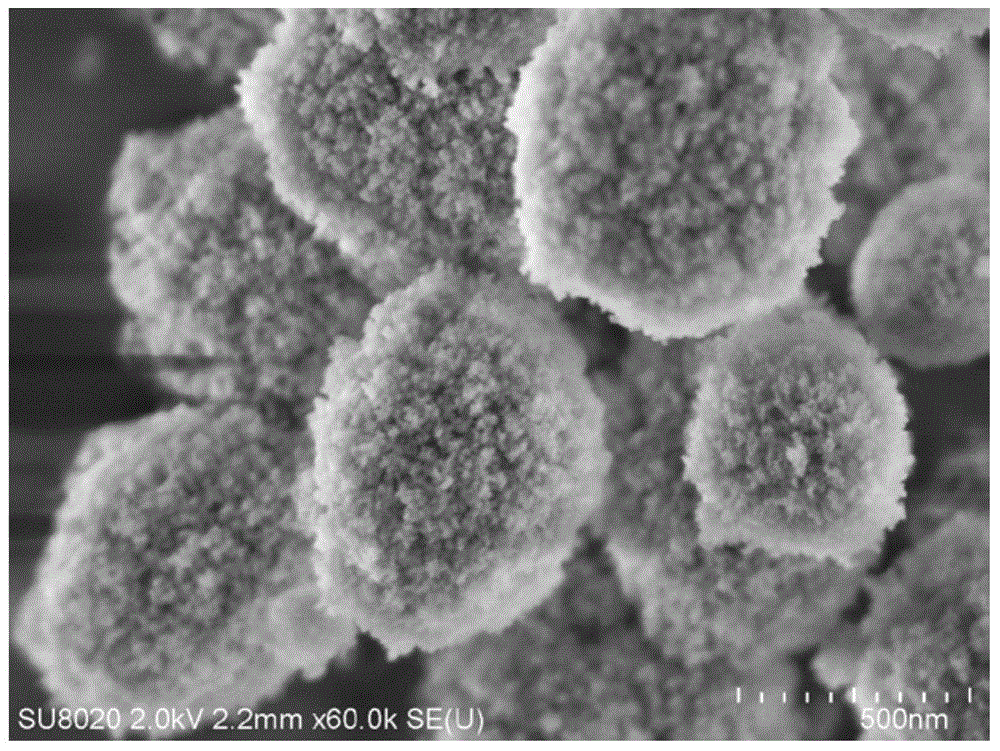
Preparation method of Beta molecular sieve with multistage pore structure
A molecular sieve and pore size technology, applied in molecular sieves and alkali exchange compounds, chemical instruments and methods, crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable acquisition, large-scale industrial production, and high prices of other raw materials. To achieve the effect of cheap and easy-to-obtain raw materials and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1: Preparation of Samples 1-40
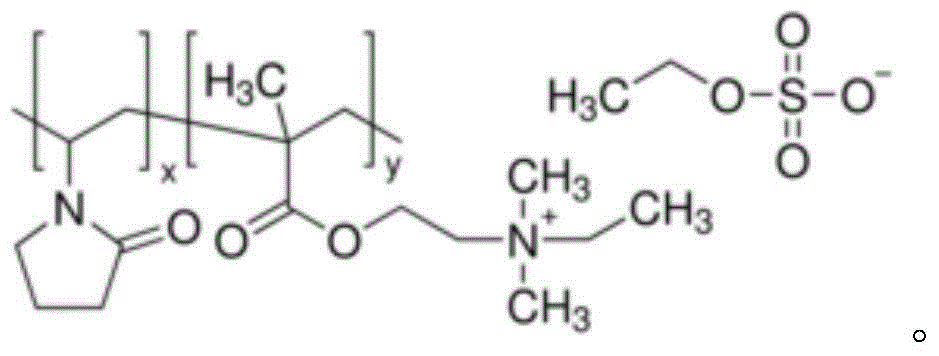
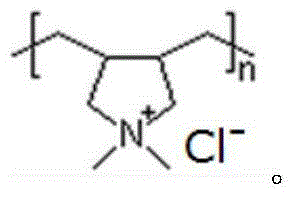
[0058] First, add the aluminum source into deionized water and stir evenly. Then add sodium hydroxide and / or potassium hydroxide to it, mix evenly, add silicon source, continue stirring at room temperature until a uniform silica-alumina gel is formed, finally add polyquaternium P, stir evenly, and obtain the initial gel . Move the initial gel into a stainless steel reaction kettle lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, directly put it into an oven for static crystallization, or put it into a rotating oven for dynamic crystallization, and the obtained solid product is centrifuged and washed with deionized water to medium properties, dried in air at 110°C, and finally calcined in a muffle furnace at 550°C for 8 hours to obtain a Beta molecular sieve with a hierarchical pore structure. The types and proportions of raw materials in the initial gels of the prepared samples 1-40, crystallization mode, crystallization temperature, crysta...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2: XRD characterization of sample 1-40
[0066] Samples 1-40 prepared in Example 1 were characterized by XRD to confirm that they were Beta zeolite molecular sieves. The instrument used is Philips X’Pert PROX X-ray diffractometer, copper target, K α radiation source The working voltage of the instrument is 40kv, and the working current is 40mA. The XRD spectrum of the obtained sample 1-40 and the characteristic spectrum of the standard Beta zeolite molecular sieve Figure 1 Sincerely. The typical XRD pattern is represented by sample 1, and the positions and peak intensities of the main diffraction peaks at 2θ at 5°-50° are shown in Table 2. Comparing the data results of other samples with those in Table 1, the position and shape of the diffraction peaks are the same, and the relative peak intensity fluctuates within ±5% according to the change of synthesis conditions, indicating that the synthesized product has the characteristics of Beta structure.
[...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3: Chemical composition of samples 1-40 prepared in Example 1
[0071] The chemical composition of samples 1 to 40 prepared in Example 1 was measured by an elemental analyzer. The instrument used was a Magix (PHILIPS) X-ray fluorescence analyzer. + The standard-free quantitative analysis program corresponds the fluorescence intensity of the standard sample to its standard composition, and deducts the influence of interference spectral lines.
[0072] The result measured by the elemental analyzer is the percentage content of oxides of each element. The chemical composition and silicon-aluminum ratio of the sample can be obtained by inverting the percentage content of the oxide of the element, as shown in Table 3.
[0073] Table 3 Chemical composition of samples 1 to 40
[0074]
[0075]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mesopore | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com