Cellulose nano-fibril/epoxy resin composite film preparation method
An epoxy resin and nanofibril technology, applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems of difficulty in meeting, low impact strength, easy cracking, etc., and achieve the effect of uniform fiber diameter distribution and good thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1, such as figure 1 ,
[0029] Preparation of cellulose nanofibrils / epoxy resin composite film,
[0030] Purification of raw materials: screen poplar wood powder with a 60-70 mesh sieve, then perform benzene alcohol extraction (v / v=2:1) to remove oil and other wood powder impurities in the wood powder, and wash the wood with absolute ethanol after extraction powder, remove the excess toluene in the wood powder, then place the washed wood powder in a petri dish, ventilate in the fume hood for 24~48h, wait for the wood powder to dry, take an appropriate amount of wood powder for the preparation of cellulose nanofibrils chemical treatment.
[0031] Chemical treatment:
[0032]The first acid treatment: Dissolve 10g of wood powder in 390ml of distilled water, add 3.9g of sodium chlorite to make a sodium chlorite solution with a concentration of 1%, and at the same time, add 3~4ml of acetic acid to ensure that the wood powder solution At this time, the pH value...
Embodiment 2
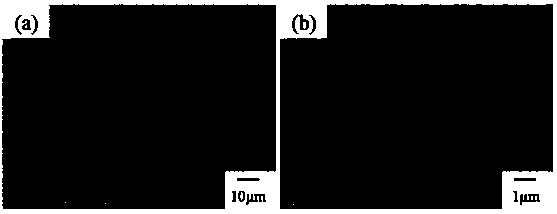
[0051] Changes in the appearance of wood fiber solution during chemical acid-base treatment:
[0052] Wood fiber contains cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. The cellulose content in wood is about 40%~50%. There is hemicellulose around the original fine fiber, and there is lignin around the cellulose. , thus, cellulose can only be observed after delignification and protofibrils can only be observed after hemicellulose hydrolysis. In order to extract as much cellulose as possible, chemical treatment is used to remove hemicellulose and lignin. It can be seen that the cellulose has been sinking at the bottom of the glass bottle during the chemical treatment process, and the sodium chlorite treatment mainly removes the lignin in the wood powder, and after the acid treatment, it can be clearly seen that the color of the wood powder changes from the original The yellow color changes to white, which indicates that most of the lignin has been removed during the first acid treatm...
Embodiment 3
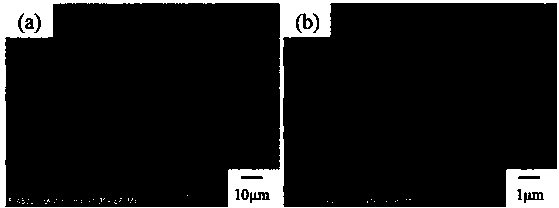
[0054] Cellulose solution after chemical acid and alkali treatment after physical and mechanical treatment:
[0055] After chemical treatment of wood fibers, what remains is almost entirely composed of cellulose, which requires physical and mechanical treatment to disperse the cellulose into microfibrils. Microfibril is not a new substance, it is the most basic unit of cell wall skeleton material. When forming the cell wall, many chain-like cellulose molecules are regularly arranged into molecular clusters (micelles), which are further combined into biological structural units called microfibrils. Aggregations of many microfibrils can become macrofibrils, cellulose, visible under a light microscope. After the wood powder is chemically treated, the color turns white and almost all settle at the bottom of the glass bottle. This is because the undispersed cellulose contains too many aggregates. The density of cellulose is greater than that of water, so it has been sinking at...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com