Method for preparing high dielectric constant barium titanate ceramic
A high dielectric constant, barium titanate technology, applied in the field of electronic ceramic materials, can solve the problems of difficult to meet electronic components, low product activity, large powder particle size, etc., and achieve high reliability, easy chemical reaction, powder The effect of small particle size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
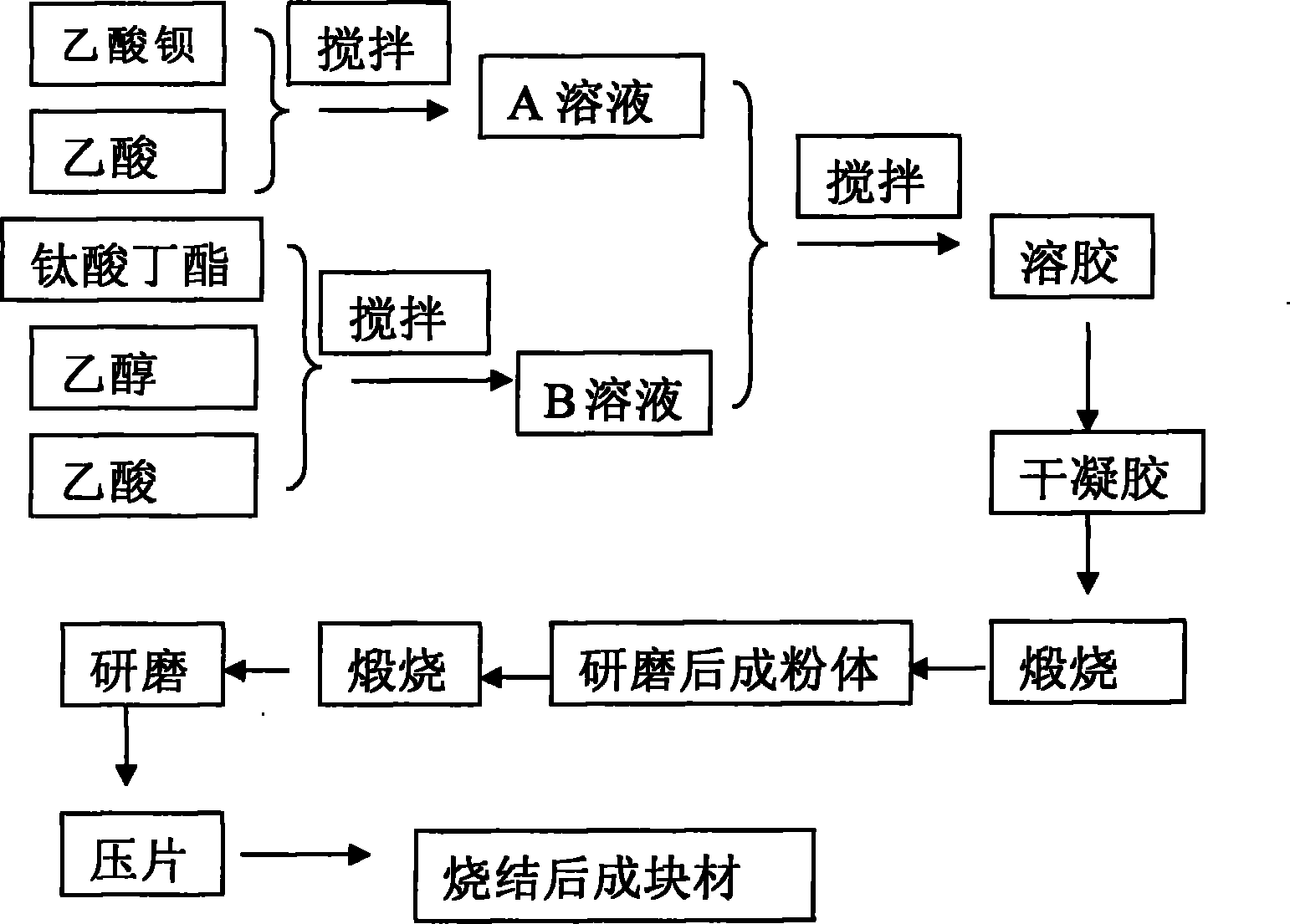
[0031] 1. Weigh 0.1mol (25.542g) of barium acetate and dissolve it in 90ml of acetic acid solution with a mass fraction of 36% (32.4ml for acetic acid, 57.6ml for water) and mix well as solution A;
[0032]2. Measure 0.1mol (35ml) butyl titanate, 0.6mol (35ml) ethanol, 0.3mol (17.16ml) acetic acid and mix them uniformly as B solution;
[0033] 3. Mix A and B solutions in a water bath at 60°C for 20 minutes, and they are in a sol state.
[0034] 4. Then sink in the air for four hours, and bake at 120°C for 12 hours to obtain a dry gel.
