Patents
Literature
136 results about "Electron excitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
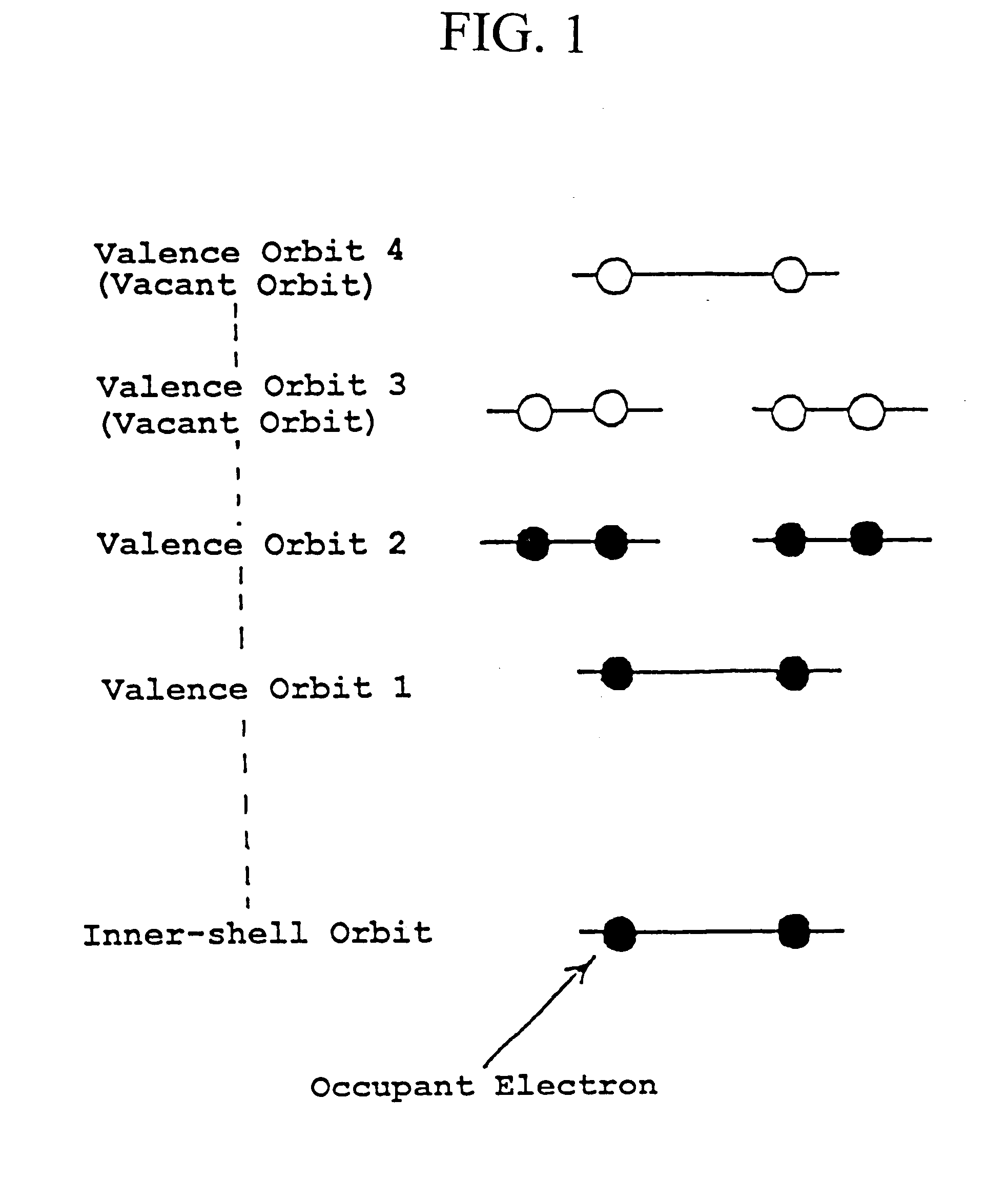
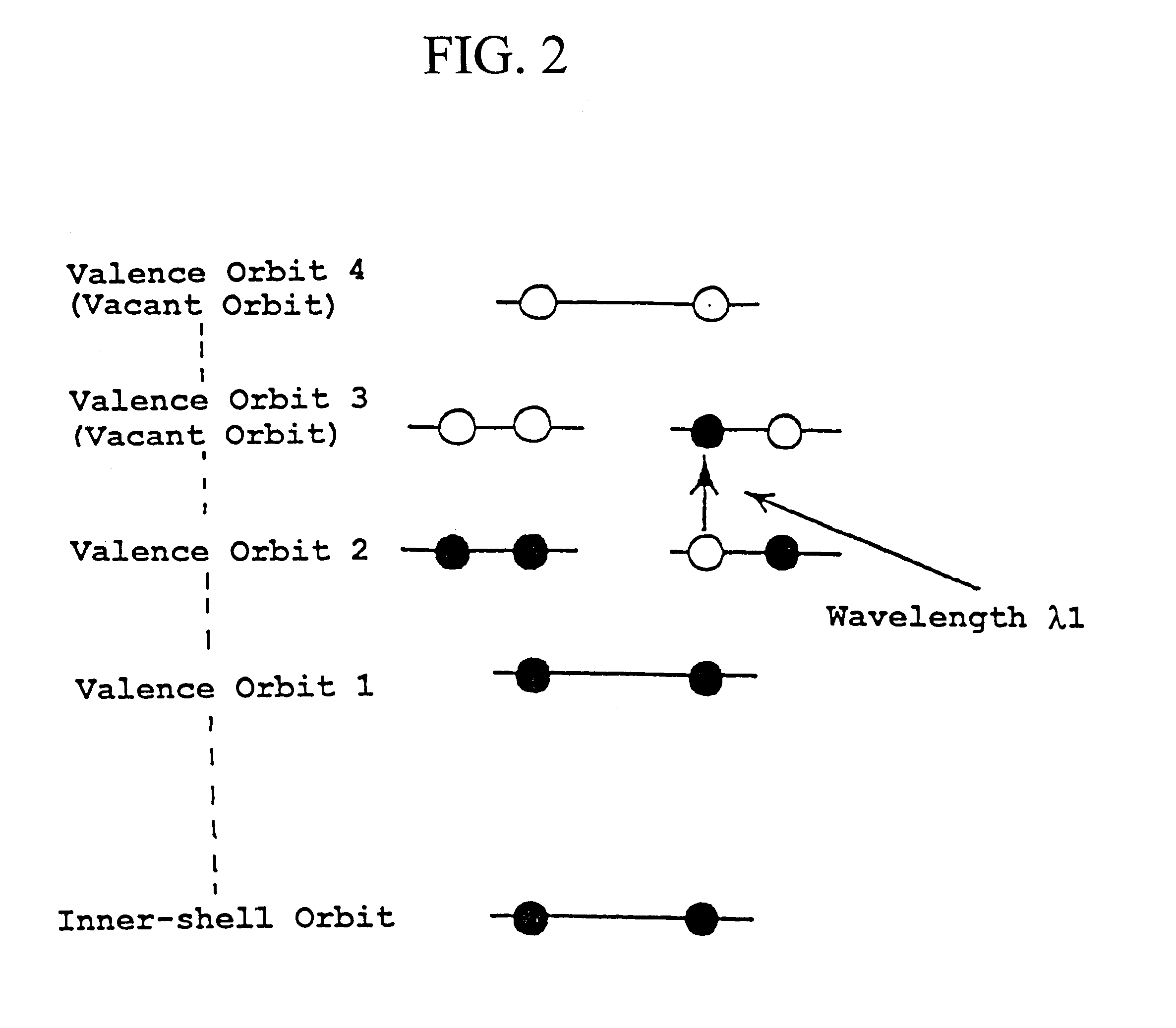
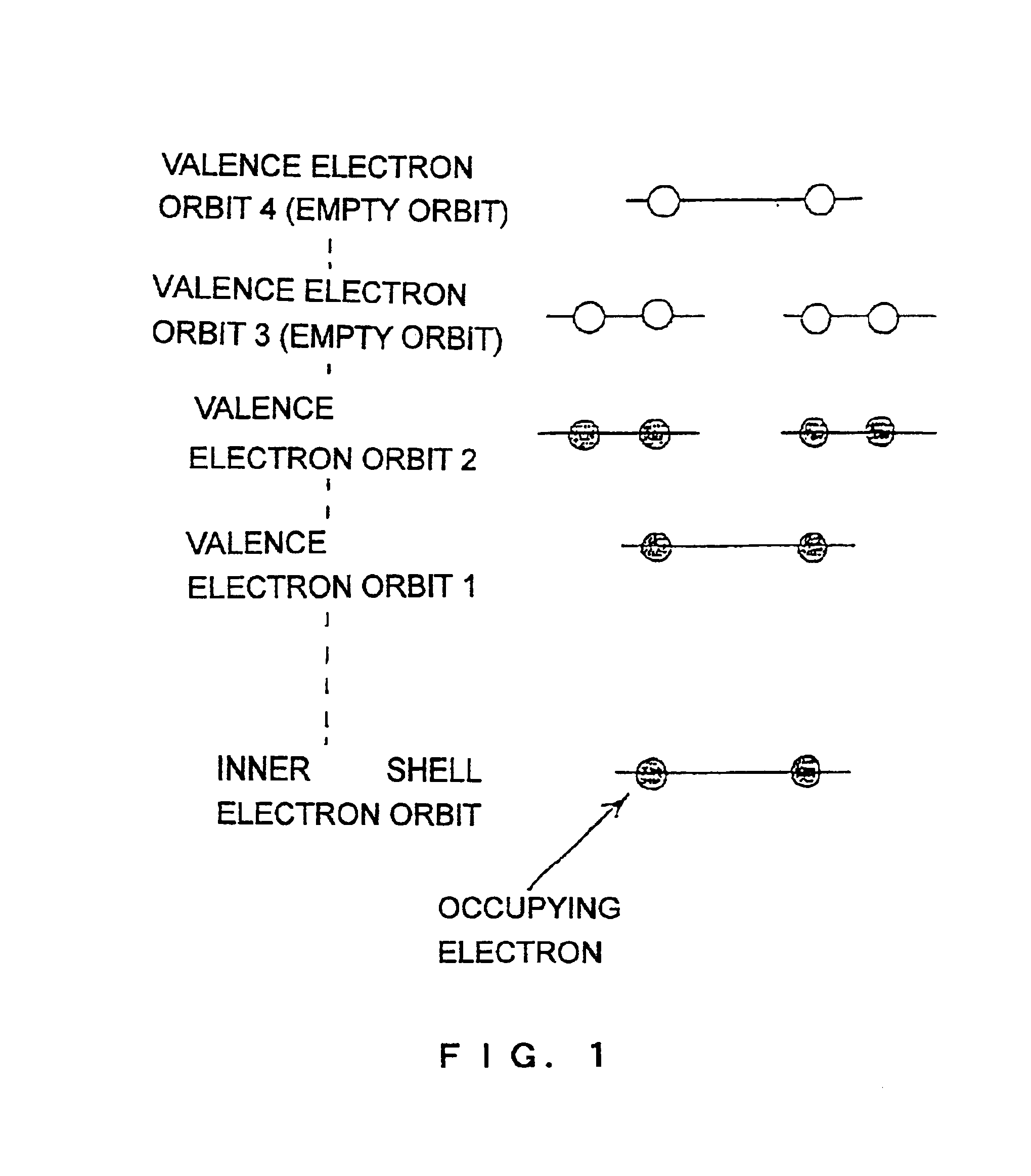
Electron excitation is the transfer of a bound electron to a more energetic, but still bound state. This can be done by photoexcitation (PE), where the electron absorbs a photon and gains all its energy or by electrical excitation (EE), where the electron receives energy from another, energetic electron. Within a semiconductor crystal lattice, thermal excitation is a process where lattice vibrations provide enough energy to transfer electrons to a higher energy band such as a more energetic sublevel or energy level. When an excited electron falls back to a state of lower energy, it undergoes electron relaxation. This is accompanied by the emission of a photon (radiative relaxation) or by a transfer of energy to another particle. The energy released is equal to the difference in energy levels between the electron energy states.
Super-resolution microscope system and method for illumination
InactiveUS6667830B1High resolutionReducing diffractive limitPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersElectronic statesExcited state
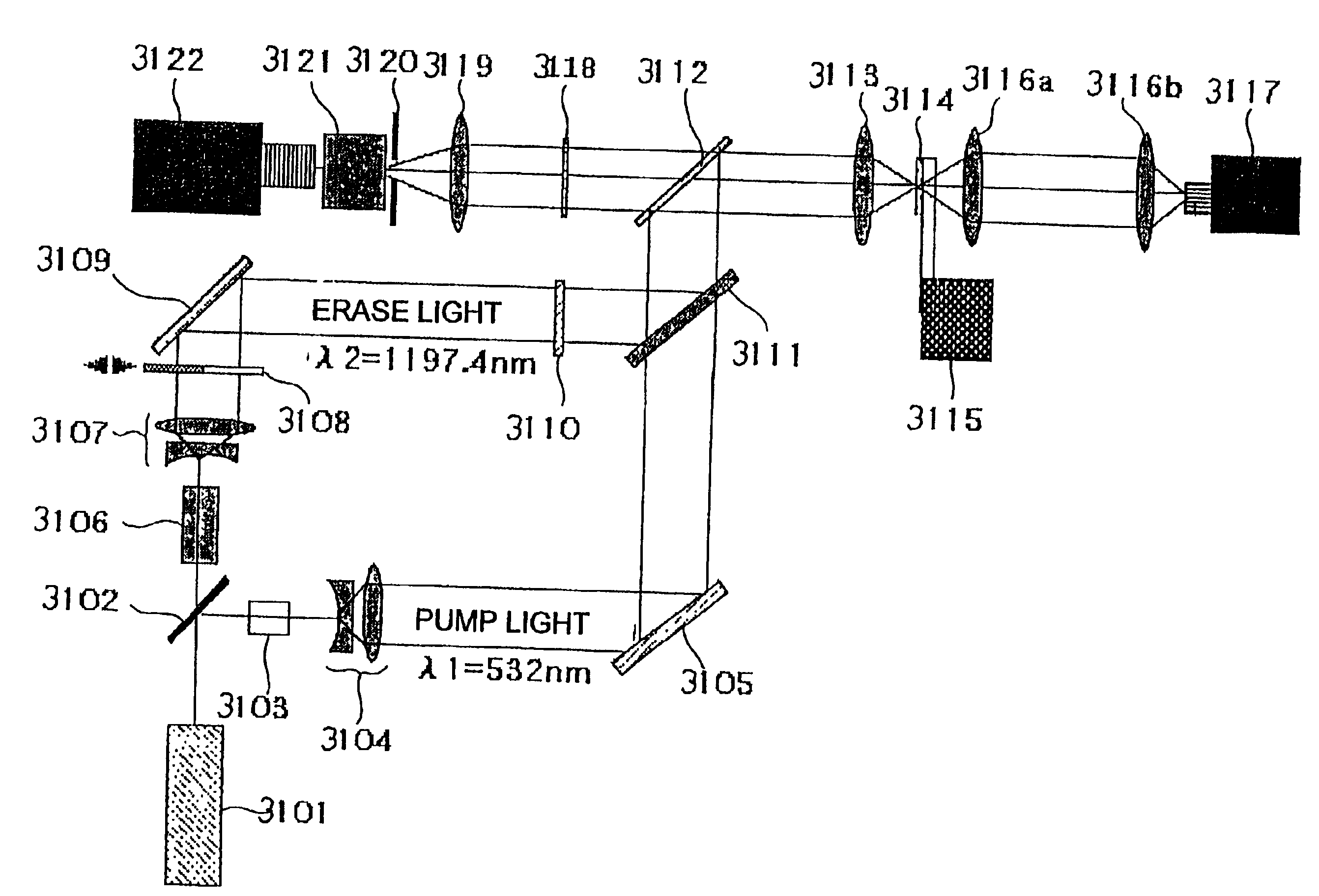
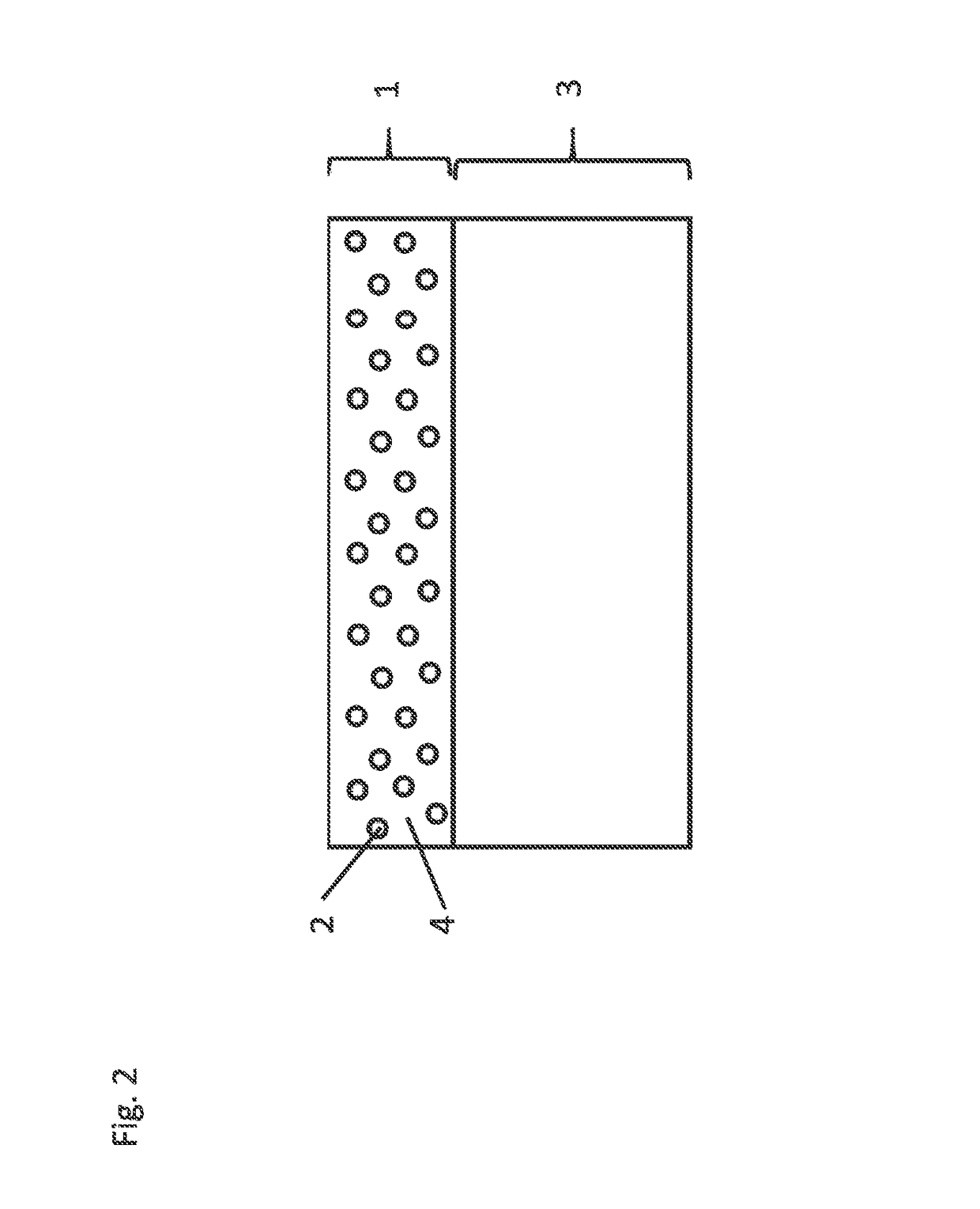
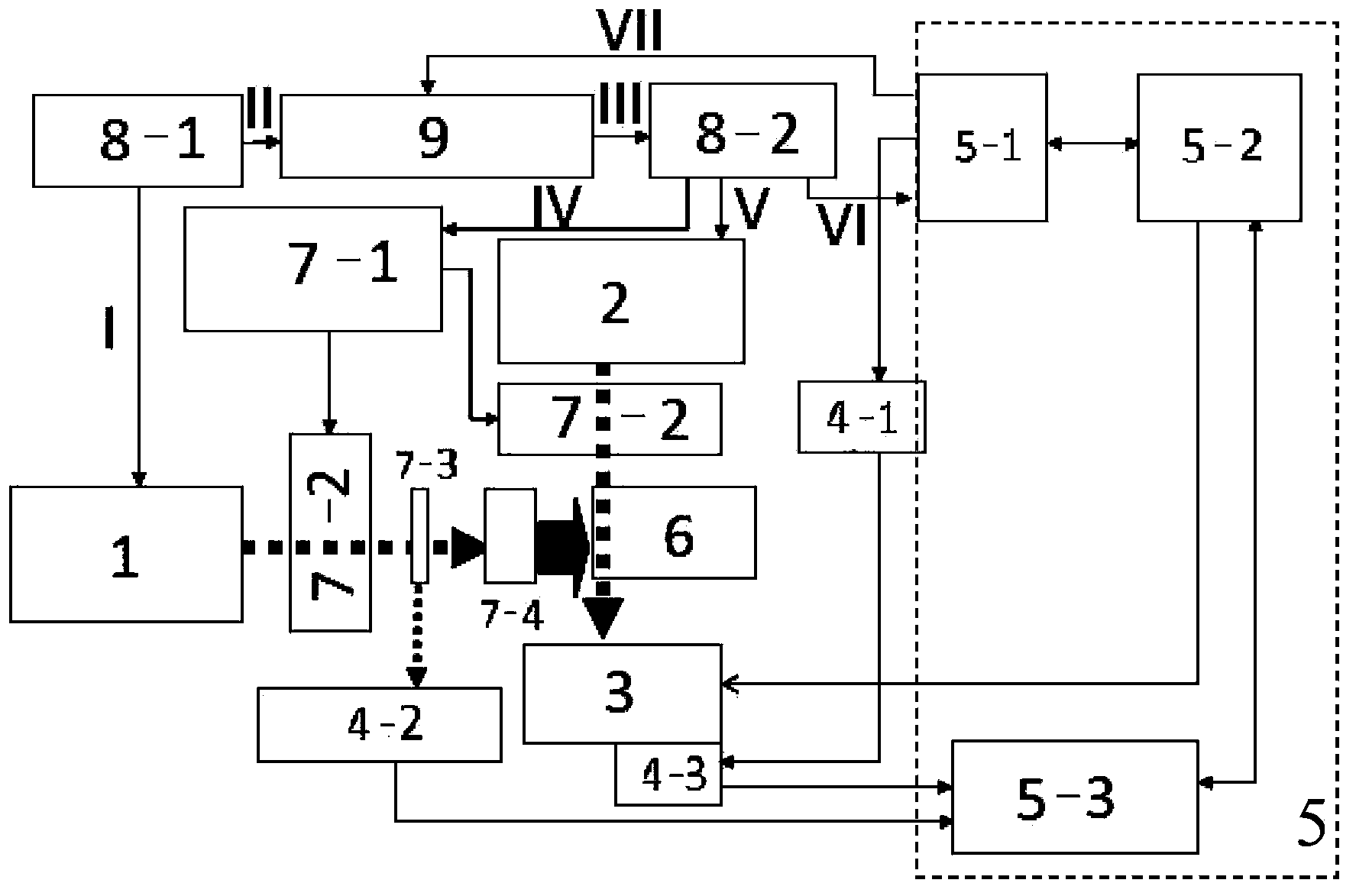
A microscope system comprising an adjusted specimen and a microscope body, wherein the adjusted specimen is dyed with molecule which has three electronic states including at least a ground state and in which an excited wavelength band from the first electron excited state to the second electron excited state overlaps a fluorescent wavelength band upon deexcitation through a fluorescence process from the first electron excited state to a vibrational level in the ground state. There is provided a novel microscope system which is enabled to condense an erase light for exciting a molecule in the first electron excited state to the second electron excited state in an excellent beam profile by using a simple, compact optical system and which has high stability and operability and an excellent super-resolution.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
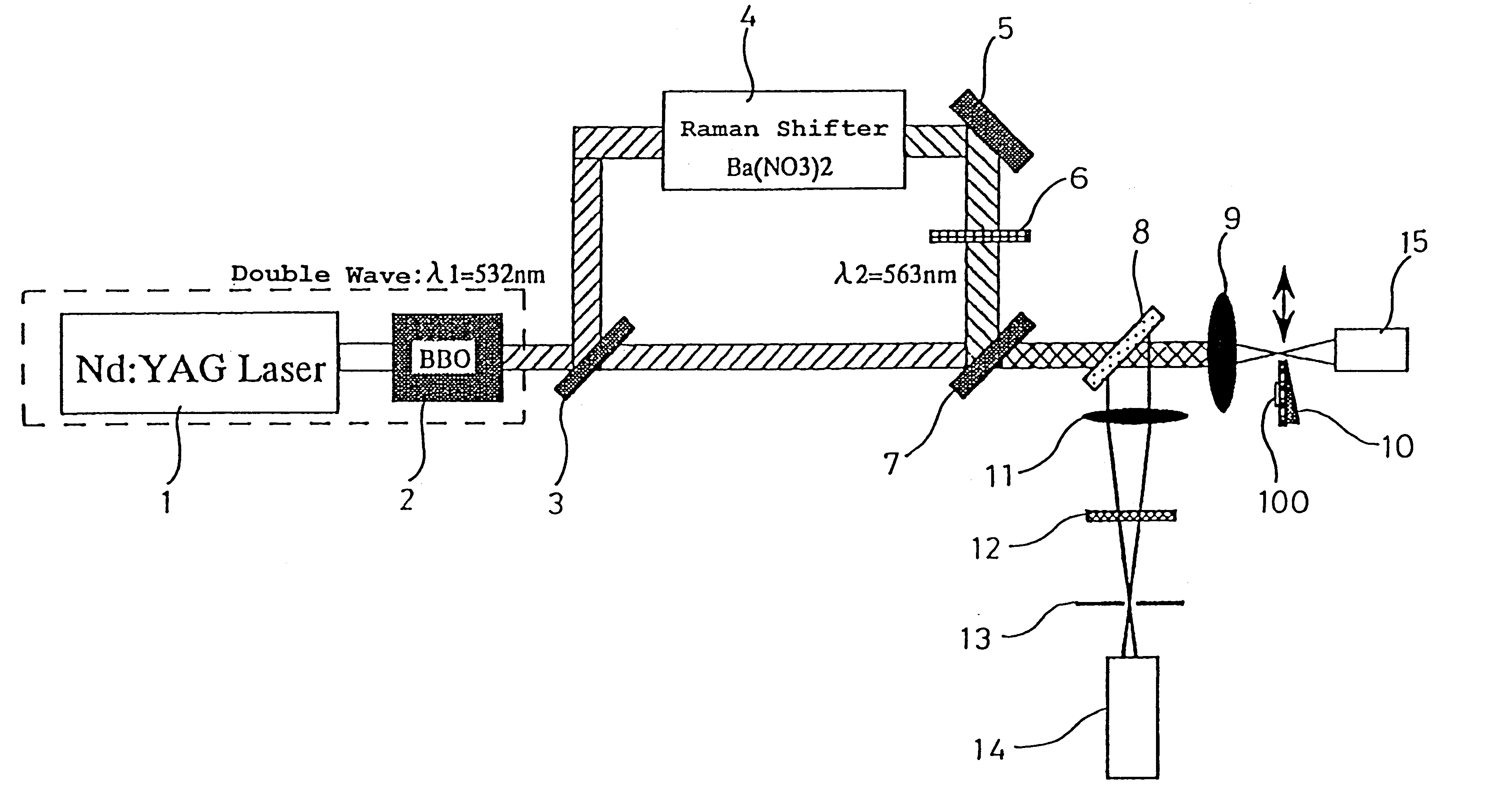
Double-resonance-absorption microscope
InactiveUS6844963B2Easy to operateImprove maintainabilityEmission spectroscopyRaman/scattering spectroscopyExcited stateResonance
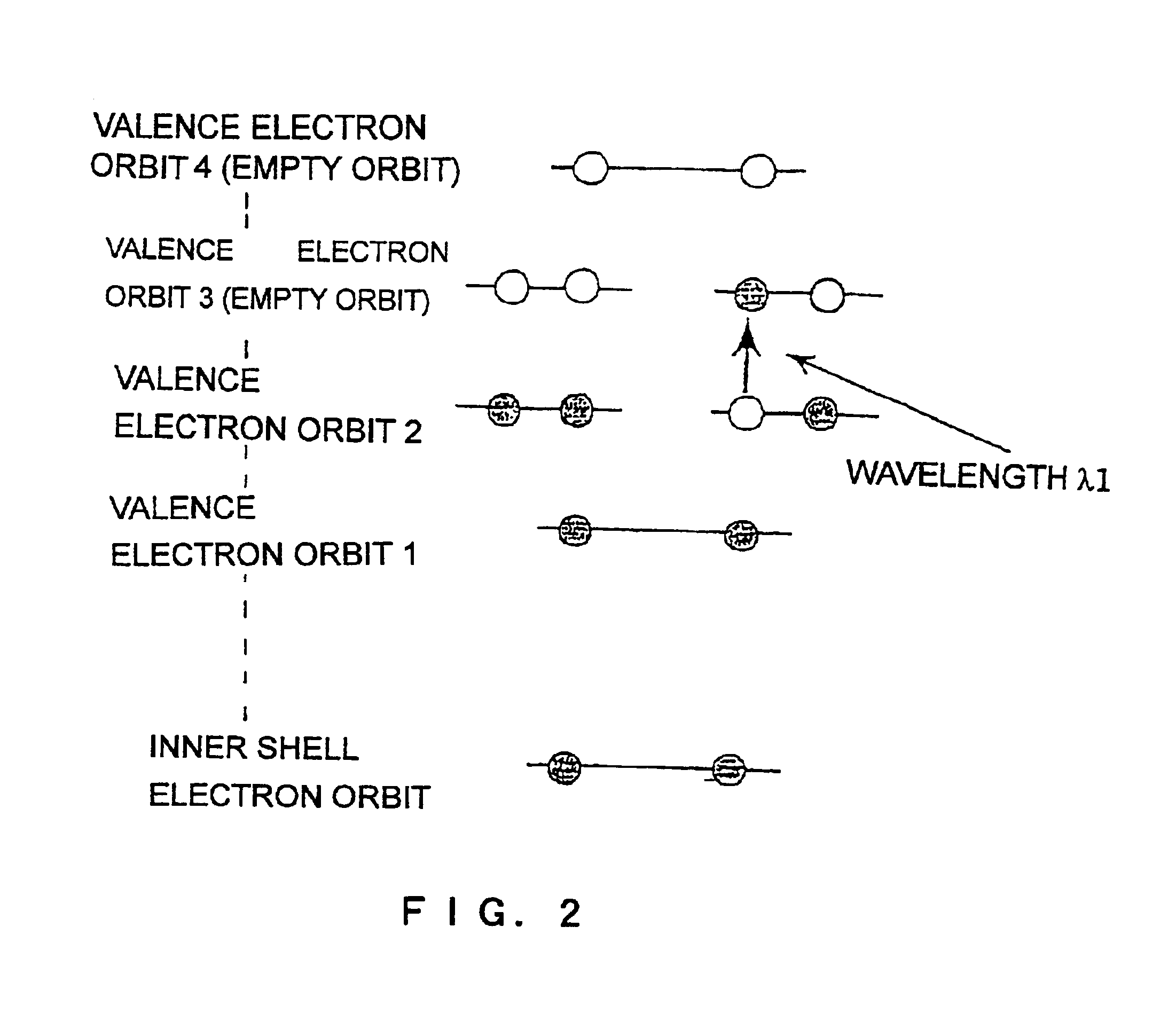
The present invention provides various embodiments of a double-resonance-absorption microscope which realizes a super-resolution by using double resonance absorption. In particular, a double-resonance-absorption microscope includes a light source for a pump light of a wavelength λ1 which excites a sample molecule to a first electronic excited state from a ground state, a light source for an erase light of a wavelength λ2 which excites the sample molecule to a second electronic excited state or a higher excited state from the first electronic excited state, and an overlap component for partially overlapping irradiating areas of the pump light and the erase light with each other. An emission area upon deexcitation of the sample molecule to the ground state from the first electronic excited state is partially inhibited by irradiating the pump light and the erase light through the overlap means. On an optical path of the erase light, a spatial filter is provided which has a condenser lens, a collimate lens, and a pinhole therebetween, and performs condensing of the erase light onto the pinhole by the condenser lens and collimating of the erase light passed through the pinhole into a parallel beam by the collimate lens.
