Method for extracting titanium from vanadium-titanium magnetite
A technology for vanadium titanomagnetite and iron concentrate, which is applied to the improvement of process efficiency, electric furnaces, furnaces, etc., can solve the problems of unrealistic utilization, unfavorable production of advanced titanium-rich materials, and high technical difficulty, and achieves efficient separation. The effect of extraction, improvement of slag fluidity, efficient and rational utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
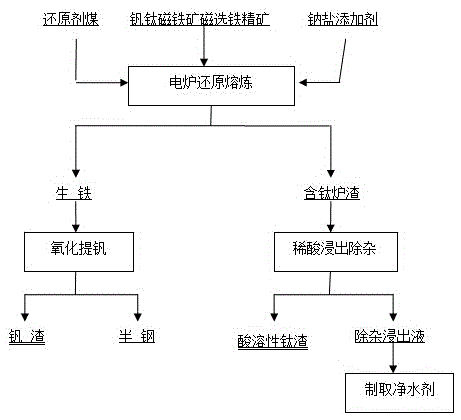
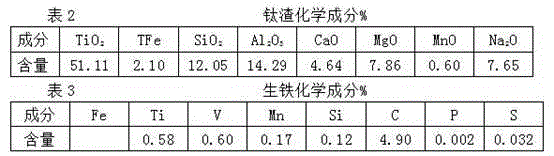
[0053] As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, it discloses a method for extracting titanium from vanadium-titanium magnetite, adding sodium or potassium salt additives (such as sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, sodium oxide, etc. , Potassium carbonate, Potassium hydroxide, Potassium oxide) to obtain molten iron and titanium-containing slag, in which: vanadium and iron are reduced into molten iron, and under high temperature conditions of smelting, silicon, aluminum impurities and sodium or potassium salt additives form soluble Sodium aluminosilicate of dilute acid is left in the titanium-containing slag with titanium and calcium and magnesium impurities; then, the titanium-containing slag is purified by hydrometallurgical impurity removal method to obtain TiO 2 >75% titanium slag products.
Embodiment approach
[0055] As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, its specific steps are as follows:
[0056] a. Reduction smelting in electric furnace: mix iron concentrate with reducing agent coal and sodium or potassium salt additives, carry out reduction smelting in submerged arc furnace (or other direct reduction furnace), vanadium and iron are reduced into molten iron, and molten iron is oxidized and extracted by converter Vanadium is separated from iron and vanadium. Under the high temperature conditions of smelting, difficult-to-reduce silicon and aluminum impurities and sodium or potassium salt additives form dilute acid-soluble aluminosilicates and titanium and calcium-magnesium impurities remain in the titanium-containing slag;
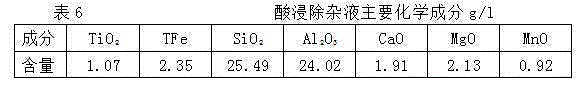
[0057] b. Purification of smelting titanium slag: Hydrometallurgical leaching of titanium-containing slag with dilute sulfuric acid or dilute hydrochloric acid with an H ion concentration of 2-3N under normal pressure, and aluminosilicate soluble i...
Embodiment 3
[0061] On the basis of embodiment 1, wherein b and c step order is exchanged.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com