Application of glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan for inhibiting growth of burkholderia cepacia complex
A Burkholderia cepacia and glutaraldehyde cross-linking technology, applied in applications, chitin polysaccharide coatings, plant growth regulators, etc., to achieve good antibacterial persistence, simple preparation process, and prevent post-harvest diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1 prepares glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan (CLCG)
[0031] Weigh 2.00g of chitosan powder with a degree of deacetylation of 85%, dissolve it in 50mL of 5% acetic acid solution, and stir it on a magnetic stirrer until it becomes a uniform mucus, then add 15mL of the freshly prepared 25% glutaraldehyde solution, and continue the magnetic Stir at room temperature on a stirrer for 24 h. After 24 hours to form a hydrogel, pour off excess glutaraldehyde solution carefully, and then gently and repeatedly rinse with sterile distilled water several times to remove uncrosslinked glutaraldehyde. Pour off the excess water, filter it dry with filter paper, and put it in a -70°C refrigerator to pre-cool. Dry the glutaraldehyde hydrogel pre-cooled at -70°C in a vacuum freeze dryer, and put it in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
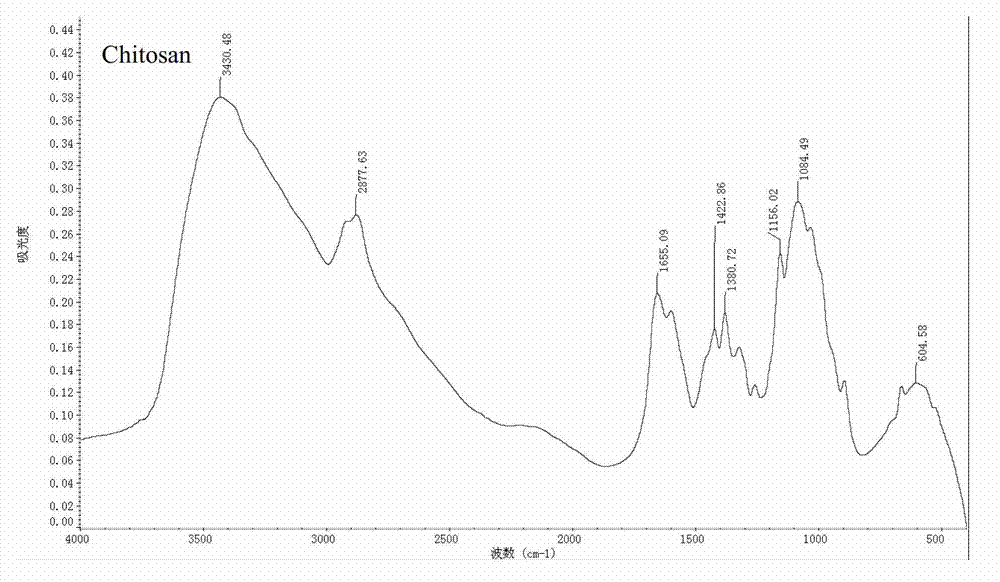
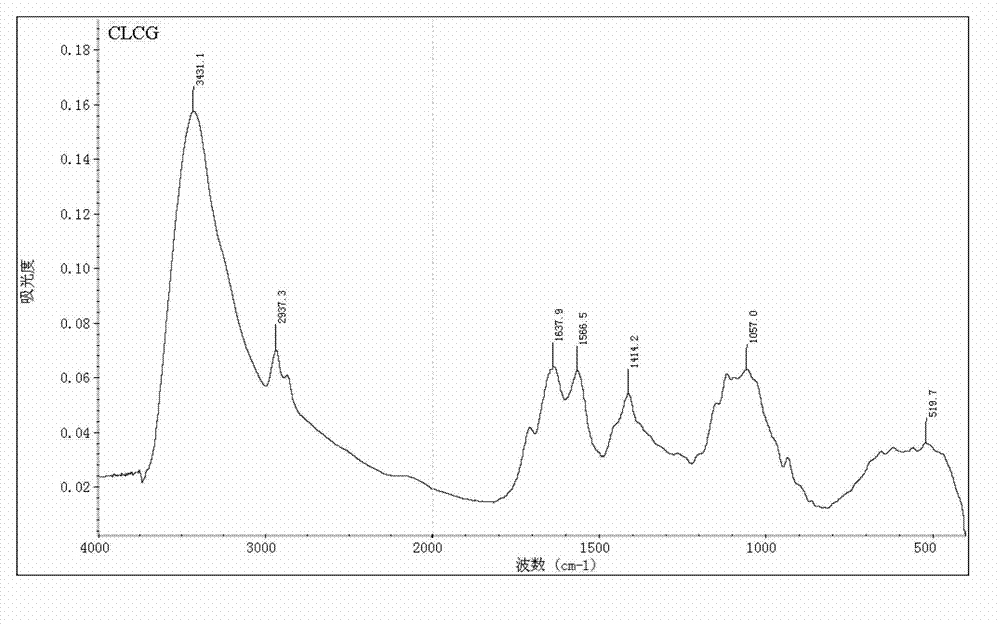
[0032] The infrared spectrometry of embodiment 2 glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan (CLCG)
[0033] Take 1-2mg of glutaraldehyde cross-...