Owner:NIPON ROPER KK +1
Multi element, multi color solid state LED/laser
InactiveUS7084436B2Efficient changeEfficient emissionsSemiconductor laser arrangementsSolid-state devicesHigh energyRare earth
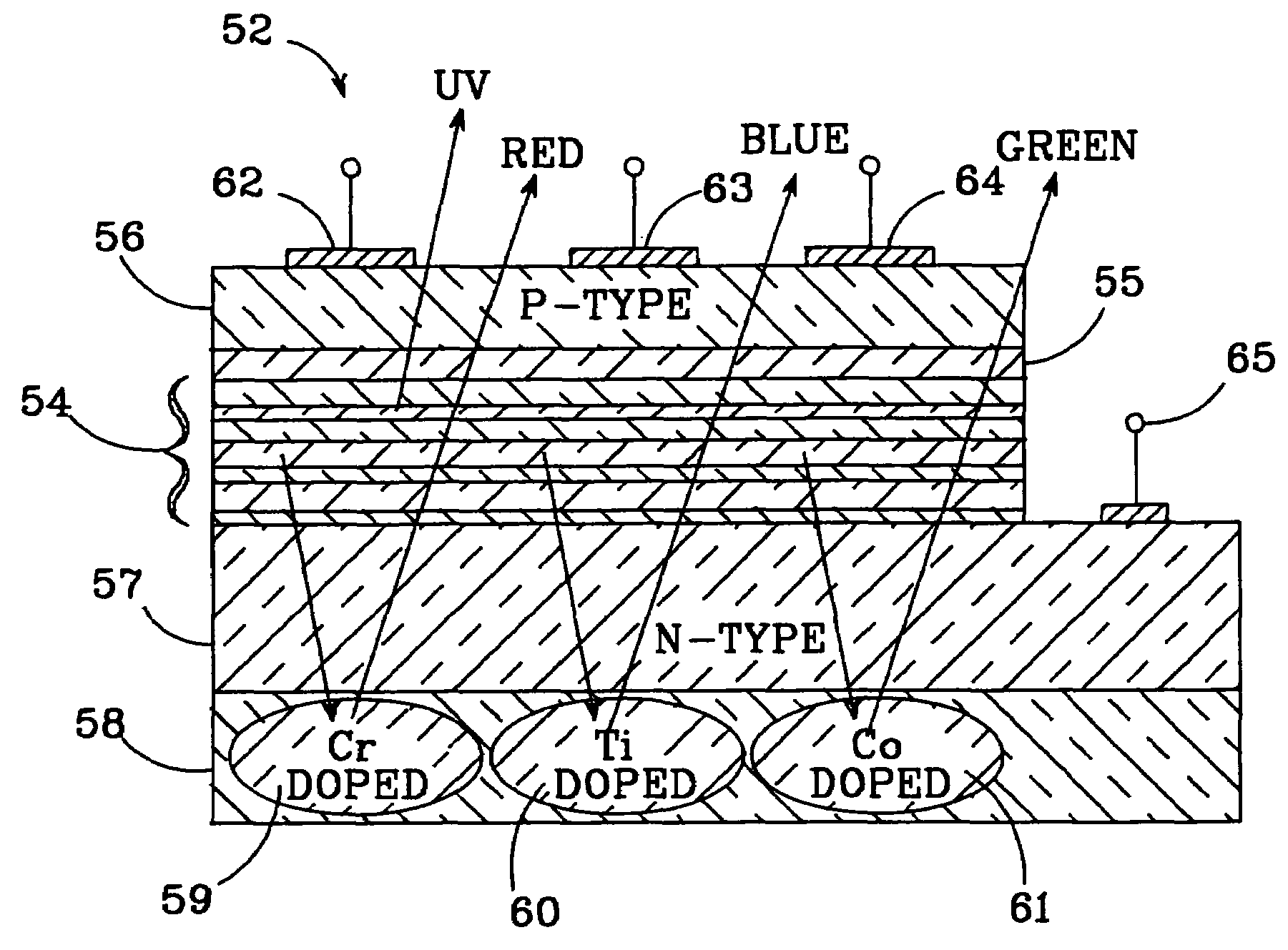
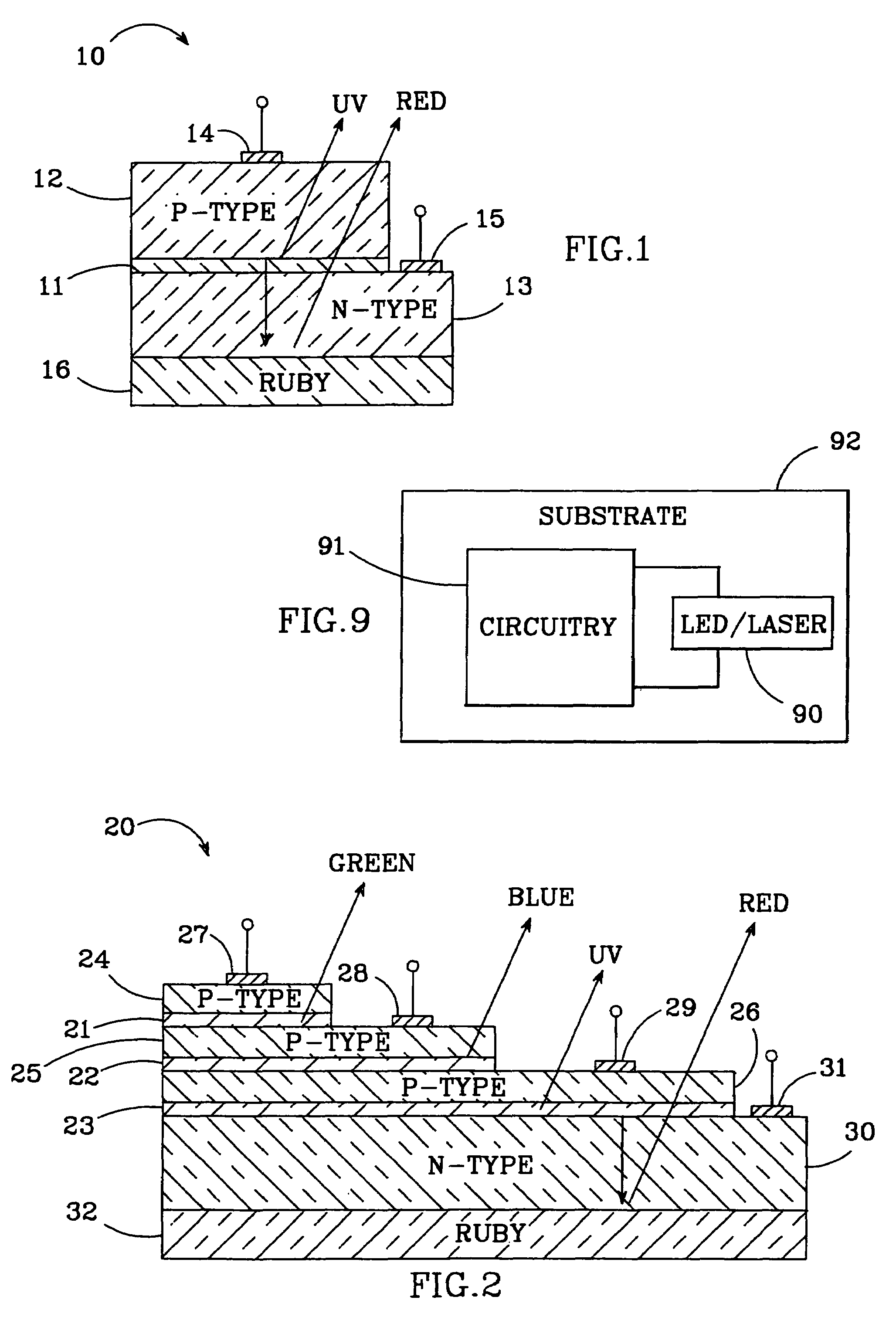
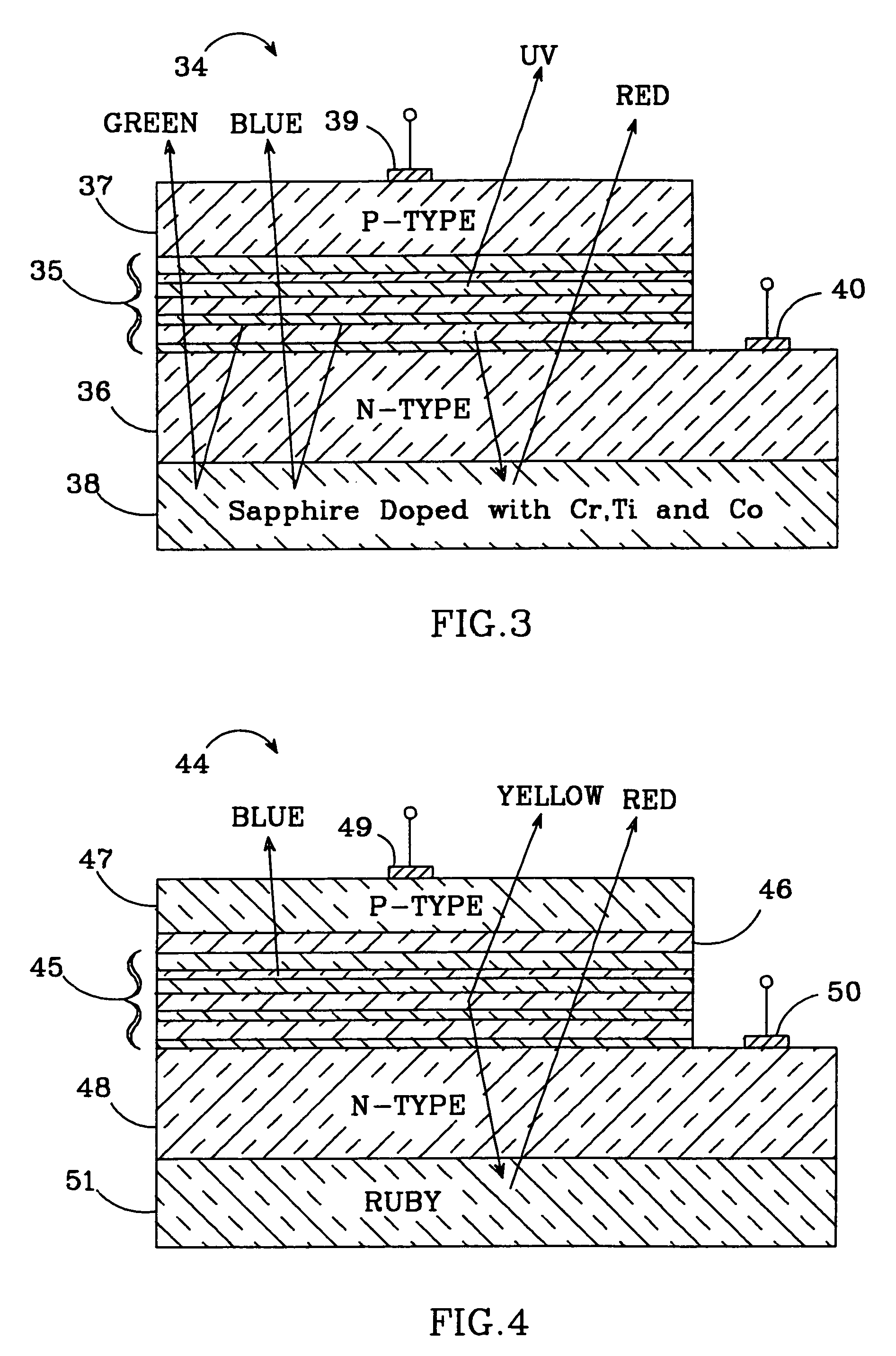
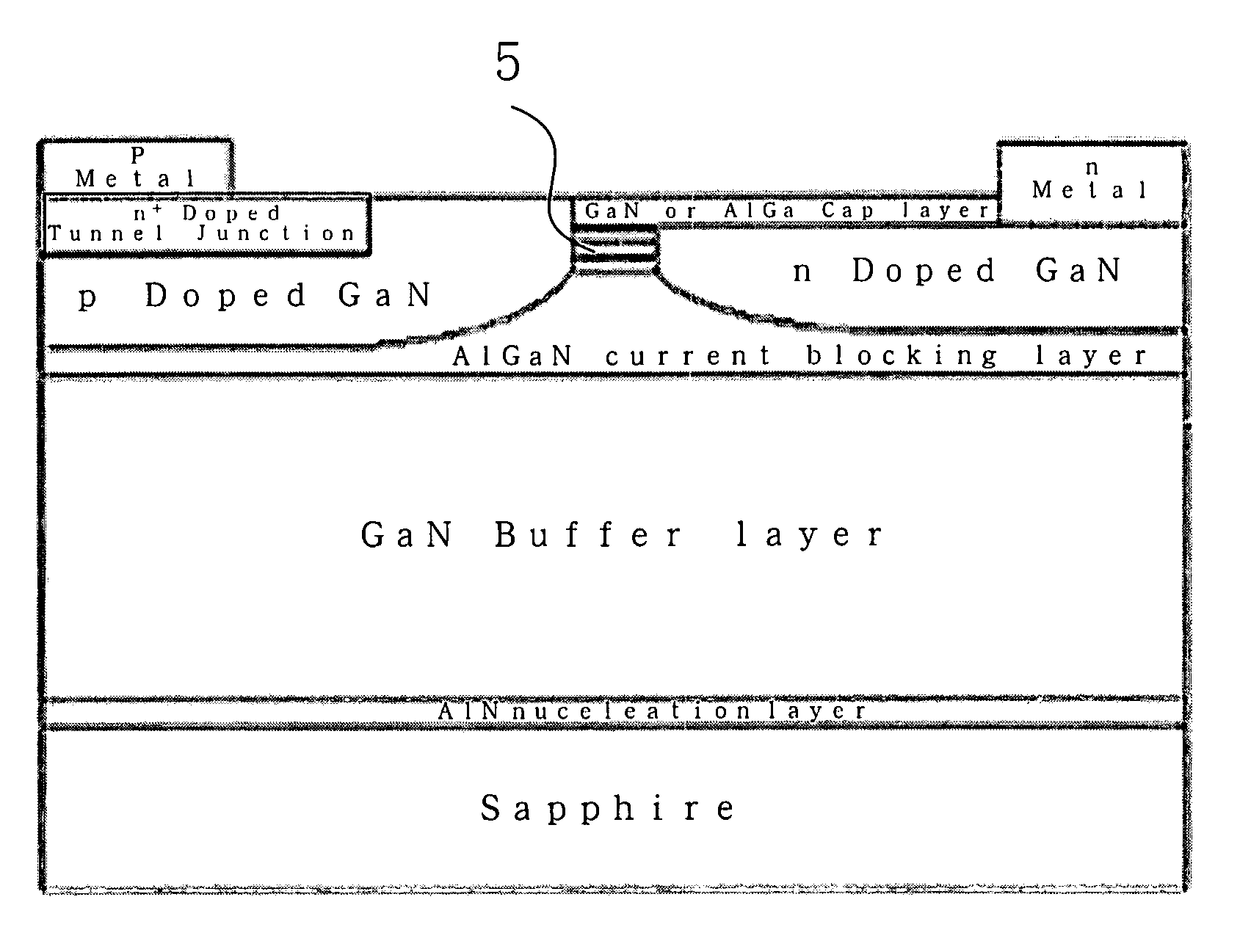
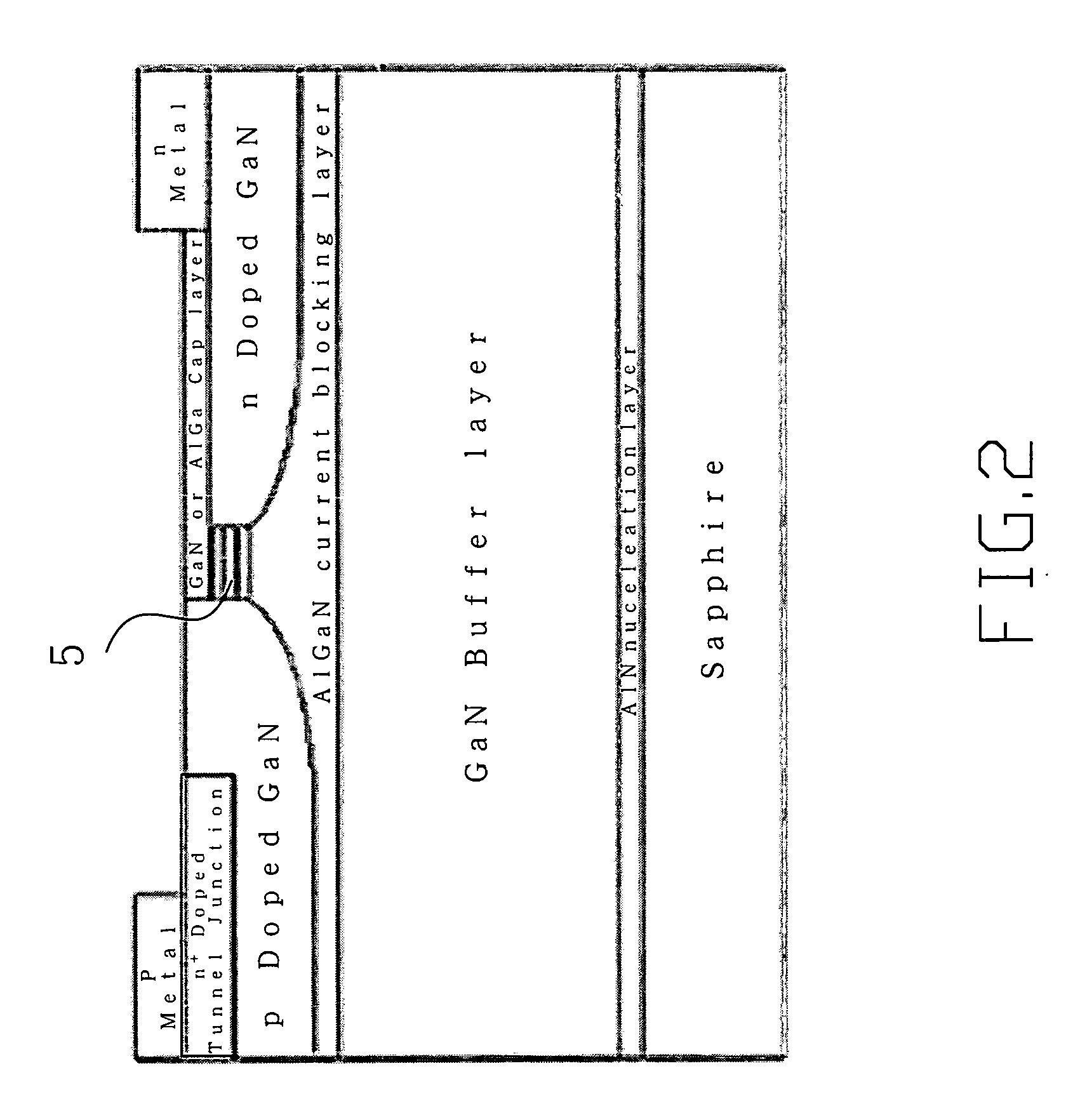
A light emitting diode (LED) grown on a substrate doped with one or more rare earth or transition element. The dopant ions absorb some or all of the light from the LED's active layer, pumping the electrons on the dopant ion to a higher energy state. The electrons are naturally drawn to their equilibrium state and they emit light at a wavelength that depends on the type of dopant ion. The invention is particularly applicable to nitride based LEDs emitting UV light and grown on a sapphire substrate doped with chromium. The chromium ions absorb the UV light, exciting the electrons on ions to a higher energy state. When they return to their equilibrium state they emit red light and some of the red light will emit from the LED's surface. The LED can also have active layers that emit green and blue and UV light, such that the LED emits green, blue, red light and UV light which combines to create white light. Alternatively, it can have one active layer and grown on a sapphire substrate doped with Cr, Ti, and Co such that the substrate absorbs the UV light and emits blue, green, and red light. The invention is also capable of providing a tunable LED over a variety of color shades. The invention is also applicable to solid state laser having one or more active layers emitting UV light with the laser grown on a sapphire substrate doped with one or more rare earth or transition elements.
Owner:CREE INC
Femtosecond laser-controlled silicon surface nanopillar preparation method based on dual-wavelength electronic dynamic control
ActiveCN105499792AEfficient and precise preparationAchieve optimal controlLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoNanopillar
The invention relates to a femtosecond laser-controlled silicon surface nanopillar preparation method based on dual-wavelength electronic dynamic control, and belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The method comprises the steps that on the basis of local instant electronic exciting dynamic control, the wave length of the fundamental frequency laser is converted into 400 nm from 800 nm through a frequency doubling technology, and the surface micro-nano structural morphology is controlled by adopting a dual-wavelength femtosecond laser, wherein a first beam generates a generic plasma lens structure (PL) on the surface of a material, a second beam generates surface plasma along the edge of the generic PL structure and generates a gradient field distributed along the center of a light spot, and then the material generates the force extruding towards the center under the action of the pulse to form a convex nanopillar structure; preparation of large-area uniform nanopillar arrays is achieved through control over a procedure of a processing platform. Compared with an existing method, the preparation method has the advantages that the nanopillar processing precision and processing efficiency are effectively improved, efficient and precise control over the crystalline silicon surface nano structure is achieved, and the application value on the aspects such as information storage and solar cells is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Crystal silicon surface femtosecond laser selective ablation method based on electron dynamic control
ActiveCN103658993AImprove machining accuracyImprove processing efficiencyWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoNano structuring
The invention relates to a crystal silicon surface femtosecond laser selective ablation method based on electron dynamic control, and belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The crystal silicon surface femtosecond laser selective ablation method based on the electron dynamic control enables laser polarization parameters and crystal lattice properties of crystal silicon materials to be integrated, through the operation that femtosecond laser rays or the included angel of elliptic polarization and monocrystal silicon is adjusted effectively, the selective induction generation of crystal silicon surface periodical ripple micro nano structures is controlled by regulating and