Method for fluorine removal of wastewater in bastnaesite hydrometallurgy
A technology for hydrometallurgy and bastnasite, which is applied in the fields of metallurgical wastewater treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
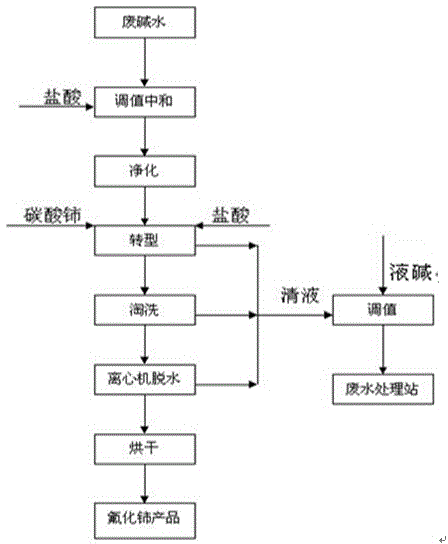
[0022] The raw material is bastnaesite (REO: 70%), which is oxidized and roasted, leached with hydrochloric acid once, and the leached residue is then subjected to alkali conversion and decomposition. The waste alkaline water is enriched with cerium and other minerals, of which F: 12.40 g / L, OH - : 0.64mol / L, cerium carbonate REO: 45.6%.
[0023] a. Take 1 liter of the above waste alkaline water and adjust the pH value to 2.5-3.0 with 31% industrial hydrochloric acid, take a sample and send it to the central control analysis room to determine the fluorine content, filter the bottle for suction purification, remove suspended matter, and measure the volume.
[0024] b. Calculate the amount of cerium carbonate actually consumed according to the fluorine content in the purified waste alkaline water after the above adjustment:
[0025] Reaction formula: Ce 2 (CO 3 ) 3 +6HCl+6NaF→2CeF 3 ↓+6NaCl+3CO 2 ↑
[0026] Calculation formula: W Ce =[(M CeO2 ×V 废水 ×C F )...
example 2
[0040] The raw material is alkaline-to-alkali wastewater produced in the workshop, of which F: 11.8g / L, OH - : 0.56mol / L, lanthanum carbonate REO: 40.5%.
[0041] a. Take 1 liter of waste alkaline water, use 31% industrial hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value to 2.5-3.0, take the supernatant and send it to the central control analysis to determine that the F is 10.92g / L, and the volume of the filter bottle is 1.07 liters.
[0042] b. Calculate the amount of lanthanum carbonate that needs to be added in the beaker according to the above volume and fluorine content. The reaction formula is: 6NaF+6HCl+La2(CO3)3→2LaF3↓+2CO2↑+3H2O+6NaCl.
[0043] c. Calculate the amount of hydrochloric acid that needs to be added according to the amount of lanthanum carbonate added, the reaction formula: La 2 (CO 3 ) 3 +6HCl→2LaCl 3 +3CO 2 +3H 2 O.
[0044] d. Add hydrochloric acid slowly, and control the reaction speed by the amount of hydrochloric acid added. After the reaction is com...
example 3
[0048] Accurately weigh 200 grams of oxidized ore after roasting: REO: 77.35%, CeO 2 : 37.38%, F: 8.63%, Ce 2 (CO 3 ) 3 : 45.6%.
[0049] a. Use a 500ml beaker to take 300ml of bottom water, 160ml of industrial hydrochloric acid for a dip, the reaction temperature is 80 degrees, slowly add 31% hydrochloric acid, add it in 1 hour, react for 3 hours, use flocculant to settle, wash twice, tetravalent cerium and trivalent rare earth fluoride remain in the beaker in solid phase.
[0050] b. Add 95ml of NaOH liquid with a content of 50% to the above-mentioned first immersion solid phase, and carry out alkali conversion on a 500W electric furnace at a temperature of 95-110 degrees, and react for 1 hour.
[0051] c. Wash several times of alkali slurry: transfer all the washing water into a 2000ml beaker, the volume of waste alkali water: 1800ml, send it to the central control analysis room for measurement: F: 8.15g / L, OH - : 0.15mol / L.
[0052] d. According to the calculation, F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com