Method for producing isoprene
A technology of isoprene and synthetase, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of high pollution, low production efficiency, high energy consumption, etc., achieve good activity, simple production method, and increase production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
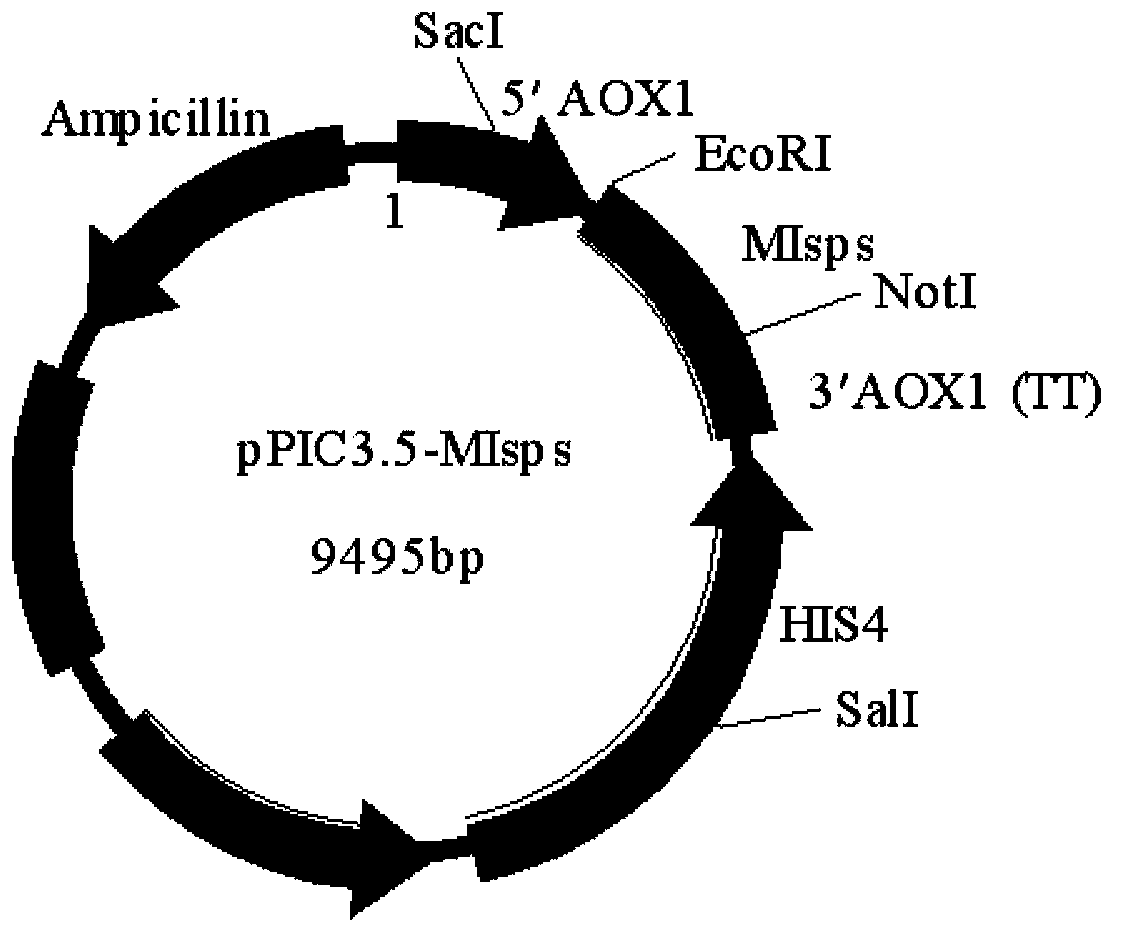
[0023] Example 1 Construction of isoprene synthase mutant MIsps and pPIC3.5-MIsps expression vector
[0024] The amino acid sequence of isoprene synthase (Isps) from Pueraria montana var. lobata is SEQ ID NO:3, and its coding nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO:4. Through the analysis of the amino acid sequence and molecular structure of the enzyme, it was found that the replacement of individual amino acids in the active center of isoprene synthase can effectively improve its enzyme activity, thereby increasing the production of isoprene. The applicant found that replacing Ser at position 408 with Asp can enhance the enzyme activity. The amino acid sequence of the mutated isoprene synthase is SEQ ID NO: 1, and its encoded nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO: 2 (MIsps ).
[0025] Primers were designed, and MIsps were constructed by fusion PCR method, and restriction enzyme cutting sites EcoRI and NotI were added at both ends.
[0026] MIsps primers were designed as follows:
[00...