controlling material surface instant electron excitation dynamic states, and the induction generation of the crystal silicon surface periodical ripple micro nano structures can be achieved effectively and accurately according to preliminary design. According to the crystal silicon face femtosecond laser selective ablation method based on the electron dynamic control, selective ablation control is carried out on the silicon surface periodic ripple nano structures with diamond lattice structures from the aspect of static laser irradiation and the aspect of laser direct writing, the processing accuracy and the processing efficiency of the surface processing of the silicon surface periodic ripple nano structures are improved greatly, and the application value of the method on the aspects such as information storage is high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and system for raman, fluorescence, lithographic, stimulated emission and photochemical imaging beyond the diffraction limit
InactiveUS20120069332A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioMinimizes parasitic two-photon absorption effectsSpectrum investigationPhotomechanical apparatusResistFluorescence
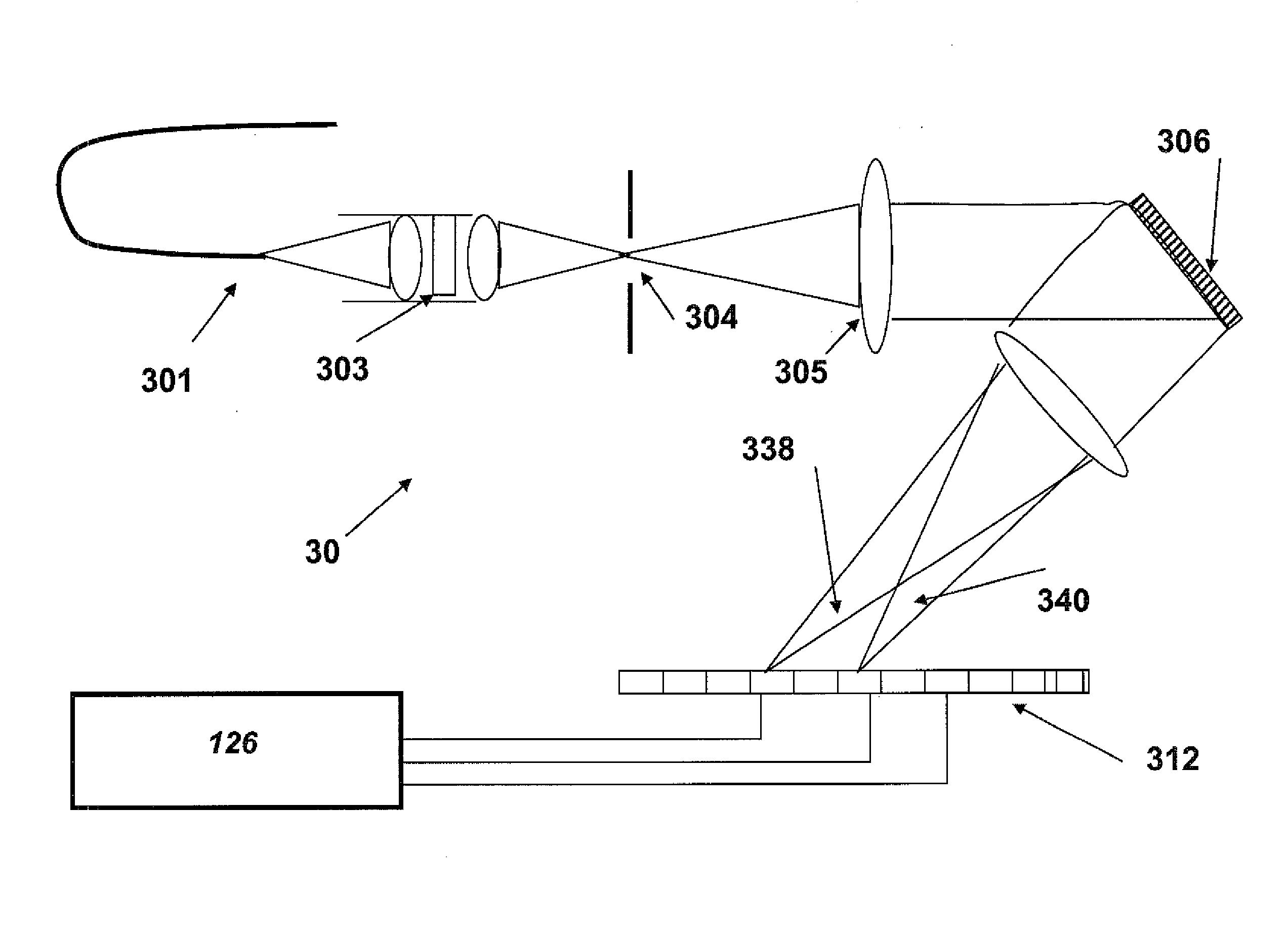
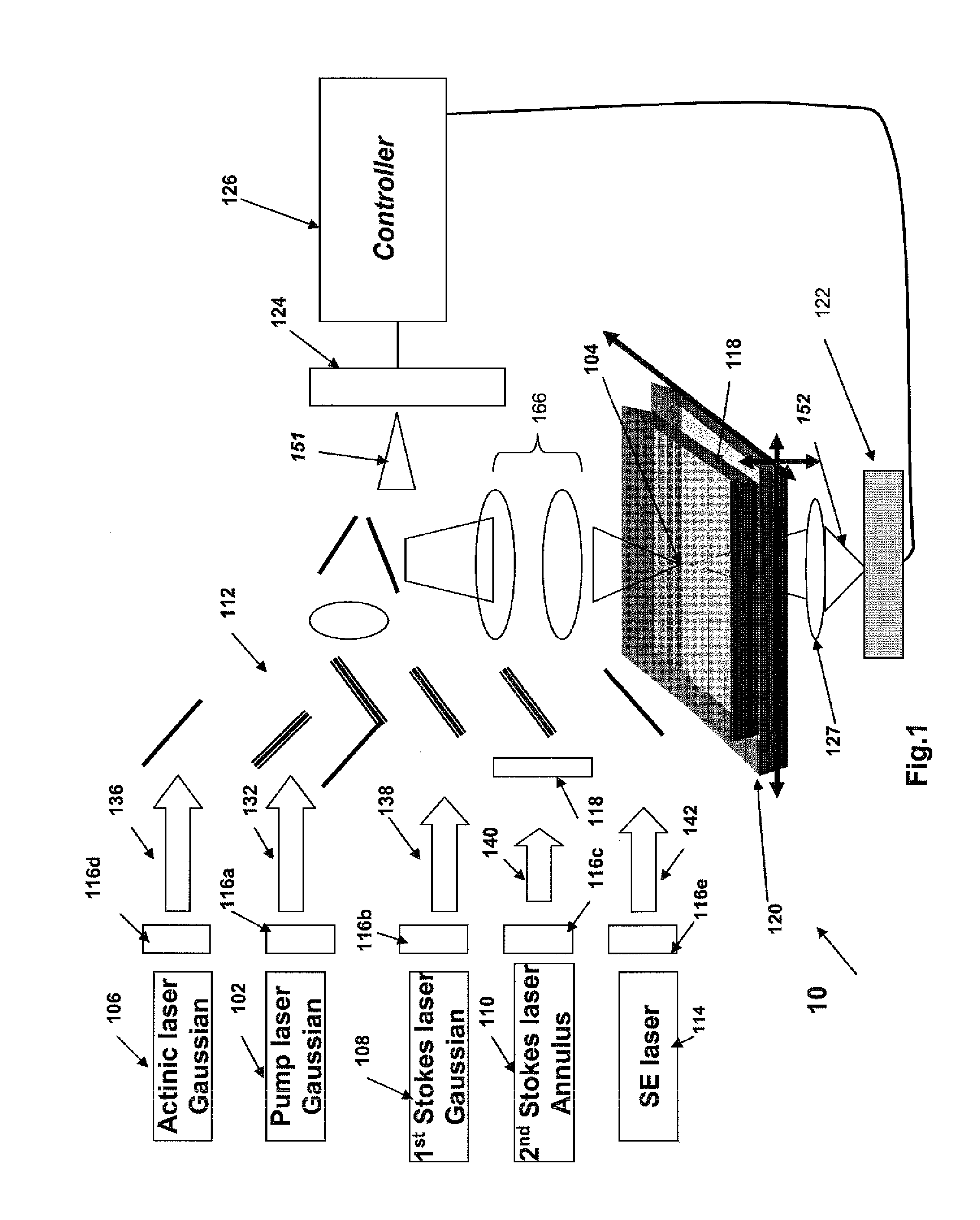
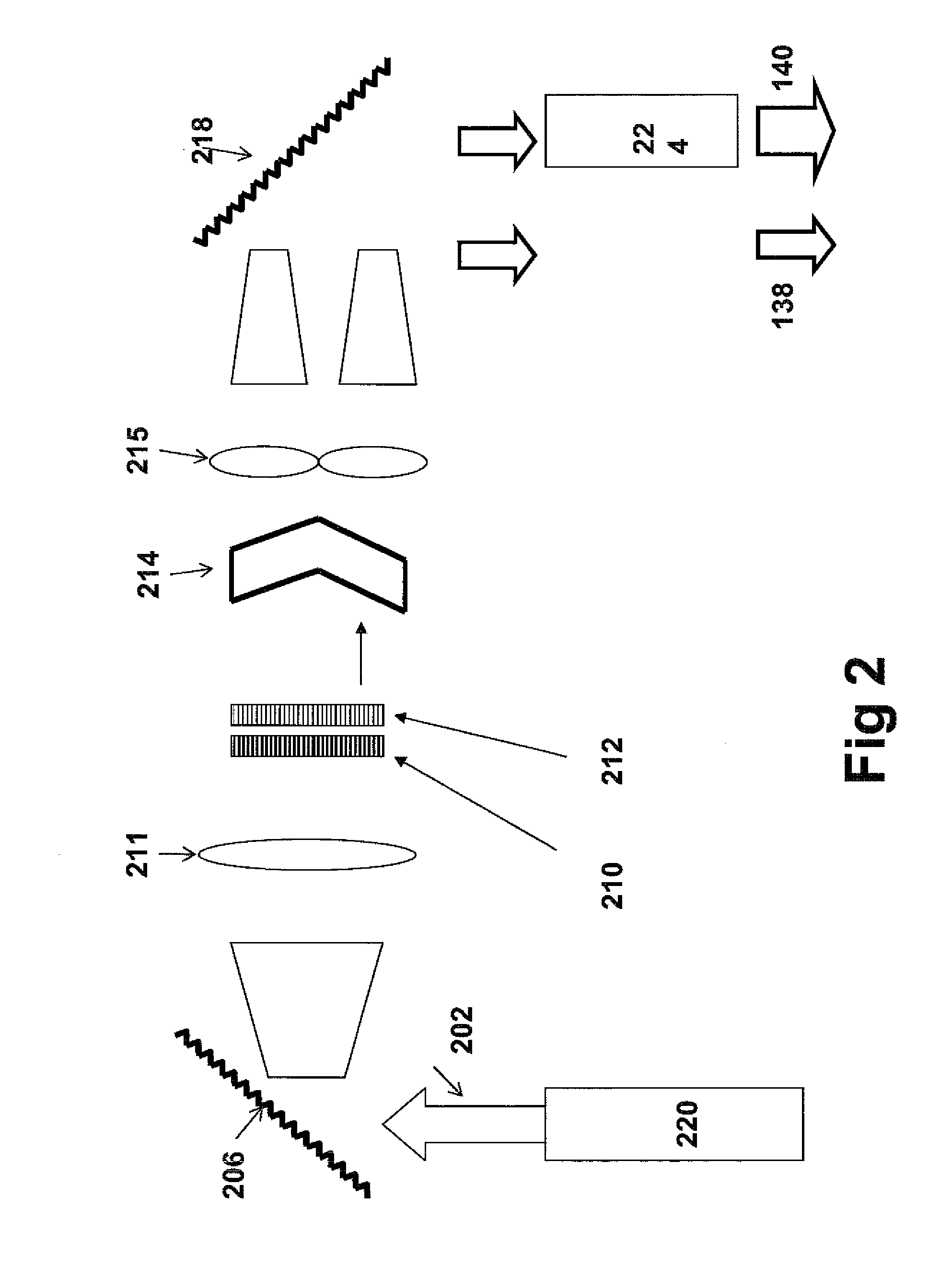
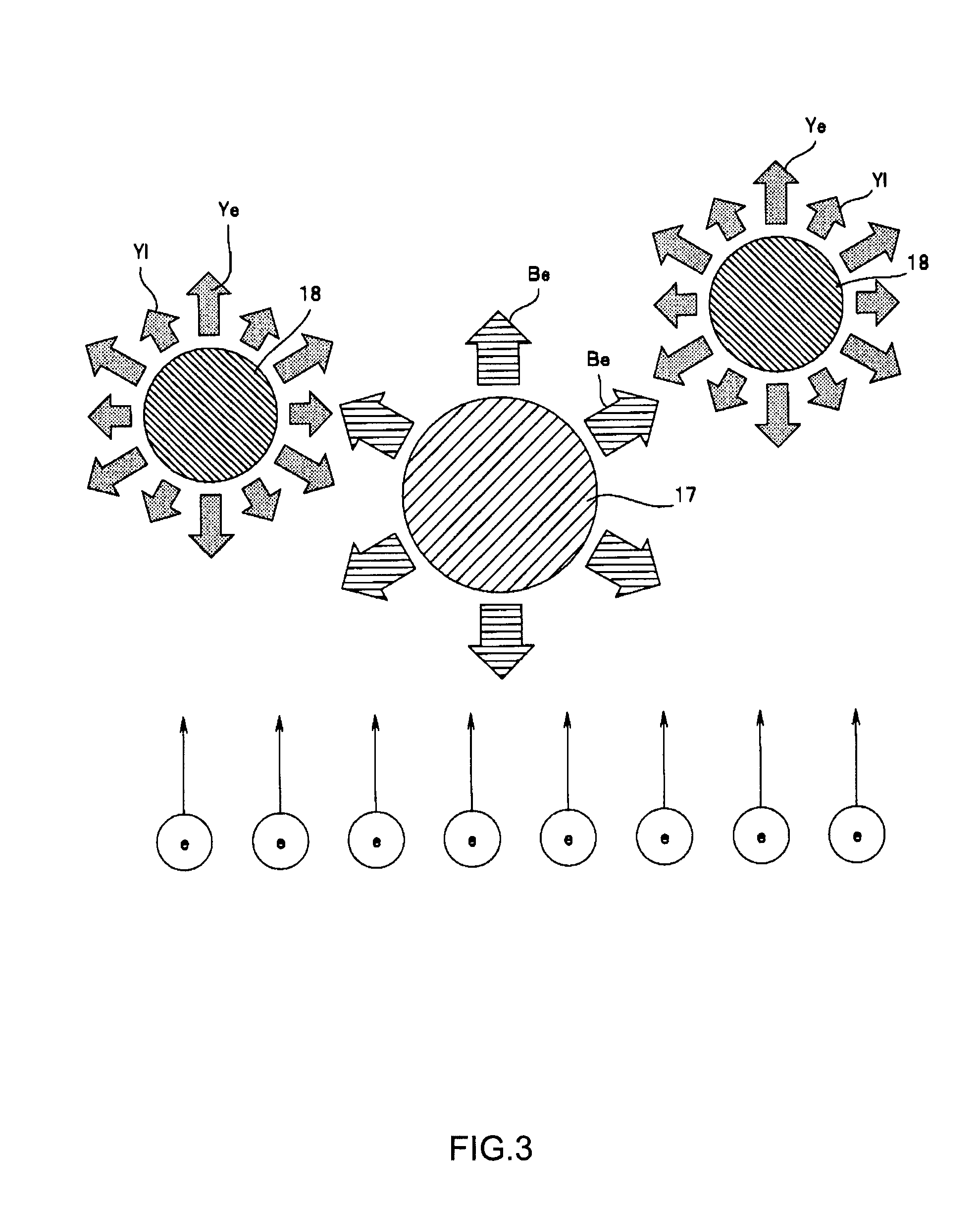
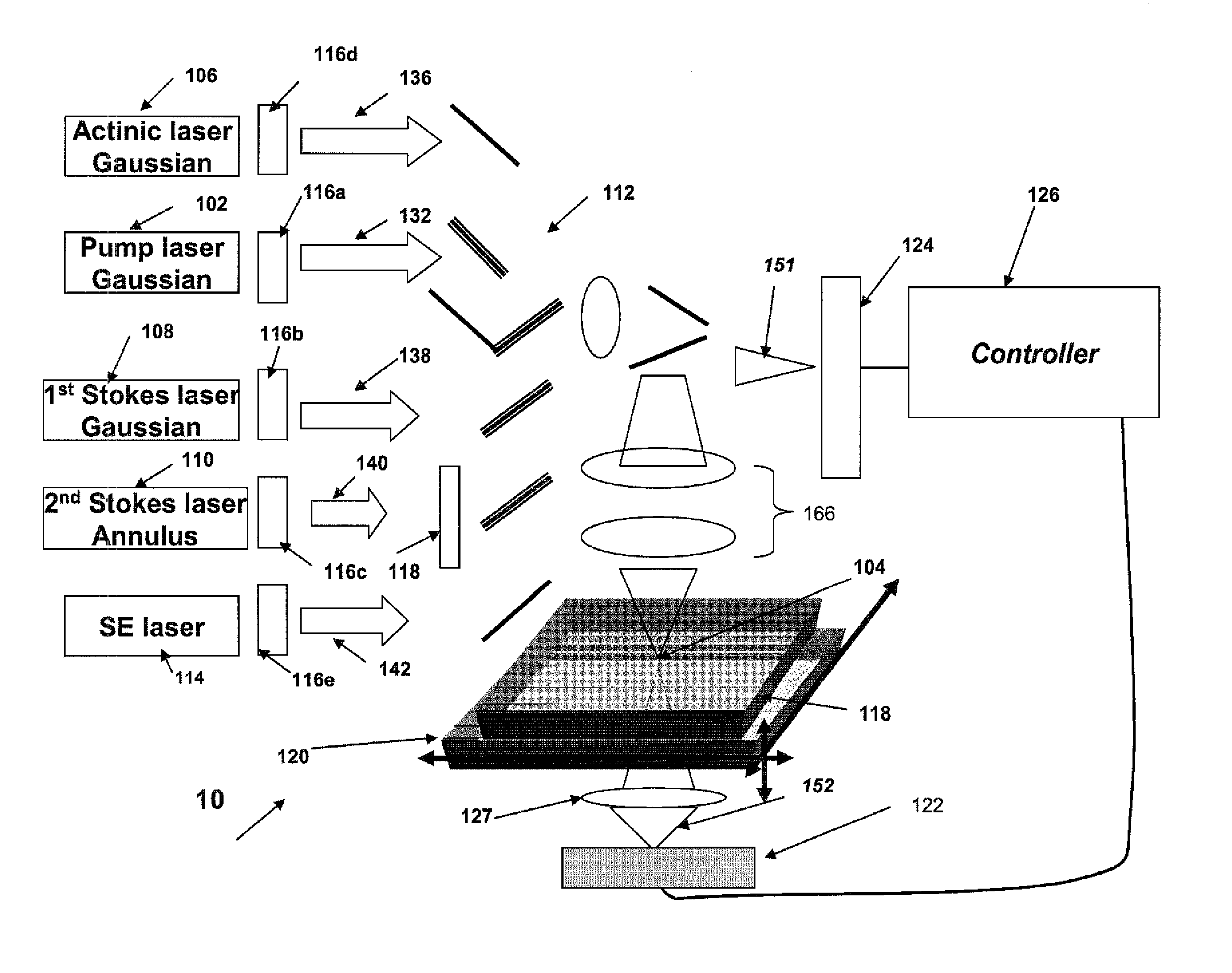
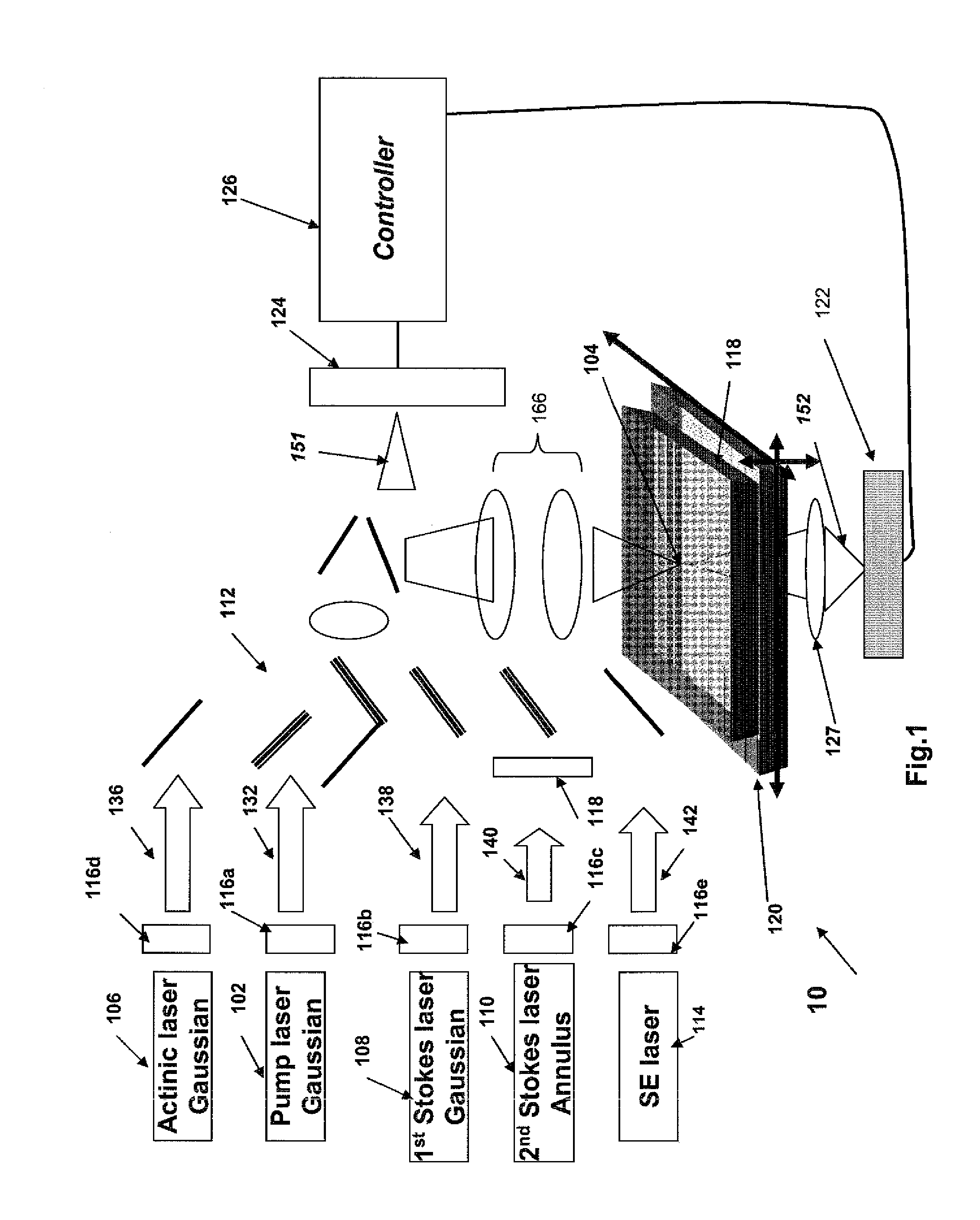
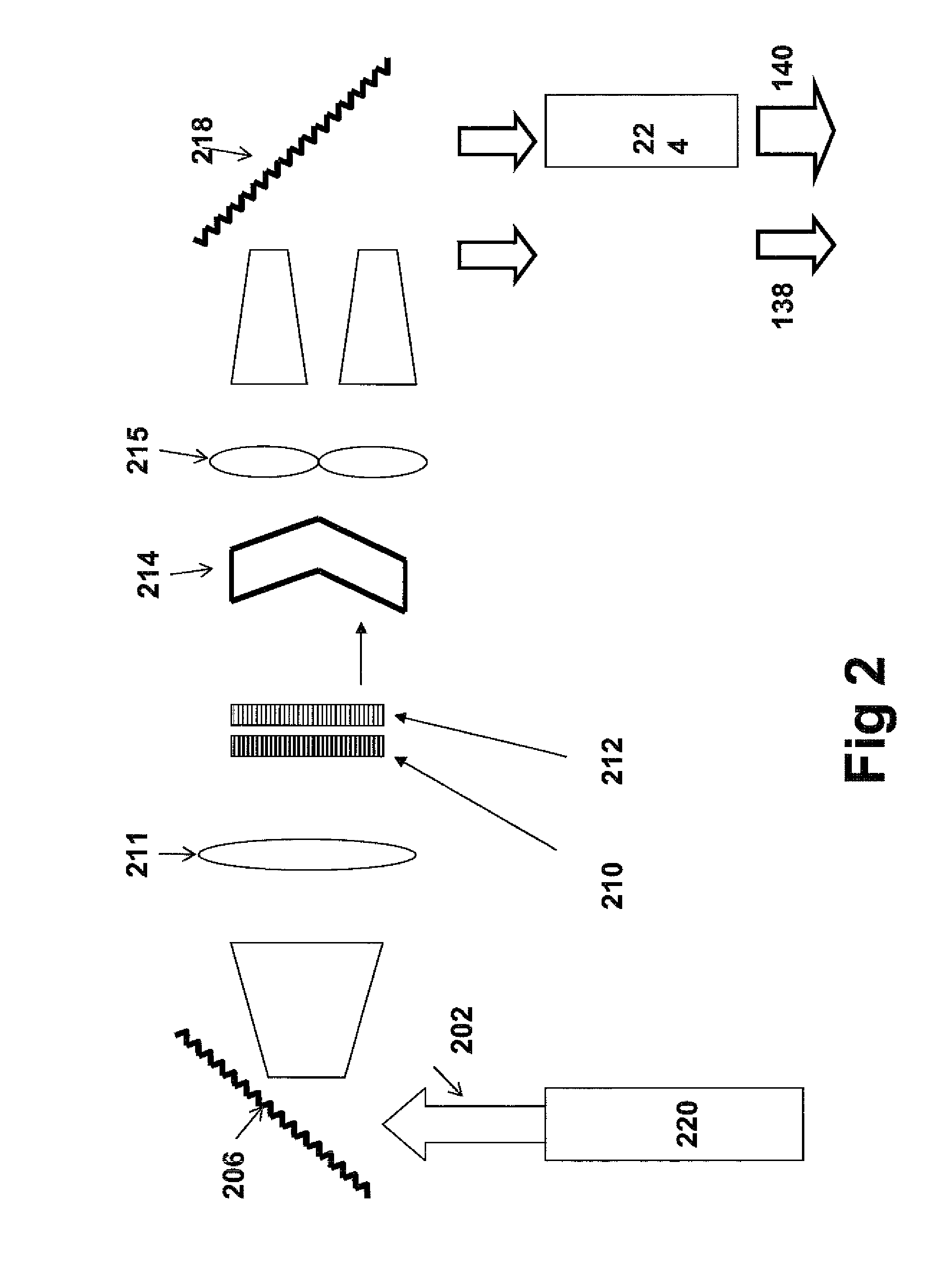
Systems and methods for hyper-resolution beyond the diffraction limit of optical microscopes for applications in spectroscopy, absorption and lithographic photochemical patterning are described. These systems are based on interference of a pump pulse and a Stokes laser pulse which interfere to localize the population of an excited vibrational state in an area that is smaller than the scanning resolution of the microscope. Another (interfering) Stokes pulse has an annular shape at focus and destructively interferes with the the Stokes laser pulse. This destructive interference causes narrowing of the population distribution of the vibrational excited state well below the diffraction limit, which in turn localizes the population of the central electronic excited state by a separate actinic laser pulse having a lower energy than the ground state excitation energy of the molecule.A stepped photolithography system uses two photomasks to produce photoresist images capable of printing features smaller than 10 nm.
Owner:FREL ROBERT D
Method and apparatus for electronically controlled scanning of micro-area devices
InactiveUS6246046B1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splitterFluorescence
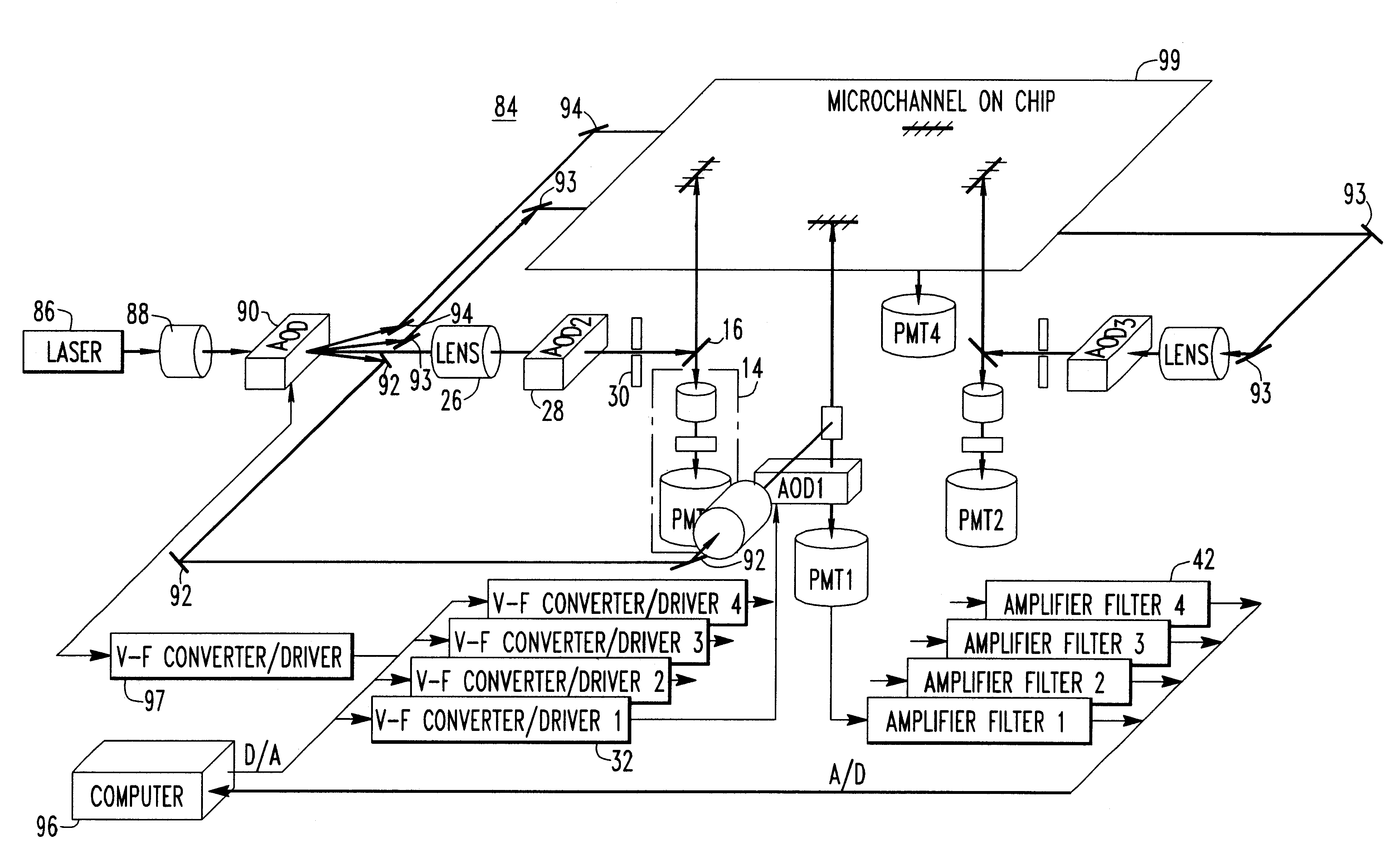
The present invention provides an excitation source which may be used, for example, in conjunction with the scanning of multi-channel electrophoresis chips or capillary arrays. The excitation source is comprised of a source of light, such as a laser beam. A beam expander, an acousto-optic deflector, and a filter are optically aligned with the source of light. A driver is connected to the acousto-optic deflector for controlling the angle of deflection. A system is disclosed which includes the excitation source, a detector for detecting fluorescence from a target chip, and a beam splitter or other device for optically connecting the excitation source to the chip and for optically connecting the chip to the detector. The excitation source may be based on an acousto-optic deflector, an electrooptic deflector, a piezoelectric deflector, or any other electronically controlled device. Methods of focusing a beam of collimated light and electronically exciting a plurality of micro-areas of a target chip, either serially or in parallel, are also disclosed.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
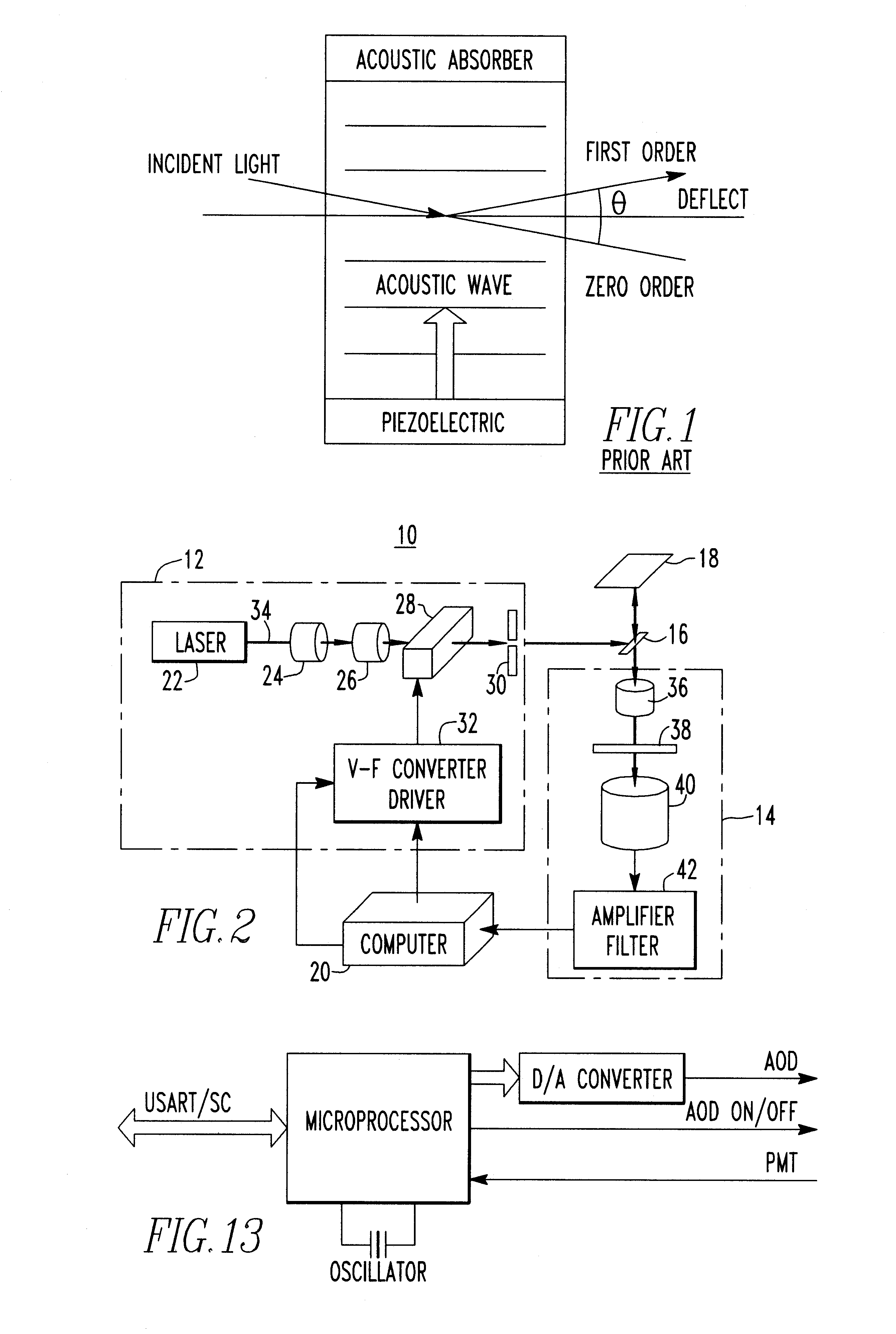
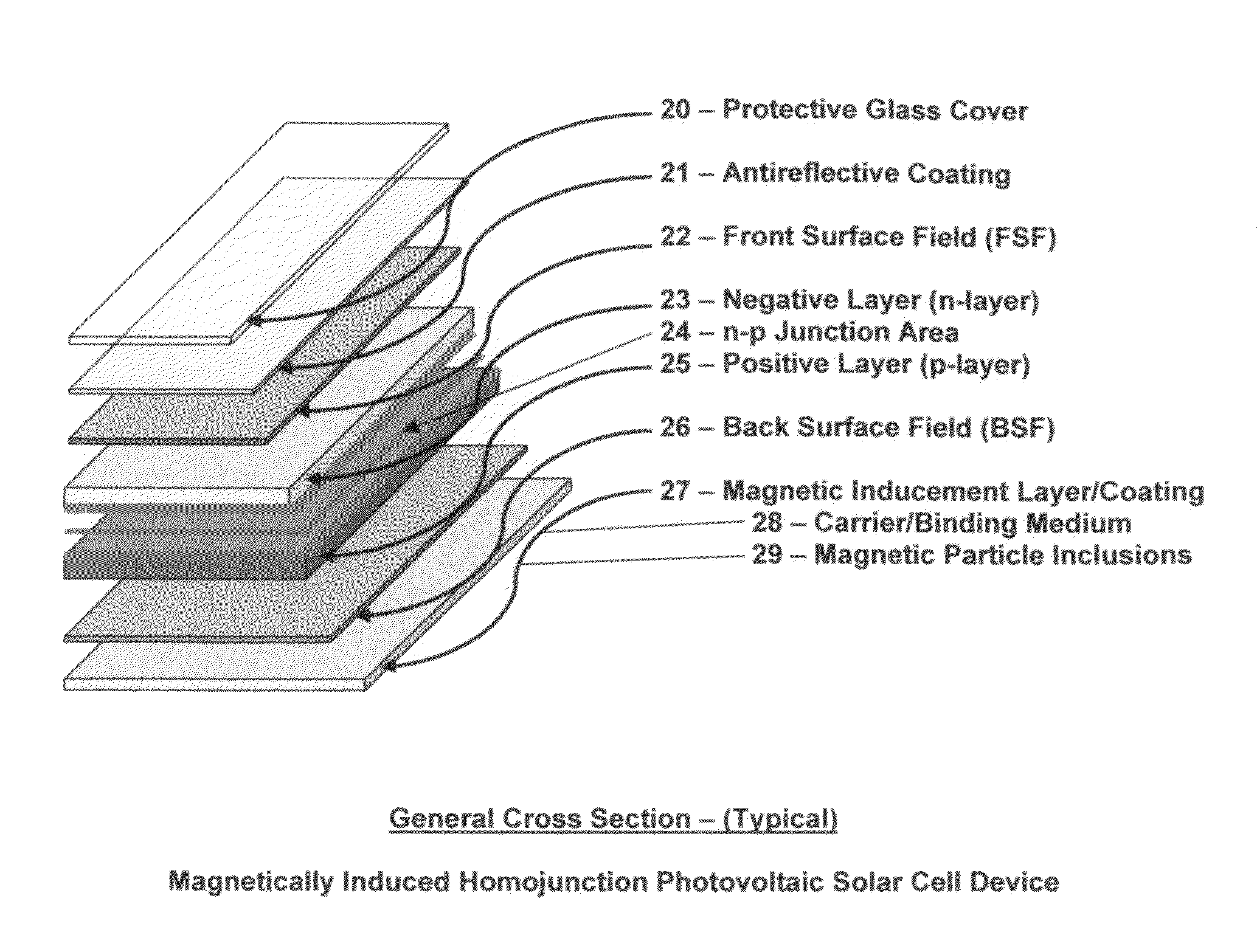
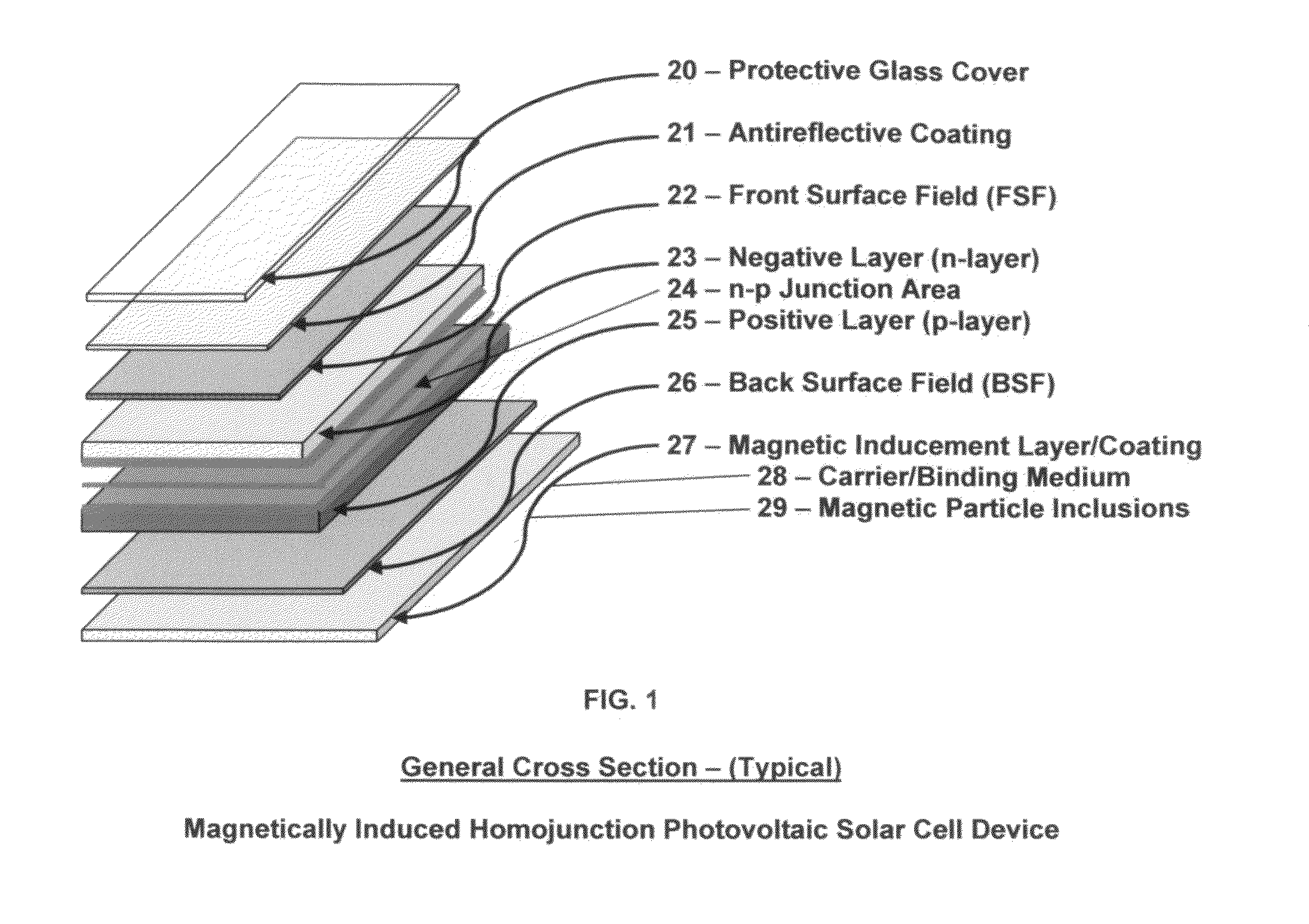
Article of manufacture for a magnetically induced photovoltaic solar cell device and the process for creating the magnetic and/or electromagnetic field
InactiveUS20100096003A1Facilitate the processMore efficientPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesElectron excitationElectromagnetic field
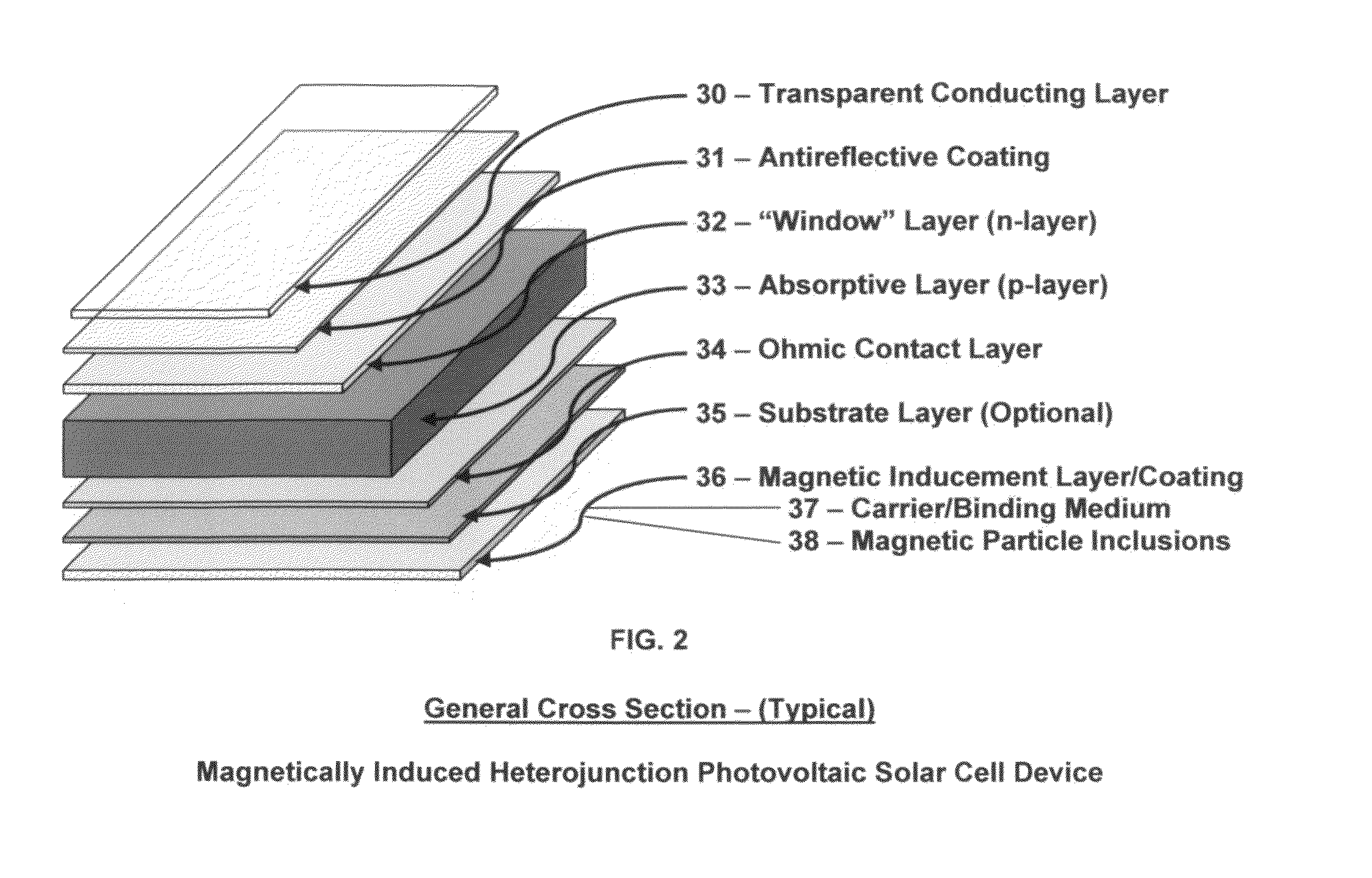
