Sulfate reducing bacteria with tolerance on arsenic
A sulfate and tolerance technology, applied in the field of environmental microorganisms, can solve problems such as low efficiency, arsenic toxicity, and secondary pollution, and achieve the effects of a wide range of carbon sources, strong growth and metabolism activity, and high conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
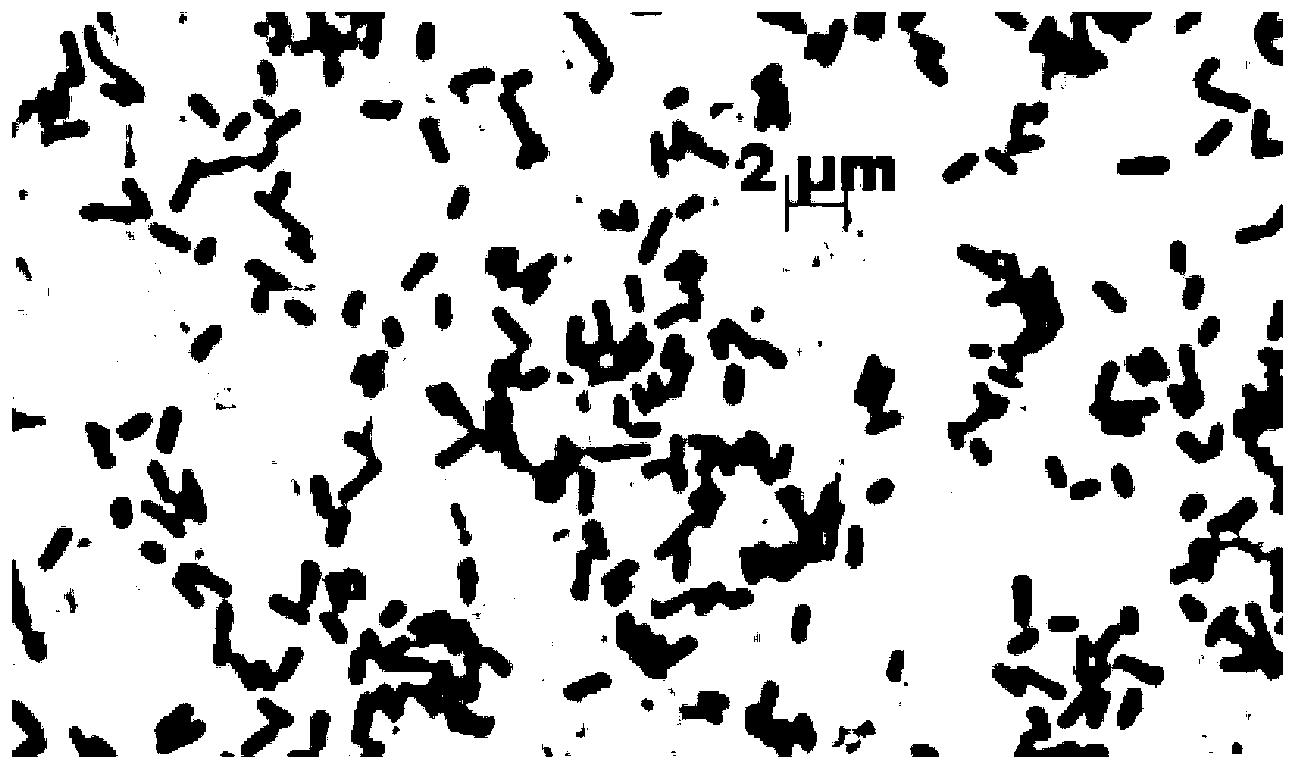
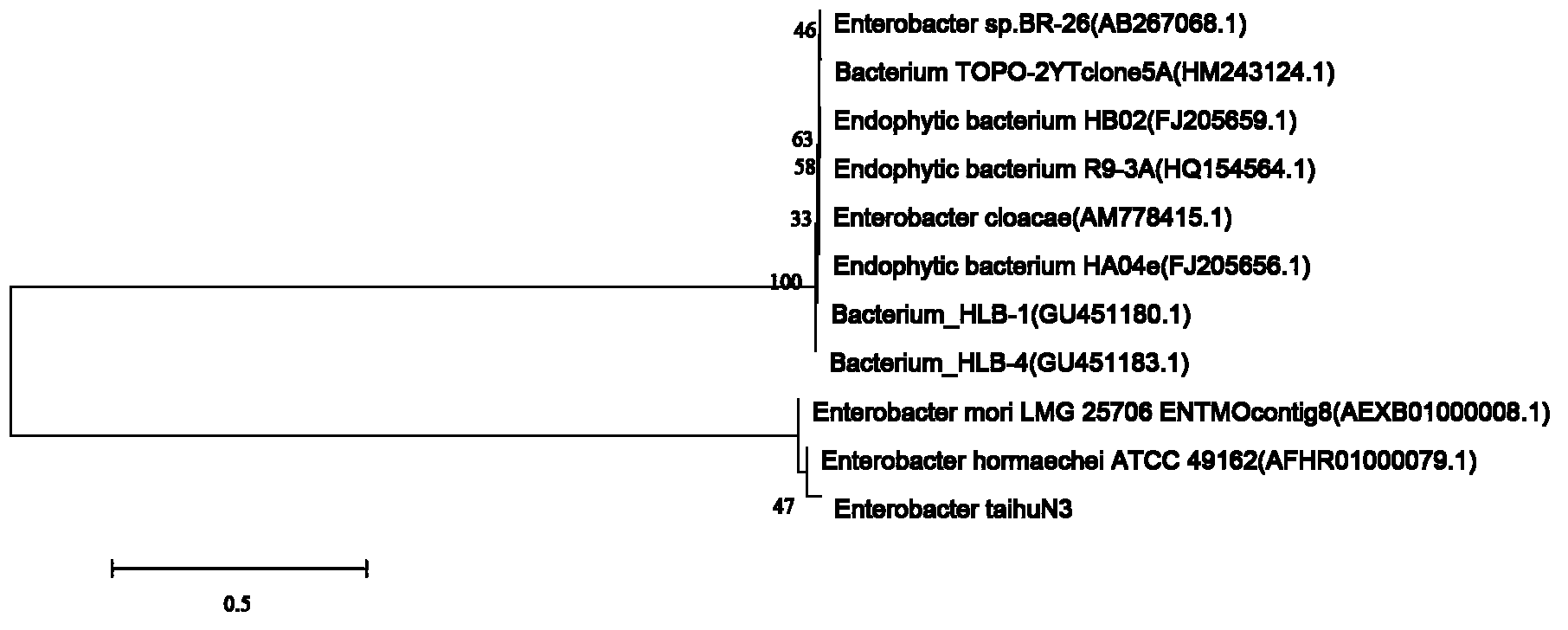
[0027] Example 1: Isolation and identification of the bacterial strain of the present invention.
[0028] (1) Isolation and purification of Enterobacter taihuN3.
[0029] Using liquid culture medium with ferrous sulfate as an indicator, the metabolite hydrogen sulfide of sulfate-reducing bacteria can form ink color with ferrous ions, which can be used as a sign of the enrichment of sulfate-reducing bacteria flora. Use a small-caliber container (500ml serum bottle) with a screw-top stopper, dispense a certain volume of enriched medium and then sterilize it under high pressure. Inoculate the bottom mud of Taihu Lake with 20% of the inoculum until it is full, cover it tightly and culture it in a 30°C incubator, and keep it in the dark for about a week, until the color of the enrichment solution becomes ink-colored. 2 The rotten egg smell of S means that the enrichment is successful.
[0030] The enriched bacterial solution was made into bacterial suspensions with different dilu...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Growth characteristics of the strains of the present invention.
