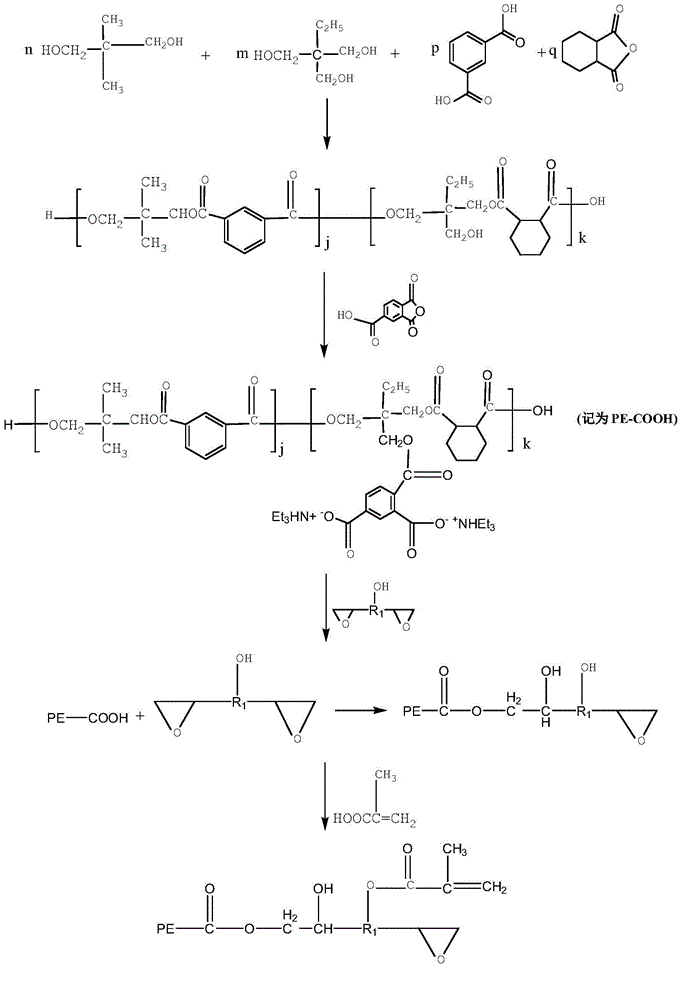
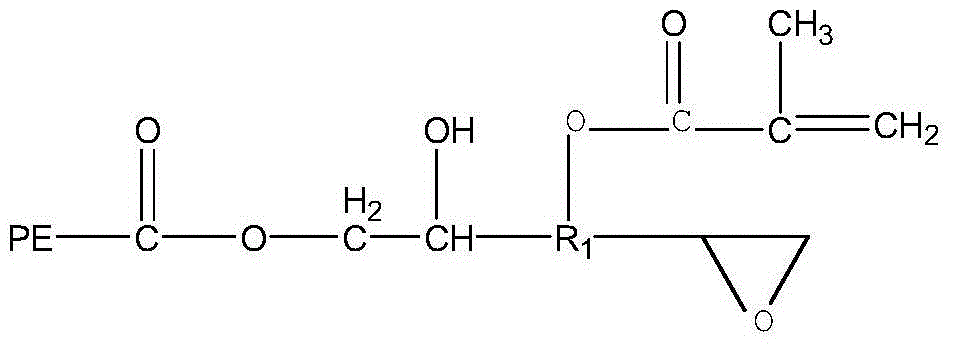
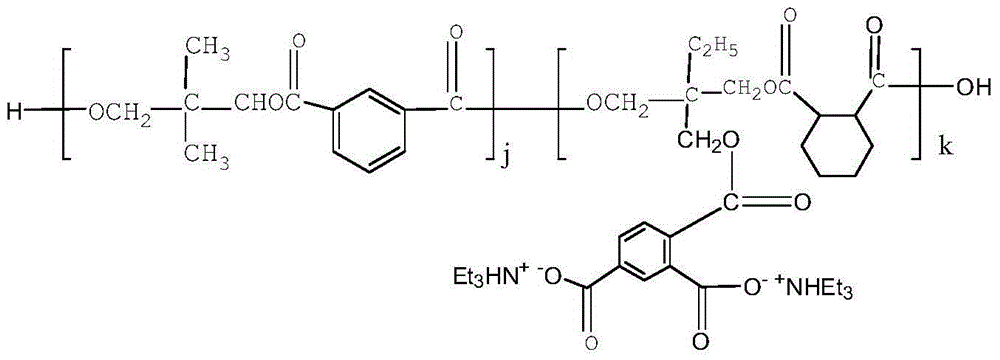
Modified foam thermal insulation material based on waterborne polyester resin and preparation method of modified foam thermal insulation material
A technology of water-based polyester resin and hydroxyl polyester resin, which is applied in the field of preparation and high-strength light-weight non-combustible cement-based water-based polyester resin modified foam insulation materials, which can solve the problems of cement foam material collapse, thermal conductivity increase, and thermal insulation. Avoid foam material overflow and other problems, and achieve the effect of small shrinkage, high compressive strength and low density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] A high-strength light non-combustible cement-based water-based polyester resin modified foam insulation material, which includes the following components by weight percentage:
[0048]
[0049] Wherein, the cement is a mixture of Portland cement and aluminate cement in a mass ratio of 8:1.
[0050] Wherein, the inorganic filler is a mixture of talcum powder, calcium oxide, magnesium hydroxide and calcium chloride in a mass ratio of 1:4:1:1.
[0051] Wherein, the foaming agent is a mixture of 4,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, pentane and sodium bicarbonate in a mass ratio of 3:1:4.
[0052] Wherein, the curing agent is a mixture of diethylenetriamine and amide in a mass ratio of 9:5.
[0053] Wherein, the catalyst is a mixture of triethylenediamine and dibutyltin dilaurate in a mass ratio of 5:1.
[0054] Wherein, described coagulant is lithium carbonate.
[0055] Wherein, the foam stabilizer is a mixture of oleic acid and sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate in a mass ra...
Embodiment 2
[0065] High-strength light non-combustible cement-based water-based polyester resin modified foam insulation material, which includes the following components by weight percentage:
