Organic phosphorus-based flame retardant and process for producing the same
A technology of organophosphorus and flame retardants, applied in the field of organophosphorus flame retardants and their preparation, can solve the problems of reduced flame retardant effect and thermal stability, low decomposition temperature, and reduced heat resistance, and achieve excellent dispersion And compatibility, excellent flame retardant effect, high decomposition temperature effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
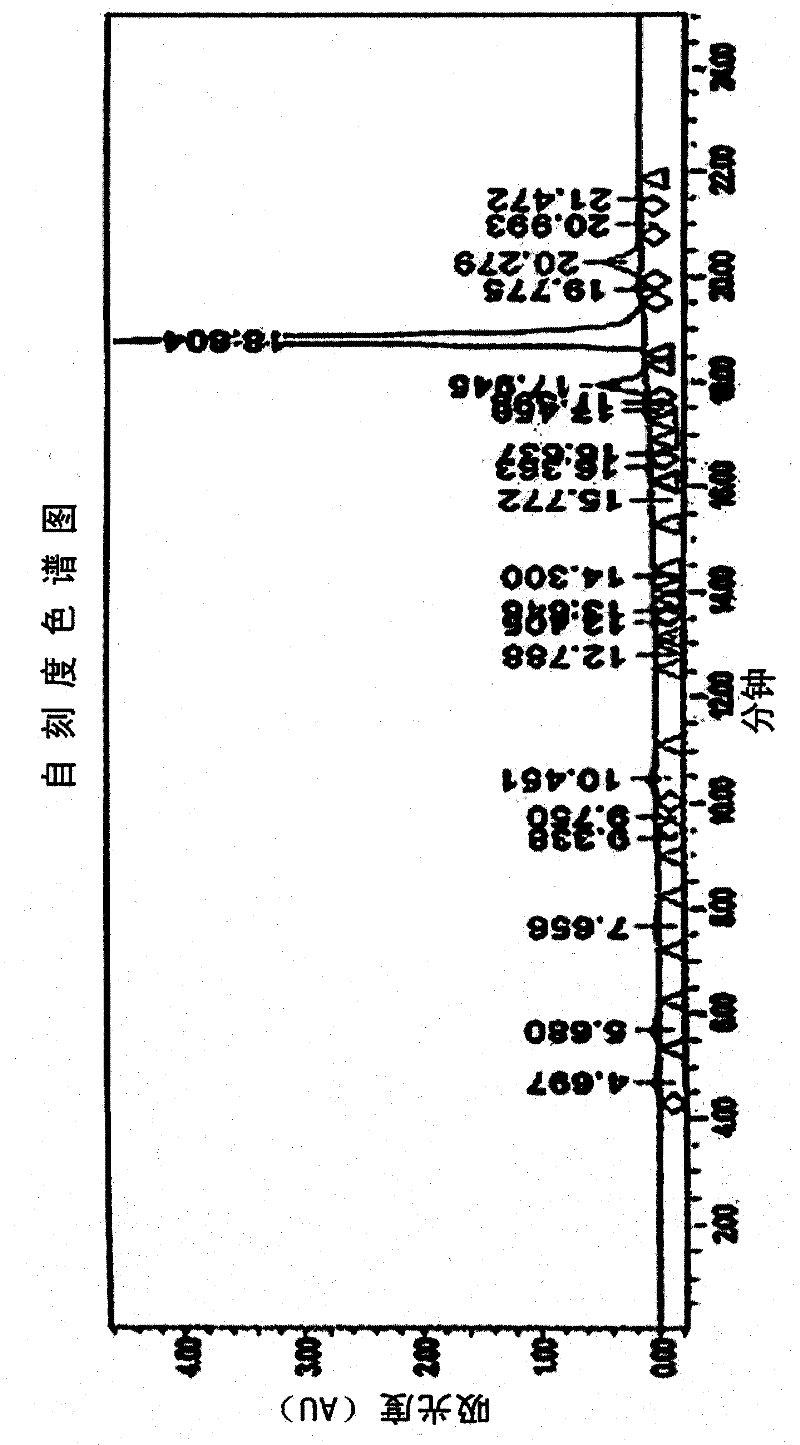
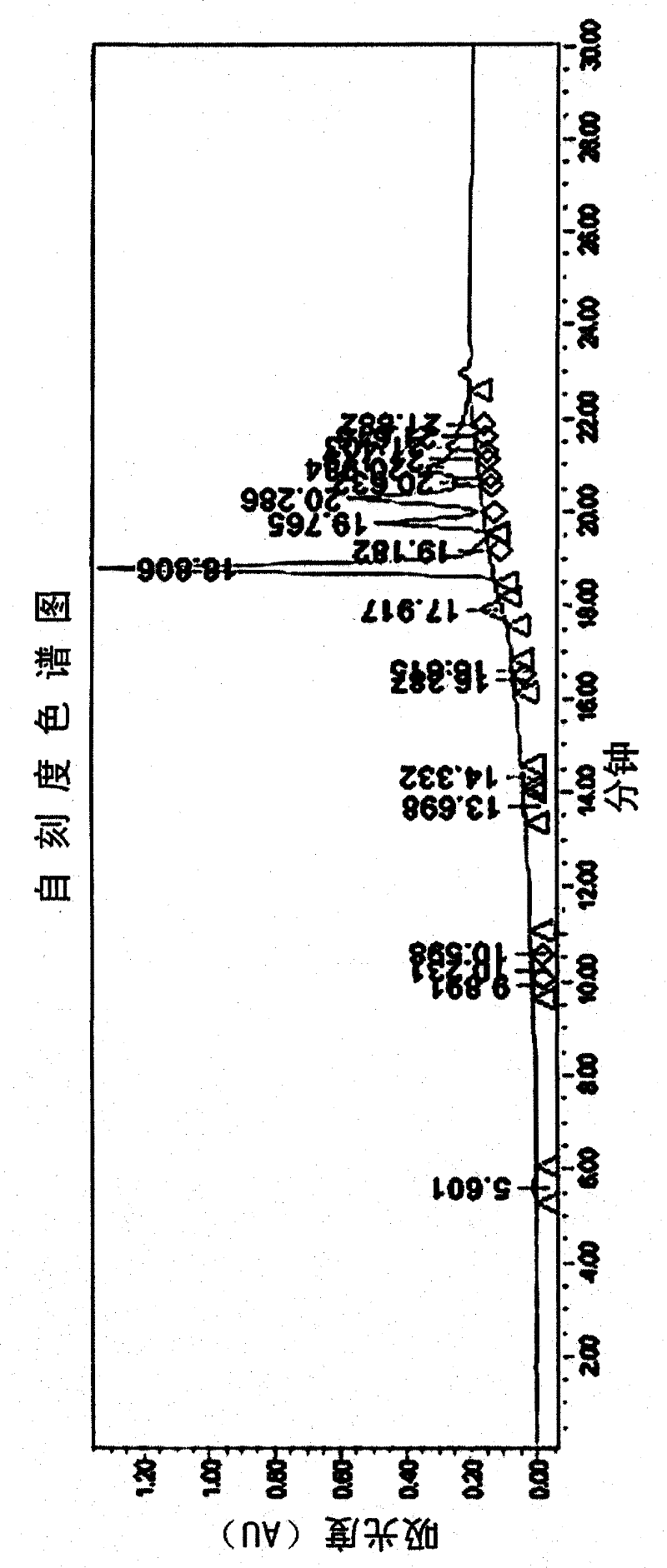
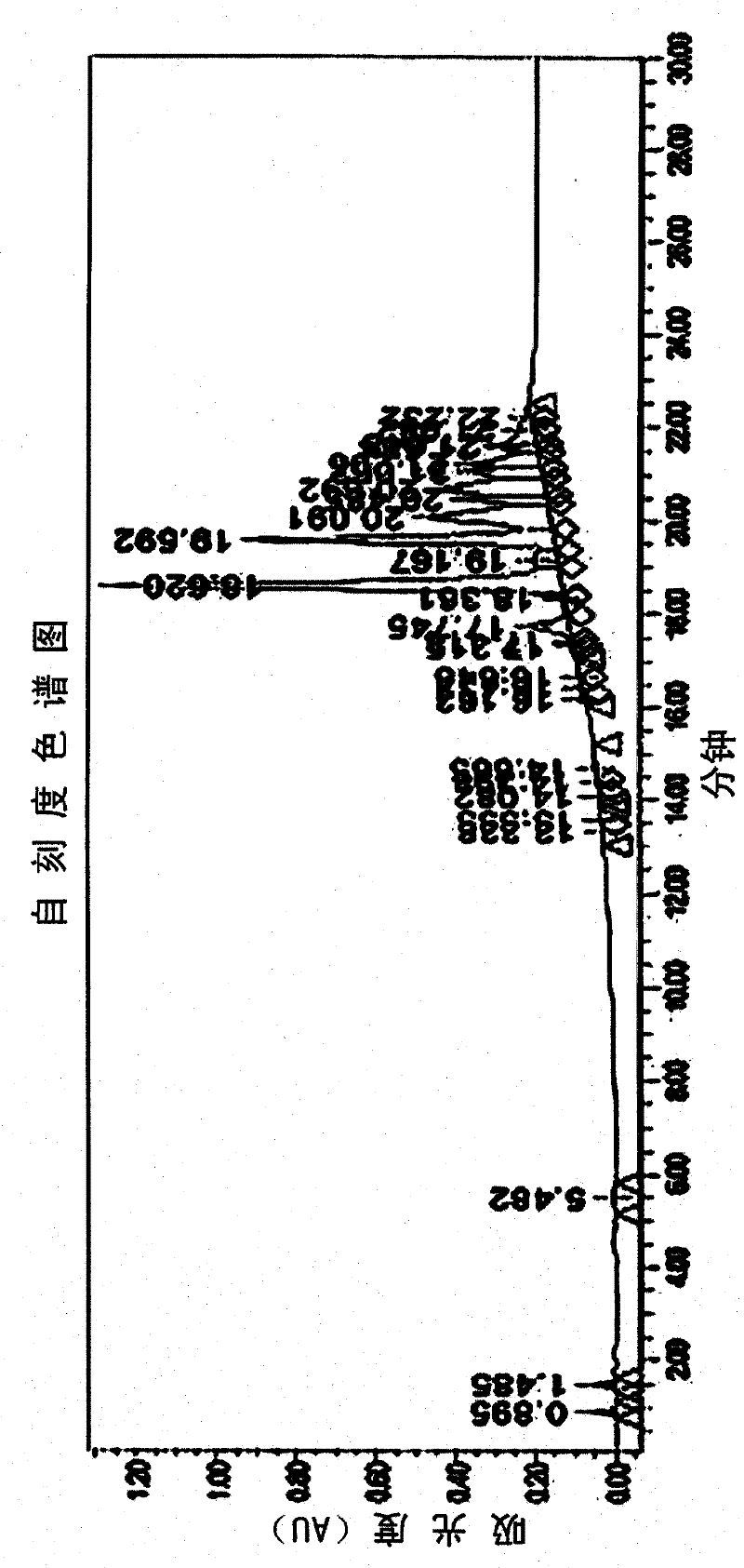
[0042]In the preparation method of the organophosphorus flame retardant of the present invention, the HPLC used in the analysis step is Waters 2690 high-performance liquid chromatography of Waters (Waters) Company, and the column adopts cosmosil C18 (4.6×150mm) for analysis. Use 10% methanol aqueous solution (A) and 100% methanol (B) as the mobile phase, use 60% A solution and 40% B solution for 5 minutes for elution, then change to 100% B solution for 15 minutes. eluted, then eluted with 100% B solution, and then analyzed.
[0043] 2. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA, thermogravimetric analyzer)
