Method for distinguishing raw milk, pasteurized milk and UHT (Ultra Heat Treated) milk
A technology for pasteurized milk and raw milk, which is applied in suspension and porous material analysis, measuring device, particle suspension analysis, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, long detection time, and troublesome operation of isoenzyme electrophoresis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
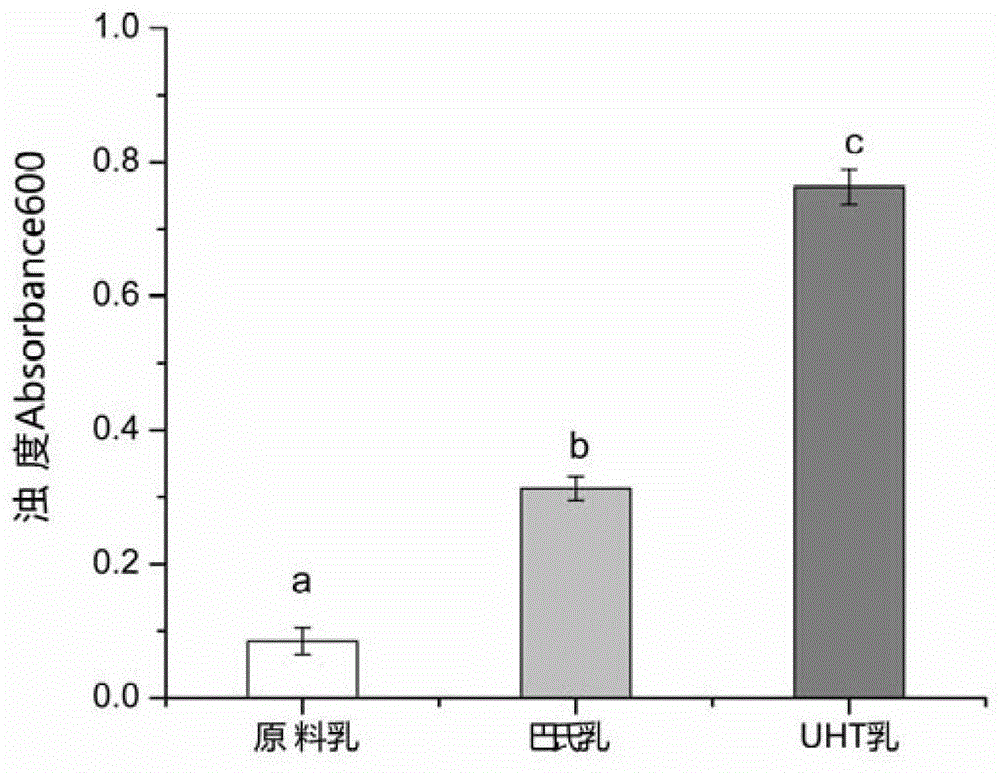
[0031] Embodiment 1, the influence of different chelating salt solutions on raw milk, pasteurized milk and UHT milk turbidity
[0032] The aqueous solution of 0.4M calcium chelate salt was mixed with raw milk, pasteurized milk and UHT milk at a volume ratio of 1:1 to carry out chelation reaction for 30min, then centrifuged at 4°C and 15000g for 15min to remove the upper layer of fat. The turbidity at 600 nm of the lower liquid obtained by centrifugation was measured by photometer.
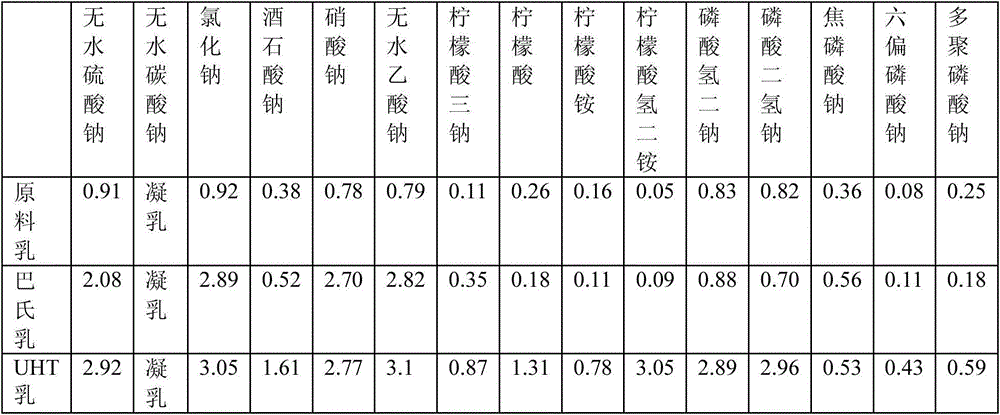
[0033] The calcium chelate salts used are: anhydrous sodium sulfate, anhydrous sodium carbonate, sodium polyphosphate, sodium chloride, sodium tartrate, sodium nitrate, anhydrous sodium acetate, trisodium citrate, citric acid, ammonium citrate, Diammonium hydrogen citrate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium pyrophosphate, sodium hexametaphosphate, sodium polyphosphate.
[0034] The obtained turbidity test results are shown in Table 1.
[0035] Table 1, 600nm turbidit...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2, the influence of different chelation reaction temperature on raw milk, pasteurized milk and UHT milk turbidity
[0039] Take raw milk, pasteurized milk and UHT milk and mix them with 0.4M trisodium citrate in a volume ratio of 1:1, respectively, after chelating reaction at 4, 25 and 37 °C for 30 min, and then at 4 °C, 15000 g The upper layer of fat was removed by centrifugation for 15 min, and the turbidity of the lower layer liquid obtained by centrifugation at 600 nm was detected by a spectrophotometer. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0040] Table 2. Effects of different reaction temperatures on raw milk, pasteurized milk and UHT milk
[0041]
[0042] *Different letters in the same column represent P<0.05 differences
[0043] It can be seen from Table 2 that the storage time at 4°C, 25°C and 37°C can well identify the three milks. However, the turbidity of raw milk, pasteurized milk and UHT milk was significantly reduced after being placed at 3...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3, the influence of different chelation reaction time on raw milk, pasteurized milk and UHT milk turbidity
[0045] Take raw milk, pasteurized milk and UHT milk and mix with 0.4M trisodium citrate in a volume ratio of 1:1, carry out chelation reaction at 25°C for 0min, 20min, 40min, 60min and 80min respectively, remove the upper layer fat, Centrifuge at 4°C and 15000g for 15min, and use a spectrophotometer to detect the turbidity of the lower liquid obtained by centrifugation at 600nm. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0046] Table 3. Effects of different treatment time on milk A600
[0047]
[0048]The results of 0min, 20min, 40min, 60min and 80min showed that the time of chelation reaction had no significant effect on the turbidity after mixing the different heat-treated milk and trisodium citrate in equal proportions. Therefore, after the milk sample is mixed with trisodium citrate, its turbidity can be measured by centrifugation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com