An article of manufacture for a magnetically induced photovoltaic solar cell device and the process for creating the magnetic and / or electromagnetic field(s) utilizing a basal underlying structure consisting of the body of any and all types of photovoltaic solar cell devices within which a magnetic and / or electromagnetic field will be created and / or generated through the overlayment of the previously mentioned photovoltaic device structure with a magnetic inducement layer and / or coating which is comprised of a carrier / binding medium and magnetic particle inclusions. The addition of the magnetic inducement layer serves the specific purpose of creating and / or generating greater photon and electron excitement, retention and absorption within the crystalline matrix of the underlying photovoltaic solar cell device.
Owner:HOBBIE DALE JAMES
Super-Resolution Microscope
ActiveUS20070291353A1Improve reliabilitySimple and inexpensive arrangementLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansExcited stateFluorescence
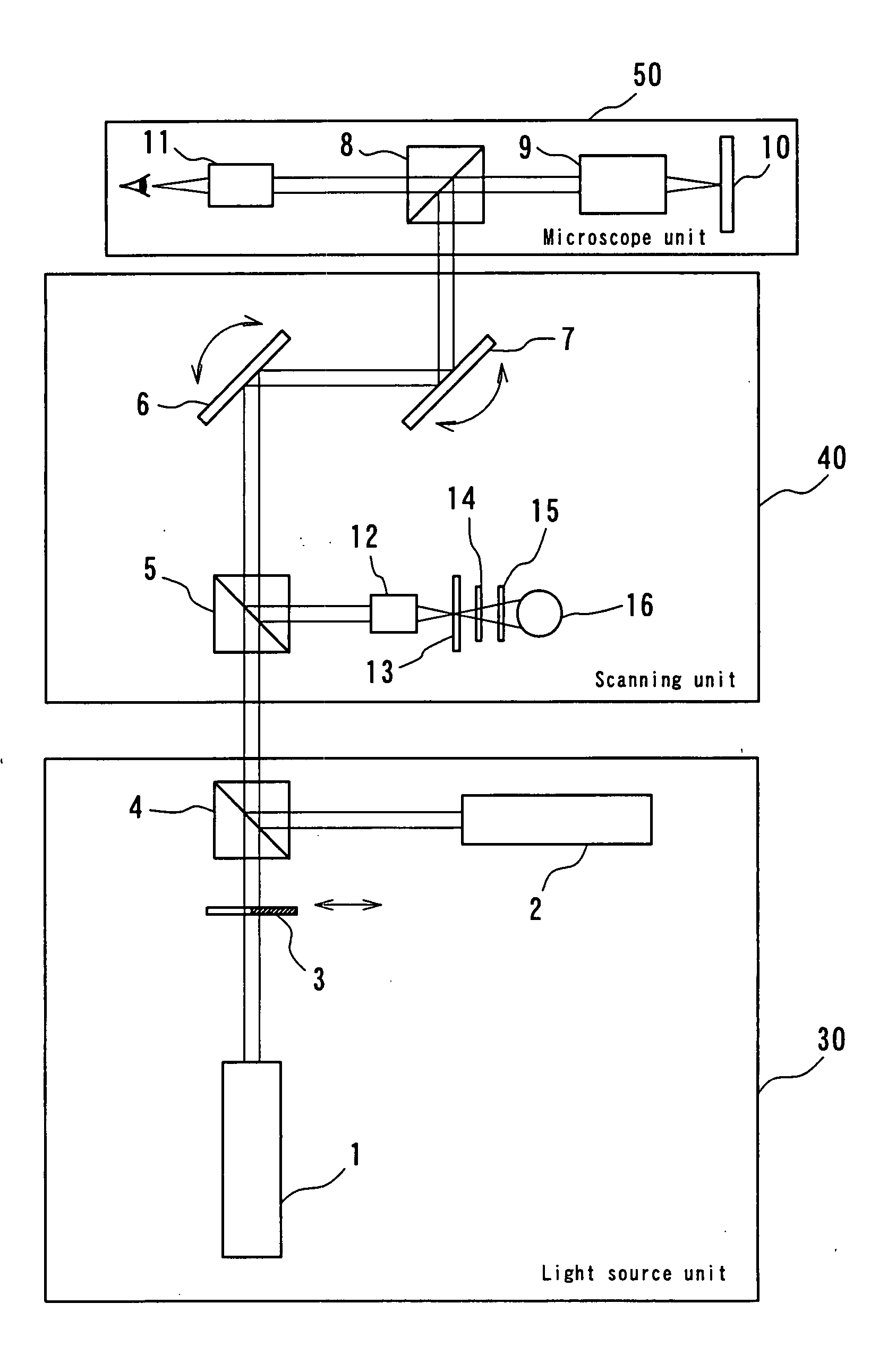
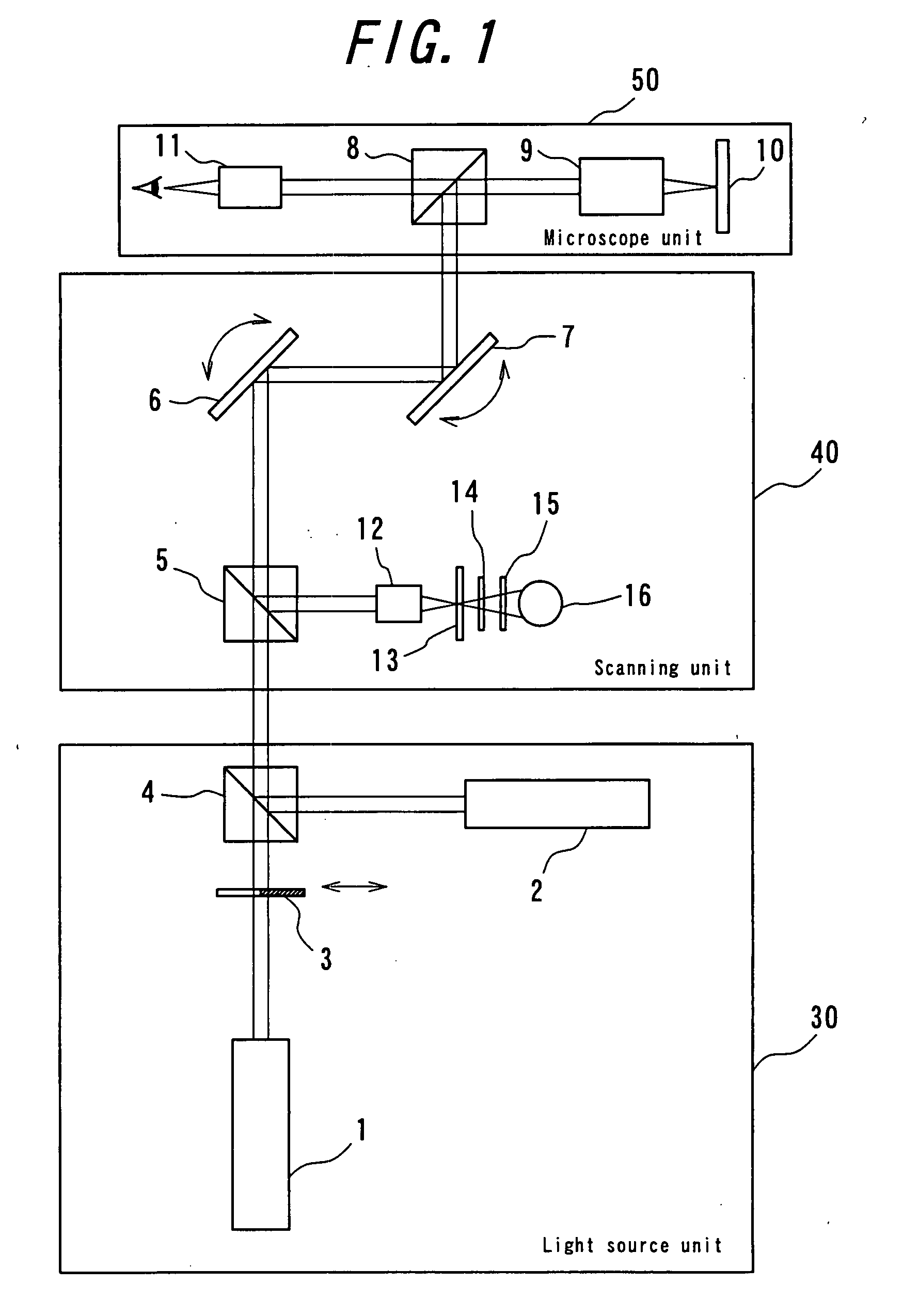
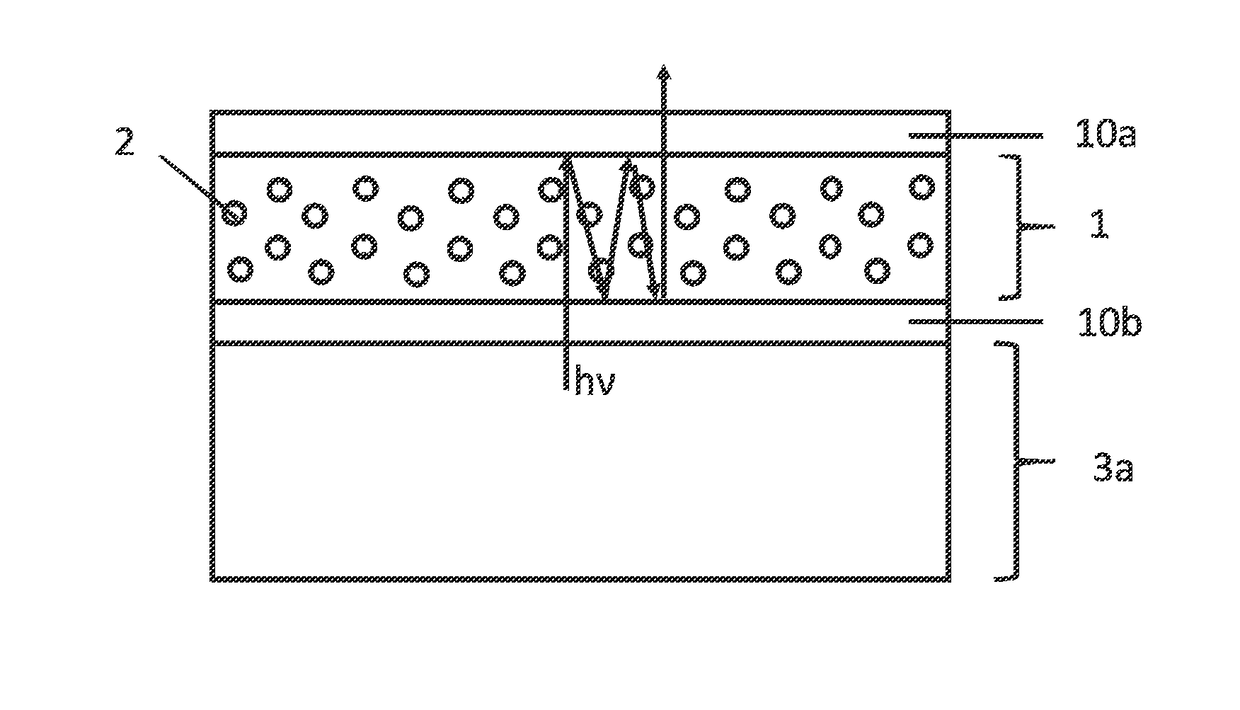
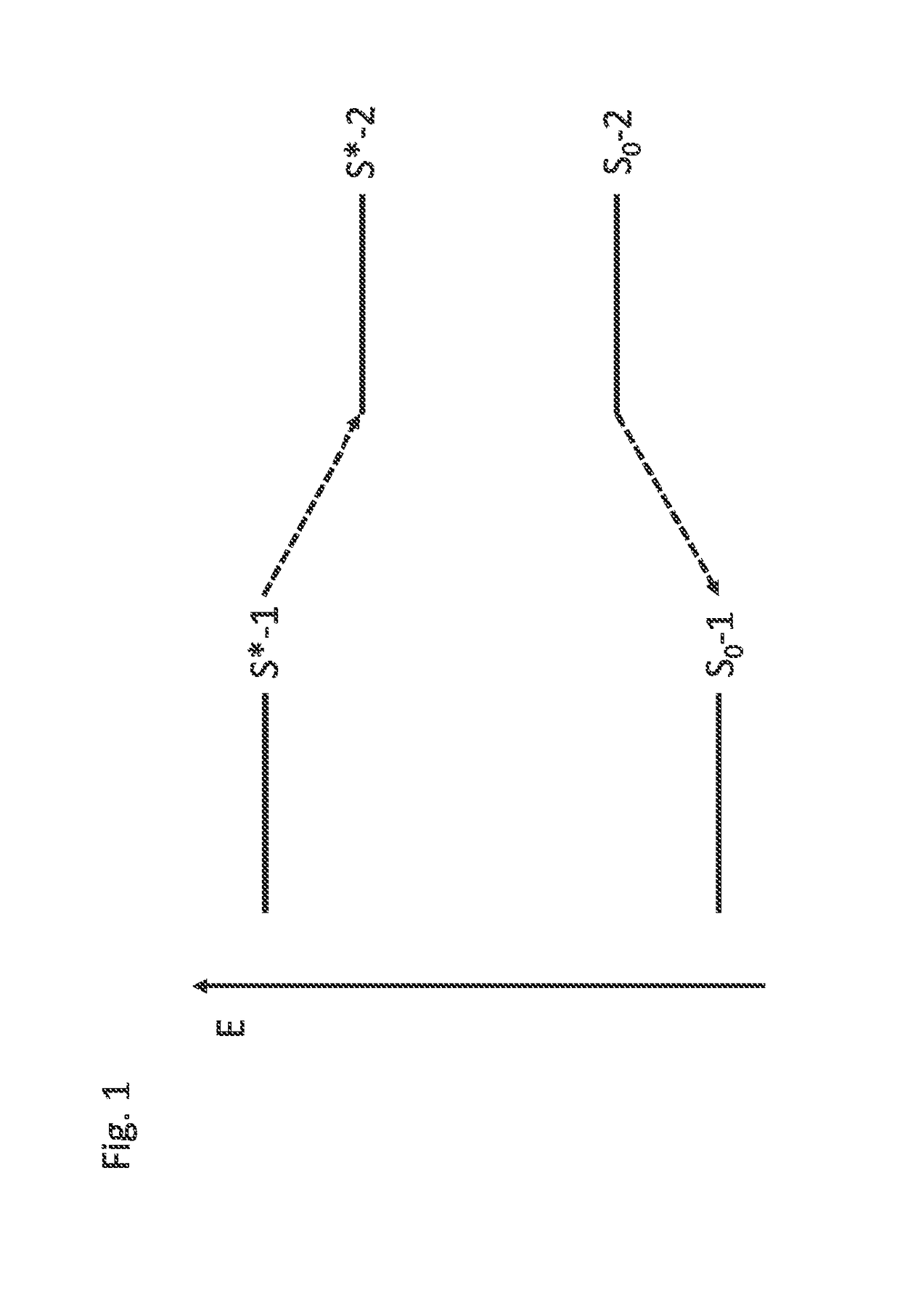
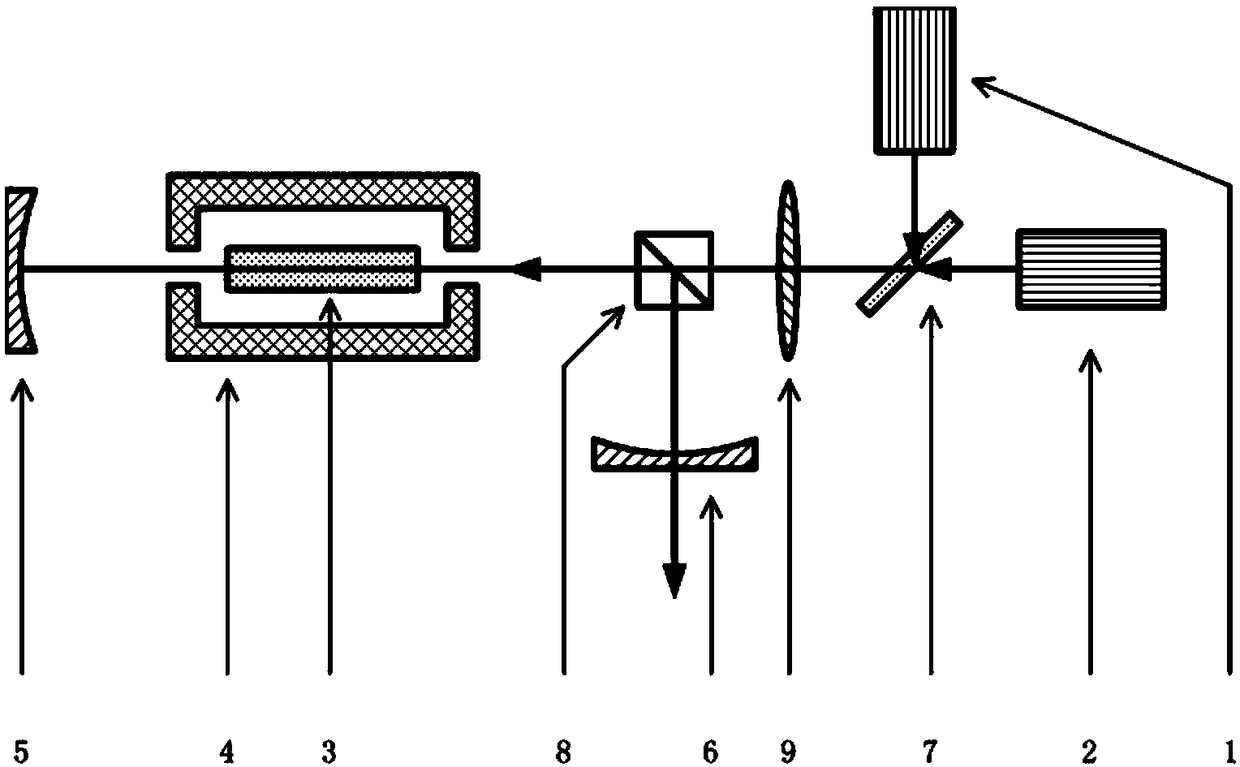
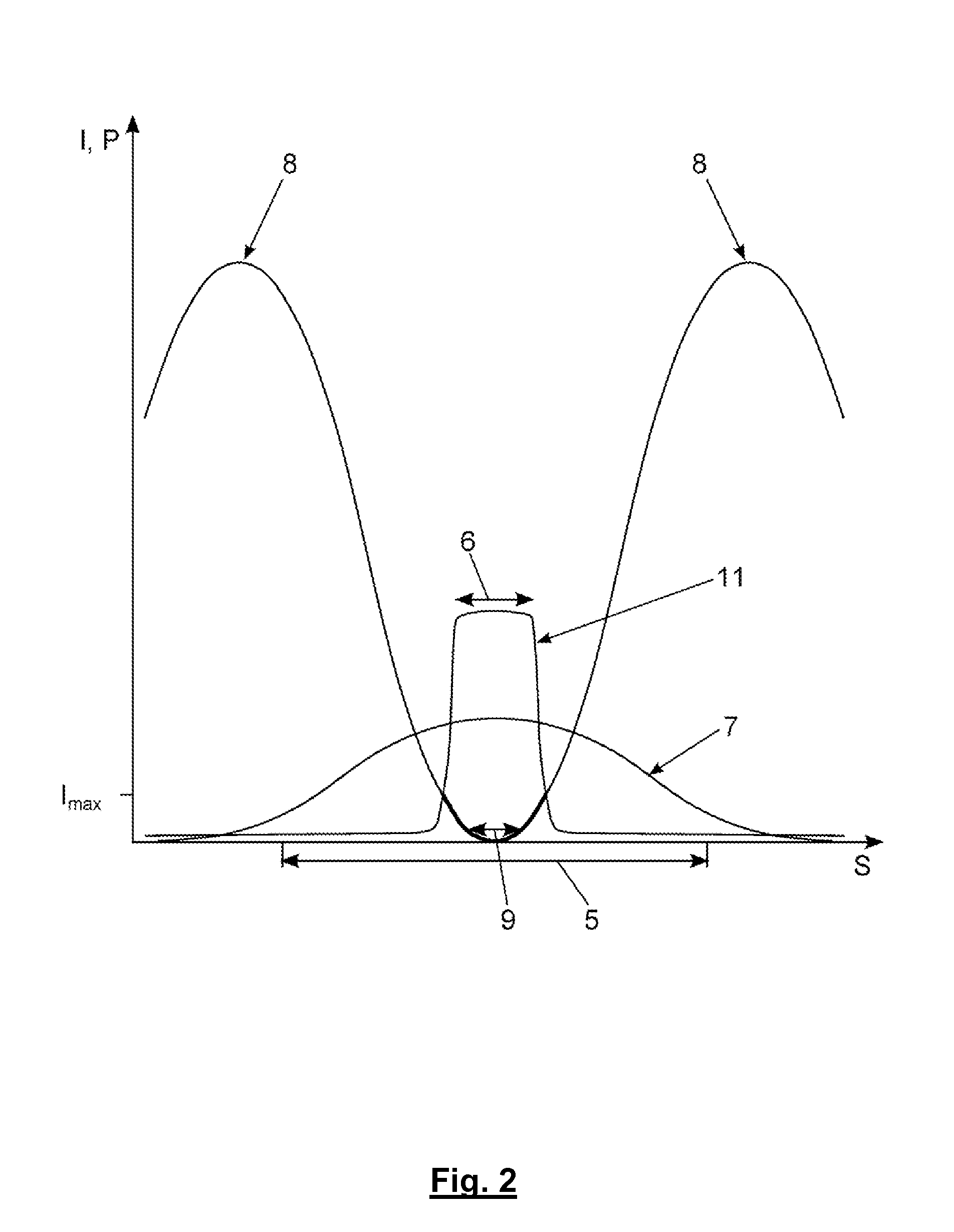
[Task] To provide a super-resolution microscope whereby the light source of pump light and erase light can be selected easily and a super-resolution can be reliably achieved through a simple and inexpensive arrangement. [Solution of the Task] A super-resolution microscope includes an optical system (3, 4, 9) for combining a part of a first coherent light from a first light source (2) and a part of a second coherent light from a second light source (1) and focusing the coherent lights onto a sample (10), scanning means (6, 7) for scanning the coherent lights, and detecting means (16) for detecting an optical response signal from the sample (10). The microscope is configured so as to satisfy the following conditions: σ01Ipτ≦1, and 0.65(λe / λp)≦τσdipIe where λp is the wavelength of the first coherent light, λe is the wavelength of the second coherent light, τ is the excited lifetime in which the molecule is excited by the first coherent light from the ground state to the first electron-excited state, Ip is the maximum photon flux on the sample surface of the first coherent light, Ie is the maximum photon flux on the sample surface of the second coherent light, σ01, is the absorption cross-sectional area when the molecule is exited from the ground state to the first electron-excited state, and σdip is the fluorescence suppression cross-sectional area.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP +1
Semiconductor apparatus for white light generation and amplification
ActiveUS20060065886A1Solve uneven generationAvoid energy lossSolid-state devicesNanoopticsFluorescenceLight-emitting diode
The present invention is a semiconductor apparatus for white light generation and amplification, where, under different current bias, white light can be generated steadily and evenly by folding up multi-wavelength quantum wells and by side-injecting a current. And, the white light can be excited out electronically without mingling with a fluorescent powder so that the cost for sealing is reduced. Because the light is directly excited out by electricity to prevent from energy loss during fluorescence transformation, the light generation efficiency of the present invention is far greater than that of the traditional phosphorus mingled with light-emitting diode of white light. Besides, concerning the characteristics of the white light, the spectrum of the white light can be achieved by adjusting the structure and / or the number of the quantum wells while preventing from being limited by the atomic emission lines of the fluorescent powder.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
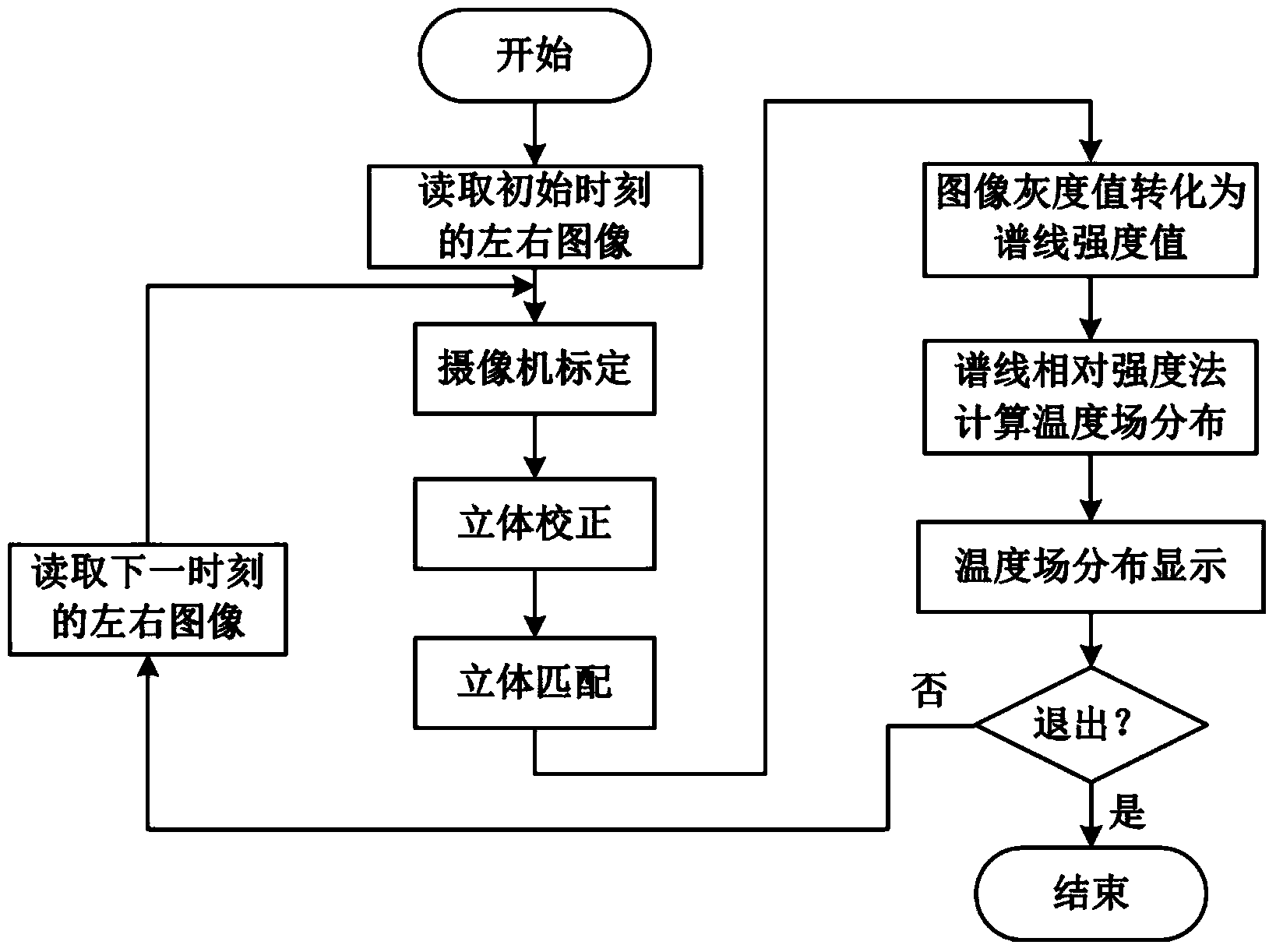
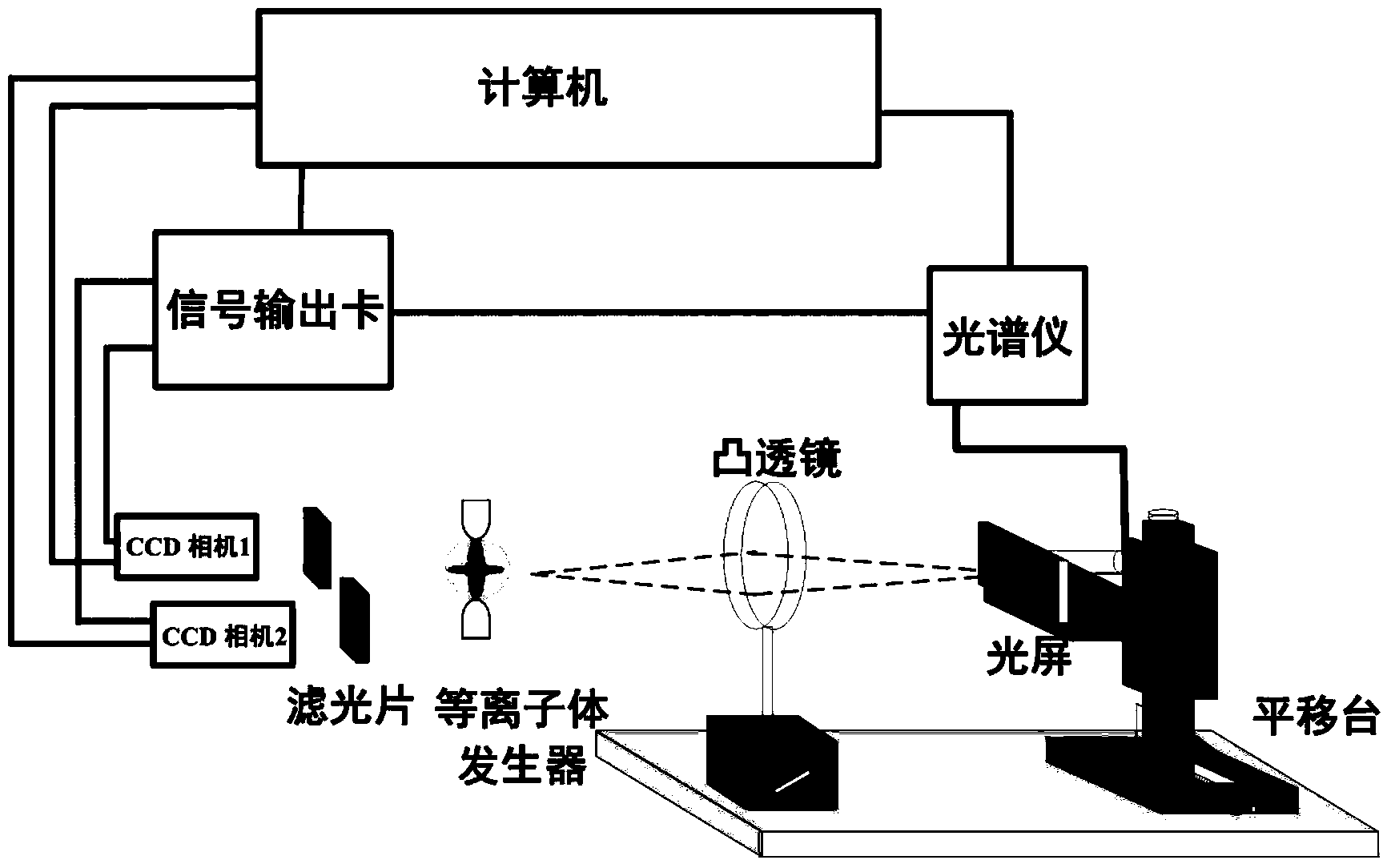
Method for measuring dual-jet direct-current arc plasma space temperature field in real time
ActiveCN103968958AThe method is simple and feasibleHigh resolutionPyrometry using electric radation detectorsPlasma generatorSpectrograph
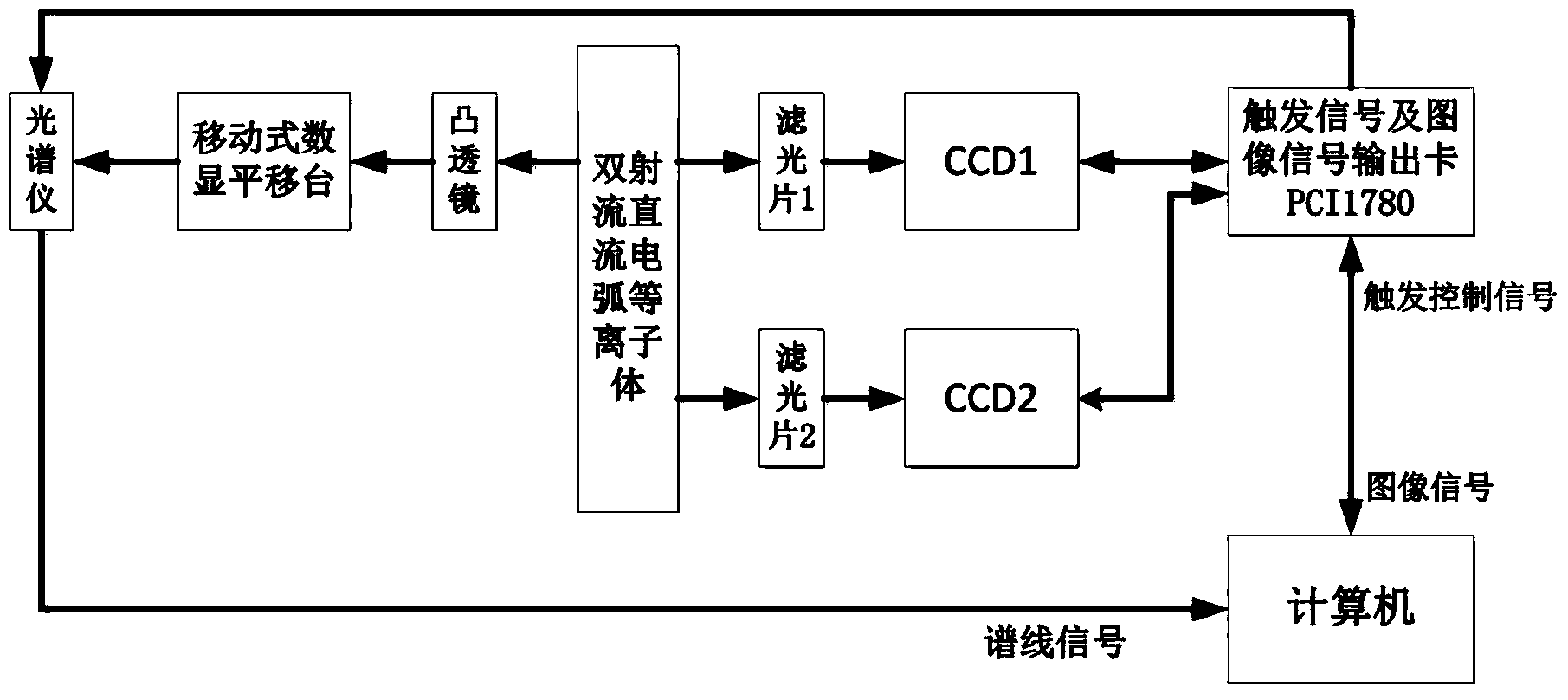
