Method for extracting grease from oleaginous microorganisms
A technology for oil-producing microorganisms and oil extraction, which is applied in the field of microbial engineering, can solve the problems of reduced oil content, poor oil yield, and small ultrasonic processing capacity, and achieves mild reaction conditions, is conducive to industrial production, and high oil yield. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
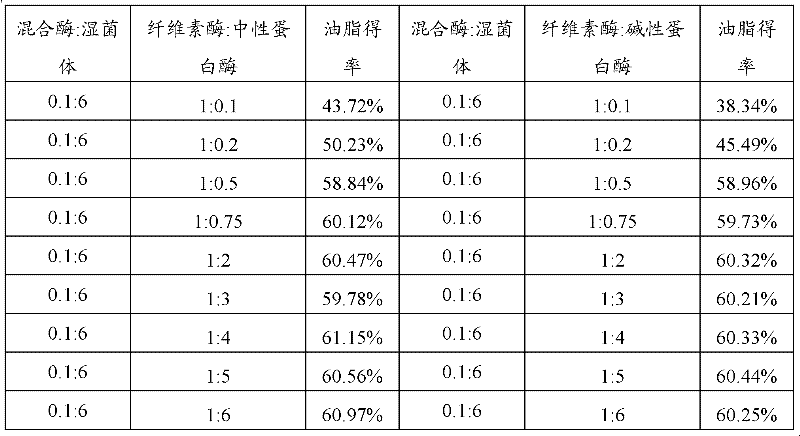
[0032] Embodiment 1: Extract oil from chlorella
[0033] The chlorella fermentation broth was centrifuged at 7000rpm / min for 10min, the supernatant was removed to obtain the wet chlorella cells, and 0.6g of the wet chlorella cells were weighed in a 100ml Erlenmeyer flask. Weigh 0.057g cellulase, 0.043g neutral protease, cellulase activity is 1000U / g, neutral protease activity is 60000U / g, add citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution with pH=4 to dilute to 100ml, prepared as a 0.1% enzyme solution, 10ml of the enzyme solution was added to the wet chlorella cell, the hydrolysis temperature was 40°C, and stirred for 4h. The hydrolyzed suspension was centrifuged at 4800r / min for 10min, the supernatant was removed, and then No. 6 organic solvent was added to the obtained precipitate for repeated extraction three times to obtain oil, and the yield of oil was 60.12%.
Embodiment 2
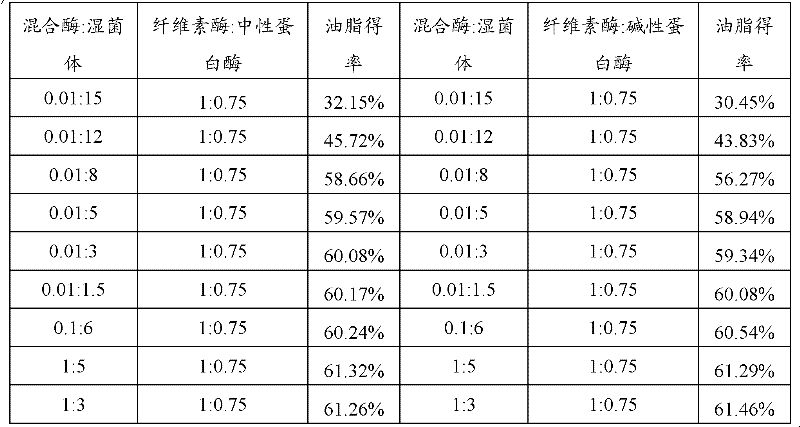
[0034] Embodiment 2: extract oil and fat from spirulina
[0035] Centrifuge the spirulina fermentation broth at 7000rpm / min for 10min, remove the supernatant to obtain the wet spirulina cells, weigh 1.0g of the wet spirulina cells into a 100ml Erlenmeyer flask. Weigh 0.05g cellulase, 0.05g alkaline protease, cellulase activity is 1200U / g, alkaline protease activity is 2.02×10 5 U / g, add citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution with a pH value of 5 to settle to 100ml, prepare 0.1% enzyme solution, get 15ml enzyme solution and add it to the spirulina wet thallus, the hydrolysis temperature is 40°C, Stir for 5h. The hydrolyzed suspension was centrifuged at 4800r / min for 10min, the supernatant was removed, and then No. 6 organic solvent was added to the obtained precipitate for three times of leaching to obtain oil, and the yield of oil was 61.3%.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: Extract oil from Rhodotorula viscosus
[0037] Centrifuge the Rhodotorula viscosum fermentation broth at 7000rpm / min for 10min, remove the supernatant to obtain the Rhodotorula viscosum wet cell, weigh 0.6g of the Rhodotorula viscose wet cell into a 100ml Erlenmeyer flask. Weigh 0.1g of neutral protease, the activity of neutral protease is 60000U / g, add citric acid-sodium citrate buffer solution with pH=7 to set the volume to 100ml, prepare 0.1% enzyme solution, take 10ml enzyme solution, appropriate amount Tween 20 was added to the wet cells of Rhodotorula viscosus, the hydrolysis temperature was 42°C, and the hydrolysis was performed at 60 rpm / min for 36 hours. The hydrolyzed suspension was centrifuged at 4800r / min for 10min, the supernatant was removed, and then No. 6 organic solvent was added to the obtained precipitate for three times of leaching to obtain oil, and the yield of oil was 60.3%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com