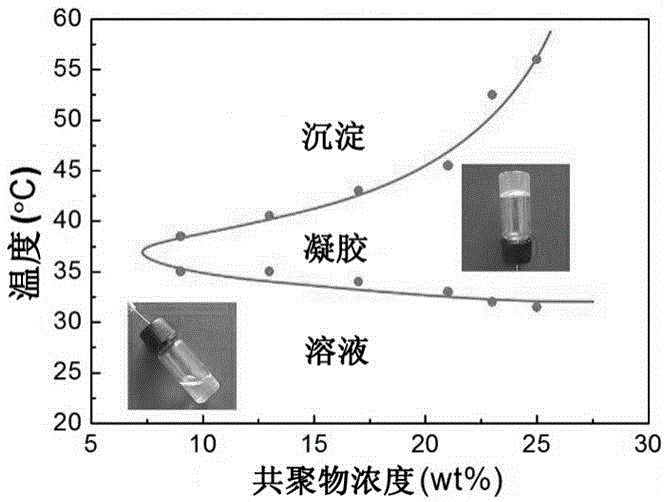
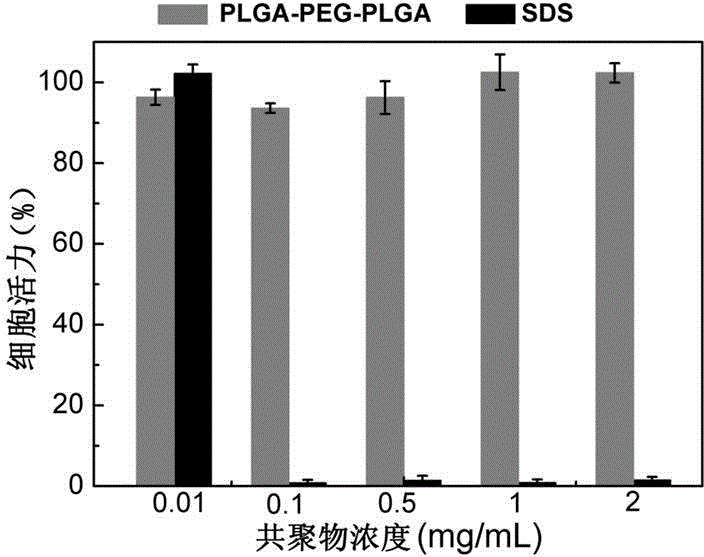
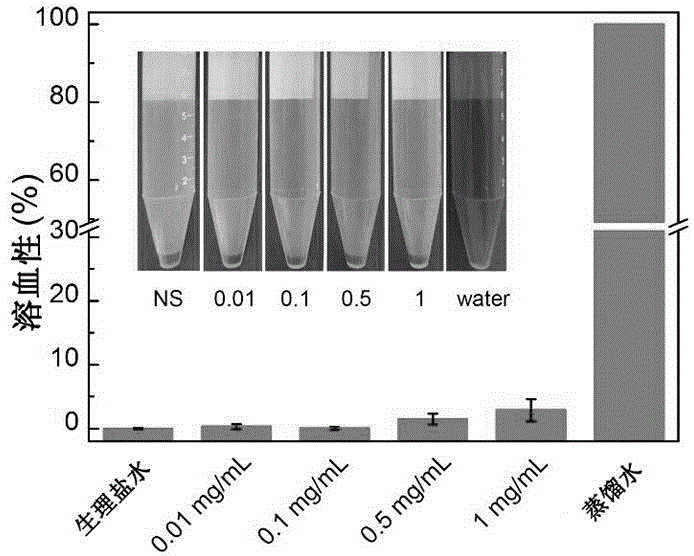
Polymer composite material with hemostasis and anti-adhesion properties and preparation method and application thereof
A composite material and polymer technology, applied in polymer materials and medical fields, can solve problems such as poor adhesion and aggravation of cerebrospinal fluid leakage, and achieve convenient application, good biocompatibility, and prevention of adhesions Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of PLGA-PEG-PLGA block copolymer
[0031] Add 30 g PEG (1500) into a 250 mL four-neck flask, heat the oil bath to 130 °C, vacuum filter for 3 h with stirring to remove the residual moisture in the PEG, and then add 58 g DL-lactate under the protection of argon After the ester (LA) and 6 g glycolide (GA) were completely melted, 0.1 wt% stannous octoate was added, and the oil bath was heated to 150 °C to continue the reaction for 12 h. After the reaction was completed, the unreacted monomers and low-boiling products in the system were removed by vacuum filtration for 2 h. Finally, the initial product was placed in hot water at 80°C, stirred and washed, allowed to stand for precipitation, and the upper layer solution was removed. The washing was repeated three times, and the residual water was removed by freeze-drying to obtain the final product with a yield of about 80%. The number-average and weight-average molecular weight ( M n , M w )...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of MPEG-PLGA block copolymer
[0033] Add 11 g of monomethoxy-terminated polyethylene glycol MPEG (550) into a 250 mL four-necked flask, heat the oil bath to 130 °C, and vacuum filter for 3 h while stirring to remove residual moisture in MPEG, and then 26.7 g DL-lactide (LA) and 4.3 g glycolide (GA) were added under gas protection, and after complete melting, 0.1 wt% stannous octoate was added, and the oil bath was heated to 150 °C to continue the reaction for 12 h. After the reaction was completed, the unreacted monomers and low-boiling products in the system were removed by vacuum filtration for 2 h. The initial product was dissolved in dichloromethane solution and precipitated with ether, the yield was about 85%. The number-average and weight-average molecular weight ( M n , M w ) are 2850 and 3730 respectively, the molecular weight distribution coefficient ( M w / M n ) is 1.31.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of PCGA-PEG-PCGA block copolymer
[0035] Add 30 g PEG (1500 °C) into a 250 mL four-neck flask, heat the oil bath to 130 °C, and vacuum filter for 3 h with stirring to remove the residual moisture in the PEG, during which the argon gas was replaced more than three times. Then, 50 g ε-caprolactone (CL) and 25 g glycolide (GA) were added under the protection of argon. After complete melting, 0.1 wt% stannous octoate was added, and the temperature of the oil bath was raised to 150 °C to continue the reaction for 12 h. After the reaction was completed, the unreacted monomers and low-boiling products in the system were removed by vacuum filtration for 2 h. The initial product was dissolved in dichloromethane solution, ether precipitated, and the yield was about 80%. The number-average and weight-average molecular weight ( M n , M w ) are 7260 and 9570 respectively, the molecular weight distribution coefficient ( M w / M n ) is 1.32.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com