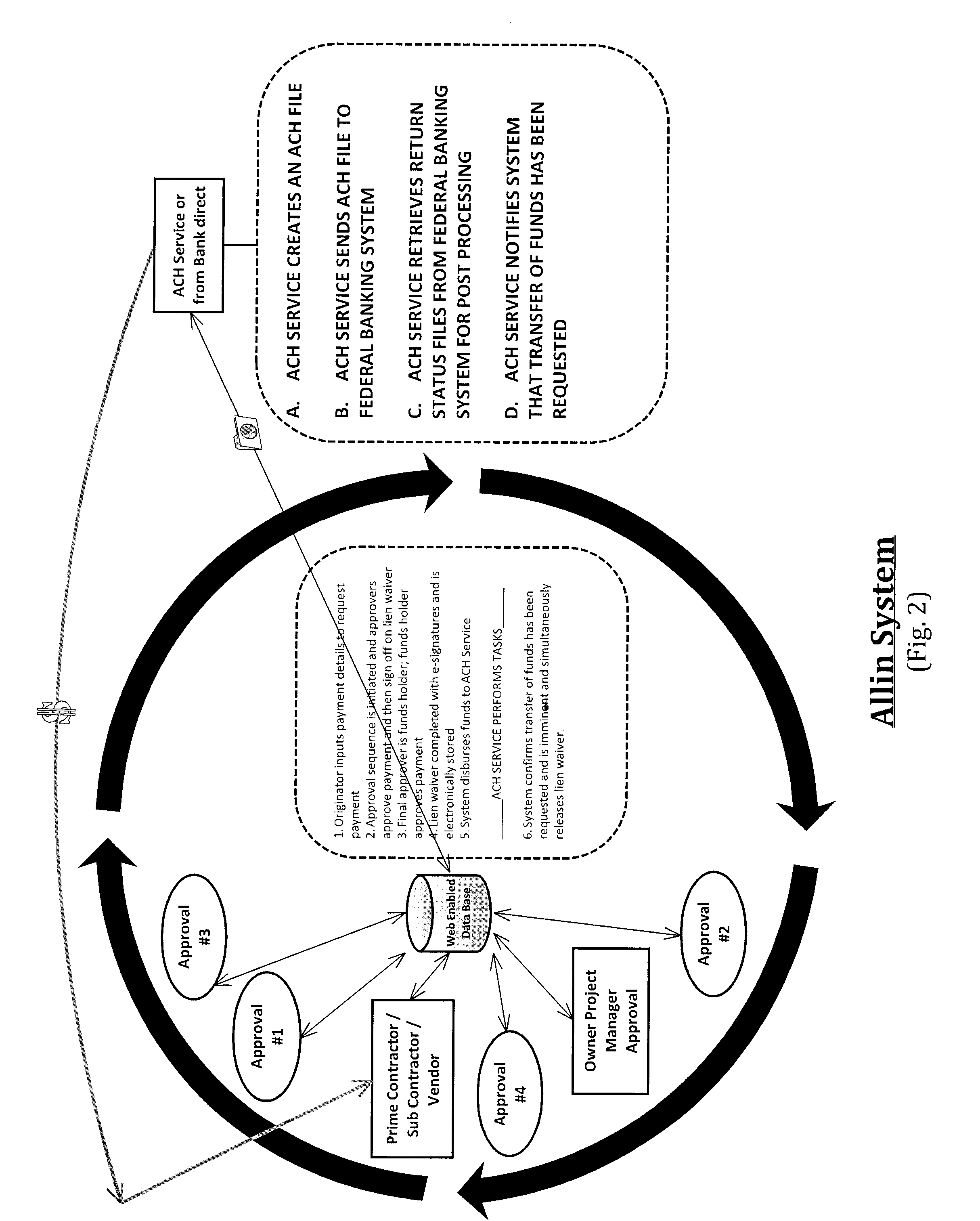
This web enabled system is capable of facilitating the management of unlimited projects within which an unlimited number of parties may participate to complete an unlimited number of stages, substages and tasks. The system facilitates the efficient disbursal of monies while reducing the inefficiencies that result when money is not timely disbursed. It uses a quasi-escrow system to secure waivers and distribute money simultaneously. Projected timelines for completion, tracking of materials used and materials stored, and partial payments and releases are all managed by the system based on inputs by participating parties. Allowed inputs are governed by each party's function and the password security level provided therefore, in balance with checks against required approvals or releases by other affected parties and intrasystem consistency checks.