The invention provides a method for measuring a dual-jet direct-current arc plasma space temperature field in real time, and belongs to the technical field of hot plasma temperature measurement. The method is characterized in that in a real-time measurement system, internal and external parameters of given cameras are worked out, calibration and stereo correction are conducted, two matched target images preprocessed through a set parallax deviation are obtained, the intensities of spectral lines on corresponding pixel points at the same moment are obtained from a spectrograph, a gray value-spectral line intensity mapping table is built, and the electron excitation temperature of a spatial point corresponding to the similar spectral lines is calculated through the relative intensities of the spectral lines, wherein the real-time measurement system is composed of a plasma generator, an image information acquisition device, a spectrum acquisition device and a computer, the image information acquisition device is formed by splicing the two CCD cameras, optical filters with different central wavelengths are arranged in front of lenses on the two sides, the spectrum acquisition device is mainly composed of the spectrograph, and the computer is connected with a triggering signal output card used for synchronously triggering the two CCD cameras and the spectrograph. The method is simple and feasible, the resolution ratio and temperature measurement accuracy are high, and dynamic performance is good.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
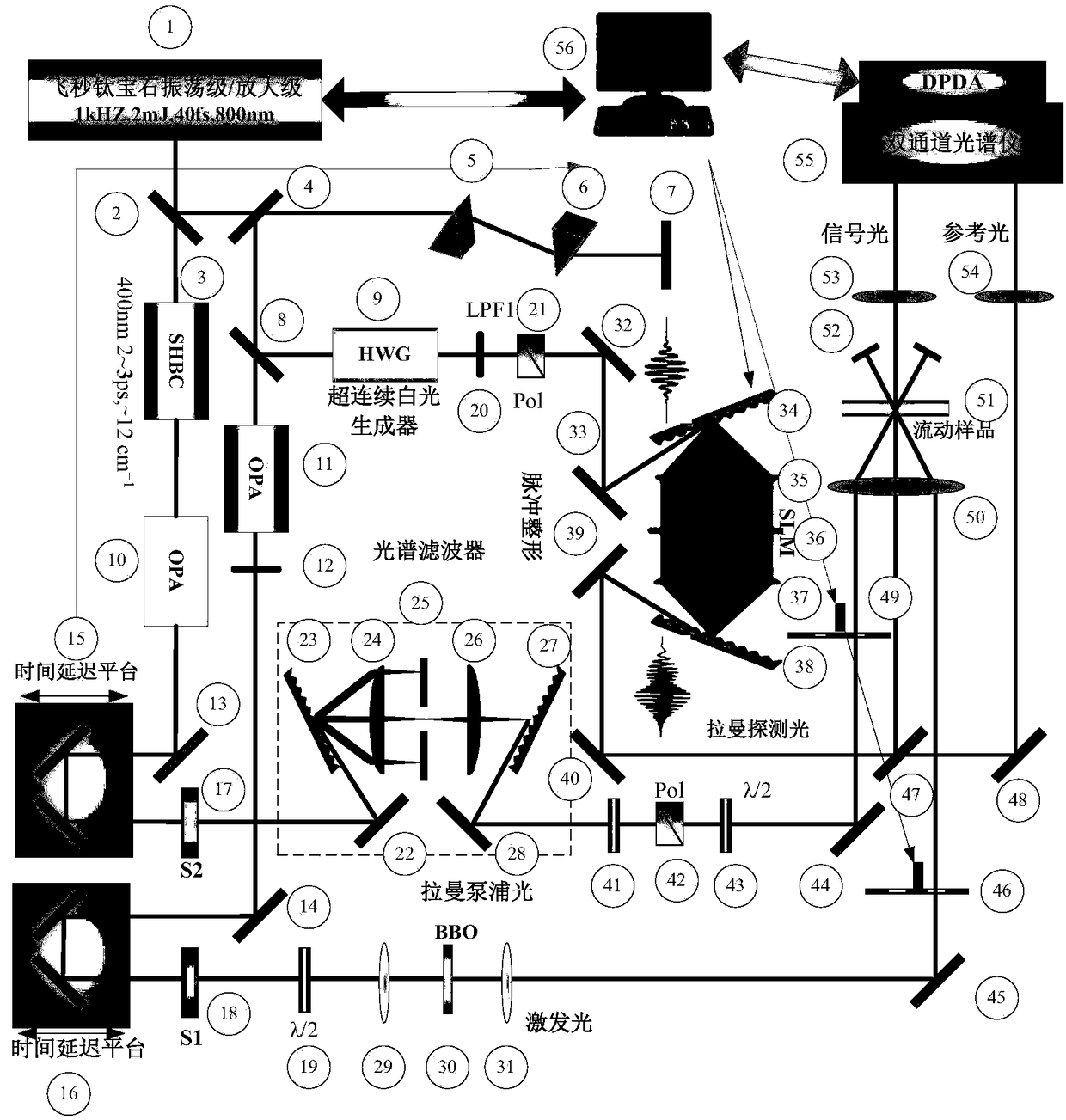
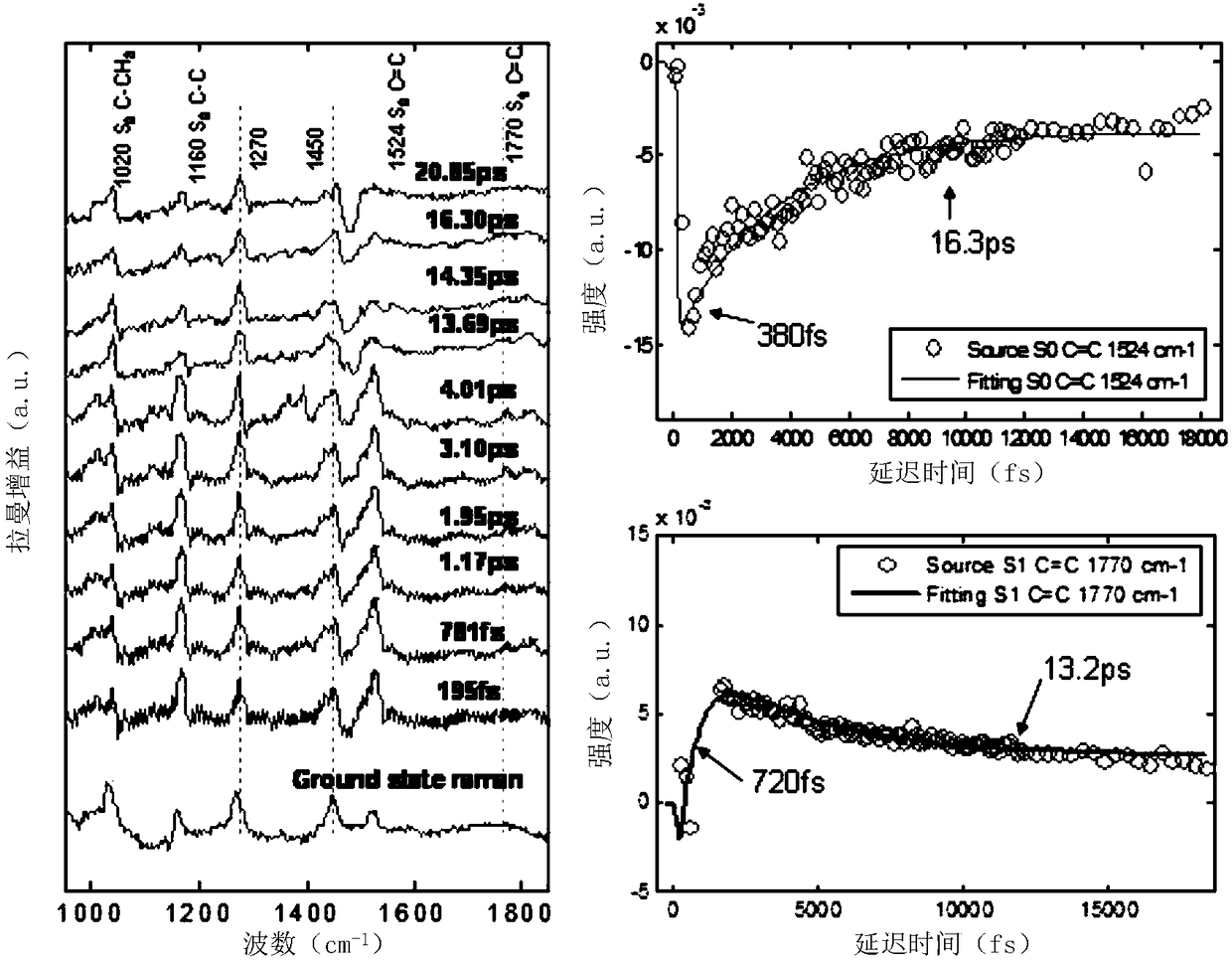
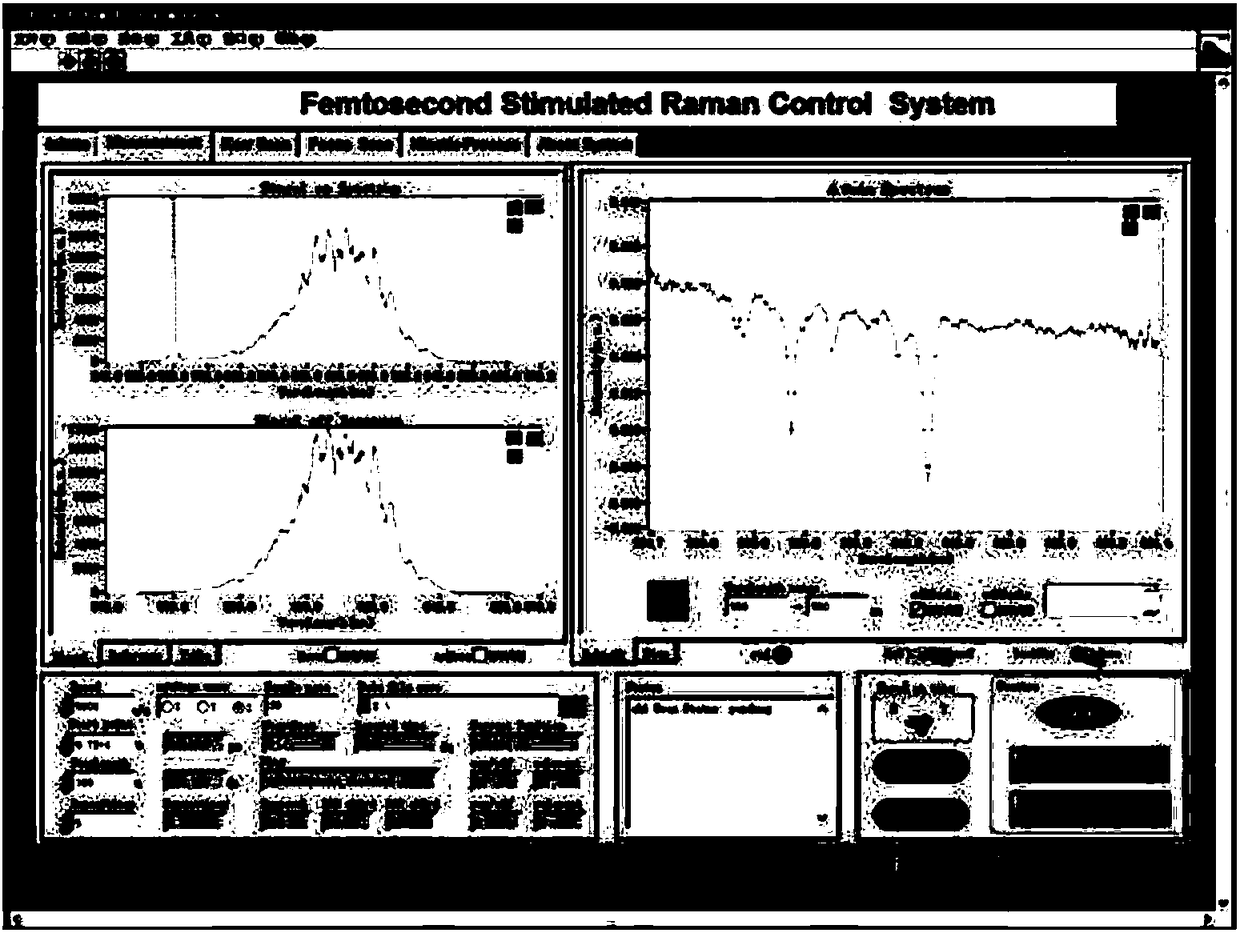
Femtosecond time resolved excited Raman spectrum system
InactiveCN108872181AAvoid fluorescence interferenceImprove time resolutionRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryExcited stateFluorescence
The invention discloses a femtosecond time resolved excited Raman spectrum system, which can be used for detecting the vibration dynamics of the molecular electron base state, can also be used for detecting the vibration dynamics of the molecular electron excitation state, and can give out rich information relevant to molecular electron excitation state properties, particularly vibration excitation state dynamics. The Raman spectrum system generates excitation light, Raman pumping light and detection light; a spectrum instrument can perform double chopping modulation on the excitation light and the Raman pumping light, and can control the time sequence of the excitation light, Raman pumping light and detection light reaching the samples. The wavelength of the Raman pumping light can be continuously tuned; the whole-frequency excited Raman spectrum from visible light to near ultraviolet waveband can be obtained; in addition, the proper wave length can be selected to effectively avoid the fluorescence interference; the intensity of the excited Raman spectrum can be improved under the resonance conditions; the defects of low sensitivity and fluorescence interference of the conventional Raman spectrum are overcome.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Two-photon or higher-order absorbing optical materials for generation of reactive species
Disclosed are highly efficient multiphoton absorbing compounds and methods of their use. The compounds generally include a bridge of pi-conjugated bonds connecting electron donating groups or electron accepting groups. The bridge may be substituted with a variety of substituents as well. Solubility, lipophilicity, absorption maxima and other characteristics of the compounds may be tailored by changing the electron donating groups or electron accepting groups, the substituents attached to or the length of the pi-conjugated bridge. Numerous photophysical and photochemical methods are enabled by converting these compounds to electronically excited states upon simultaneous absorption of at least two photons of radiation. The compounds have large two-photon or higher-order absorptivities such that upon absorption, one or more Lewis acidic species, Lewis basic species, radical species or ionic species are formed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
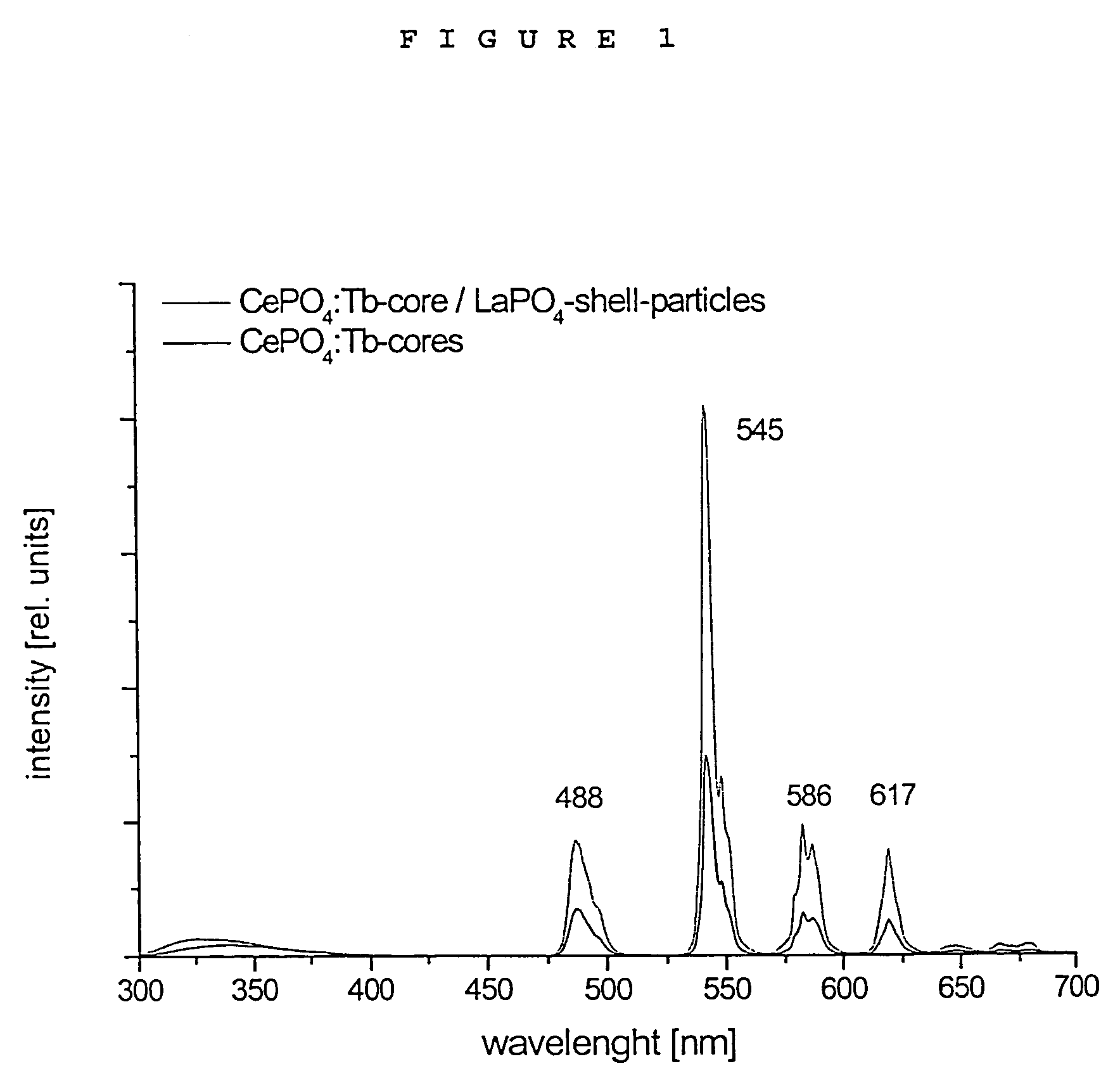
Luminescent core/shell nanoparticles comprising a luminescent core and method of making thereof
The present invention relates to Luminescent nanoparticles comprising (a) a core made from a luminescent metal salt selected from phosphates, sulfates or fluorides, being surrounded by (b) a shell made from a metal salt or oxide capable of preventing or reducing energy transfer from the core after its electronic excitation to the surface of the nanoparticle, e.g. a shell made from a non-luminescent metal salt or oxide, which are characterized by higher quantum yields and can be used in various fields including light generation and security marking.