[0044] In order to determine the decomposition temperature of organophosphorus flame retardants, TGA 2050 from TA Instruments was used, and the flowing gas was helium. determined.
[0045] 3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance)
[0046] For nuclear magnetic resonance analysis, a Germini200 from Varian Company of the United States was used, and DMSO-d6 was ...
Embodiment 1
[0048] 105.1 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), 300 g of bisphenol A and 426.6 g of formaldehyde aqueous solution (35%) were added into the reactor, and reacted at 45° C. for 15 hours. Analysis was performed by HPLC during the reaction, and the reaction was terminated when the content of tetramethylol bisphenol A reached 75.2% by weight. Then the above mixture was cooled at room temperature for 1 hour, added to 2L of 1-butanol, and then added dropwise to the hydrochloric acid solution obtained by diluting 35% of 267g of concentrated hydrochloric acid solution with 250g of distilled water to make it acidified, and then extract the product layered. After the upper organic layer was washed with distilled water, 2 kg of the reaction product was obtained.
[0049] HPLC analysis: tetramer-(75.2% by weight), trimer-(6.8% by weight), dimer-(1.6% by weight), monomer-(0.6% by weight), oligomer (15.8% by weight )
[0050] After concentrating 2kg of the above reaction product, add 885g of D...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Add 280.34g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) aqueous solution (50%), 400g of bisphenol A and 601.3g of formaldehyde aqueous solution (35%) into the reactor, and react at 80°C. Analysis was performed by HPLC, and the reaction was terminated when the content of tetramethylol bisphenol A reached 50% by weight. Then the above mixture was cooled at 10°C for 1 hour, then added to 2L of 1-butanol, and then added dropwise to the hydrochloric acid solution obtained by diluting 35% of 267g of concentrated hydrochloric acid solution with 250g of distilled water to make it acidified, and extracted The product was separated. After the upper organic layer was washed with distilled water, 2 kg of the reaction product was obtained.
[0060] HPLC analysis: tetramer-(56.0% by weight), trimer-(5.0% by weight), dimer-(1.4% by weight), monomer-(0.3% by weight), oligomer (37.3% by weight )
[0061] After 2 kg of the above reaction product was concentrated, 787.9 g of DOPO / 900 mL of 1-methoxy-2-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com