Embodiment 2
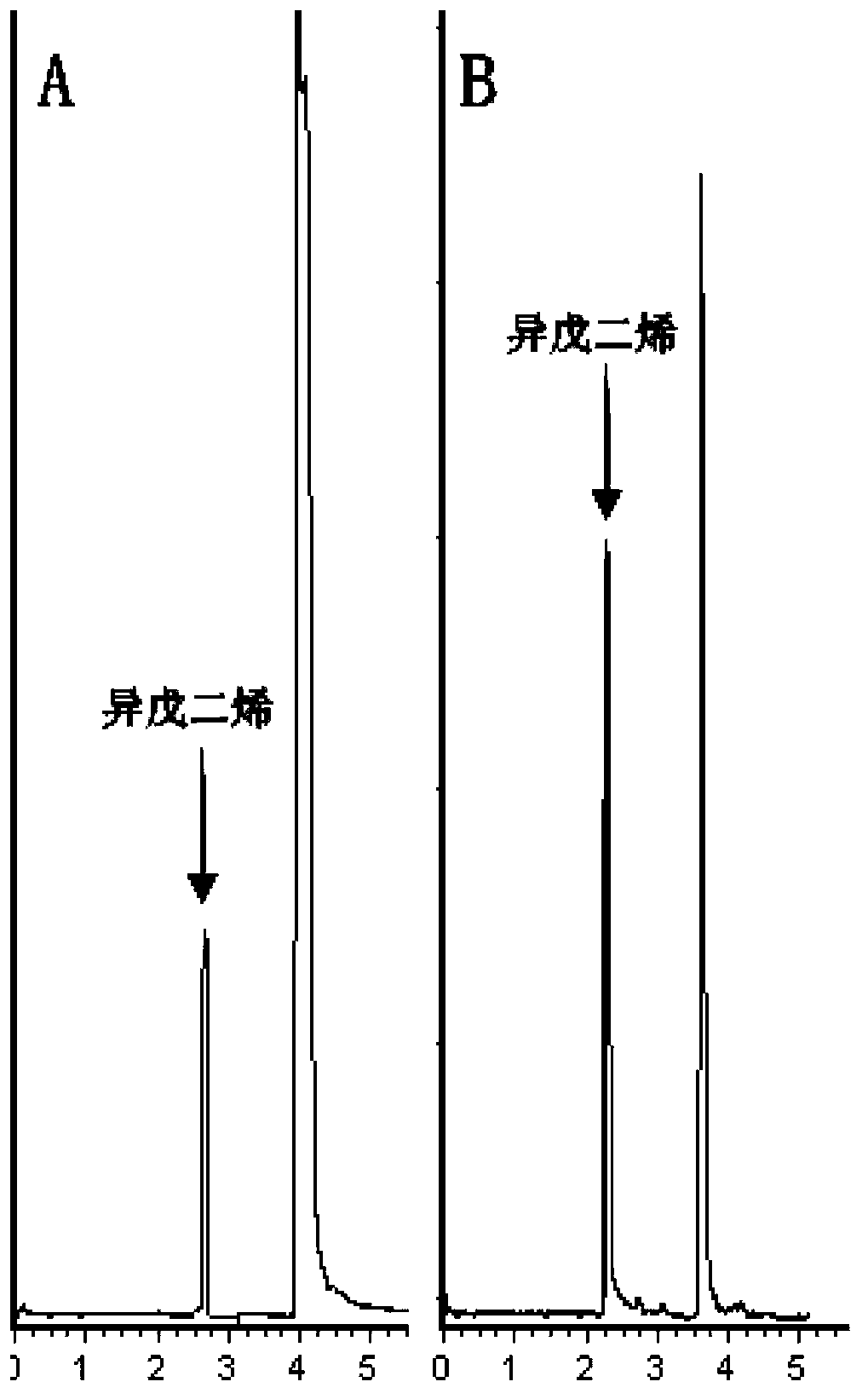
[0034] Embodiment 2pPIC3.5-MIsps transforms Pichia pastoris and fermentation culture
[0035] Digest pPIC3.5-MIsps with restriction endonuclease SacI or SalI to linearize it, which is more conducive to the homologous recombination of the target gene into the chromosome of Pichia pastoris. After the yeast cells were treated with 1M sorbitol, they were mixed with the purified linear plasmid containing the MIsps gene, and transformed with an electrotransformer. The revived yeast cells were spread on MD plate and cultured at 30°C for 3-4d. Pick the single colony grown on the MD plate, inoculate into 25mL BMGY (250ml shake flask), shake at 30°C, 250-300rpm until OD600=2-6 (logarithmic growth, about 16-18h). Centrifuge at room temperature at 1500-3000g for 5min, collect the cells, remove the supernatant, resuspend the cells with BMMY to OD600=1.0 (about 100-200ml), add 0.5% methanol to induce expression. Add the above-mentioned culture into a 1L shaker flask, cover with two layers...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com