Owner:CENT FUR ANGEWANDTE NANOTECH
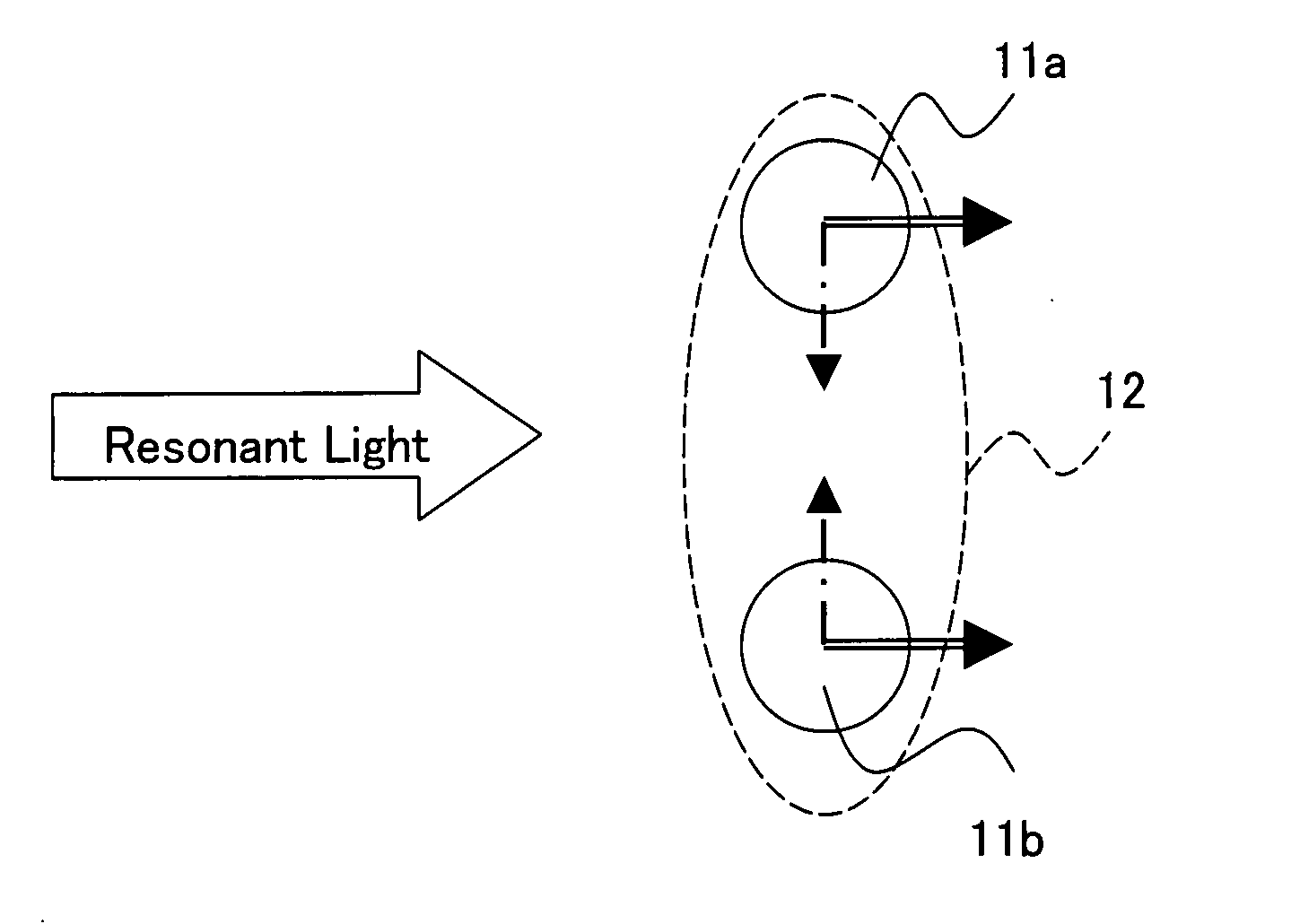
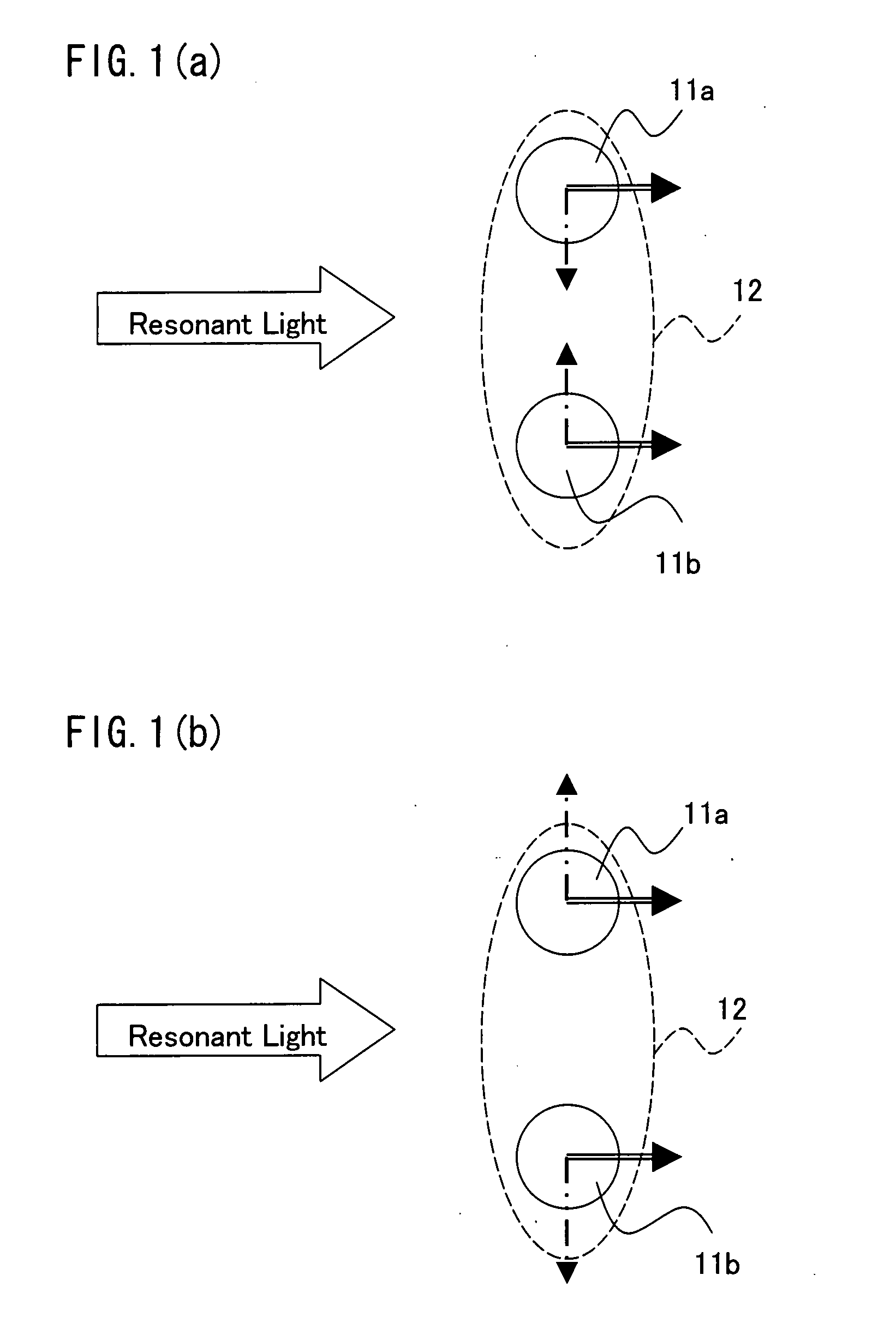
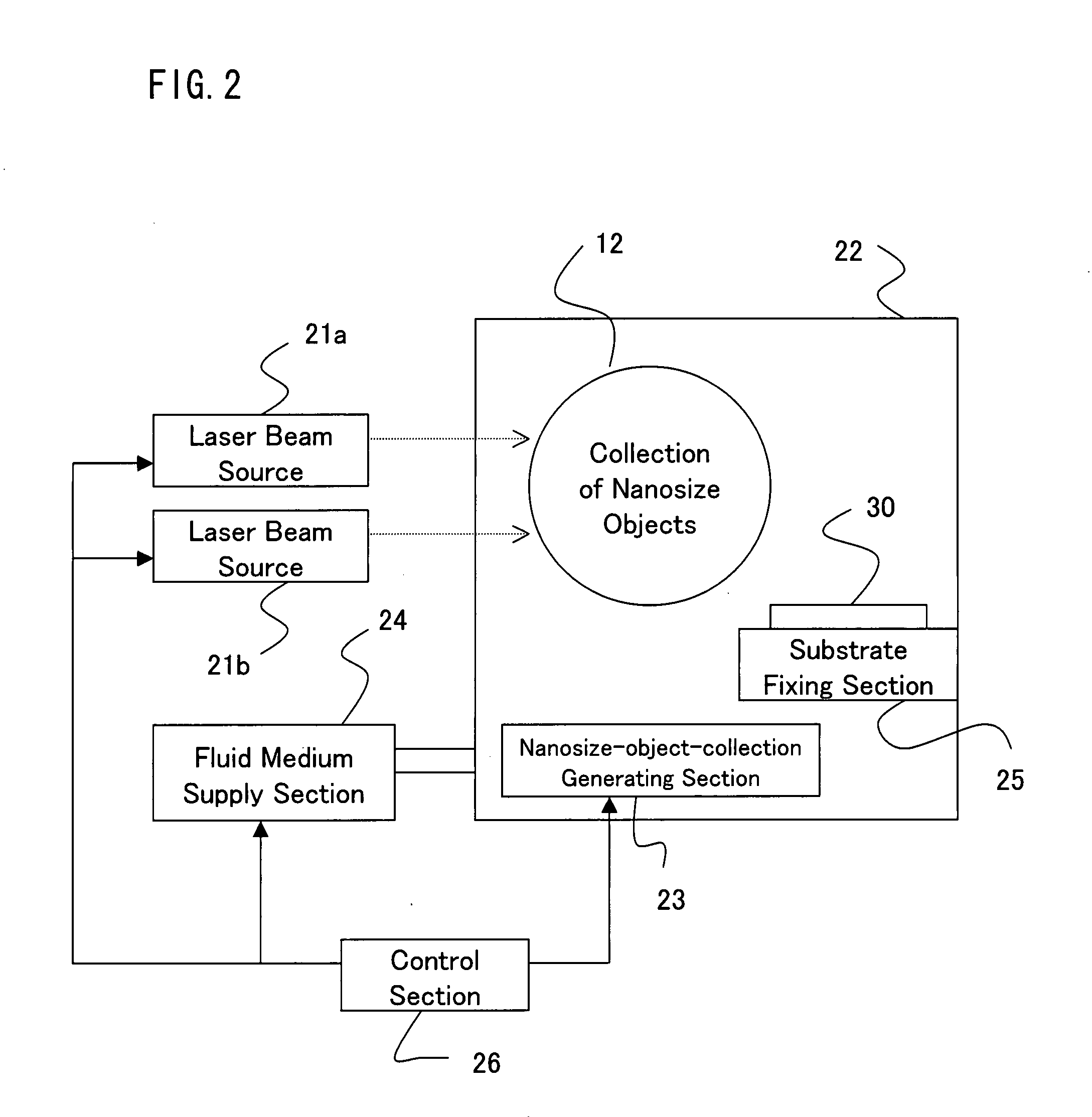
Method Of Manipulating Nanosize Objects And Utilization Thereof
InactiveUS20070284544A1Manipulated more efficiently and more freelyMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCarbon nanotubeQuantum dot
Light resonant with an electronic excitation level of nanosize objects is projected onto a plurality of closely located nanosize objects, such as quantum dots, quantum dot pairs, and a carbon nanotube, in a collection of nanosize objects is disclosed. In so doing, to control the mechanical interaction induced between the nanosize objects, the projected resonant light is changed in polarization. This enables the collective manipulation of the nanosize objects.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
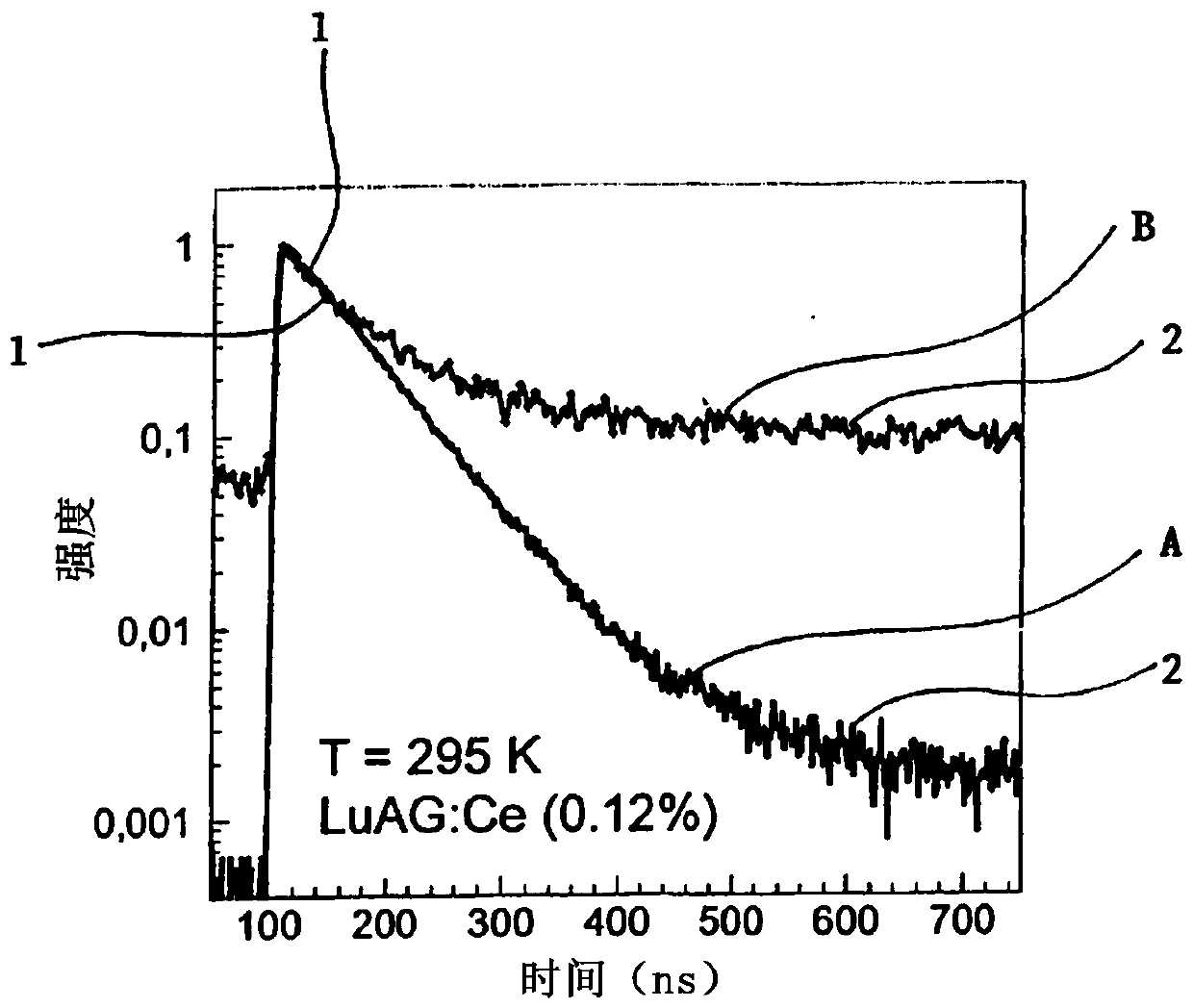
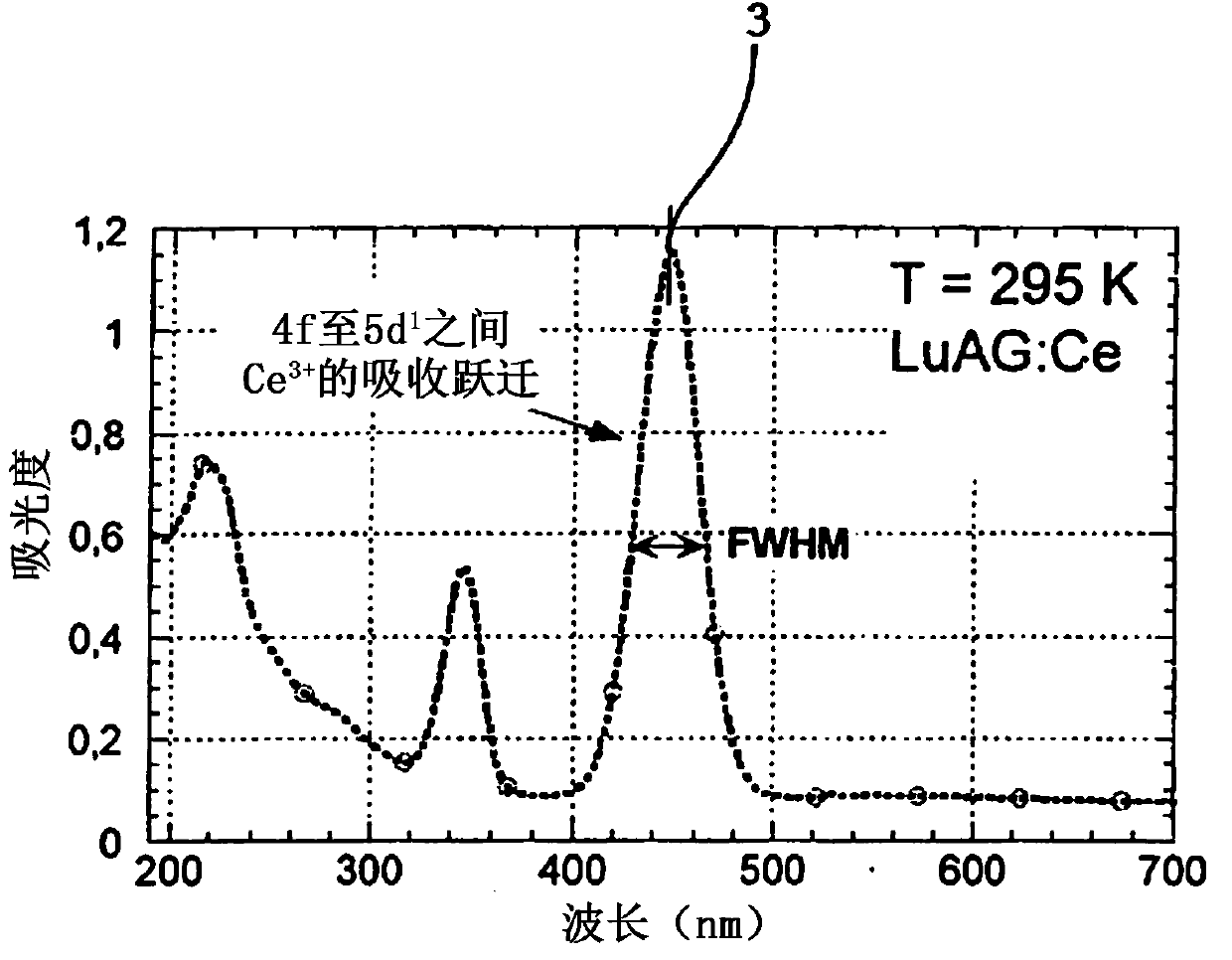
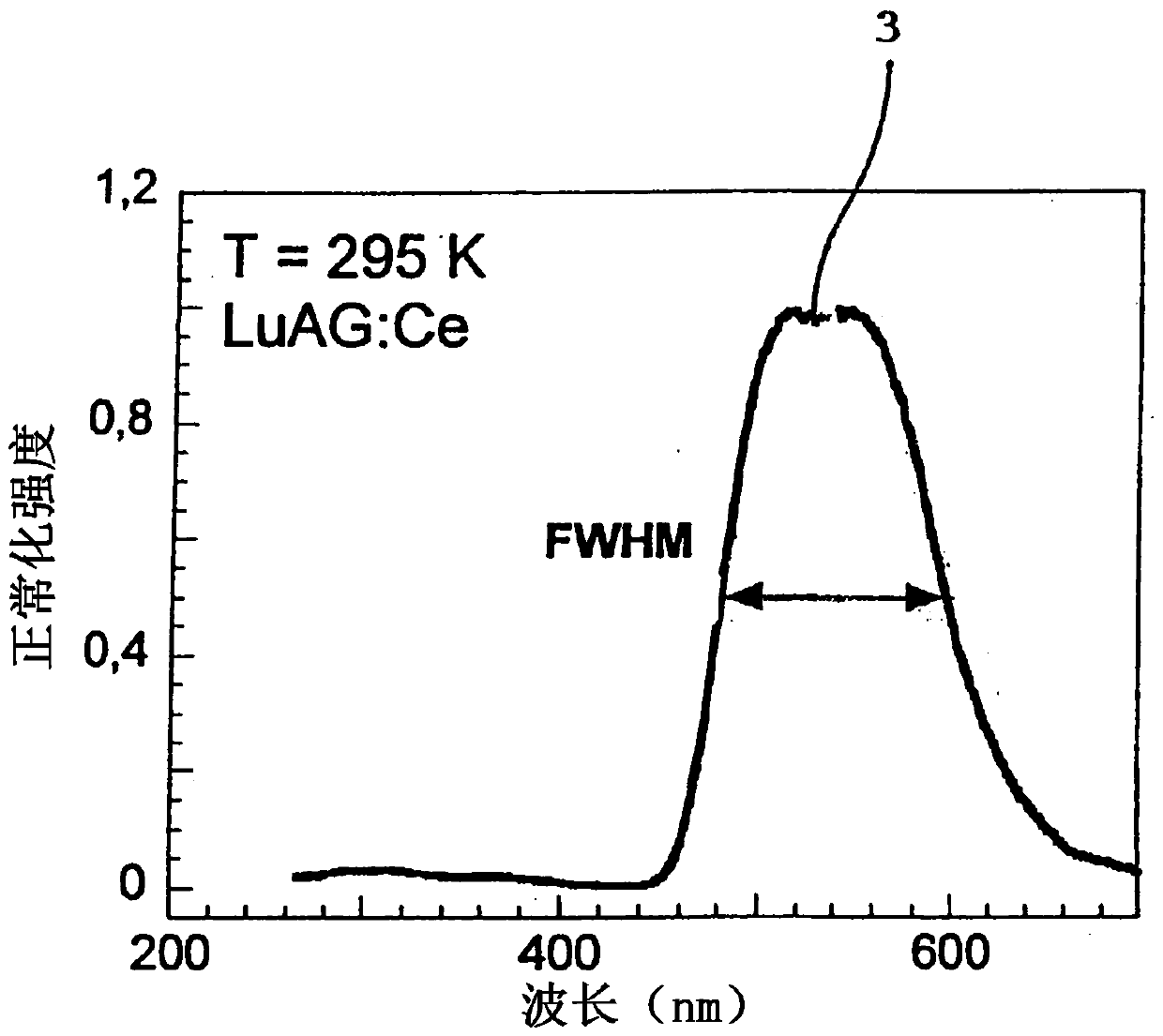
Manner of shortening scintillation response of luminescence centres and material of scintillator with shortened scintillation response
ActiveCN108139492AReduce blink response timeX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentLuminescent compositionsLanthanideElectron excitation
Problem to be solved: Currently, the known manner of shortening the scintillation response of scintillation material is to suppress the amplitude-minor slower components (2) of the scintillation response, whereas the possibilities of significant shortening of the amplitude-dominant component of the scintillation response in this manner are limited. Solution: The invention concerns the manner of shortening the scintillation response of scintillator luminescence centres which uses co-doping with Ce or Pr together with co-doping with ions from the lanthanoids, 3d transition metals, 4d transitionmetals or 5s2 or 6s2 ions group. Having had the luminescence centres electrons excited as a result of absorbed electromagnetic radiation, the scintillator created in this manner is capable of taking away a part of the energy from the excited luminescence centres via a non-radiative energy transfer, which results in a significant shortening of the time of duration of the amplitude-dominant component (1) of the scintillation response.
Owner:CRYTUR SPOL SRO +1
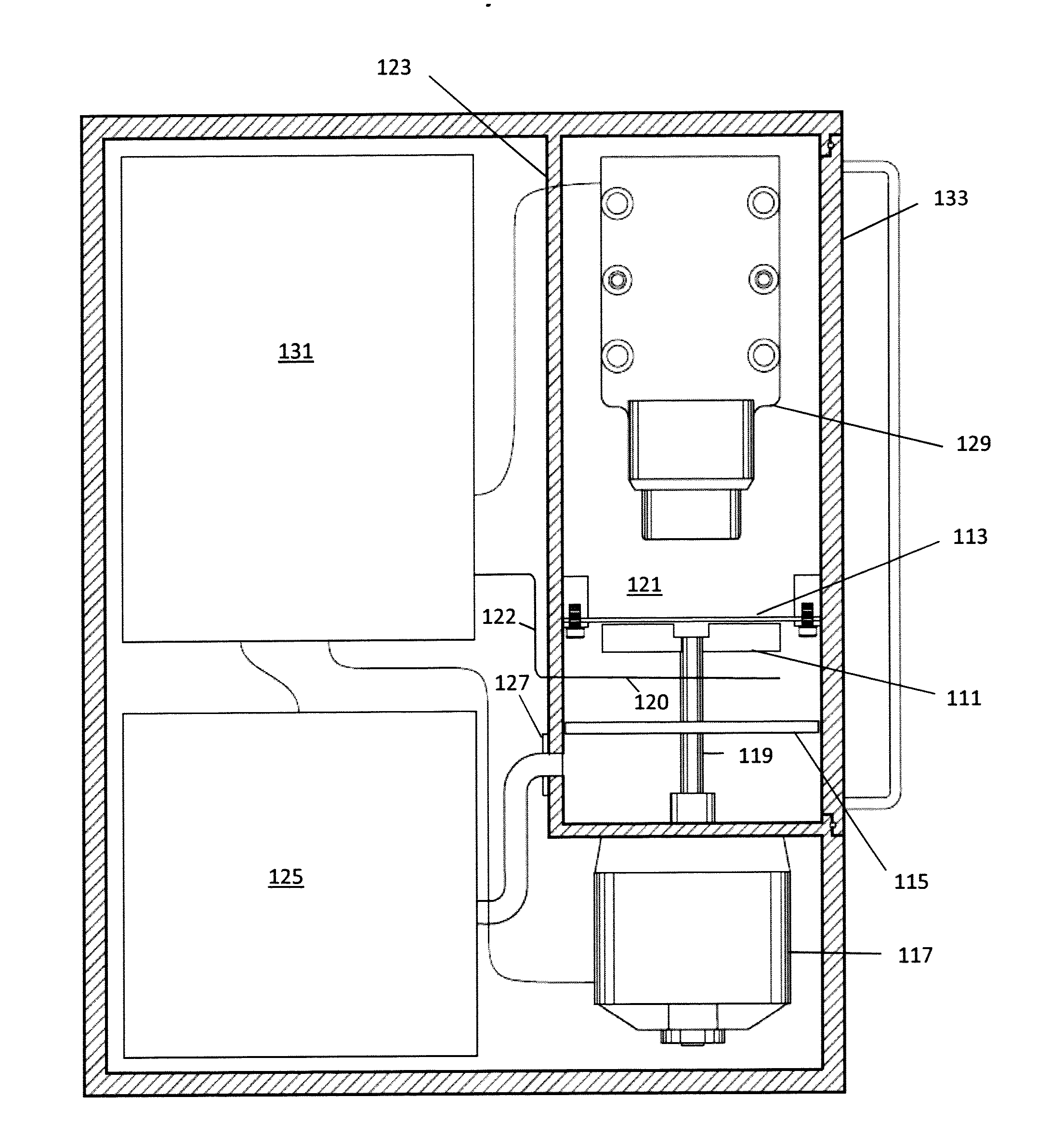
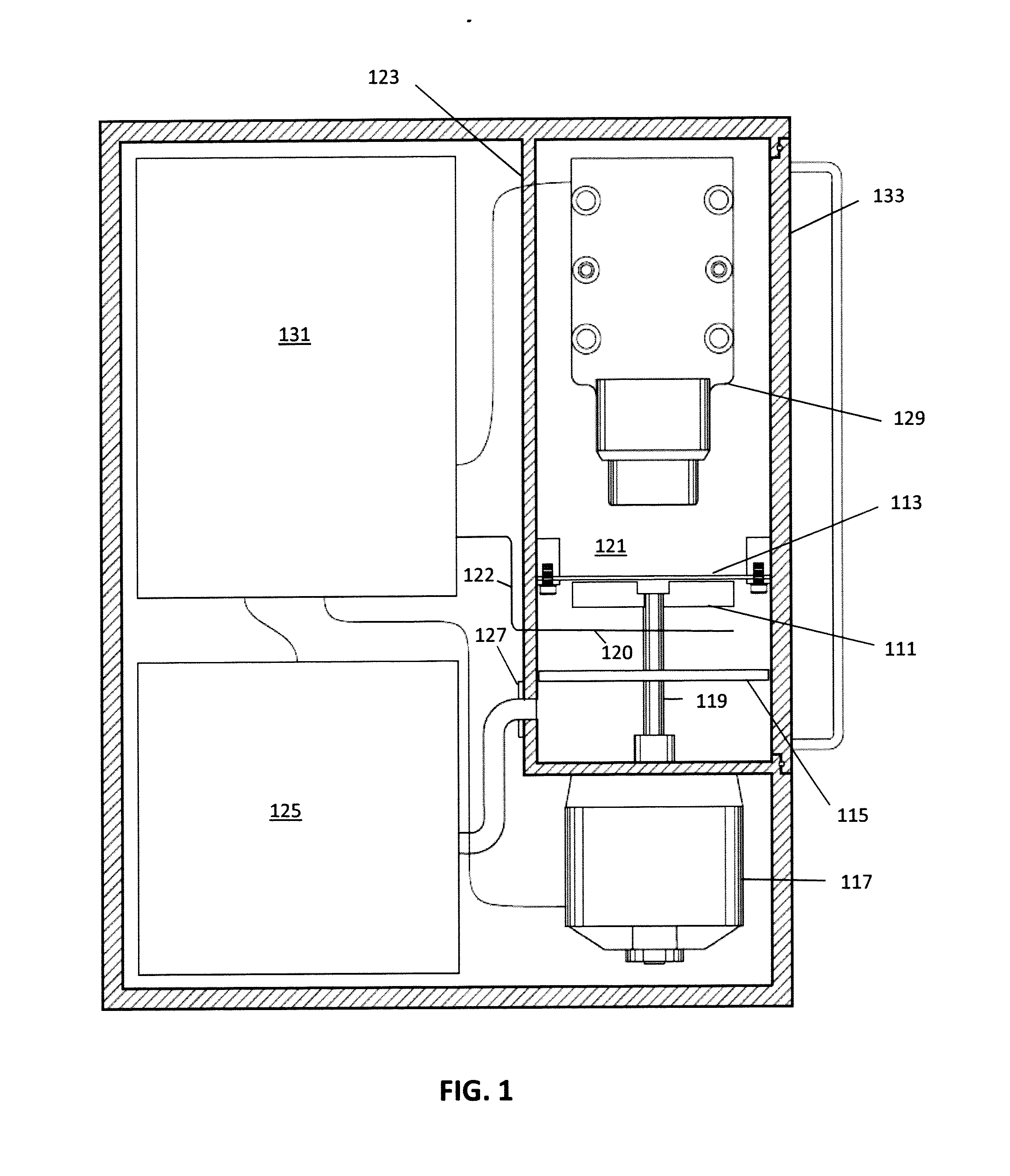
Electron excited x-ray fluorescence device
A device for providing for electron excited x-ray fluorescence may include means for driving two contacting surfaces against each other in a low fluid pressure environment, such that high energy electrons strike a sample under test and provide for x-ray fluorescence of the sample. The sample under test may be in or on a sample holder, whose position with respect to the contacting surfaces is adjustable. For example, the sample holder may be positionable to be a different distances from the contacting surfaces.
