Wavelength up-conversion semiconductor structure and optical detection method thereof
A technology of semiconductors and wavelengths, which is applied in semiconductor devices, using electric radiation detectors for photometry, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of high dark counts of detectors and the inability to obtain a high enough signal-to-noise ratio, and achieve the goal of reducing dark counts Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
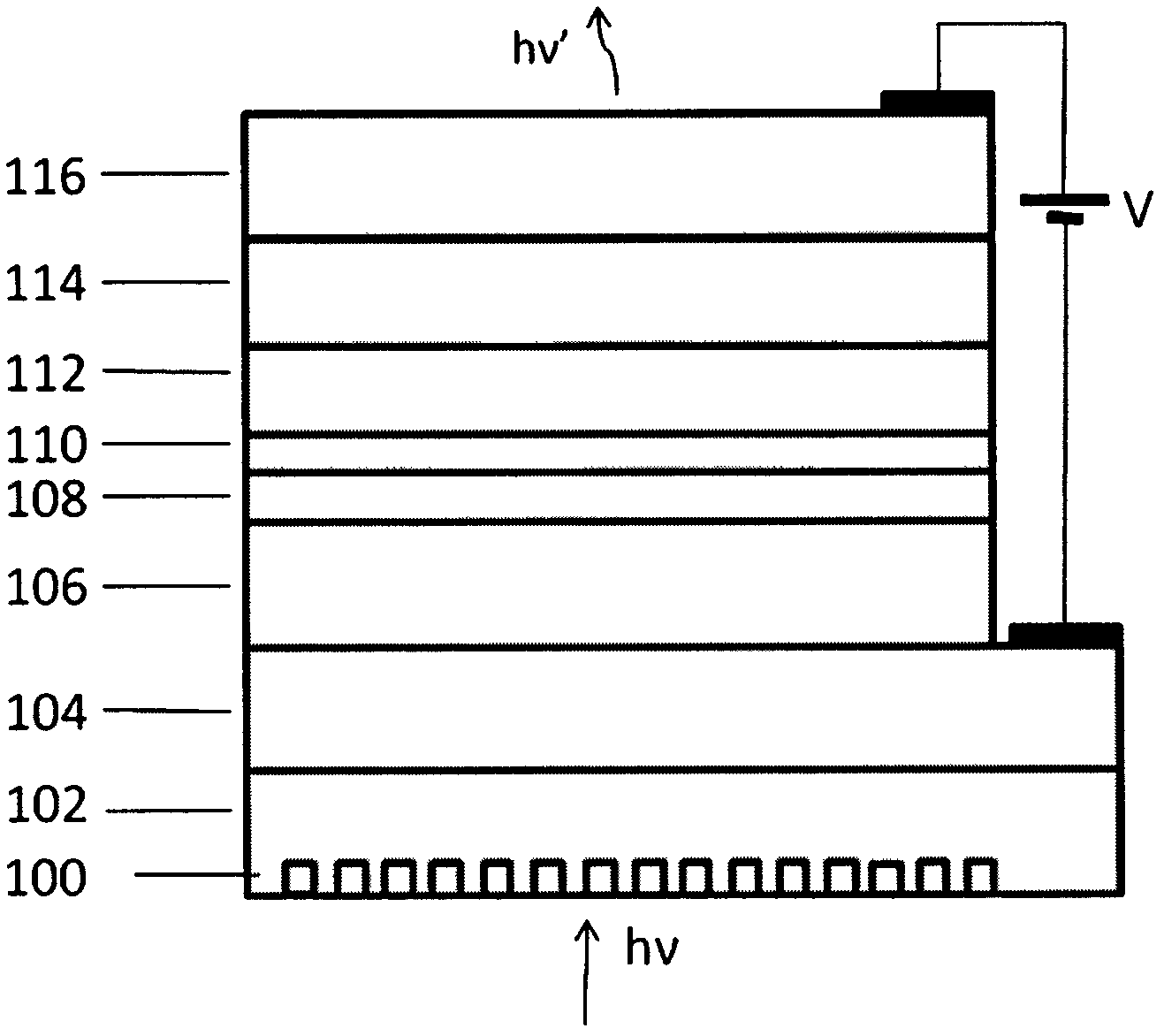
[0023] The structure of the 7μm infrared light up-conversion device described in this example is as follows figure 1 As shown, the structural material is sequentially grown on a GaAs substrate using typical semiconductor material epitaxy techniques such as molecular beam epitaxy and metal-organic chemical vapor deposition techniques. The grating structure on the GaAs substrate is made by semiconductor processing technology.
[0024] Among them, 100 is a grating structure, which is used to convert the infrared light incident on the vertical surface into components that can be absorbed by the quantum well subband, 102 is the GaAs substrate, 104 is the n-type GaAs lower electrode contact layer, and 105 is 30nm n-type Al 0.3 Ga 0.7 As transition layer, 106 is 50nm Al 0.8 Ga 0.2 As transition layer, 108 is a doping concentration of 8×10 18 cm -3 , an n-type GaAs quantum well layer with a thickness of 4nm, 110 is a 2nm AlAs barrier layer, and 112 is an 8nm Al 0.2 Ga 0.8 As qu...
