Water-based polymer coated controlled release fertilizer and method for preparing same
A technology of water-based polymers and controlled-release fertilizers, applied in fertilizer mixtures, fertilization devices, applications, etc., can solve the problems of high manufacturing costs for large-scale applications, polymers are difficult to degrade, and secondary pollution, etc., to achieve controlled fertilizer nutrient release , Good controlled release effect, environment-friendly effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0074] 1. Preparation of coating liquid - firstly, the selected coating liquid monomer and emulsifier are fully stirred and emulsified in water to make a coating mother liquid. The coating mother liquid should be stored at a temperature of 10°C to 25°C, and the storage time should not be longer than 30 days; then the coating mother liquid, water and the selected cross-linking agent should be mixed to prepare a coating liquid, which is ready for immediate use.
[0075] 2. Fertilizer granulation - general chemical fertilizers, such as nitrogen fertilizers (ammonium bicarbonate, ammonium sulfate, ammonium chloride, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfur nitrate, sodium nitrate, calcium nitrate, calcium ammonium nitrate, urea, etc.), Calcium phosphate, double superphosphate, calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, etc.), potassium fertilizer (potassium sulfate, potassium chloride, etc.), multi-component fertilizer (ammoniated calcium superphosphate, nitrate phosphate fertilizer, ammoniu...
Embodiment 1
[0083] 1 Catalyst preparation
[0084] Measure 40 mL of deionized water into a 100 mL beaker, and add 3 g of ammonium persulfate thereto at room temperature. After being stirred by an electric mixer for 10 min, the catalyst was divided into two parts: 30% (about 12 g) of it was measured as the initiator; the remaining 70% was used for the preparation of the pre-emulsifier.
[0085] 2 mixed monomer preparation
[0086] The amount of each monomer used is as follows:
[0087] Monomer Name Consumption (g)
[0088] Unsaturated silicone monomer: Vinyltrimethoxysiloxane 12
[0089] Hard Monomer: Methyl Methacrylate 200
[0090] Soft Monomer: Butyl Acrylate 250
[0091] Functional Monomer: Acrylic 8
[0092] Methacrylic acid 3
[0093] Acrylamide 8
[0094] 3 Preparation of pre-emulsion
[0095] Measure 150 mL of deionized water and add 5 g of emulsifier to it. After being emulsified for 30 minutes, 70% of mixed monomers (about 337g) and 70% of catalyst (about 30.1g) were ad...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Increase the amount of methyl methacrylate in the mixed monomer to 210g; reduce the amount of butyl acrylate to 240g. Other operations for preparing the coating solution are the same as in Example 1. When preparing the coating solution, add 1% of the cross-linking agent based on the dry weight of the emulsion. The fluidized bed coating parameters are the same as in Example 1.
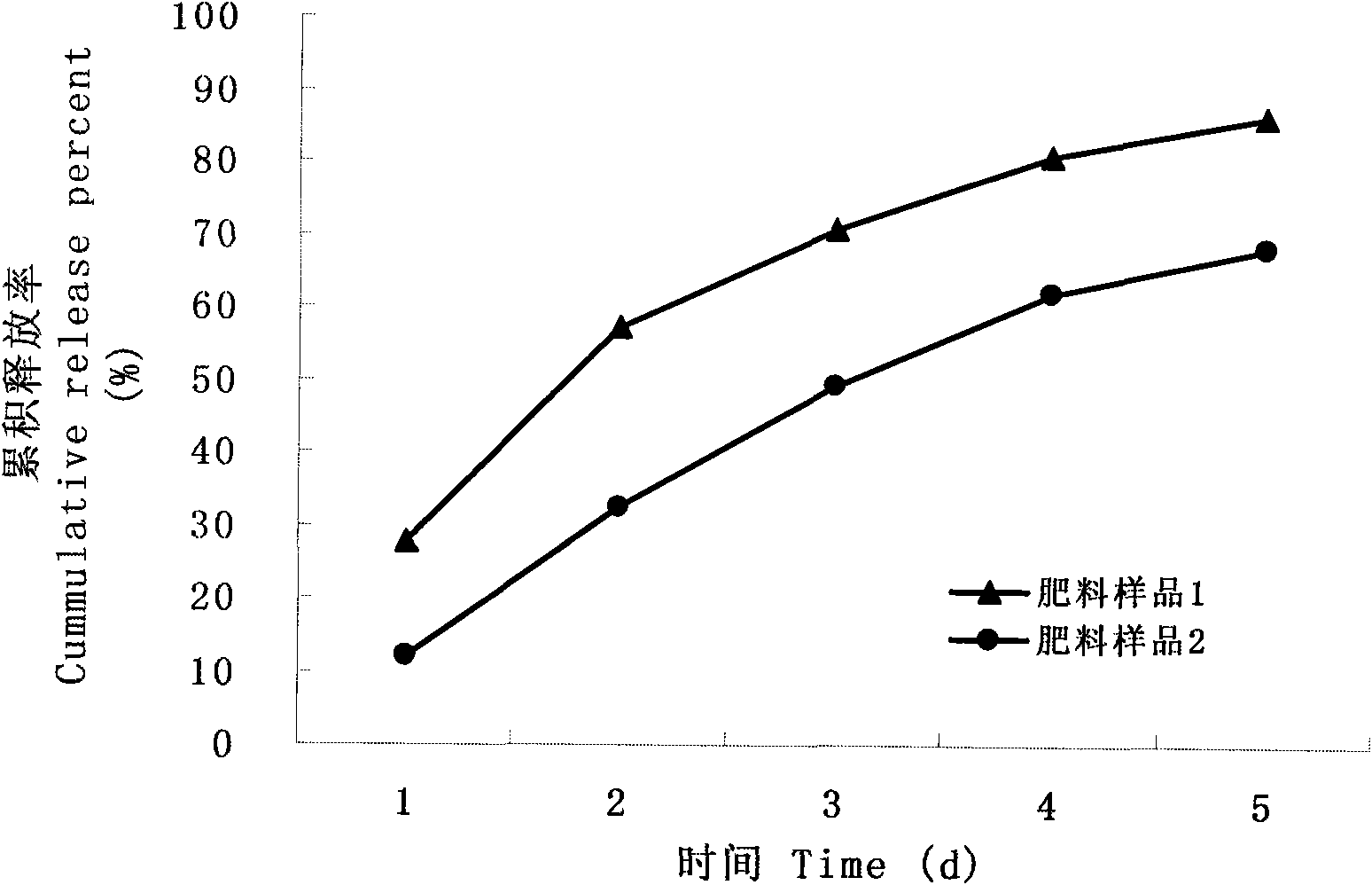
[0103] The controlled release time in water at 40°C is 10 days, and the release pattern is similar figure 1 The cumulative dissolution profile of fertilizer sample 2 is shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com