[0040] Add 9.8ml medium into the anaerobic tube, inoculate 0.2ml logarithmic phase Enterobacter (Enterobacter) taihuN3 bacterial solution, and culture in an anaerobic box at 30°C in the dark. (The medium formula is the same as the above-mentioned enrichment and separation medium), samples were taken at 0, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 60, 70h, 80h, 90h, and 100h after inoculation, and measured The absorbance of the bacterial solution at 600nm. Filter the sample with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and measure SO in the sample by ion chromatography 4 2- concentration.
[0041] Enterobacter (Enterobacter) taihuN3 growth curve and SO in the medium 4 2- The concentration change curve is as Figure 4 As shown, 10-40 hours after inoculation is the logarithmic growth phase, and 40-80 hours is the stable period. After 80 hours, the absorbance of the bacterial solution decreases, and the bacteria...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Enterobacter (Enterobacter) taihuN3 growth curve and SO in the medium 4 2- The concentration change curve is as Figure 4 As shown, 10-40 hours after inoculation is the logarithmic growth phase, and 40-80 hours is the stable period. After 80 hours, the absorbance of the bacterial solution decreases, and the bacterial body gradually declines. The sulfate content in the culture medium did not change within 20 hours of starting the culture, the sulfate concentration in the medium gradually decreased at 30-80 hours, and the sulfate concentration tended to be stable at 80 hours. The sulfate content in the medium dropped from the initial 1400mg / L to 430mg / L, and the sulfate conversion rate was 70%. The decrease of sulfate content was consistent with the growth of the strain, and the sulfate content of the medium in the stationary phase of the growth of the strain decreased the fastest. Example 3: Utilization of different carbon sources by the strain of the present inventio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com