Method for co-producing butanol and hydrogen by utilizing lignocellulose biomass
A technology of lignocellulose and biomass, which is applied in the field of efficient resource utilization of organic solid waste, can solve the problems of low substrate conversion efficiency, incomplete substrate fermentation, and high substrate cost, and achieve energy conversion efficiency improvement and low cost. The effect of reducing and increasing butanol production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
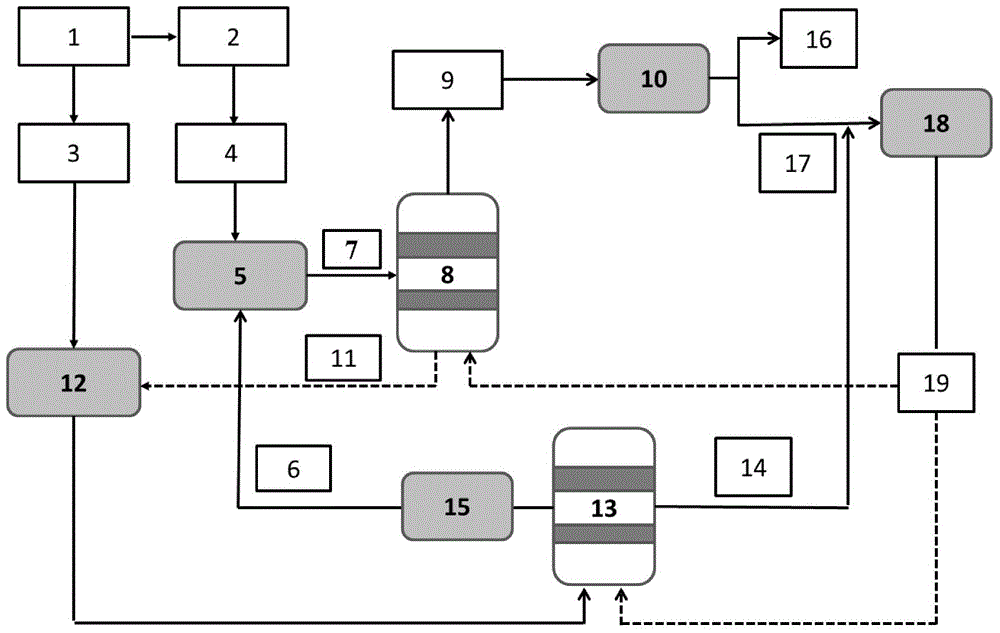
[0020] Specific embodiments: the present embodiment utilizes lignocellulosic biomass to co-produce the method for butanol and hydrogen according to the following steps:
[0021] 1. Lignocellulose is pretreated: the hemicellulose in lignocellulose is made into soluble xylose liquid to obtain hemicellulose xylose liquid and solid;
[0022] 2. The solid pretreated in step 1 is hydrolyzed with cellulase by enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification method, and after concentration, glucose hydrolyzate is obtained;
[0023] Three, get the microorganism that can utilize glucose to produce butanol, place in the butanol fermenter that contains butanol medium, ferment and produce butanol, obtain the fermented liquid that contains butanol, then the fermented liquid that contains butanol is dehydrated through distillation, Obtain butanol with a mass percentage of 10-15%, and collect the butanol fermentation residue after distillation and dehydration for subsequent use;
[0024] 4. Add the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0032]Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the lignocellulose described in step 1 is pretreated as follows: the lignocellulose and the HCl solution with a mass percentage of 1 to 2% are pressed Mix at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1g:10mL, treat at 80-120°C for 1-2 hours, and centrifuge to obtain hemicellulose xylose liquid and solid. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0033] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the amount of cellulase described in step two is added to the enzyme solution according to 30 ~ 50U / (g pretreated solid substrate), at 50 Under the condition of 150-200 r / min, the enzyme hydrolysis is carried out for 48 hours at the temperature of ℃, and the glucose hydrolyzate is obtained. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com