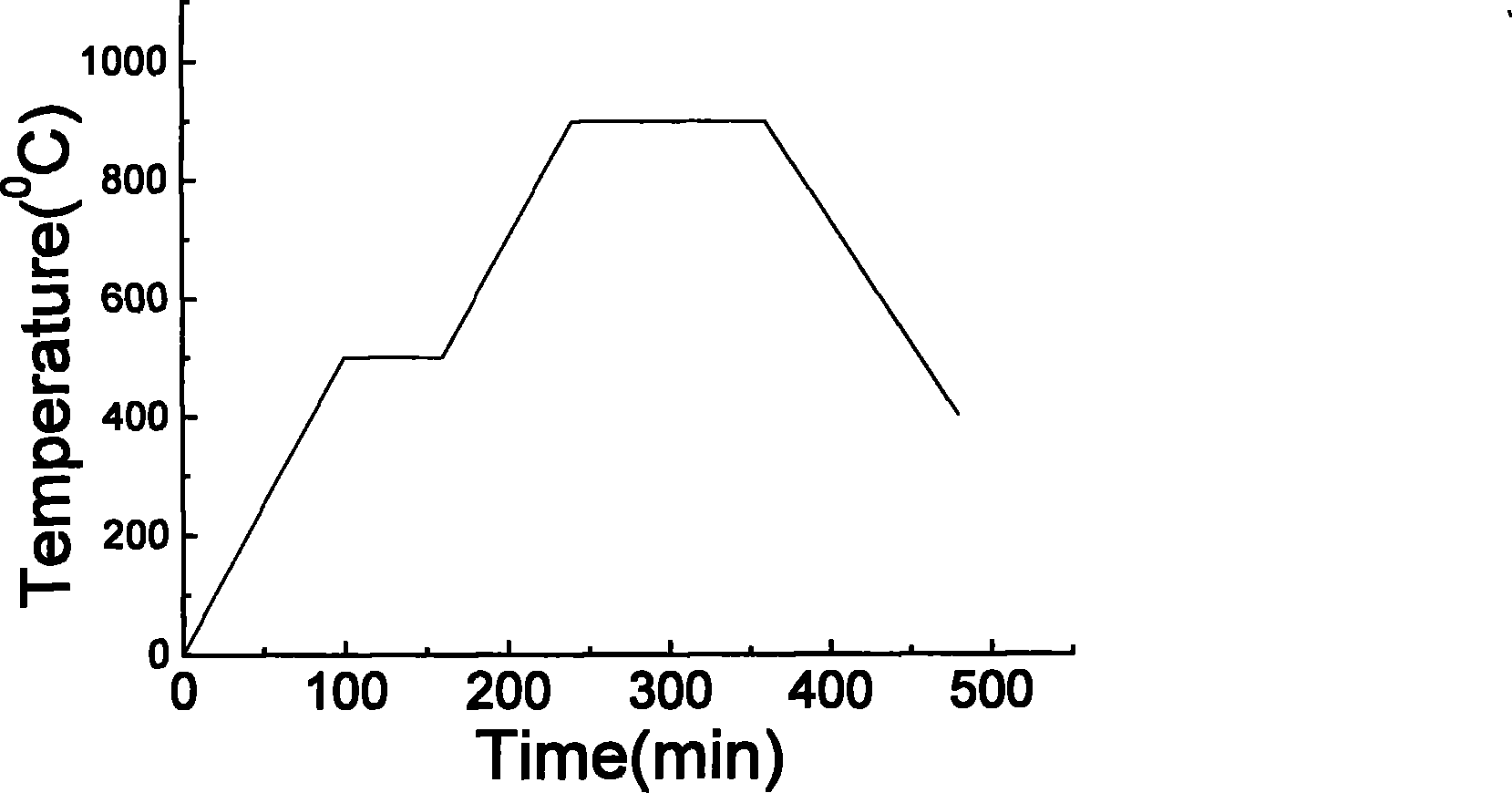
[0035] 5. The first sintering in the muffle furnace, the sintering curve is as follows figure 2 The sintering curve of barium titanate powder sintering temperature changes with time,
[0036] 6. Take out the powder and grind it in the air for 1 hour under the condition of ethanol as the solvent, put the obtained powder into the muffle furnace for secondary sintering, the sintering curve is as follows figure 2 The sintering curve of barium ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] 1. Weigh 0.1mol (25.542g) of barium acetate and dissolve it in 33.4ml of acetic acid solution with a mass fraction of 36% (12ml of acetic acid and 21.4ml of water) and mix well as solution A;
[0041] 2. Measure 0.1mol (35ml) butyl titanate, 0.2mol (11.67ml) ethanol, 0.1mol (5.72ml) acetic acid and mix well as B solution;
[0042] 3. Mix the A and B solutions in a water bath at 40°C for 40 minutes to be in a sol state;
[0043] 4. Then sink in the air for four hours, and bake at 100°C for 20 hours to obtain a dry gel;
[0044] 5. The first sintering in the muffle furnace, the sintering curve is as follows figure 2 The sintering curve of barium titanate powder sintering temperature changes with time (the sintering rate is constant, the sintering temperature is 800°C, and the holding time is constant);
[0045] 6. Take out the powder and grind it in the air for 1 hour under the condition of ethanol as the solvent, and put the obtained powder into the muffle furnace for...