Owner:TRIBO LABS
Apparatus and method for measuring vapor flux density
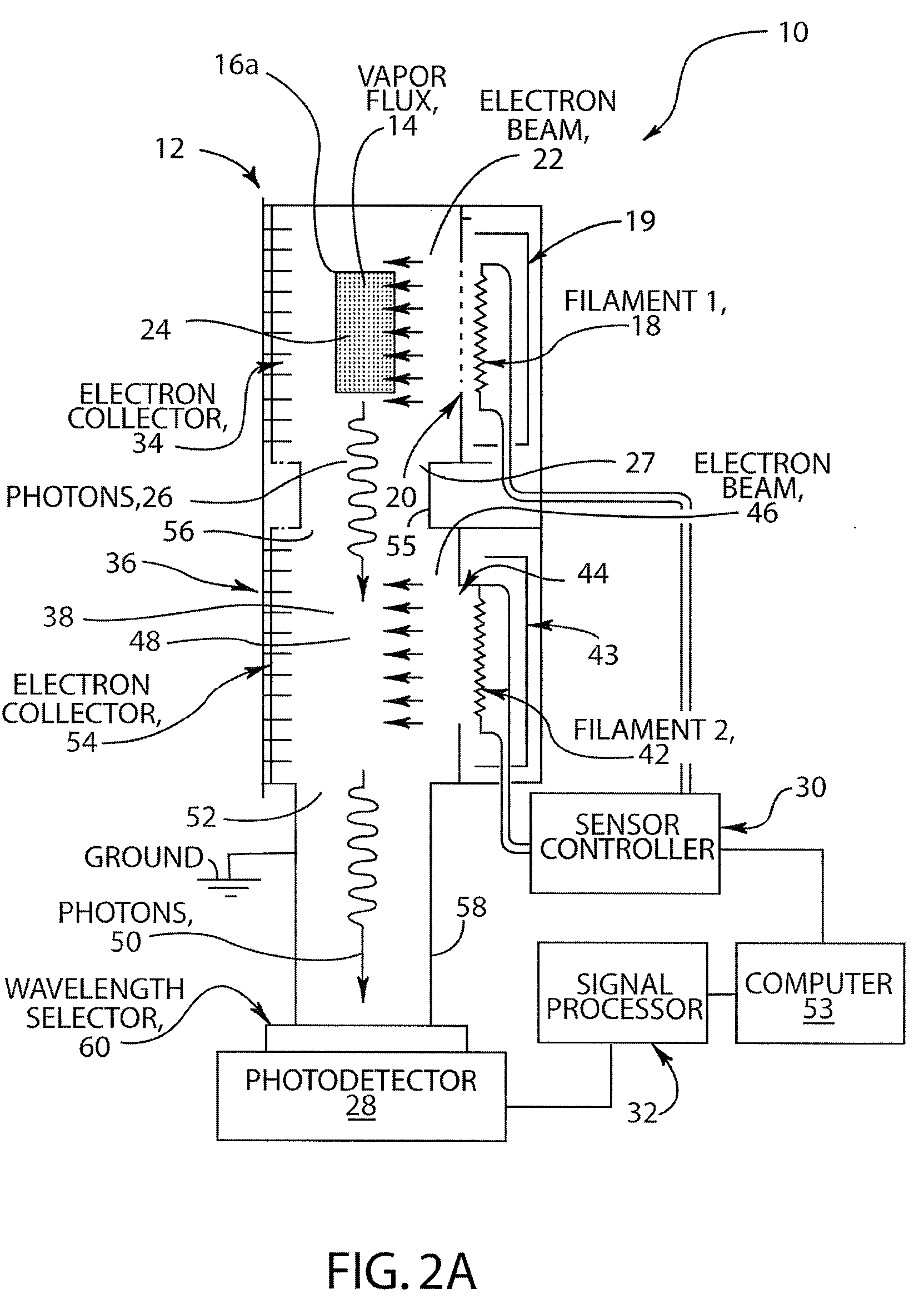
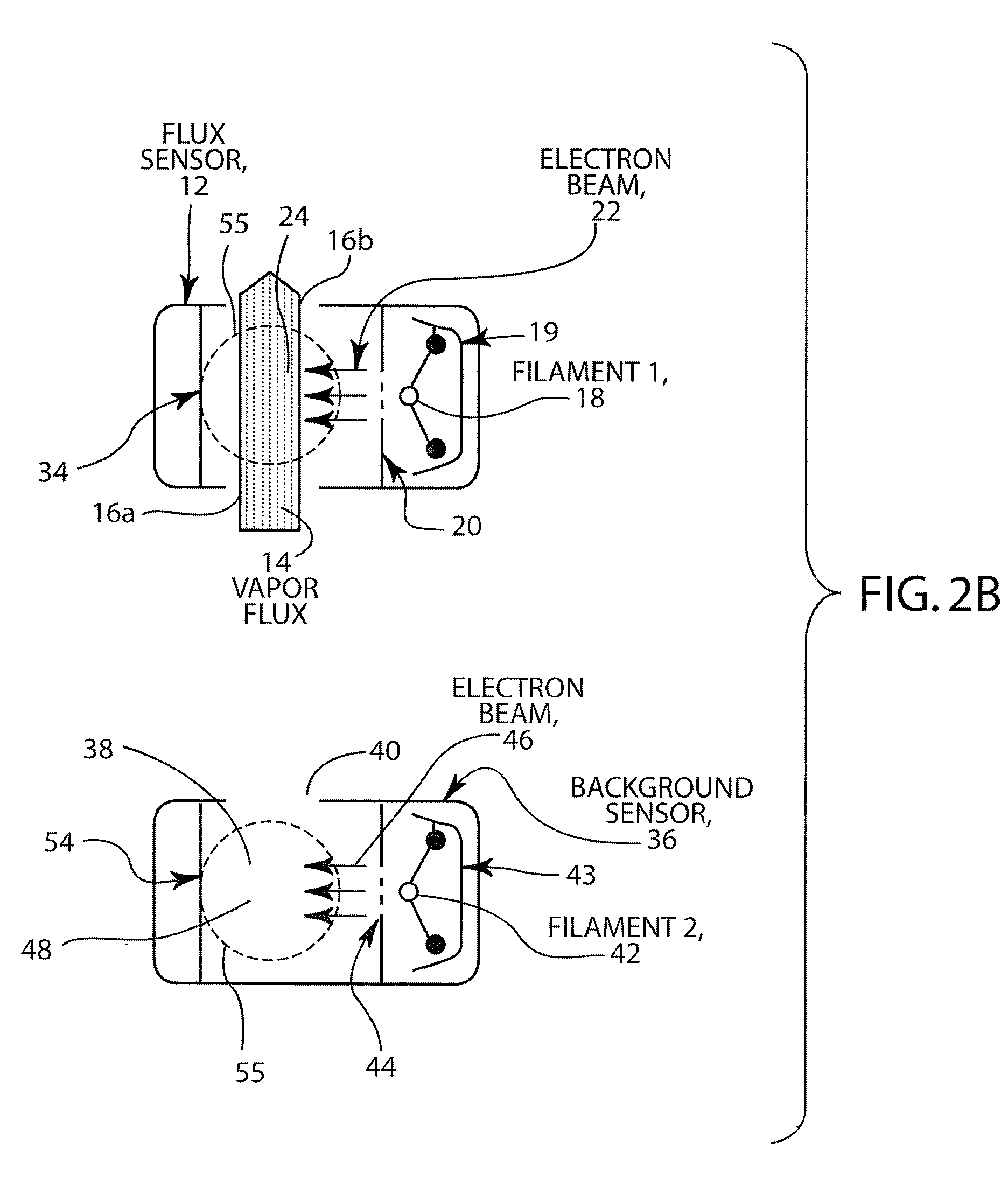
ActiveUS20090095616A1Increase profitBetter signal to noise ratioCellsEmission spectroscopyPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A two-chamber electron impact emission sensor effective for monitoring vapor flux of materials in the presence of interfering species is described. The sensor includes two independent electron excitation regions and one photodetector for monitoring emission from excited species from both chambers. Copper vapor flux from an evaporation source was accurately measured in the presence of interfering H2O vapor, and Ga vapor flux from an evaporation source was accurately monitored in the presence of interfering CO2 gas. The invention permits deposition rates to be monitored using electron-impact emission spectroscopy with significantly improved accuracy in the presence of interfering gases at high partial pressures.
Owner:INFICON INC
Light-emitting appartus
InactiveUS20090009056A1Avoid low lightGenerate efficientlyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsElectron excitationLight emission
A light emitting apparatus capable of efficiently generating high luminance white light is provided. The present invention permits white light to be generated, without using low-emission efficiency white light emitters, by forming a light emitter layer 16 using a high-light emission efficiency blue light emitter and yellow light emitter. In this case, having at least a part of the blue light emitter particles 17 and at least a part of the yellow light emitter particles 18 exposed at a surface of the light emitter layer 16, respectively, allows both of such particles to be directly bombarded with electrons, thereby effecting a highly efficient electron excitation. Furthermore, the use of YAG or the like, as a yellow light emitter, which emits yellow light not only by electron excitation but also through photoexcitation by the blue light, permits said blue light to contribute to the emission of the yellow light, even when part of the blue light emitted by the blue light emitter particles, as it passes through the light emitter layer 16, is blocked by the yellow light emitter particles 18, whereby white light can be generated efficiently with a reduction in energy loss.
Owner:SUBARU CORP +1
Method and system for raman, fluorescence, lithographic, stimulated emission and photochemical imaging beyond the diffraction limit
InactiveUS8432543B2Minimizes parasitic two-photon absorption effectsRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationResistFluorescence
Systems and methods for hyper-resolution beyond the diffraction limit of optical microscopes for applications in spectroscopy, absorption and lithographic photochemical patterning are described. These systems are based on interference of a pump pulse and a Stokes laser pulse which interfere to localize the population of an excited vibrational state in an area that is smaller than the scanning resolution of the microscope. Another (interfering) Stokes pulse has an annular shape at focus and destructively interferes with the the Stokes laser pulse. This destructive interference causes narrowing of the population distribution of the vibrational excited state well below the diffraction limit, which in turn localizes the population of the central electronic excited state by a separate actinic laser pulse having a lower energy than the ground state excitation energy of the molecule.A stepped photolithography system uses two photomasks to produce photoresist images capable of printing features smaller than 10 nm.
Owner:FREL ROBERT D
Optoelectronic device, use of a dual emitter as wavelength conversion material
ActiveUS9954147B2Improve efficiencyOrganic chemistrySpectral modifiersExcited stateSecondary radiation
An optoelectronic apparatus is disclosed. In an embodiment, the apparatus includes at least one wavelength conversion region which includes at least one dual emitter as wavelength conversion material, wherein the wavelength conversion region converts primary radiation at least in part into secondary radiation, and wherein the dual emitter includes a first electronic base state and a second electronic base state, together with a first electronically excited state and a second electronically excited state which may be reached from the first electronically excited state. The dual emitter further includes emission proceeding from the second electronically excited state into the second base state.
Owner:OSRAM OLED
Excimer broadband pumped alkali metal blue laser
ActiveCN109309336AImprove efficiencyImprove scalabilityActive medium materialGas laser constructional detailsHigh energyRubidium
The invention relates to an excimer broadband pumped alkali metal blue laser, comprising a pump source a, a pump source b, an alkali metal vapor pool, a heating furnace, a high reflectivity mirror, and an output coupling mirror. The alkali metal laser is suitable for using an alkali metal such as potassium, rubidium or caesium as a gain medium. By means of the cascade pumping method, the pump source a outputs a narrow linewidth laser to excite the alkali metal of the n2P3 / 2 level. The first electronically excited alkali metal and inert gases form an A2pi3 / 2 level excimer with a higher bindingenergy, and a pump source b outputs a wide linewidth laser to excite the A2 pi 3 / 2 level excimer to the I2 sigma +1 / 2 level. The I2 sigma +1 / 2 level is rapidly decomposed into inert gases and alkali metal atoms of the (n+1)2P3 / 2 level. The alkali metal atoms return to the n2S1 / 2 level from the (n+1)2P3 / 2 level, directly producing blue laser. Through the method, an alkali metal blue laser can be applied to the field of high-energy blue laser; and extended to a violet laser or other laser with a shorter wavelength. In the method, a laser structure is similar in design to current diode-pumped alkali metal lasers and is easy to implement.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
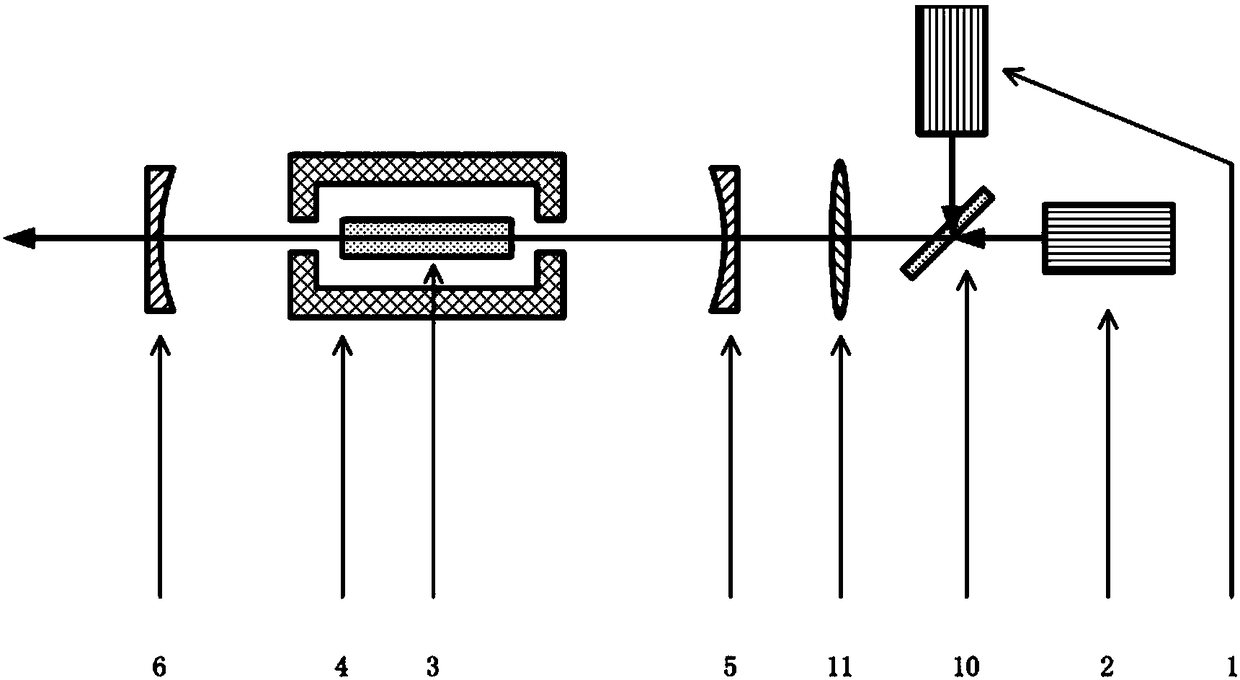
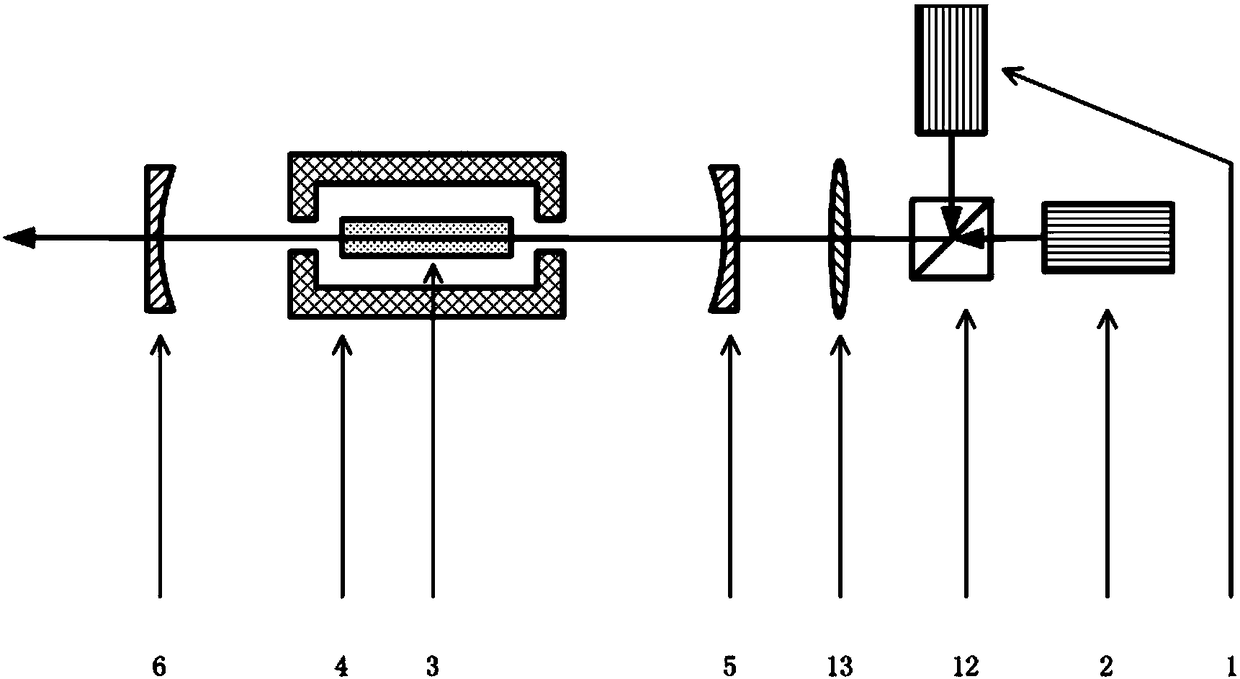
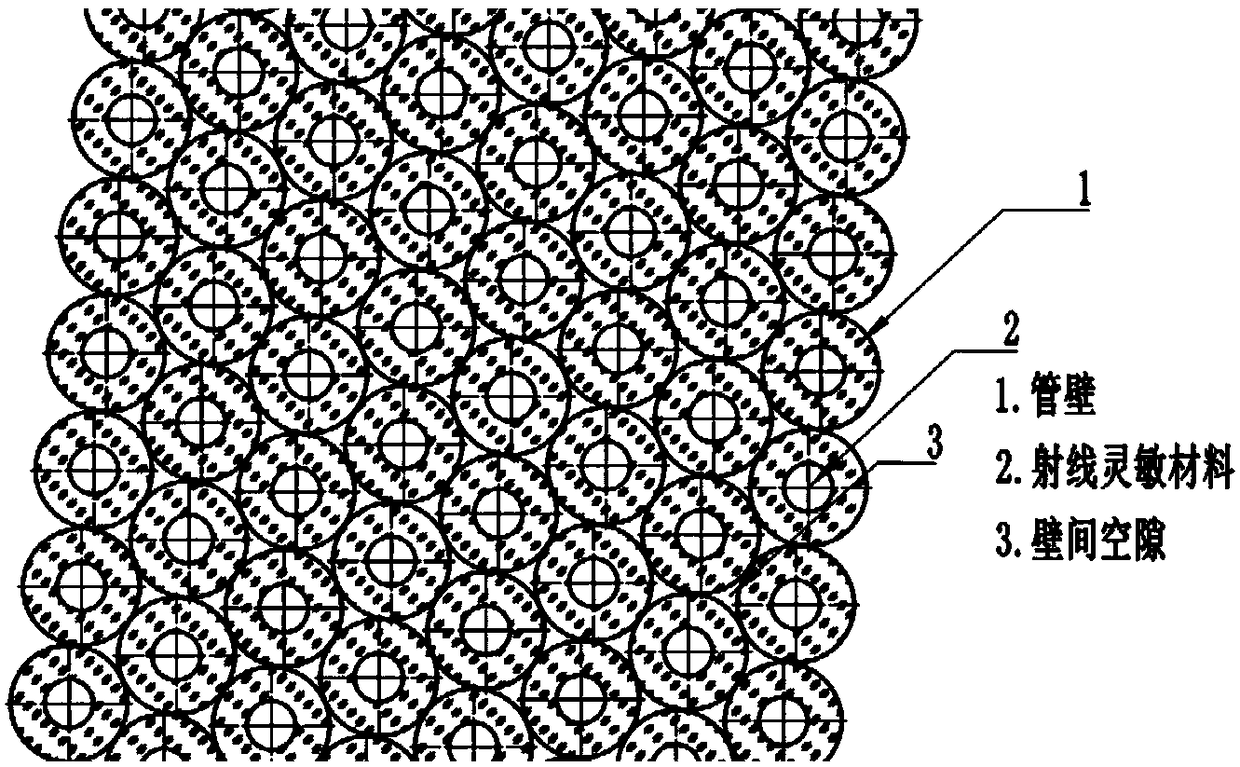
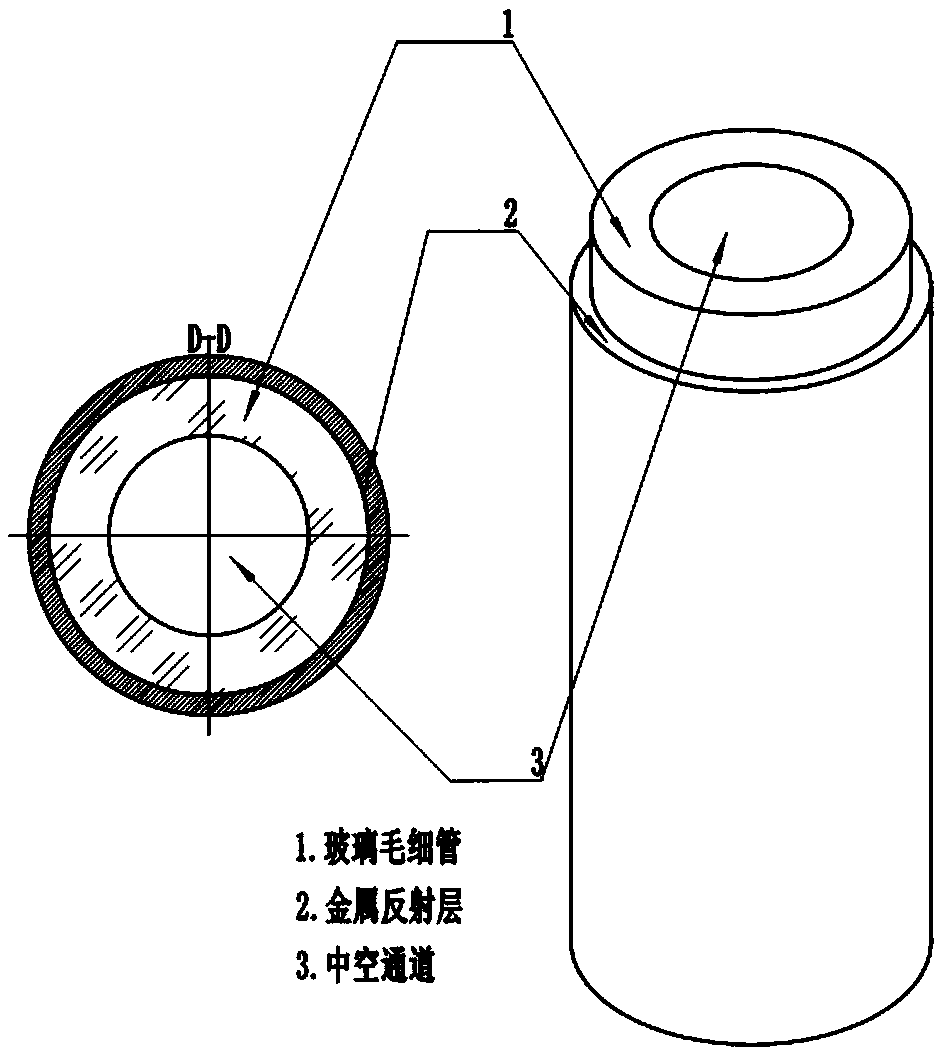
Fast neutron image detection device and manufacturing method of fast neutron detector array
The invention relates to a fast neutron image detection device and a manufacturing method of a fast neutron detector array, and belongs to the technical field of fast neutron detection. The fast neutron image detection device comprises the fast neutron detector array which is constituted by a plurality of glass capillaries; the outer wall of each glass capillary is plated with a reflective film, and thus light is constrained in the current glass capillary and only transmitted to the two ends of the current glass capillary; and each glass capillary is filled with a ray sensitive material, thusfast neutrons and light nucleus in the ray sensitive materials generate elastic scattering, recoil charged nucleus enable organic molecules pi to be subjected to electron excitation on a flight path,the ground state is jumped into the excitation state, and glowing is conducted in a de-excitation mode. The outer wall of each glass capillary is plated with the reflective film, reflective layers exist, thus the visible light generated in each glass capillary is almost entirely transmitted to the two end faces of the glass capillary, and the problem of crosstalk of the light between the glass capillaries is avoided accordingly.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Titanium alloy surface ion carbonitriding treatment device
ActiveCN112795863ALower the activation energy of the atomic reactionLower activation energyHollow article cleaningSolid state diffusion coatingTitanium alloyIon pairs
