High-entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
A high-entropy alloy and uniform mixing technology, applied in the field of high-entropy alloys, can solve the problems of difficult to control the structure and properties of high-entropy alloy materials, difficult to exert the mechanical advantages of high-entropy alloys, and thin film thickness of high-entropy alloys. The effect of electrochemical corrosion, good passivation, excellent corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Take aluminum, chromium, iron, nickel, copper, and molybdenum powders in equimolar ratios, mix them with a ball mill for 24 hours, put them into an abrasive tool, and press the sample with a hydraulic universal testing machine at a pressure of 120kN for 5 minutes. The pressed sample was sintered in a vacuum sintering furnace under the protection of argon at a heating rate of 10°C / min, kept at 600°C for 2 hours, and finally heated to 1800°C, then cooled with the furnace.
[0039] The potentiodynamic polarization curve of the alloy in 3.5% NaCl solution was tested by an electrochemical workstation at room temperature. A three-electrode system was used: the reference electrode was a saturated calomel electrode, the auxiliary electrode was a platinum electrode, and the working electrode was a high-entropy alloy. A cylindrical sample with a diameter of 10mm is used, and the surface to be tested is reserved, and the rest is covered with epoxy resin, polished with sandpaper, ul...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Take aluminum, chromium, iron, nickel, copper, and molybdenum powders in an equimolar ratio, mix them with a ball mill for 24 hours, put them into an abrasive tool, use graphite as a release agent, and press them with a pressure of 120kN on a hydraulic universal testing machine Samples were kept under pressure for 5 minutes. The pressed sample was sintered in a vacuum sintering furnace under the protection of argon at a heating rate of 10°C / min, kept at 600°C for 2 hours, and finally heated to 1800°C, then cooled with the furnace.
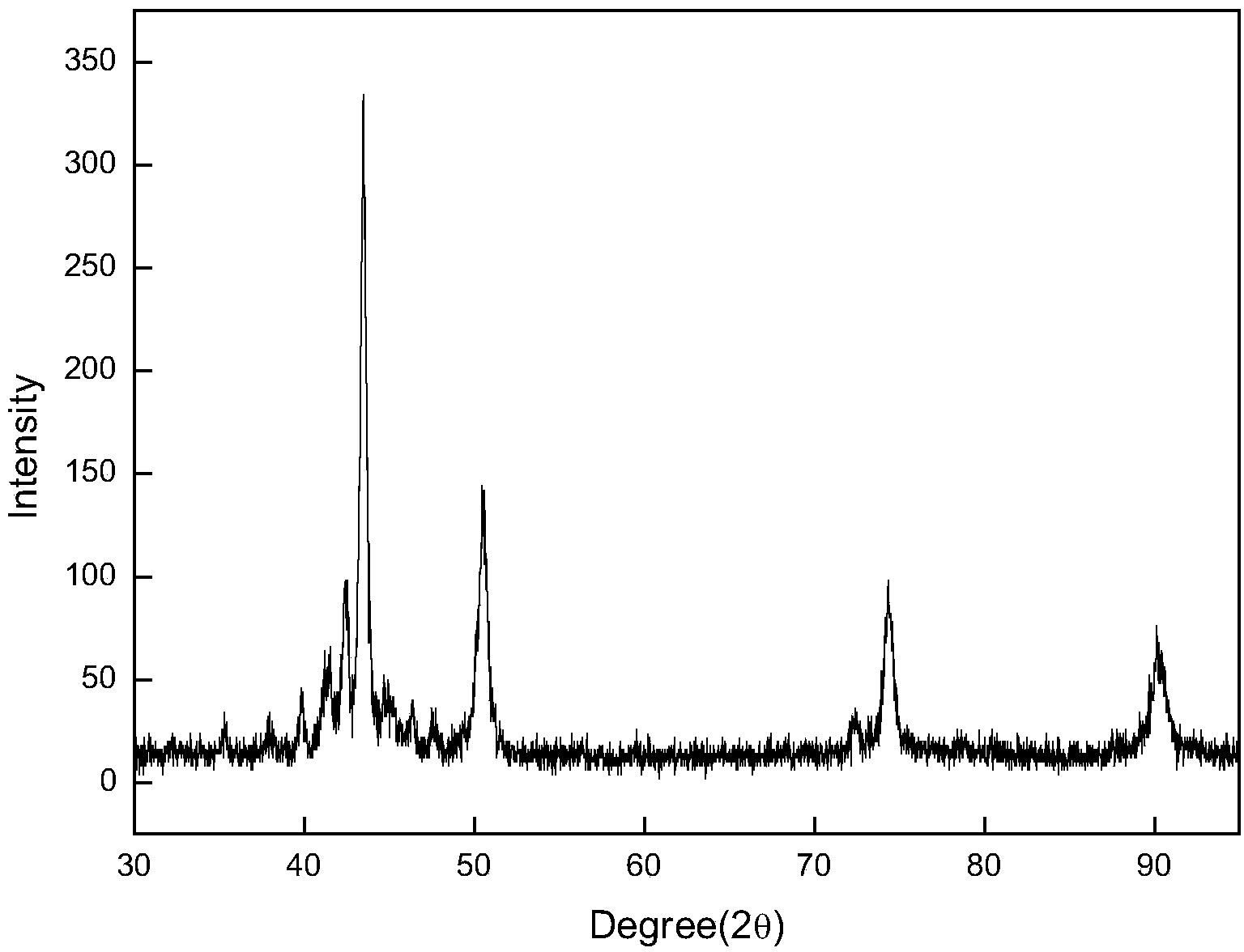
[0043] Use X-ray diffractometer to analyze alloy phase composition, the conditions are: Cu target, voltage 40kV, current 40mA, scanning angle 30°~95°, scanning speed 4(°) / min, the results are as follows figure 1 shown.
