Preparation method of low-temperature sintering nano copper conductive ink
A conductive ink, low temperature sintering technology, applied in the direction of ink, conductive pattern formation, household appliances, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the choice of printed substrates, high sintering temperature, reducing ink conductivity, etc., to achieve large-scale production, simple process , the effect of high conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A preparation method of low-temperature sintering nano-copper conductive ink, comprising the steps of:
[0028] 1) Dissolve 20mmol of copper sulfate pentahydrate and 1mmol of polyvinylpyrrolidone with a molar mass of 40,000g / mol in 100ml of diethylene glycol, gradually raise the temperature to 80°C, and adjust its Ph value with ammonia water with a concentration of 25% by mass After completely dissolving, add 50ml of sodium borohydride dropwise at a rate of 8ml / min with a concentration of 8mol / L sodium borohydride in the solution to be reacted and continue stirring. After reacting for 30 minutes, stop heating and continue stirring for 60 minutes, then cool naturally;
[0029] 2) Add ethanol to the above-mentioned cooled solution to wash, centrifuge, and dry to obtain nano-copper powder with high oxidation resistance;
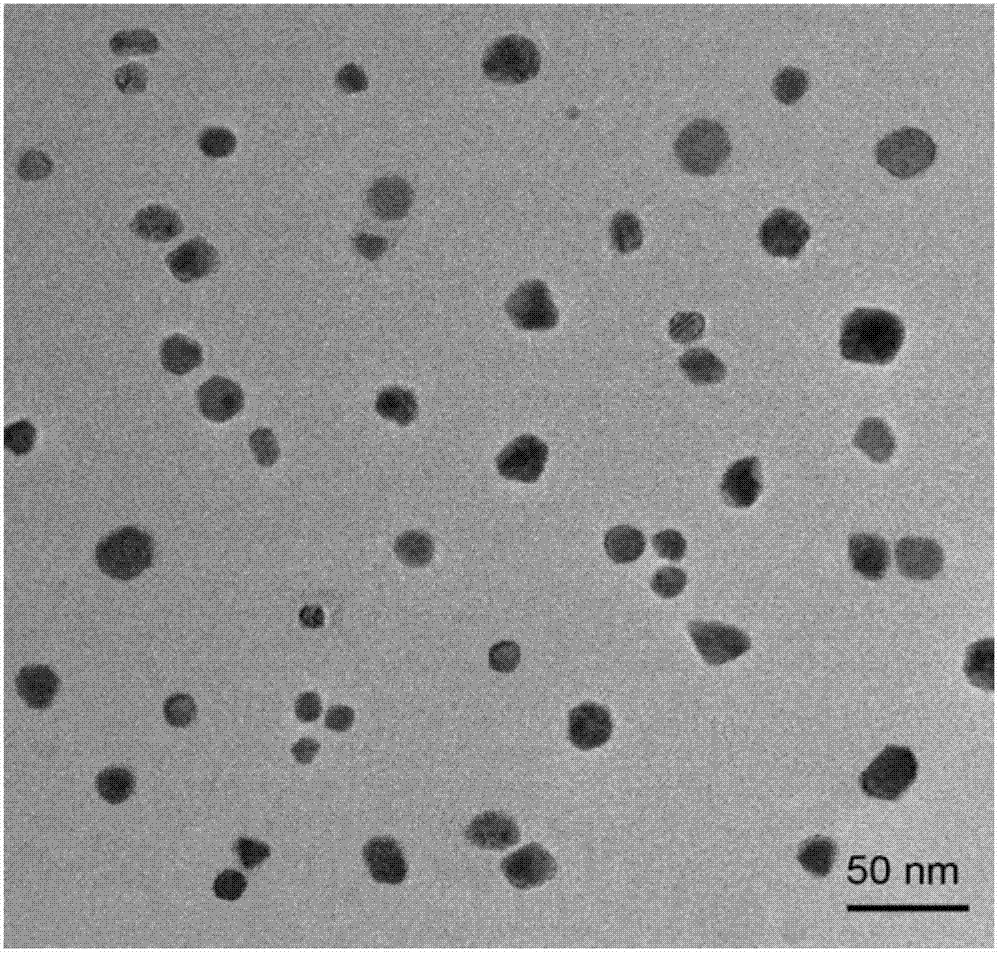
[0030] figure 1 This is the TEM photo of the nano-copper powder, which shows that the nano-copper particles are 5-30nm in size.
