Encoding mutation EPSPS (5-enolpyruvyl-shikimate-3-phosphate synthase) gene, and expression vector, expression product and application of encoding mutation EPSPS gene
A technology of CTP2-EPSPS and expression vectors, which is applied in the fields of encoded mutated EPSPS genes, its expression vectors, expression products and its applications, can solve the problems of large damage to crops, difficult selection of herbicides to eliminate weeds, etc., and achieve gene Less silencing, strong resistance to glyphosate, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
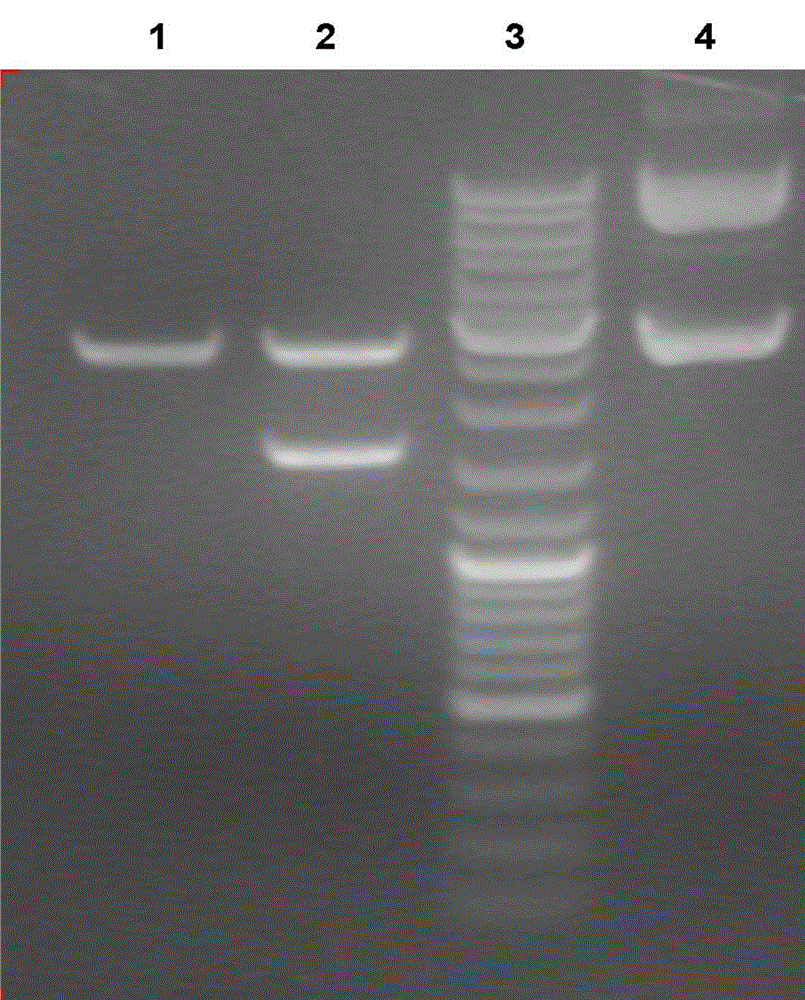
[0039] Example 1 coding mutant EPSPS gene synthesis
[0040] On the basis of a large number of previous screening experiments, the bacterial culture screened and isolated the gene CP4- EPSPS (SEQ ID NO.1) was modified to replace the codons corresponding to the sequence with part of the codons, while excluding the commonly used restriction enzyme sites (SacI and XbaI), and then corrected and eliminated by replacing the codons, and in 3 Add a stop codon TAG to the end, and realize the amino acid mutation from the second serine to leucine by artificial synthesis, and obtain a modified mutation EPSPS Gene sequence (as shown in SEQIDNO.2), and its corresponding amino acid sequence as shown in SEQIDNO.3; In addition, in the transformed EPSPS The chloroplast guide peptide sequence of CTP2 (as shown in SEQ ID NO.4) is added in front of the 5 end of the gene to obtain the herbicide resistance gene CTP2- EPSPS (SEQ ID NO.5); then determine and chemically synthesize CTP2- EPSPS Cod...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2 Plant expression vector pCAMBIA1300-CTP2- EPSPS Agrobacterium transformation of maize
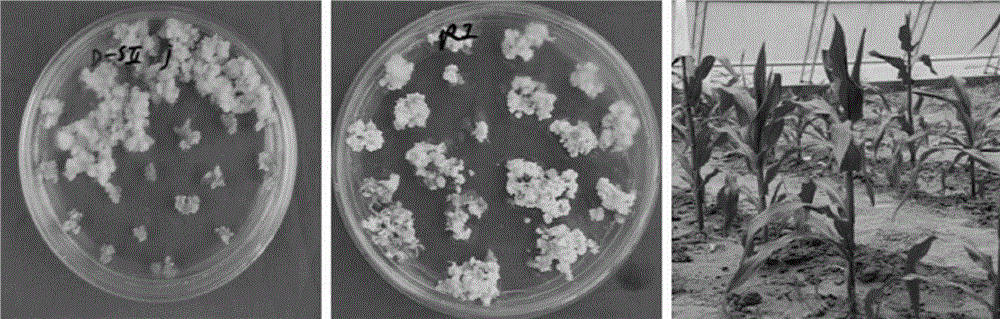