[0044] Use a micro / Vickers hardness tester to test the hardness of the alloy. During the experiment, load 20g, hold the pressure for 10s, measure 7 sets of data, and take the average value. The hardness of the alloy is 506H...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Take aluminum, chromium, iron, nickel, copper, and molybdenum powders at a molar ratio of 1.1:1.05:1:1:1:1.05, mix the powders with a ball mill for 24 hours, put them into abrasive tools, and use a hydraulic universal testing machine at 120kN Press the sample under pressure and keep the pressure for 5 minutes. The pressed sample was sintered in a vacuum sintering furnace under the protection of argon at a heating rate of 10°C / min, kept at 580°C for 2 hours, and finally heated to 1800°C, then cooled with the furnace.
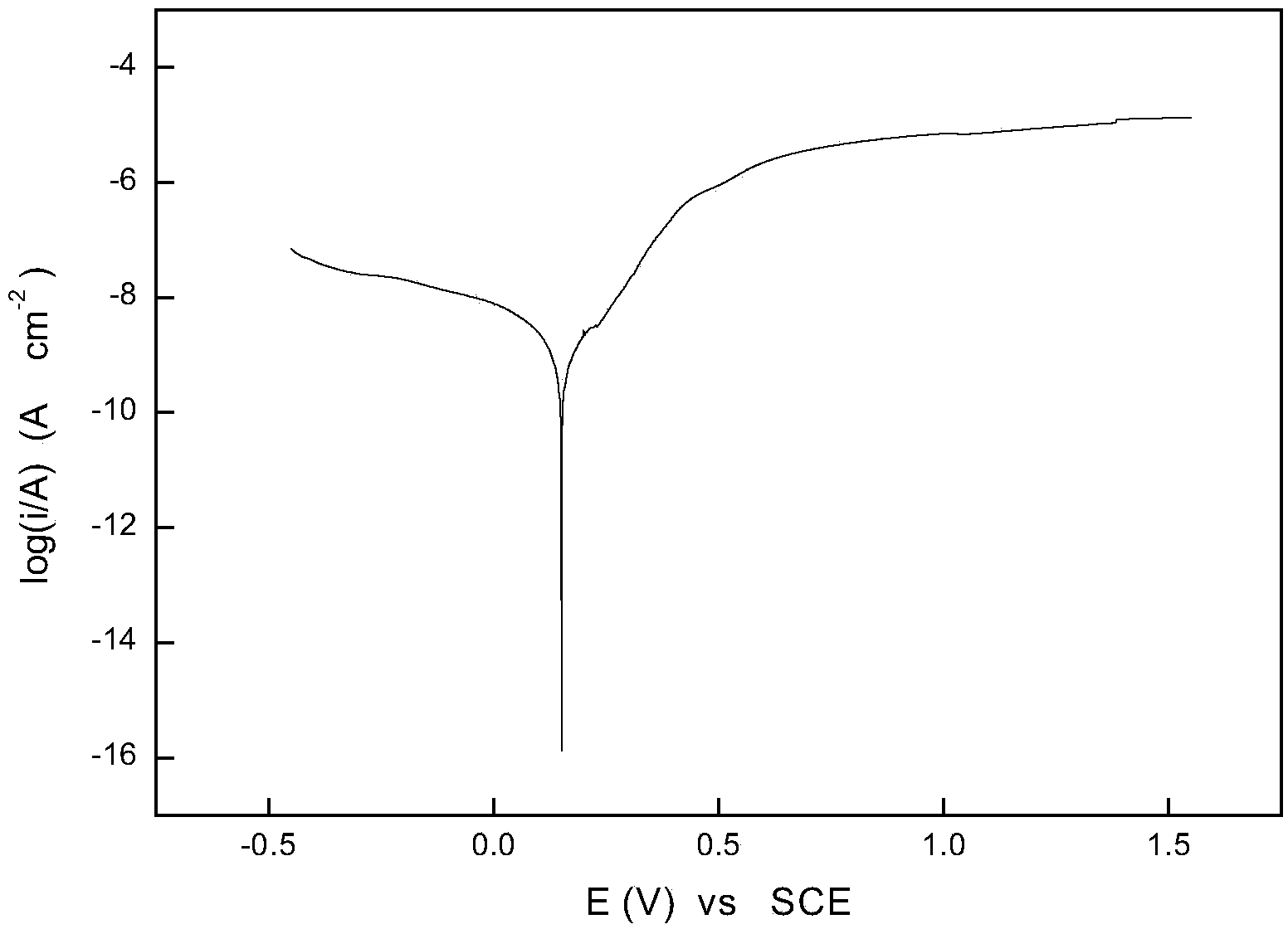
[0048] The corrosion kinetic parameters are: self-corrosion potential E corr =0.153V, self-corrosion current density I corr =4.24×10 -8 A / cm 2 , the result is as figure 2 shown. The hardness of the alloy is 502HV. The compressive strength of the alloy is 1410MPa.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com