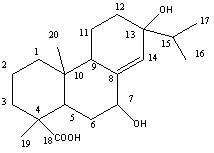
Preparation method of active abietic acid derivatives through biological conversion of rosin
A technology of derivatives and rosin, applied in the fields of fine chemicals and pharmaceutical biology, can solve the problems of limited chemical reaction complexity and little progress, and achieve the effects of high selectivity, cost saving and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
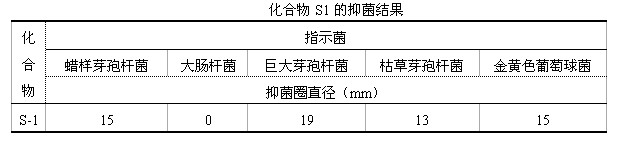
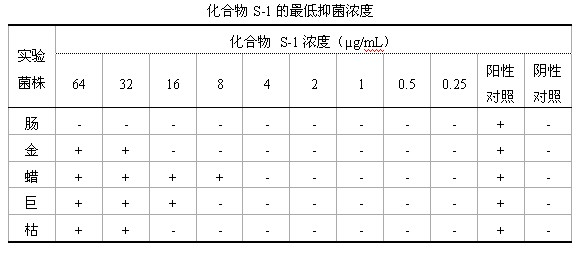
[0033] A. Trichoderma viridans B7 strain was routinely cultured in PDA medium to obtain activated strains, and then inserted into PDB medium for fermentation for 72 hours to obtain mycelium balls; PDA medium was 200g / L of potato + 20g / L of glucose +1.5% agar, pH 6, autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes; PDB medium is 200g / L potato + 20g / L glucose, pH 6, autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes;
[0034] B. Soak the fine absorbent cotton pellets in the PDB culture medium as a solid medium, and use the rosin ground into a fine powder as a substrate;
[0035] C. Add the mycelial balls obtained in step A and the substrate in step B to the fixed medium in step B, and carry out solid-state culture for 6 days;
[0036] D. The solid culture of step C is soaked and extracted with 95% ethanol;
[0037] E. The extract obtained in step D is filtered and concentrated to obtain the crude extract of the conversion product;
[0038] F. The crude extract of the conversion product was extracted wi...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A. Trichoderma viridans B7 strain was routinely cultured in PDA medium to obtain activated strains, and then inserted into PDB medium for fermentation for 60 hours to obtain mycelium balls; PDA medium was 200g / L of potato + 20g / L of glucose +2% agar, pH value is 6, autoclaved at 121°C for 20 minutes; PDB medium is 200g / L potato + 20g / L glucose, pH value is 6, autoclaved at 121°C for 20 minutes;
[0041] B. Soak the fine absorbent cotton pellets in the PDB culture medium as a solid medium, and use the rosin ground into a fine powder as a substrate;
[0042] C. Add the mycelial balls obtained in step A and the substrate in step B to the fixed medium in step B, and carry out solid-state culture for 5 days;
[0043] D. The solid culture of step C is soaked and extracted with 95% ethanol;
[0044] E. The extract obtained in step D is filtered and concentrated to obtain the crude extract of the conversion product;
[0045] F. The crude extract of the conversion produc...
Embodiment 3
[0047] A. Trichoderma viridans B7 strain was routinely cultured in PDA medium to obtain activated strains, and then inserted into PDB medium for fermentation for 48 hours to obtain mycelium balls; PDA medium was 200g / L of potato + 20g / L of glucose +1.5% agar, pH 6, autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes; PDB medium is 200g / L potato + 20g / L glucose, pH 6, autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes;
[0048] B. Soak the fine absorbent cotton pellets in the PDB culture medium as a solid medium, and use the rosin ground into a fine powder as a substrate;
[0049] C. adding the mycelial balls obtained in step A and the substrate in step B to the fixed medium in step B, and carrying out solid-state culture for 7 days;
[0050] D. The solid culture of step C is soaked and extracted with 95% ethanol;
[0051] E. The extract obtained in step D is filtered and concentrated to obtain the crude extract of the conversion product;
[0052] F. The crude extract of the conversion product was extrac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com