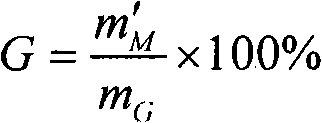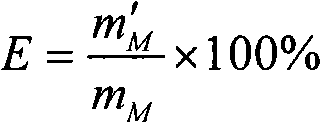Preparation method of starch grafted acrylamide flocculating agent
A technology of acrylamide and starch grafting, which is applied in the direction of flocculation/sedimentation water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of many by-products, mild reaction conditions, implosion polymerization, etc., to improve the reaction rate and conversion rate, mild reaction conditions, The effect of good flocculation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0023] Take 40g of liquid paraffin, 2.24g of Span80, 0.16g of Tween 80 and 0.80g of OP-4 in a three-necked flask, stir to dissolve, add water 30mL and starch 6.7g, and stir until an inverse emulsion is formed. The conductivity is close to 0, and the stability of the emulsion is close to 1.
[0024] Pass nitrogen into the above-mentioned emulsion until the oxygen in the three-necked flask is completely removed, heat to 50°C, continue to pass nitrogen and stir, add dropwise 1mL of potassium permanganate solution with a mass concentration of 1%, stir for 20min, add 50% potassium permanganate solution Acrylamide solution 18.8g, react for 3h, stop stirring; transfer the mixture in the beaker to a 1000mL beaker, add ethanol after cooling to room temperature, stir until no solid product is formed, filter and separate the solid in the beaker, and use ethanol and acetone Wash and filter repeatedly until the filter cake is loose and small particles, and finally dry to the moisture conte...
example 2
[0026] Take 46g of liquid paraffin, 3.6g of Span80, 0.1g of Tween 80 and 0.3g of OP-4 in a three-necked flask, stir for 4 to dissolve, add 29.2g of water and 6.7g of starch, and stir until an inverse emulsion is formed. The conductivity is close to 0, and the stability of the emulsion is close to 1.
[0027] Introduce nitrogen into the above-mentioned emulsion until the oxygen in the three-necked flask is completely removed, continue nitrogen and stirring, add 10.8g of 50% acrylamide solution, heat to 40°C, add dropwise 0.6mL of 1% potassium permanganate solution, and react 7h, stop stirring, transfer the mixture in the beaker to a 1000mL beaker, add ethanol after cooling to normal temperature, stir until a solid product is obtained, filter to separate the solid in the beaker from the mixture, and wash the filter cake repeatedly with ethanol and acetone to the filter cake It is loose and small particles, and finally vacuum-dried to the moisture content required by the product....
example 3
[0028] Example 3 Take 27g of liquid paraffin, 0.7g of Span80, 0.05g of Tween 80, and 0.25g of OP-4 in a three-necked flask, stir to dissolve, add 27.6g of water, 6.7g of starch, stir until an inverse emulsion is formed, and measure its conductivity The ratio is close to 0, and the emulsion stability is close to 1.
[0029] Pass nitrogen into the above emulsion until the oxygen in the three-necked flask is completely removed, continue to pass nitrogen and stir, add dropwise 3mL of 1% potassium permanganate solution, stir for 20min, add 26.8g of 50% acrylamide solution, and heat to 60°C , react for 1h, stop stirring, transfer the mixture in the beaker to a 1000mL beaker, add ethanol after cooling to normal temperature, stir until a solid product is obtained, filter and separate the solid in the beaker from the mixture, and wash the filter cake repeatedly with ethanol and acetone until The filter cake is loose and small particles, and finally vacuum-dried to the moisture content ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| grafting efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grafting efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| grafting efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com