Hydroxyapatite with flower-shaped level nanostructure and preparation method thereof
A hydroxyapatite and nanostructure technology, applied in nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, etc., can solve the problem of small specific surface area of hollow microspherical hydroxyapatite, low yield of hydroxyapatite, and complex process. and other problems, to achieve the effect of favorable industrialization promotion, good biocompatibility, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
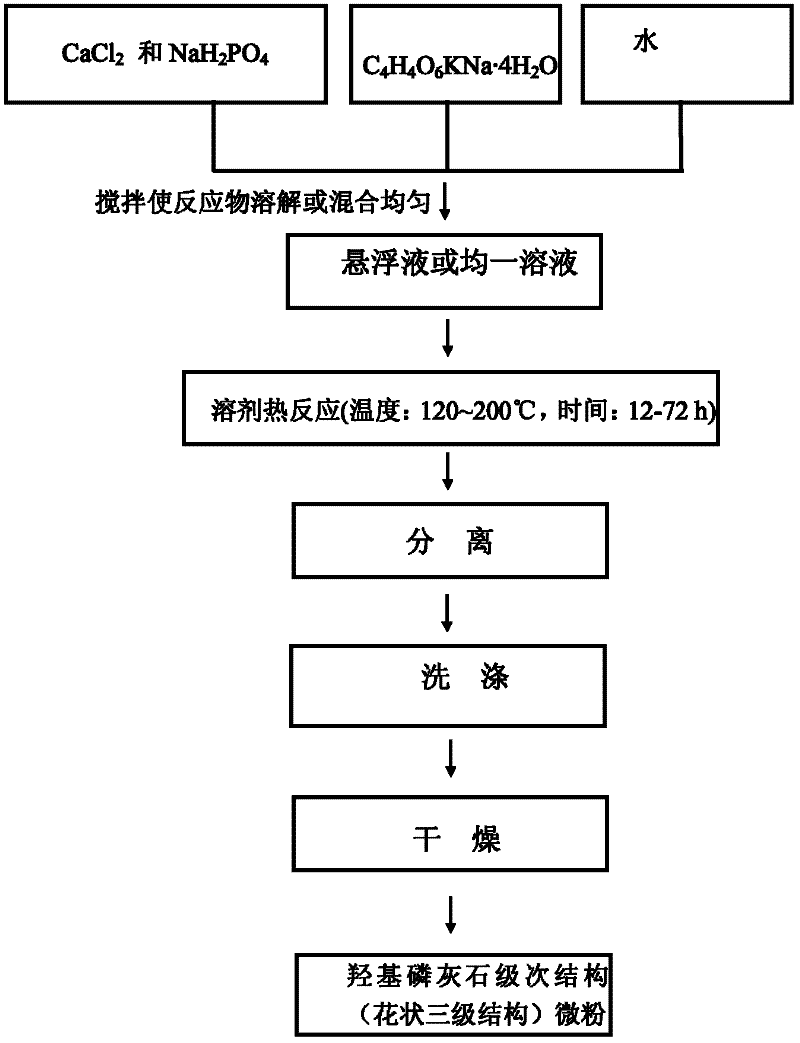
[0049] 1. At room temperature (25°C), add 0.110g CaCl 2 , 0.282g potassium sodium tartrate (C 4 h 4 o 6 KNa·4H 2 O) and 0.094g NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O was added to 15 mL of distilled water and stirred to obtain a uniformly dispersed suspension.
[0050] 2. Transfer all the suspension into a 20mL autoclave and seal it. Put the sealed autoclave into an oven, heat it to 300°C, and keep it warm at this temperature for 56 hours.
[0051] 3. After the autoclave was naturally cooled to room temperature (25°C), the product was taken out and centrifuged to separate the product. The obtained precipitate was washed twice with absolute ethanol and distilled water in turn, and then vacuum-dried at 60°C. The relative vacuum degree is -0.08MPa, and the hydroxyapatite with the flower-like secondary structure of the present invention is prepared.
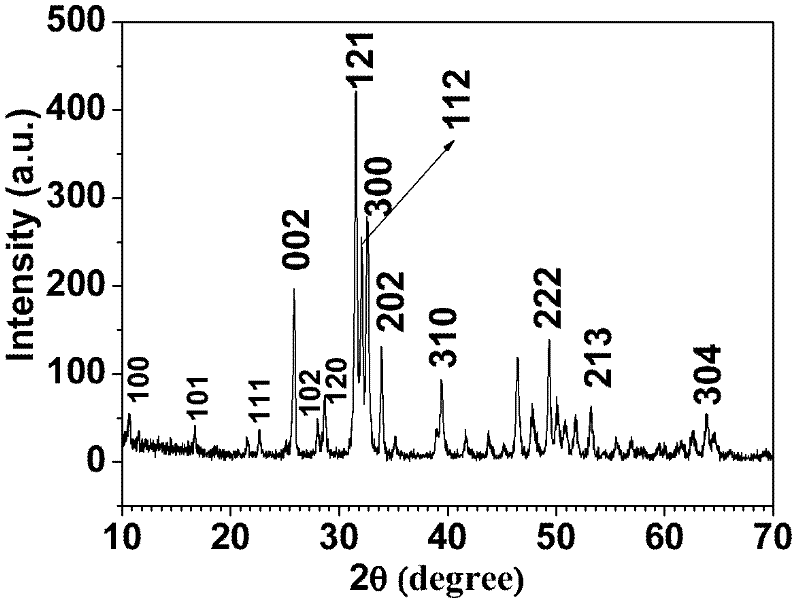
[0052] figure 2 It is the X-ray diffraction spectrum of hydroxyapatite, and its X-ray diffraction spectrum is exactly the same as that of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Except that the reactant is 0.176g C 4 h 6 o 4 Ca·H 2 O, 0.141g potassium sodium tartrate (C 4 h 4 o 6KNa·4H 2 O) and 0.054g KH 2 PO 4 15ml of distilled water was used for reaction; the reaction temperature was 250°C, and the reaction time was 52h, and the rest were the same as in Example 1.
[0057] The X-ray diffraction spectrum of the prepared hydroxyapatite is completely consistent with the standard JCPDS card (No.84-1998).
[0058] Scanning electron microscopy was used to detect the morphology of the prepared flower-like secondary structure of hydroxyapatite, and the detection results were as follows: Figure 5 as shown, Figure 5 b is a scanning electron micrograph of a single flower-like hydroxyapatite; Figure 5 c is a scanning electron micrograph of flower-like hydroxyapatite petals; Figure 5 d is a scanning electron micrograph of a single petal of flower-like hydroxyapatite.
Embodiment 3
[0060] Except that the reactant is 0.236g Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O, 0.423g potassium sodium tartrate (C 4 h 4 o 6 KNa·4H 2 O) and 0.183g K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O; 15ml of distilled water for reaction; the reaction temperature is 270° C., and the reaction time is 48h, and all the other are the same as in Example 1.
[0061] The X-ray diffraction spectrum of the prepared hydroxyapatite is completely consistent with the standard JCPDS card (No.84-1998).
[0062] Scanning electron microscopy was used to detect the morphology of the prepared flower-like hydroxyapatite, and the test results showed that the hydroxyapatite prepared in this example had a flower-like tertiary nanostructure, which was assembled from hydroxyapatite nanorods. Nanosheets, and then assembled into a flower-like structure by nanosheets. That is, the basic nanostructure unit of flower-like hydroxyapatite in this embodiment is hydroxyapatite nanorods (primary substructure), and hydroxyapatite nanorods are aggregate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com