[0066]
[0067]
[0068] Wherein, the cement is a mixture of Portland cement and aluminate cement in a mass ratio of 8:1.
[0069] Wherein, the inorganic filler is a mixture of talcum powder, calcium oxide, magnesium hydroxide and calcium chloride in a mass ratio of 1:4:1:1.
[0070] Wherein, the foaming agent is a mixture of 4,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, pentane and sodium bicarbonate in a mass ratio of 3:1:4.
[0071] Wherein, the curing agent is a mixture of diethylenetriamine and amide in a mass ratio of 9:5.
[0072] Wherein, the catalyst is a mixture of triethylenediamine and dibutyltin dilaurate in a mass ratio of 5:1.
[0073] Wherein, described coagulant is lithium carbonate.
[0074] Wherein, the foam stabilizer is a mixture of oleic acid and sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate ...
Embodiment 3
[0085] High-strength light non-combustible cement-based water-based polyester resin modified foam insulation material, which includes the following components by weight percentage:
[0086]
[0087] Wherein, the cement is a mixture of Portland cement and phosphate cement in a mass ratio of 9:1.
[0088] Wherein, the inorganic filler is a mixture of talcum powder, calcium oxide, magnesium hydroxide and calcium chloride in a mass ratio of 1:4:1:1.
[0089] Wherein, the foaming agent is a mixture of 4,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, pentane and sodium bicarbonate in a mass ratio of 3:1:4.
[0090] Wherein, the curing agent is a mixture of diethylenetriamine and amide in a mass ratio of 9:5.
[0091] Wherein, the catalyst is a mixture of triethylenediamine and dibutyltin dilaurate in a mass ratio of 5:1.
[0092] Wherein, described coagulant is lithium carbonate.
[0093] Wherein, the foam stabilizer is a mixture of oleic acid and sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate in a mass ra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com