Kelp degrading bacteria and method for preparing kelp juice utilizing same
A technology of kelp and dried kelp, applied in the field of environmental microorganisms, can solve the problems of low comprehensive utilization rate of raw materials, low technical content, single variety of formed products, etc., and achieve the effect of improving comprehensive utilization rate and edible quality, and removing algae structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Strains Tamlana alginolytica Breeding of ZJU HZ22 (CGMCC No. 5324)
[0030] The strains were isolated from surface seawater and planktonic algae samples collected in Zhoushan, East China Sea in August 2010. After the algae are properly ground, put them into a sterile shaker flask together with seawater samples, and at the same time supplement sterile fresh kelp pieces (about 1.5 cm×1.5 cm, 10 pieces) and peptone / The mixed concentrated solution of yeast extract (the final concentration is 1 g / l) was cultivated in an air bath shaker (28°C, 120 rpm), and the turbidity of the enriched solution and the changes of kelp pieces were observed regularly. After the enrichment solution was turbid, select the positive shake flask (that is, the kelp pieces are broken or become smaller), and transfer to oligotrophic 2216 medium (containing 200 g / l of fresh kelp pieces) according to 10% inoculum amount, and in the same condition The culture was continued under the condi...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Strains Tamlana alginolytica Analysis of extracellular degrading enzymes of ZJU HZ22 (CGMCC No. 5324)
[0038] Qualitative analysis on plates and quantitative analysis on shake flasks were used respectively.
[0039] Qualitative analysis of plates: Based on oligotrophic 2216 medium, add 1% sodium alginate, soluble starch, sodium carboxymethylcellulose and 0.2% pectin to prepare plates, and scrape an appropriate amount of fresh bacteria from the 2216 slope The soil was planted, and the enzyme activity was tested after culturing at 28°C until an obvious bacterial lawn was formed. Among them, amylase was stained with Lugol's iodine solution, and a transparent circle around the bacterial lawn was positive; cellulase and pectinase were spread and stained with 0.2% Congo red solution, and a transparent circle around the bacterial lawn was positive; The lyase was stained with freshly prepared 2% calcium chloride solution, and a transparent circle around the bacte...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3: the bacterium preparation technology of kelp juice
[0043] Take the common dry kelp bought in the market, soak it properly, cut it into pieces (about 1.5 cm×1.5 cm), and dry it for later use.
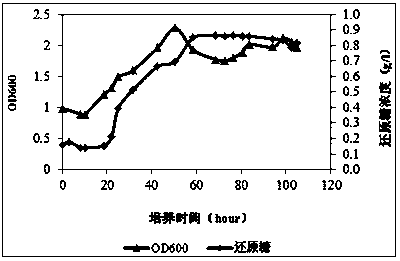
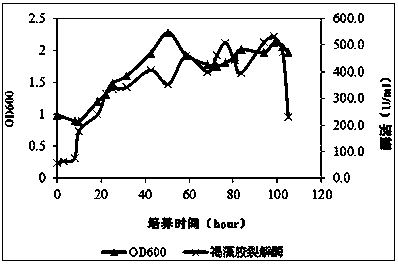
[0044] The seed medium is a degradation medium containing 10 g / l dried kelp pieces, with a liquid volume of 200 ml / 250 ml, cultured at 28°C and 120 rpm for about 4 days, and the degree of degradation of the kelp pieces can be used to judge whether the seed liquid is Mature. The seed liquid without obvious kelp block residue was transferred to the fermenter according to the inoculum amount of 1%.
[0045] Add 4.5 L of degradation medium to a 7.5 L fermenter, add 40 g of dried kelp pieces, 2.5 ml of polyether (defoamer), and sterilize at 121 °C for 20 min. After inoculation after sufficient cooling, the automatic control parameters were set as follows: temperature at 28°C, stirring speed at 300 rpm, and ventilation at 2.5 LPM. Sampling at regular intervals and mea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com