The invention belongs to the technical field of titanium and titanium alloy surface treatment and particularly relates to a titanium alloy surface ion carbonitriding treatment device. A dual-power system is adopted in the device, an auxiliary cathode is controlled by a set of direct-current power supply, ionization of argon near the auxiliary cathode can be accelerated by applying voltage to the auxiliary cathode, ion collision is excited to accelerate temperature rise, and meanwhile, a workpiece and a cavity in the furnace can be cleaned; and the negative electrode of another set of high-frequency pulse bias power supply is connected with a workpiece, and the positive electrode is grounded, so that the workpiece is in a negative potential, negative bias has an acceleration effect on the diffusion process of plasma on the surface of the workpiece, the bombardment effect of ions on the surface of the workpiece can be improved, and the adhesive force and density of a diffusion layer are enhanced. Ammonia gas and carbon dioxide serve as diffusion media, electron excitation state ions with high internal energy are formed under collision of electrons, a diffusion layer moderate in thickness and uniform in structure is prepared, and the mechanical property and the tribological property of titanium are remarkably improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
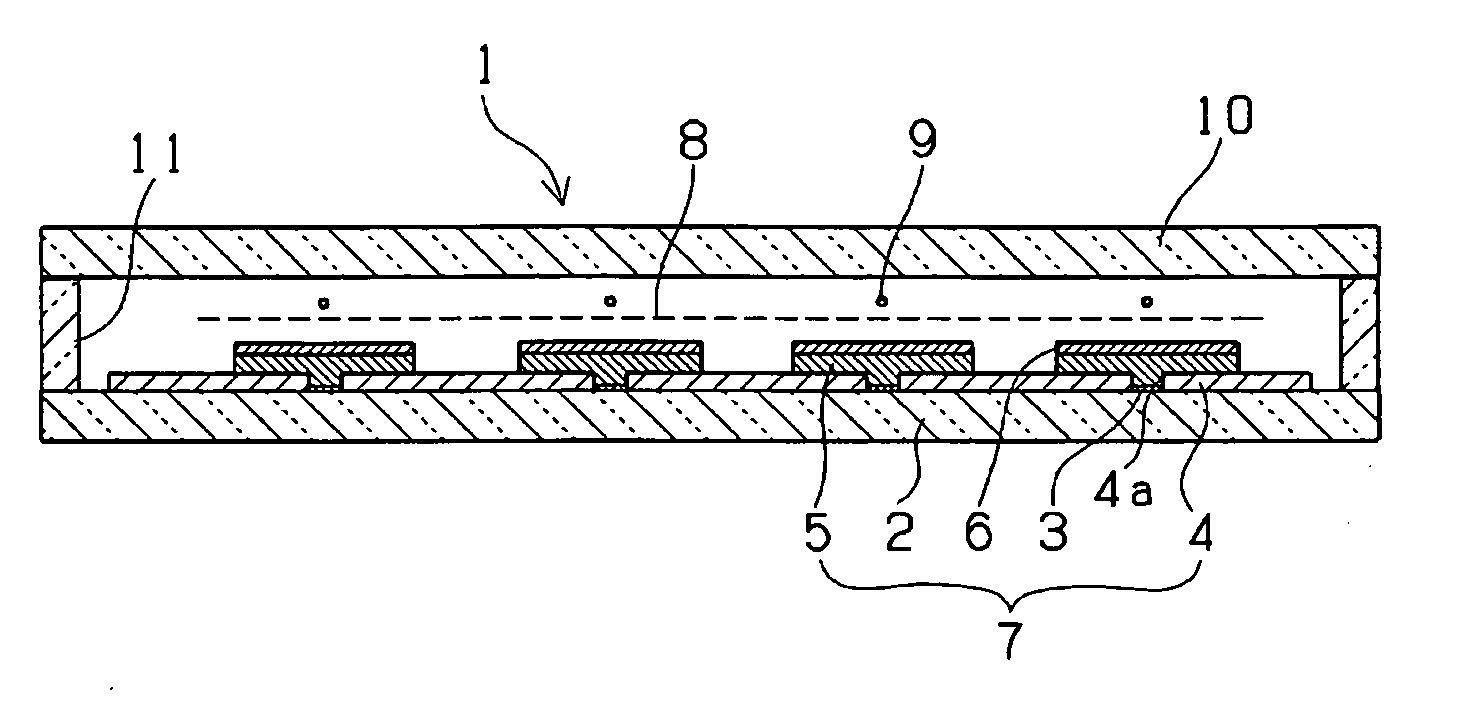
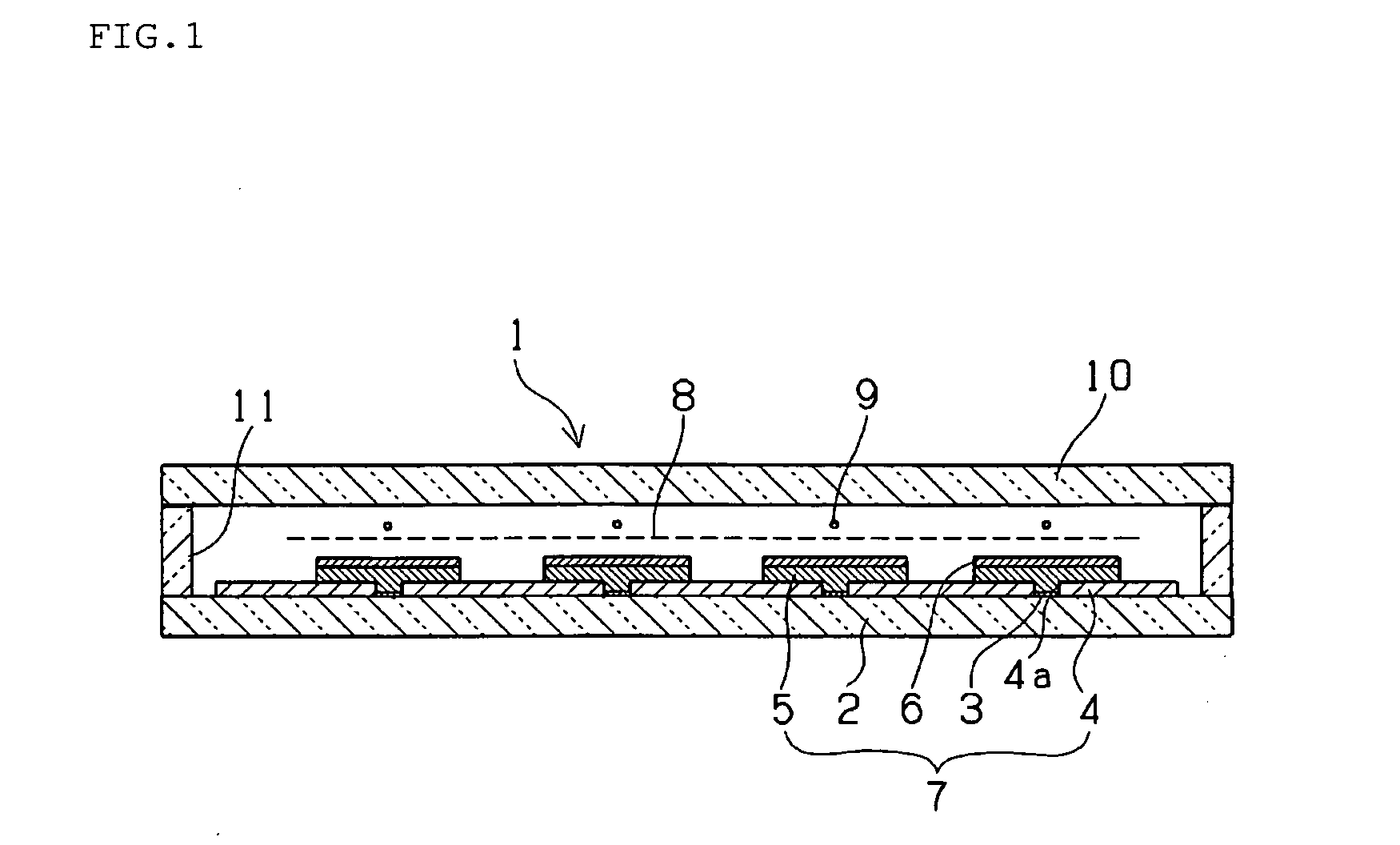
Display device
InactiveUS20070096660A1Reduce the driving voltageImprove luminous efficiencyStatic indicating devicesAuxillary electrodesDisplay deviceUltraviolet lights
A device including a first substrate and a second substrate facing each other, and including a plurality of cells defined between the first and second substrates, an electron accelerating and emitting unit, disposed between the first and second substrates, for accelerating and emitting electrons, a gas including N2 within the cell, the gas capable of being excited by the electrons emitted by the electron accelerating and emitting unit to generate ultraviolet light, and a light emitting layer disposed on an outer surface of one of the first and second substrates, the light emitting layer capable of being excited by the ultraviolet light to generate visible light.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Method of spatial high resolution imaging of a structure of a sample, the structure comprising a luminophore
ActiveUS20150308955A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometryHigh resolution imagingLuminophore
For spatial high resolution imaging of a structure of a sample comprising a luminophore, the sample is subjected to excitation inhibiting light transferring the luminophore out of an excitable electronic ground state into a protection state in which the luminophore is protected against electronic excitation by luminescence excitation light and luminescence de-excitation light. The excitation inhibiting light comprises a first local minimum. Next, the sample is subjected to the luminescence excitation light exciting the luminophore within the first local minimum into an excited luminescent state. Then, the sample is subjected to the luminescence de-excitation light returning the luminophore out of the excited luminescent state into the excitable electronic ground state. The luminescence de-excitation light comprises a second local minimum overlapping with the first local minimum. Luminescence light emitted out of the measurement area is measured and assigned to the position of the second local minimum within the sample.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
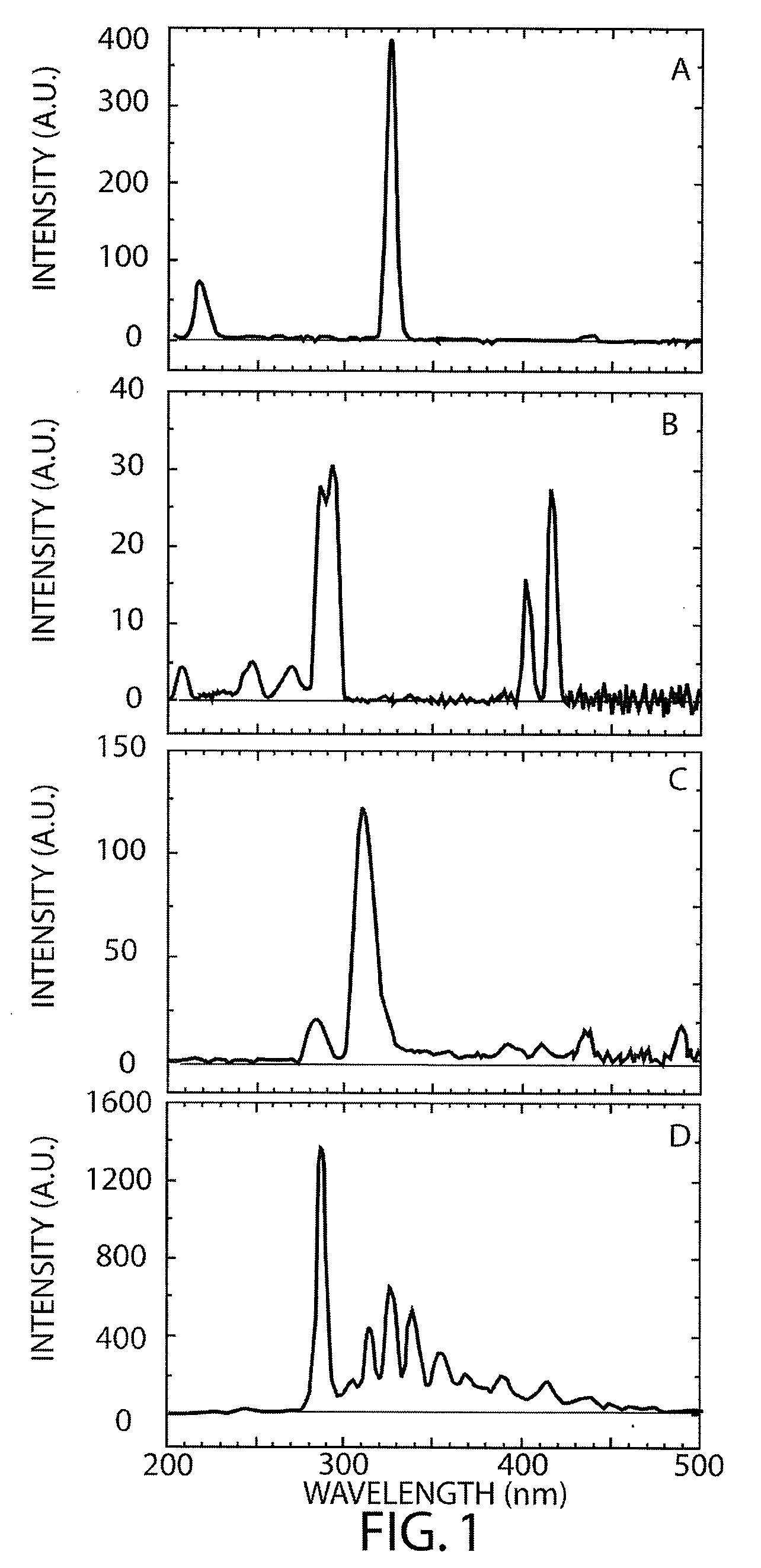
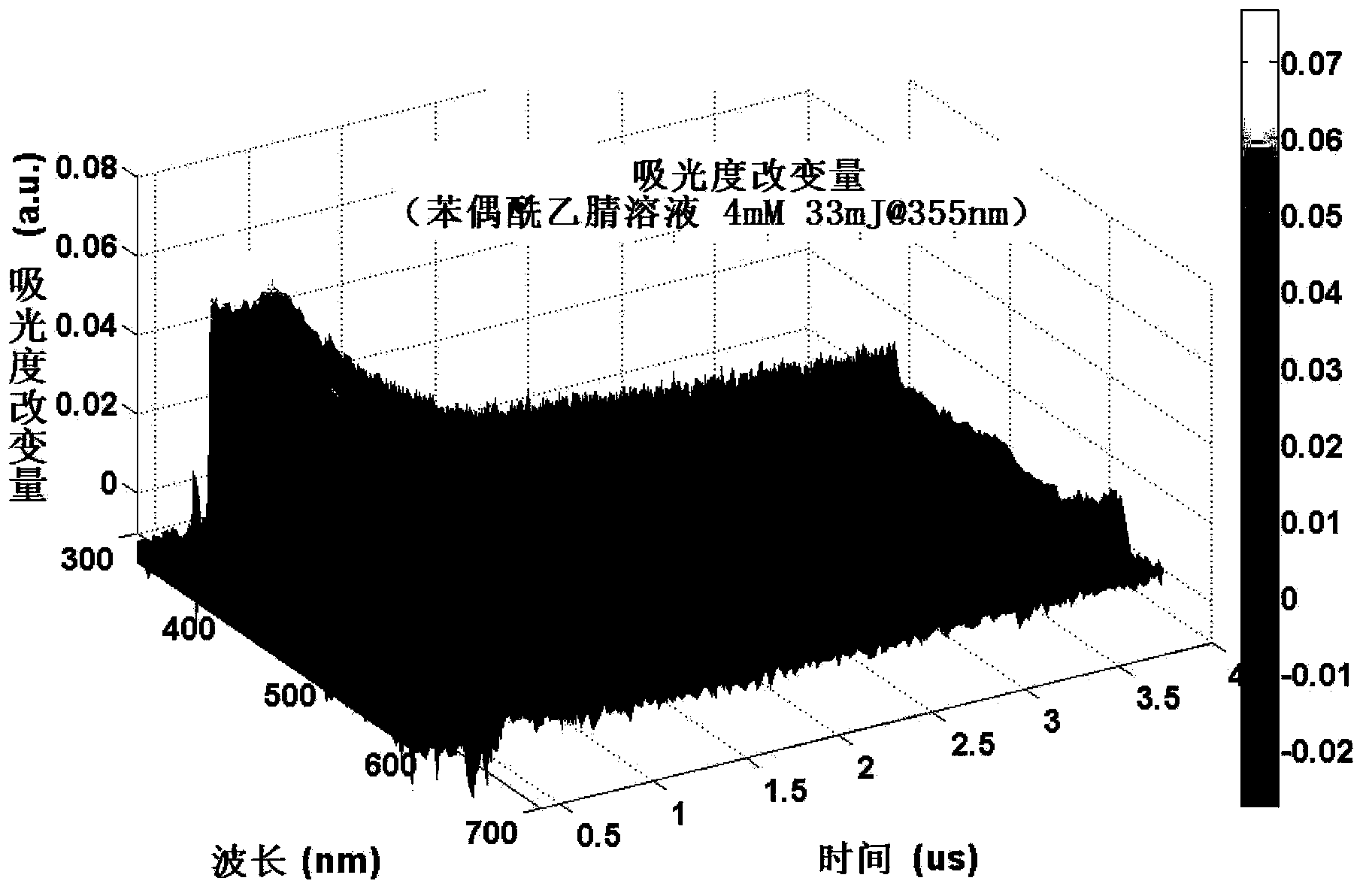
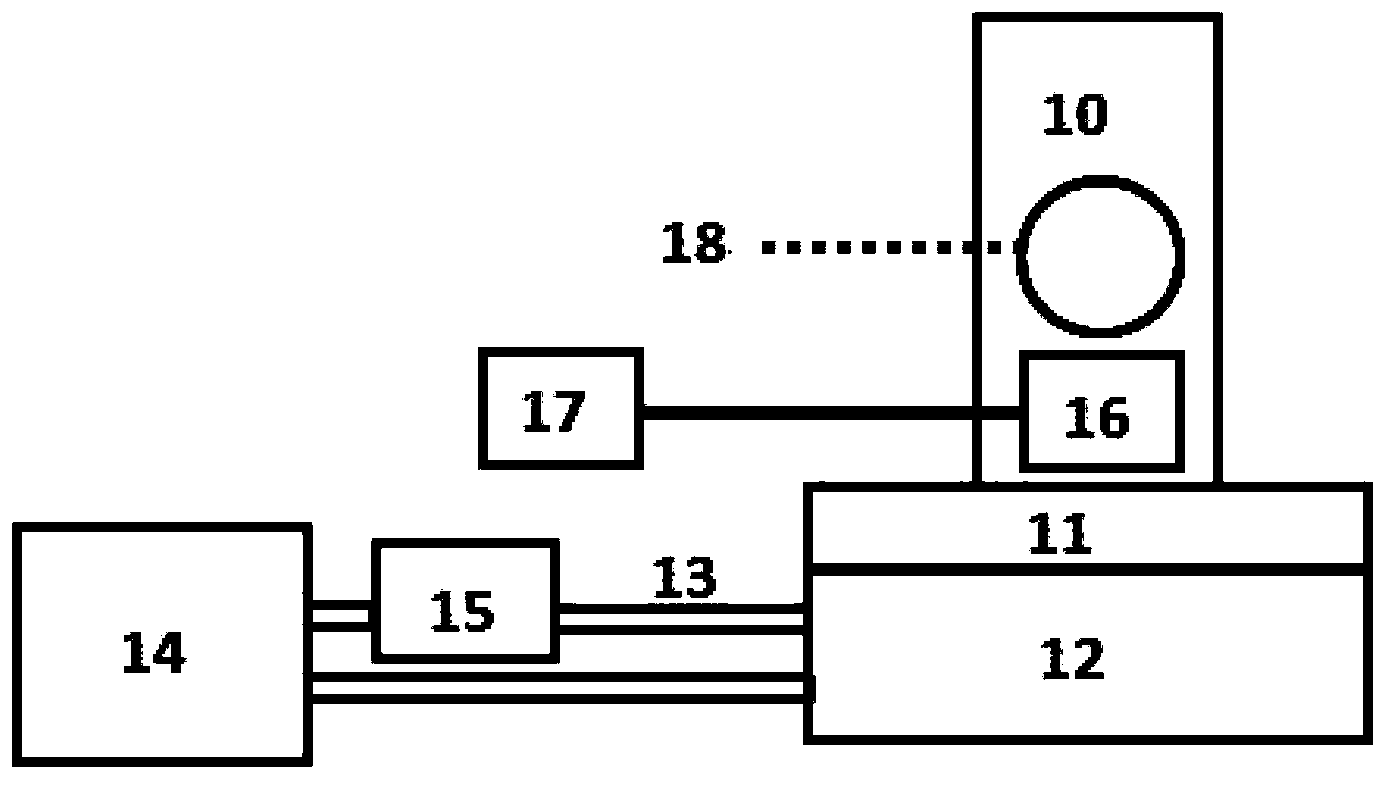
Nanosecond time-resolved absorption and emission spectrum measuring device and measuring method
ActiveCN104062269AImprove signal-to-noise ratioAnalysis by material excitationData acquisitionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention relates to a nanosecond time-resolved absorption and emission spectrum measuring device. An excitation light source is orderly connected with a first sequence pulse generator, a working frequency coordinator, a second sequence pulse generator, and a data collector; the second sequence pulse generator is respectively connected with a light path system and a detection light source; the data collector is respectively connected with the working frequency coordinator, a first light intensity detector, a second light intensity detector, a third light intensity detector, and a monochromator; the light path system and a sample cell are also disposed between the detection light source and the monochromator. The measuring method comprises: setting the temperature of a sample, irradiating the sample by light beams emitted by the excitation light source to reach an electron excitation state, obtaining zero point time of time-resolved spectrum data by part of the light beams; after pulsed white light emitted by the detection light source passes through the sample, feeding back detection light intensity signals to the data collector, and converting the signals into absorption and emission spectra. The measuring device of the invention is equipped with a temperature controllable sample cell, and obtains spectrum data with a high signal to noise ratio.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electroluminescent device
ActiveCN111261792AIncrease brightnessDelay aging cycleSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilver pasteElectron excitation
The invention relates to an electroluminescent device. The electroluminescent device comprises an electron emission layer, an energy storage reflective layer, an electron excitation layer, an electronrecovery layer, a first electrode and a second electrode, wherein the electron emission layer is made of conductive silver paste, and the conductive silver paste is formed by mixing a mixture of silver nanoparticles and silver nanowires with a high polymer material; the energy storage reflective layer is attached to the electron emission layer; the electron excitation layer is attached to the energy storage reflective layer; the electron recovery layer is attached to the electron excitation layer; the first electrode is attached to the electron emission layer; and the second electrode is attached to the electron recovery layer. The electroluminescent device provided by the invention is a low-voltage electroluminescent device, and the potential safety hazard of the electroluminescent device can be reduced and the application field is broadened within the range of the operating voltage safe to the human body.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD +1
Adhesive body between conductive polymer-metal complex and substrate and method for forming the same, conductive polymer-metal complex dispersion liquid, method for manufacturing the same and method for applying the same, and method for filling hole using conductive material
ActiveUS20150282310A1Improve stabilitySatisfactory storabilityLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive polymerUltraviolet lights
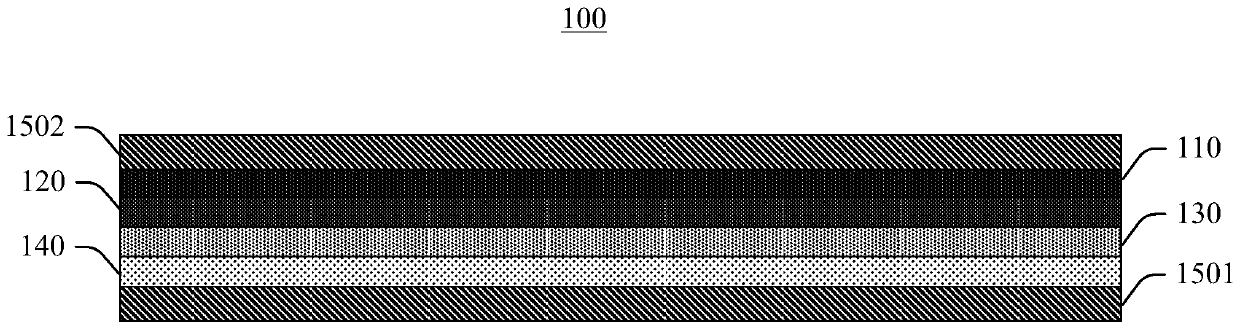
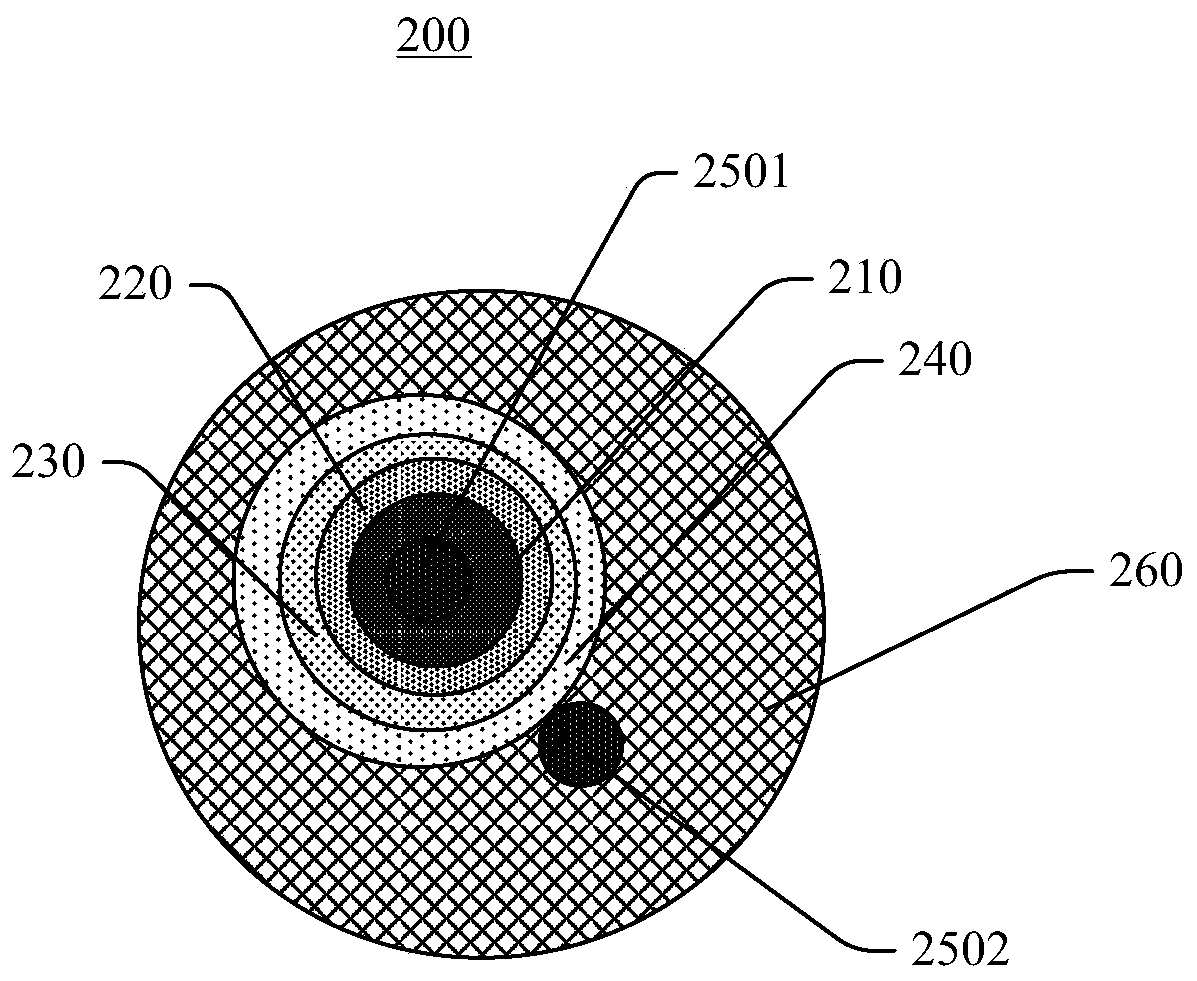
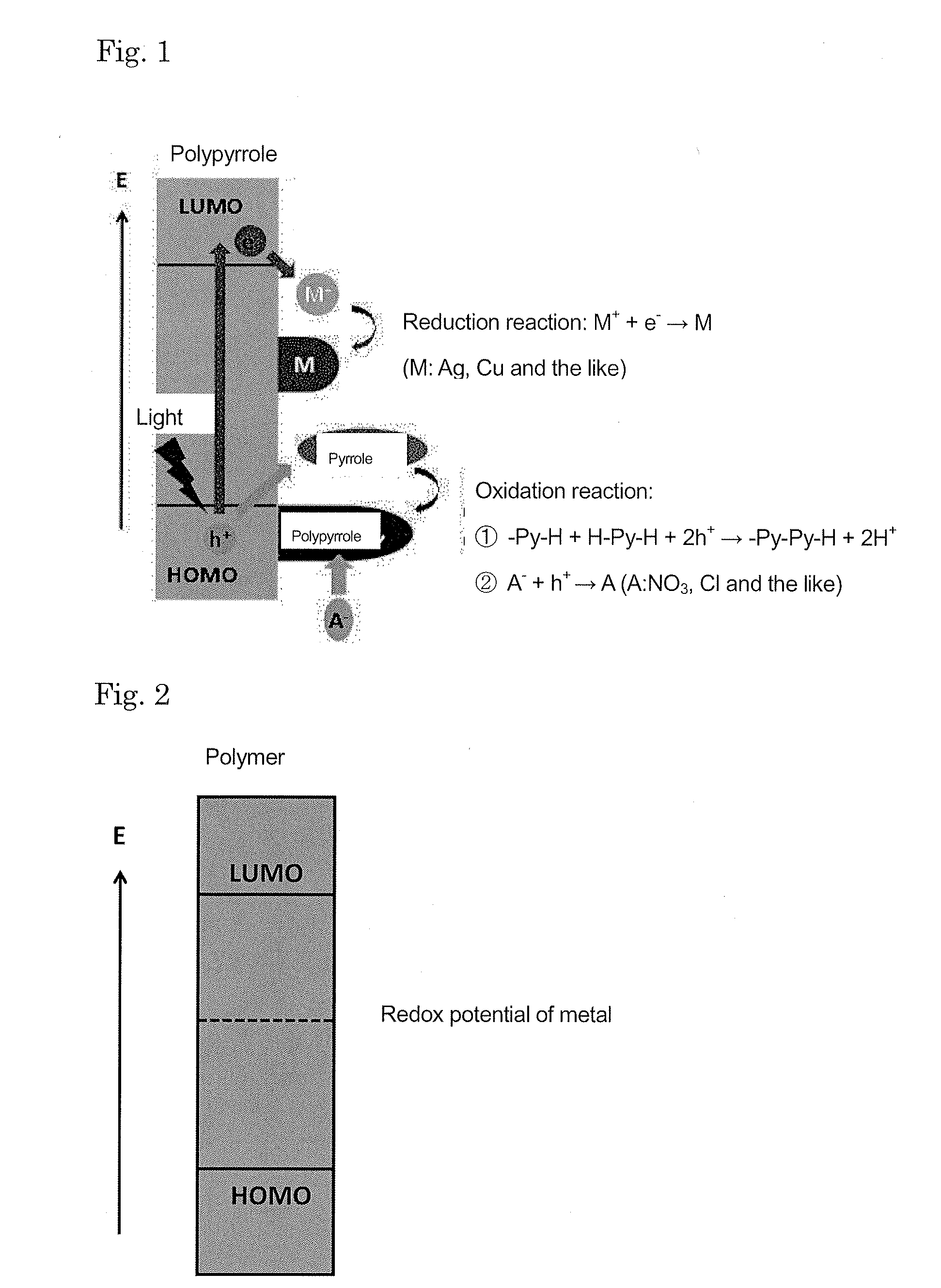
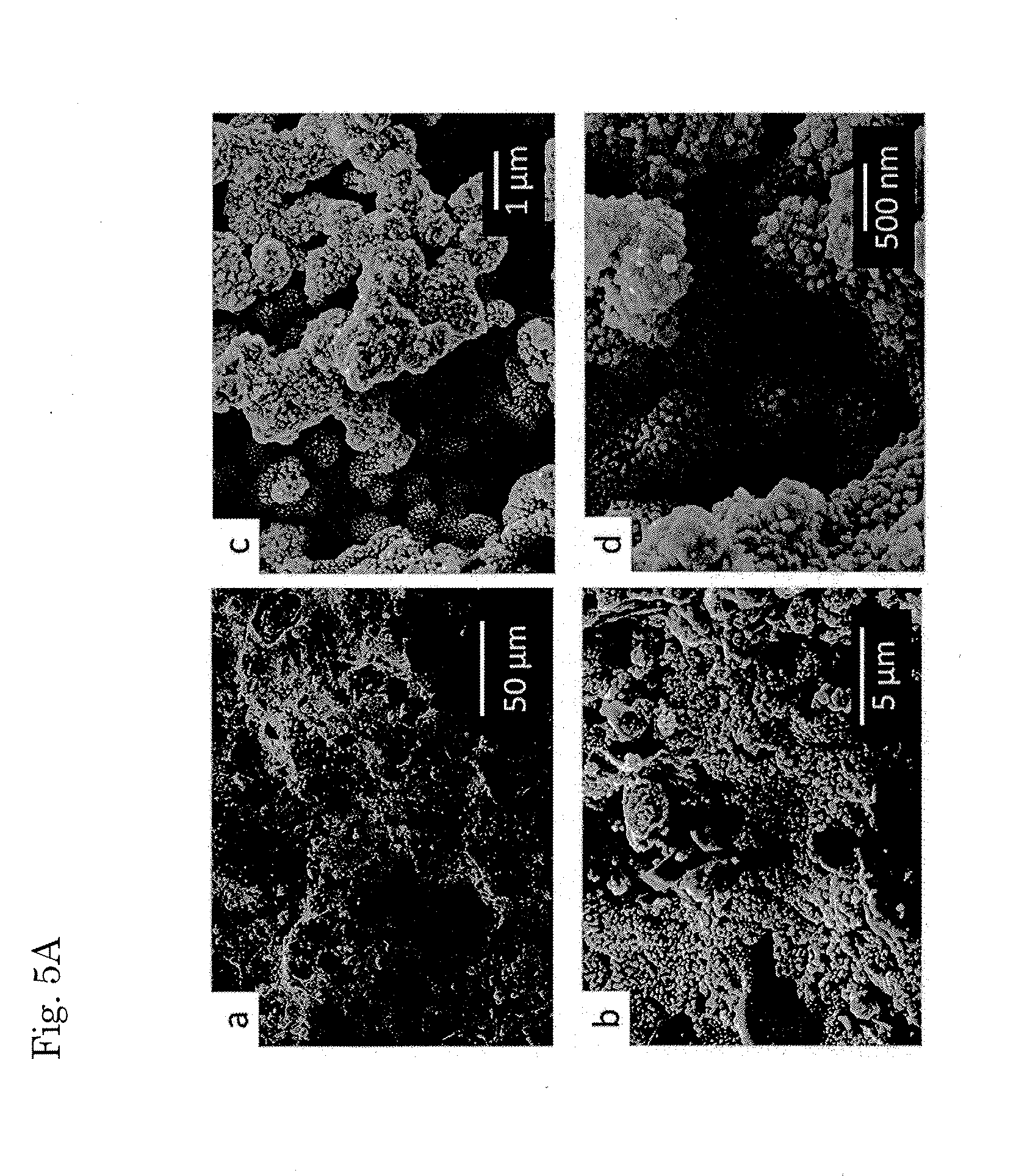
A conductive polymer-metal complex becomes to be adhered simply and strongly on the surface of a substrate such as PTFE. By subjecting a solution containing a monomer which provides a conductive polymer, an anion, and a metal ions such as Ag+, Cu2+, Cu+ and the like to an irradiation with light having an energy required for exciting an electron to an energy level capable of reducing the metal ion, such as ultraviolet light, under an appropriated condition, thereby precipitating the conductive polymer-metal complex as being dispersed in the reaction liquid. By supplying this dispersion liquid onto various substrates, the complex microparticles in the dispersion liquid enter into and mate with the narrow holes on the surface of the substrate. As a result, the complex precipitate formed on the surface of the substrate and the substrate can be adhered strongly to each other.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com