Embodiment 2
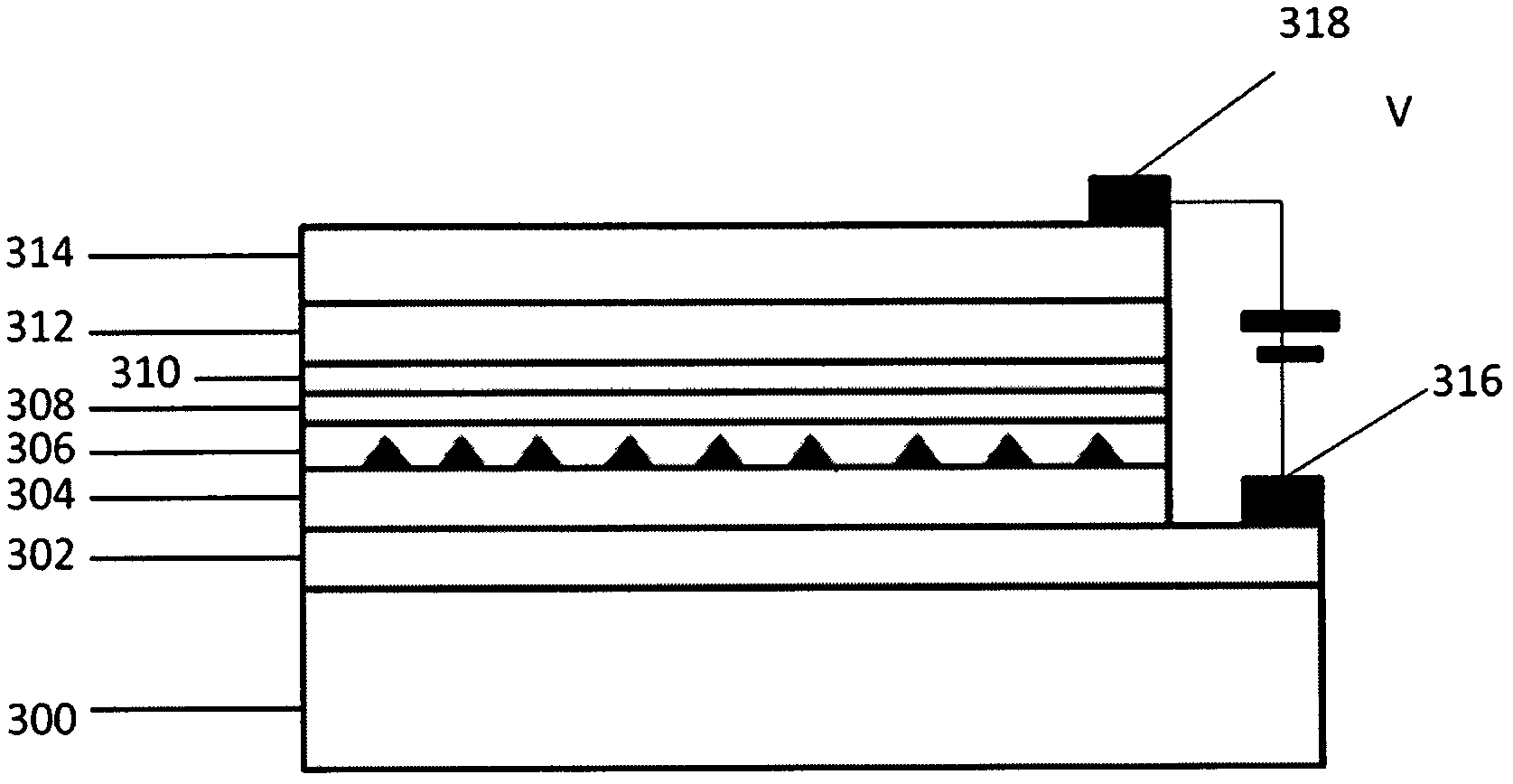
[0028] The structure of the 2μm infrared light up-conversion device described in this example is as follows image 3 As shown, the structural material is sequentially grown on a sapphire substrate using typical semiconductor material epitaxy techniques, such as molecular beam epitaxy technology, metal-organic chemical vapor deposition technology, etc.
[0029] Among them, 300 is a sapphire substrate, 302 is a 200nm n-type AlN lower electrode contact layer, 304 is a 100nm AlN transition layer, 306 is a GaN quantum dot with an average size of 4nm, 308 is a 2nm AlN barrier, and 310 is a 2nm Al 0.3 Ga 0.7 N quantum well, 312 is a 100nm AlN transition layer, 314 is a 100nm p-type GaN upper electrode contact layer, 316 is an n-type electrode, and 318 is a p-type electrode.