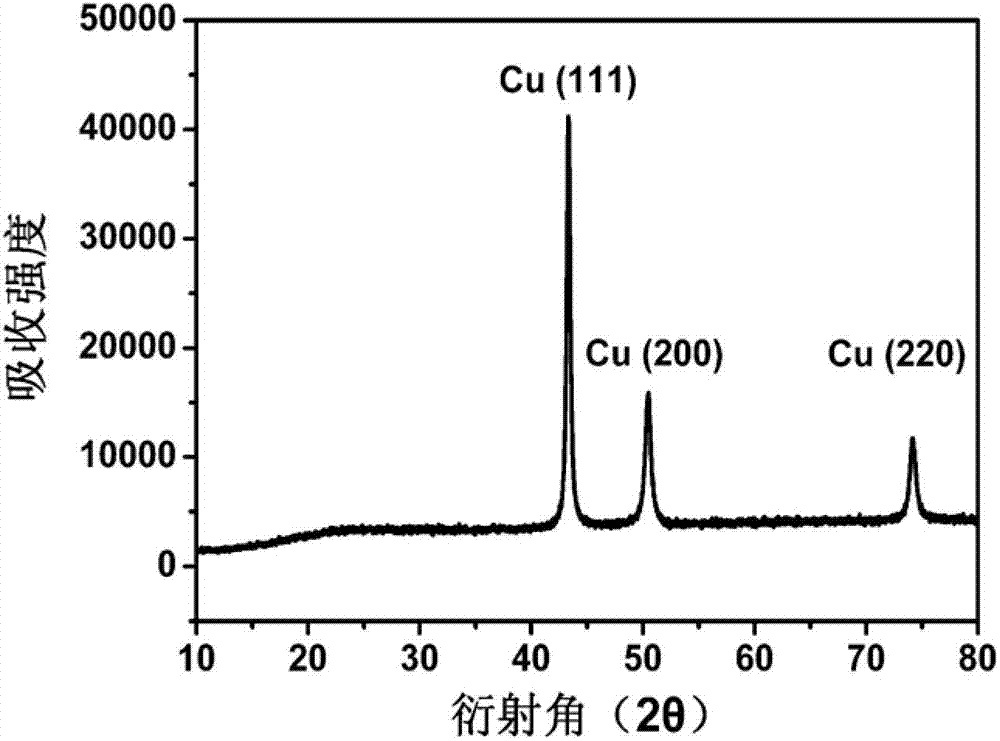
[0031] figure 2 It ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A preparation method of low-temperature sintering nano-copper conductive ink, comprising the steps of:
[0036] 1) Mix 0.2mol copper nitrate, 0.2molC 16 TAB was dissolved in 1L of ethylene glycol, and the temperature was gradually raised to 80°C. The Ph value was adjusted to 10.5 with ammonia water with a mass percent concentration of 25%. L hydrazine hydrate in the solution to be reacted and continued to stir, reacted for 30 minutes, stopped heating and continued to stir for 90 minutes, then naturally cooled;
[0037] 2) adding deionized water to the above-mentioned cooled solution to wash, centrifuge, and dry to obtain high oxidation-resistant nano-copper powder;
[0038] 3) Take 10g of nano-copper powder and dissolve it in 7.25g of the prepared mixed solvent. The mixed solvent is composed of ethanol, diethylene glycol, ethylene glycol and glycerol. The volume ratio of each component is ethanol: 1 to 2 Ethylene glycol: ethylene glycol: glycerol is 35:25:30:10, and f...
Embodiment 3
[0041] A preparation method of low-temperature sintering nano-copper conductive ink, comprising the steps of:
[0042] 1) Dissolve 0.5 mol copper octadecenoate and 3 mol oleic acid in 3 L of glycerol, gradually raise the temperature to 120°C, adjust the Ph value with 25% ammonia water with a mass percentage concentration of 25% After being completely dissolved, add 1 L of sodium hypophosphite with a concentration of 5 mol / L dropwise at a rate of 9.6 ml / min to the solution to be reacted and continue to stir. After 30 minutes of reaction, stop heating and continue to stir for 150 minutes. Then cool naturally;
[0043] 2) adding methanol to the above-mentioned cooled solution to wash, centrifuge, and dry to obtain high oxidation-resistant nano-copper powder;
[0044] 3) Dissolve 30g of nano-copper powder in 37.5g of ethylene glycol and fully ultrasonicate to obtain a stable nano-copper conductive ink.
[0045] The prepared nano-copper conductive ink was inkjet printed on the po...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com