Embodiment 3
[0049] 1. Weigh 0.1mol (25.542g) of barium acetate and dissolve it in 166.8ml of acetic acid solution with a mass fraction of 36% (60ml of acetic acid and 106.8ml of water) and mix well as solution A;
[0050] 2. Measure 0.1mol (35ml) butyl titanate, 0.6mol (35ml) ethanol, 0.2mol (11.5ml) acetic acid and mix them uniformly as B solution;
[0051] 3. Mix the A and B solutions in a water bath at 80°C for 10 minutes to be in a sol state;
[0052] 4. Then sink in the air for six hours, and bake at 100°C for 20 hours to obtain a dry gel;
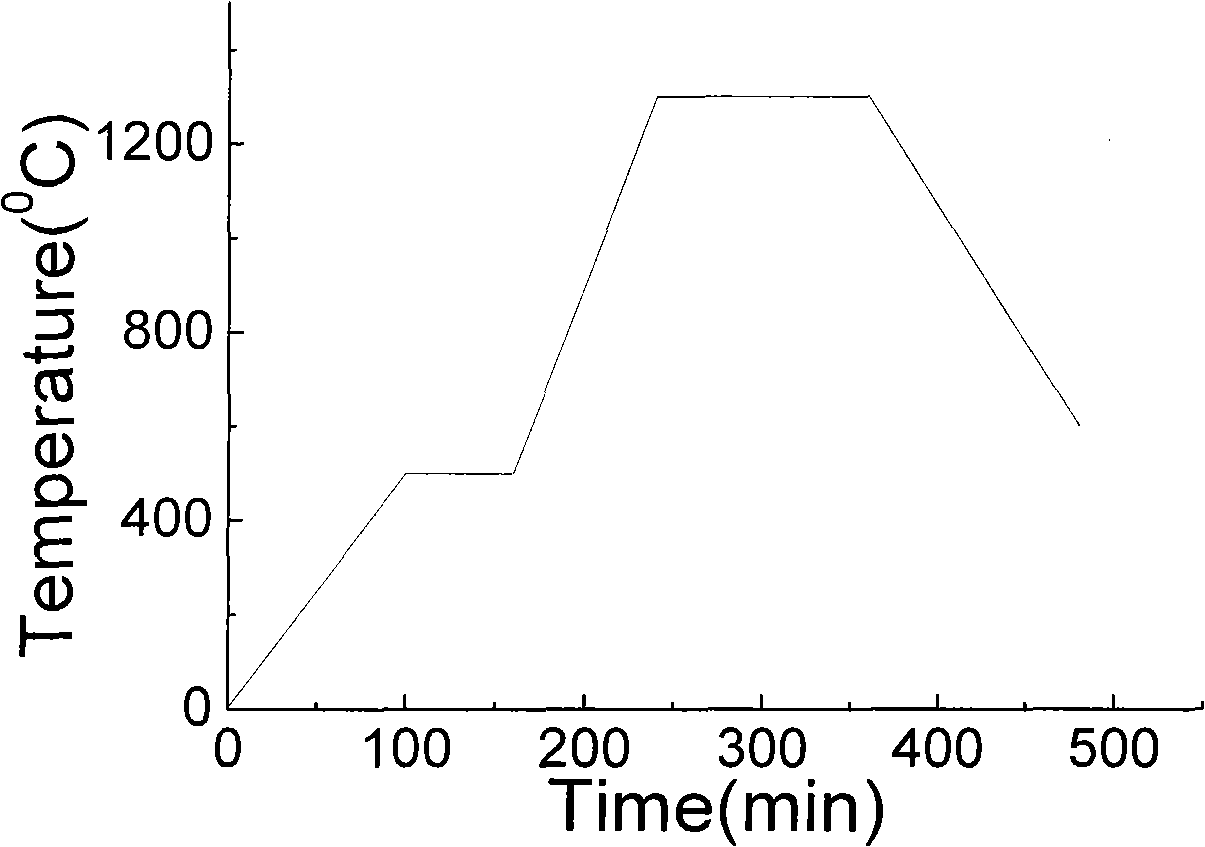
[0053] 5. The first sintering in the muffle furnace, the sintering curve is as follows figure 2 The sintering curve of barium titanate powder sintering temperature changes with time (the sintering rate is constant, the sintering temperature is 1000°C, and the holding time is constant);
[0054] 6. Take out the powder and grind it in the air for 1 hour under the condition of ethanol as the solvent, put the obtained powder into the muffle furnac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com