Owner:EZNETPAY
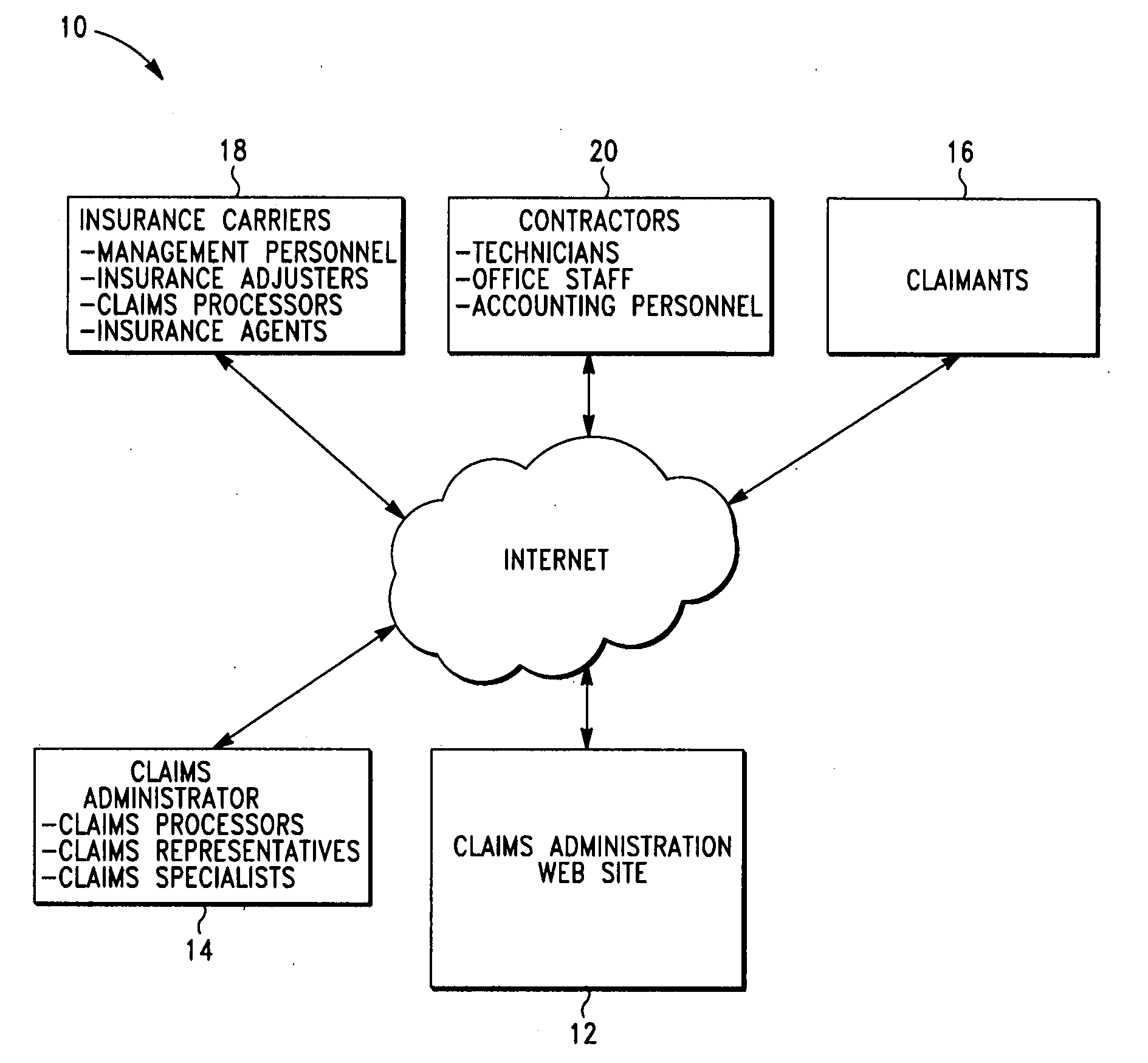
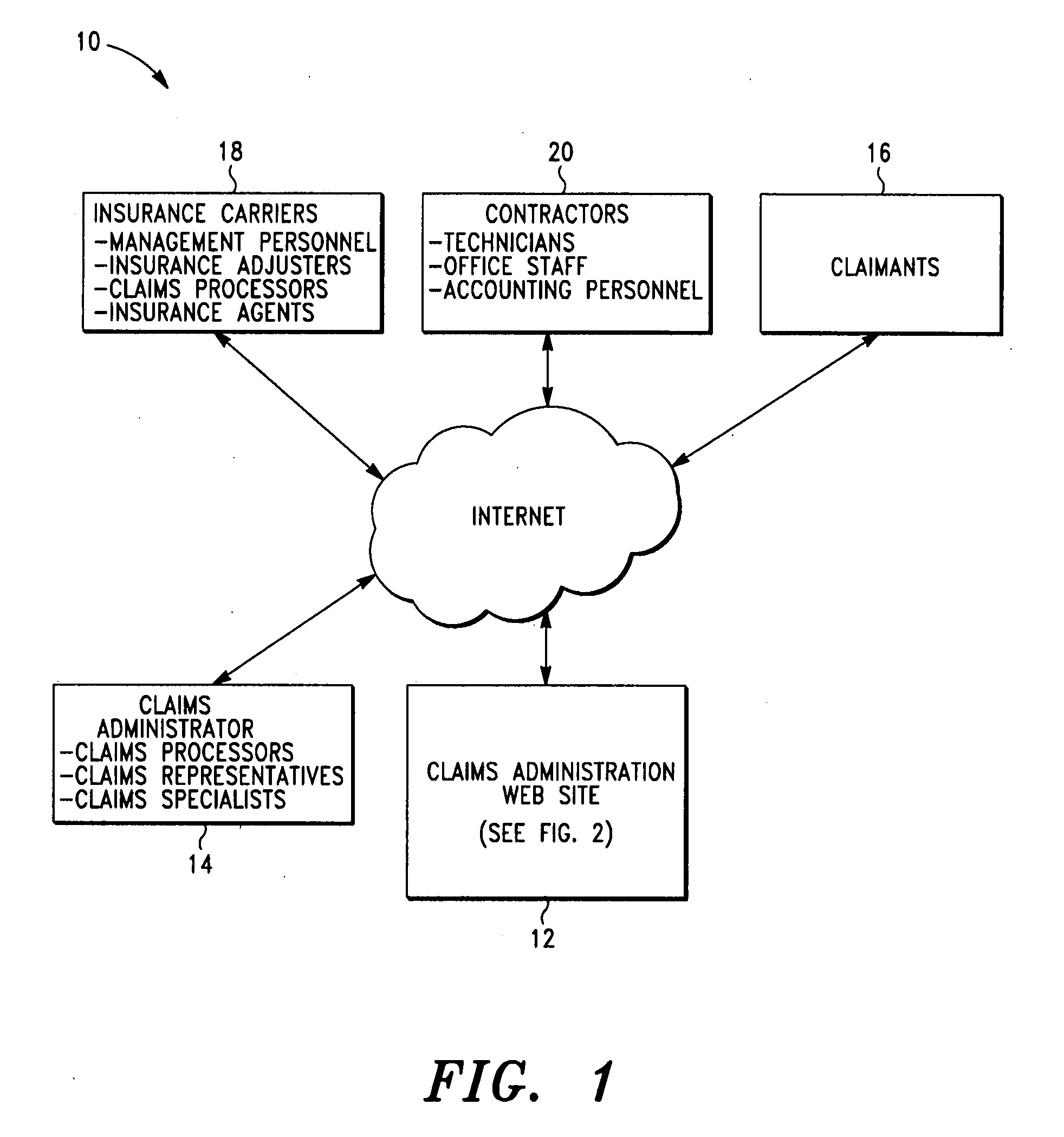
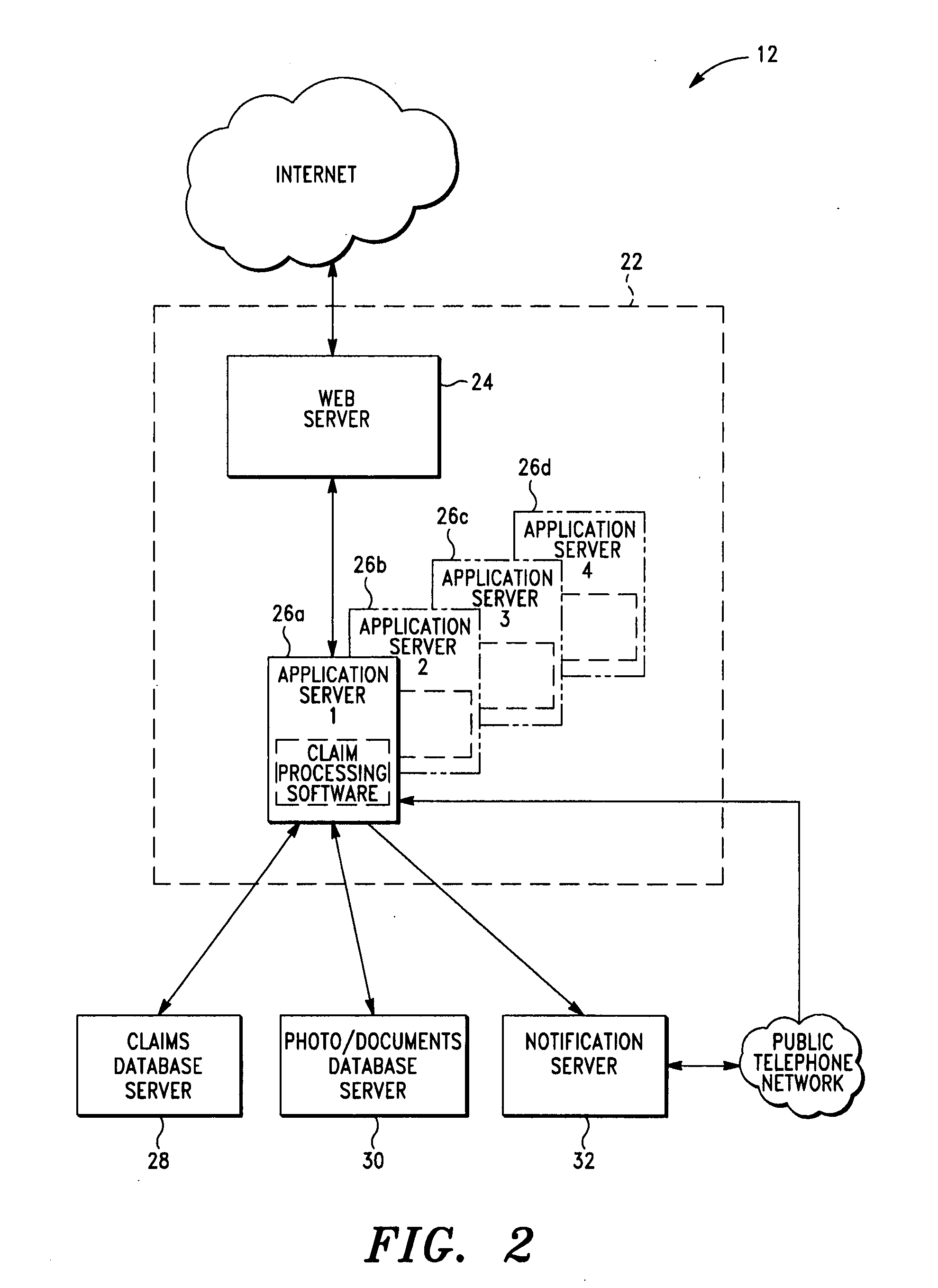
System and method for managing the sale of salvage items in connection with the management of an insurance claim
In an exemplary embodiment, a claim administrator receives a list of salvage items associated with an insurance claim. The claims administrator dispatches a contractor to retrieve and store the salvage items, wherein the contractor is preferably a member of a restoration network associated with the claim administrator. The claim administrator then sells the salvage items to one or more buyers and collects payment for the salvage items from the buyers. The claims administrator also arranges for the delivery of the salvage items from the contractor to the buyers. Finally, the claim administrator distributes a first portion of the payment to the contractor and a second portion of the payment to the insurance carrier associated with the insurance claim. Thus, the claim administrator is able to manage the sale of the salvage items in connection with the management of the insurance claim.
Owner:CODE BLUE
Methods and systems for coordinating pooled financial transactions
Methods and systems are provided for processing a financial transaction. A set of conditions is received that define circumstances for execution of the financial transaction. Funds are collected for each of a plurality of partial payments prior to satisfaction of the set of conditions, with at least two of the partial payments being collected from different persons. The collected funds are accumulated for support of the financial transaction until satisfaction or failure of the set of conditions.