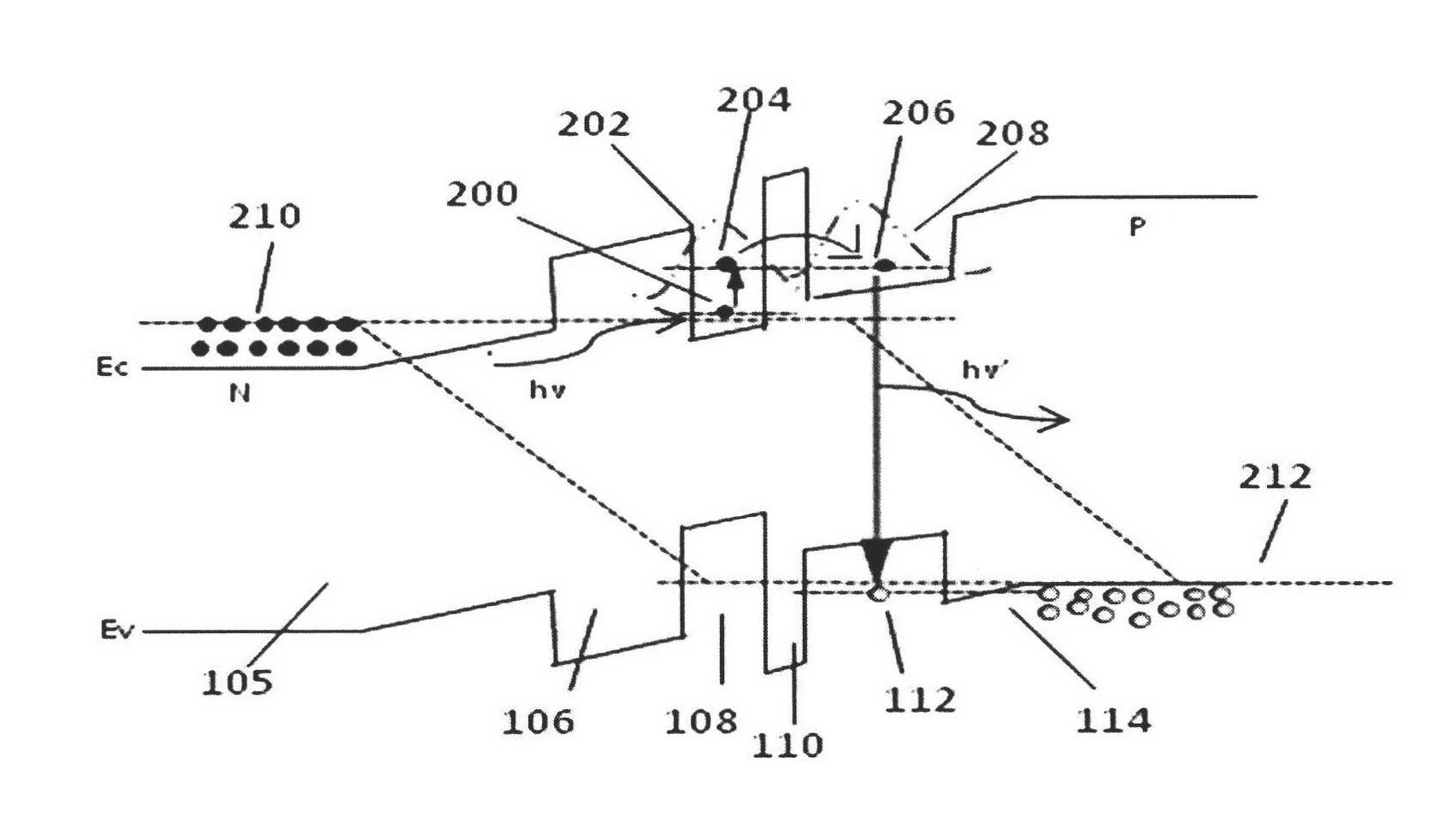
[0030] The energy band structure of the 2 μm infrared light up-conversion device described in this example is as follows Figure 4 shown. 400 is the ground state energy level of GaN quantum dot conduction ban...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The structure of the 3.1 μm infrared light up-conversion device described in this example is as follows Figure 5 As shown, the structural material is sequentially grown on a GaAs substrate using typical semiconductor material epitaxy techniques such as molecular beam epitaxy and metal-organic chemical vapor deposition techniques.
[0034] Among them, 500 is GaAs substrate; 502 is n+Al 0.5 Ga 0.5 As lower electrode contact layer, thickness 300nm; 504 is n-Al 0.5 Ga 0.5 As transition layer, thickness 500nm; 506 is i-Al 0.5 Ga 0.5 As transition layer, thickness 50nm; 508 is i-Al 0.8 Ga 0.2 As electron blocking layer, thickness 50nm; 510 is i-Al 0.5 Ga 0.5 As transition layer, thickness 50nm; 512 is i-Al 0.25 In 0.75 As quantum dots, the average size of quantum dots is 8nm, the energy difference between the conduction band ground state energy level and the excited state energy level of quantum dots is 0.4eV, and the quantum dot conduction band excited state energ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com