[0087] In this experiment, Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated method was used to transfer the herbicide-resistant gene CTP2- EPSPS Fragment recombinant expression vector pCAMBIA1300-CTP2- EPSPS Introduce corn callus, and obtain transgenic seedlings after infection, recovery, selection, regeneration, hardening and other stages (see Figure 4 ). The specific steps are as follows:
[0088] (1) Preparation of immature embryos: Disinfect ears that have been pollinated for 10-14 days, take out the ears and wash them with sterilized water for 3 times, insert the tip of an embryo stripping knife between the embryo and endosperm, and gently pry out the immature embryos. Embryos, to ensure that the immature embryos are not damaged in any way (immature embryos with a size of about 1.5 mm are taken).
[0089] (2) Agrobacterium infection: Put the freshly stripped immature embryos...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3 Molecular detection of transgenic maize plants
[0096] (1) PCR detection of transgenic maize plants
[0097] When the transformed plants grow 7-8 leaves, the leaves are taken to extract DNA, and PCR technology is used to detect exogenous genes. After flowering, the transgenic plants are bagged and self-bred or sister crossed to set fruit. Extraction of plant DNA is carried out with the CTAB method proposed by Saghai-Maroof et al.; PCR technology is used to detect exogenous genes;
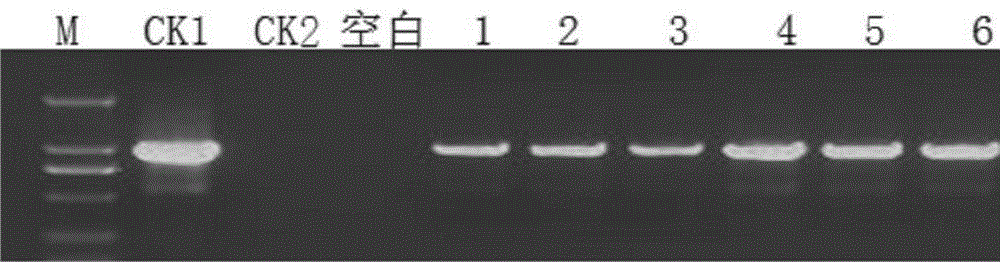
[0098] Figure 4 The target gene of the transformant is shown in EPSPS The PCR detection results of M: M: DL2000plus; CK1: positive plasmid control; CK2: non-transgenic negative control; blank: double distilled water control; 1-8: EPSPS -1 to EPSPS -6. The PCR detection primers used are (as shown in SEQ ID NO.6, SEQ ID NO.7):
[0099] EPSPS-F :5'ACCGCCCGCAAATCCTCTGGC3'
[0100] EPSPS-R :5'CGGCACCGTGACGCCCTTCAG3'
[0101] Target fragment size: 560bp, annealing temperat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com