Embodiment 3
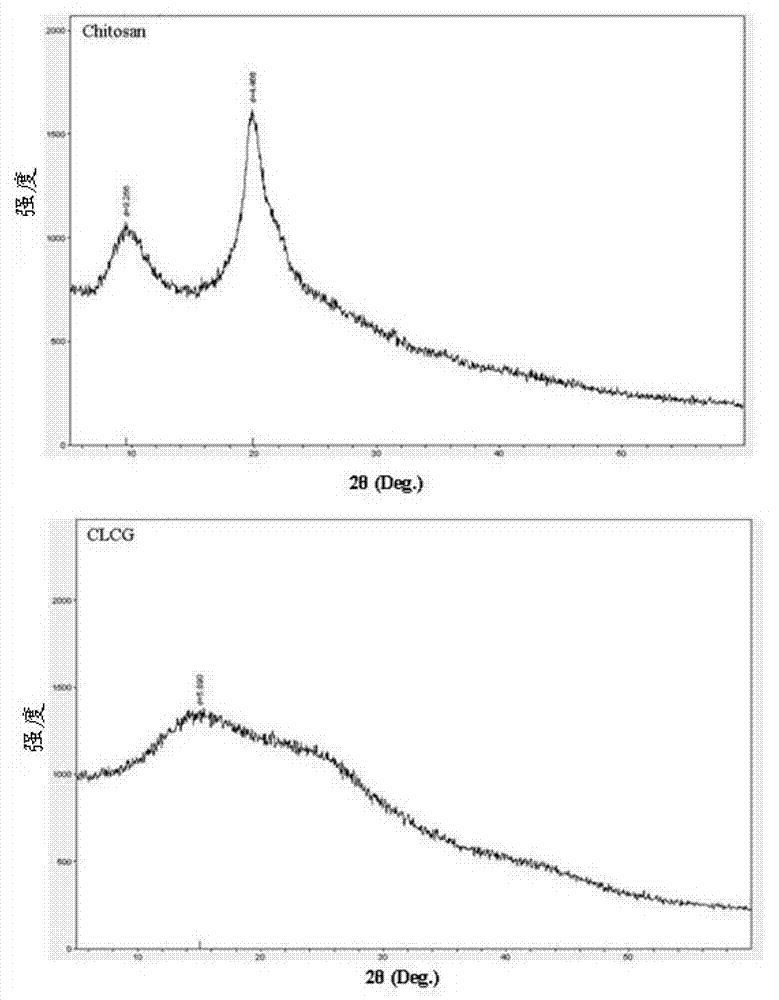
[0036] The X-ray diffraction analysis of embodiment 3 glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan (CLCG)
[0037] The chitosan and the glutaraldehyde-crosslinked chitosan prepared in Example 1 were pulverized respectively, and tested with an X-ray diffractometer (XPert PRO Holland). Working voltage 40kV, working current 25mA, Ni filter CuK 0 Line, the measured diffraction angle 2θ=5~65°.
[0038] X-ray diffraction technology is a technology that uses X-ray diffraction and scattering effects in crystals and non-crystals to perform qualitative and quantitative analysis of phases, structure types and integrity analysis. Chitosan is a high polymer that is easy to crystallize, and it has two crystal forms, namely, crystal form I and crystal form II. image 3 It is the X-ray diffraction spectrum of chitosan (Chitosan) and glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan (CLCG). It can be seen from the figure that the X-ray diffraction spectrum of chitosan shows two crystalline peaks at 2θ=11° and 2...
Embodiment 4
[0039] The scanning electron microscope analysis of embodiment 4 glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan (CLCG)
[0040] Gently rinse the glutaraldehyde-crosslinked chitosan with sterile phosphate buffer three times, then transfer to a dry, clean centrifuge tube, immerse in 2.5% glutaraldehyde and store in the refrigerator at 4°C overnight to fix the sample. Rinse 3 times with 0.1M pH 7.0 phosphate buffer, 15 min each time. Then fix with 1% (w / v) osmic acid fixative for 1-2h. Take out the fixative and rinse with 0.1M pH 7.0 phosphate buffer 3 times, 15min each time. Then use 50%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 95%, 100% (v / v) ethanol solutions to carry out gradient dehydration to the sample, then dry with a stagnation point drier, and coat the surface of the sample with palladium metal. Finally, the electron microscope (JEOL JSM-6400) was used to scan and take pictures.
[0041] The scanning electron microscope results of glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan (CLCG) are as follows: Figure 4 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com