Owner:PAYMAP
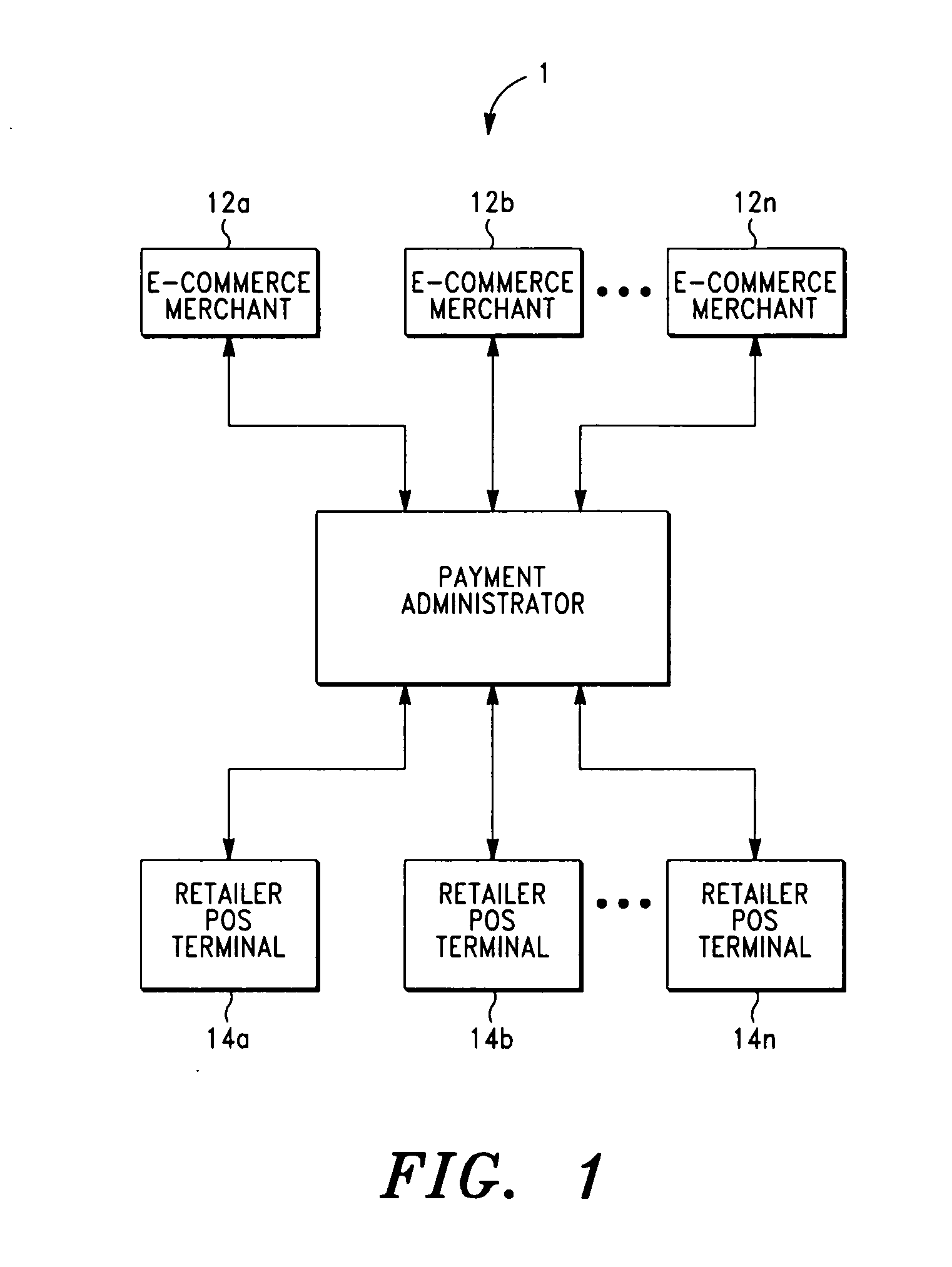
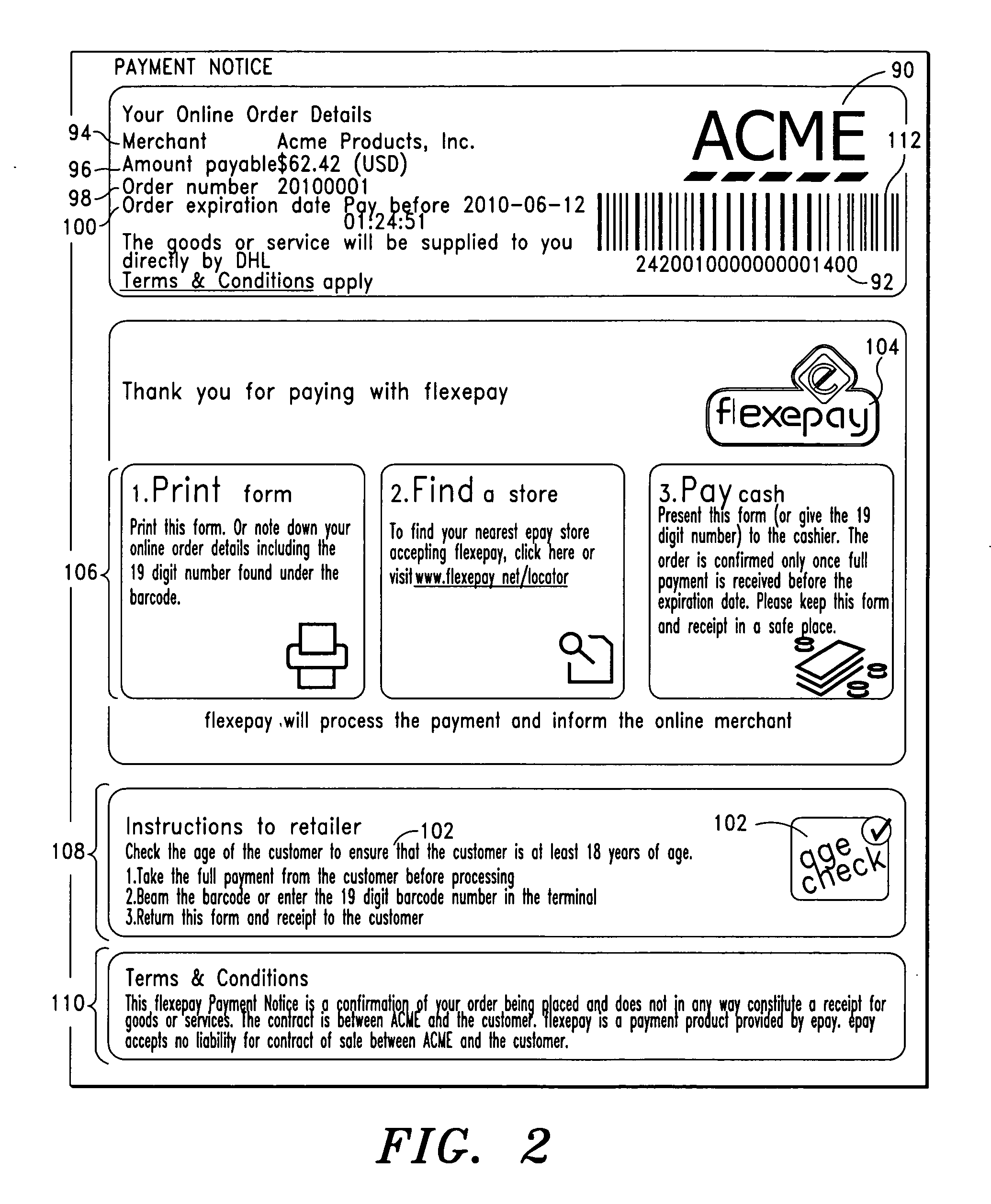
Payment System and Method for Electronic Commerce Transactions
A payment system and method for electronic commerce transactions is disclosed. In an exemplary embodiment, a payment administrator receives a request for a payment notice for an electronic commerce transaction, such as a purchase on a merchant website. In response, the payment administrator creates a payment notice comprising a transaction amount (which may be converted between different currencies), an age restriction for the purchased product (if applicable), and a unique identifier for the electronic commerce transaction. Preferably, the unique identifier is presented in both human-readable form and machine-readable form (such as a barcode) on the payment notice. The payment administrator then transmits the payment notice to the purchaser, who may print and take the payment notice to a retailer for full or partial payment of the transaction amount printed on the payment notice.
Owner:EFT SERVICES HLDG BV
Method and system for electronic national financial institution gift card creation and redemption
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, system and a point of sale device for generating and redeeming a virtual gift card. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a virtual gift card associated with a financial institution is generated, the virtual gift card being redeemable at merchants that accept forms of payment associated with a financial institution. The virtual gift card includes a computer readable code that corresponds to a gift card amount. The virtual gift card is sent to a recipient. The computer readable code is received from a wireless mobile device at a point of sale. The gift card amount is applied as at least partial payment for a purchase.
Owner:ARIEL INVENTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com