Process for synergic removal of flue gas pollutants through complexing absorption synchronous electrolytic reduction
A technology of complex absorption and pollutants, which is applied in external electrostatic separators, dispersed particle separation, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of wasting power consumption, reducing reaction conversion rate, and increasing impeller wear, and achieves simplified structure, The effect of improving conversion rate and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
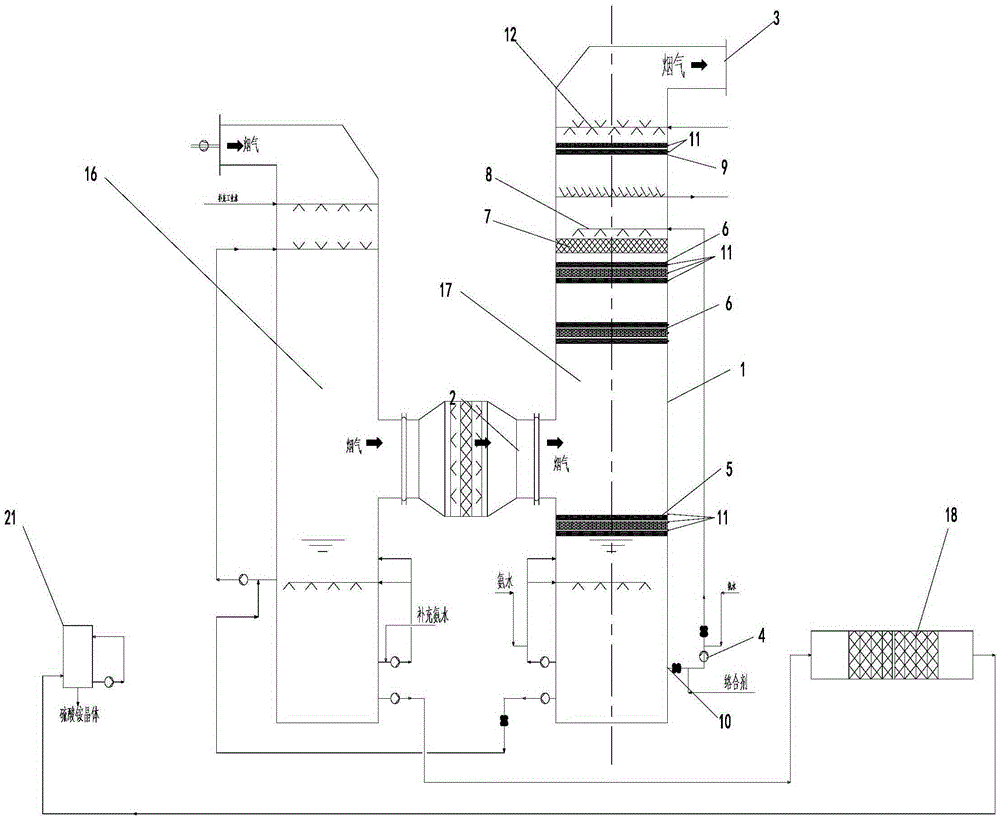
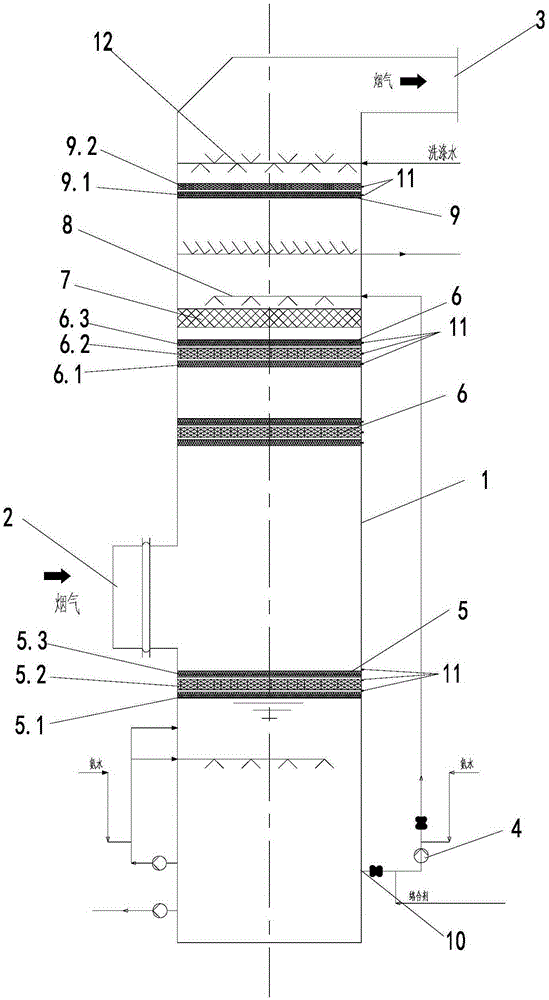
[0056] See figure 2 , The structure of the absorption tower is:
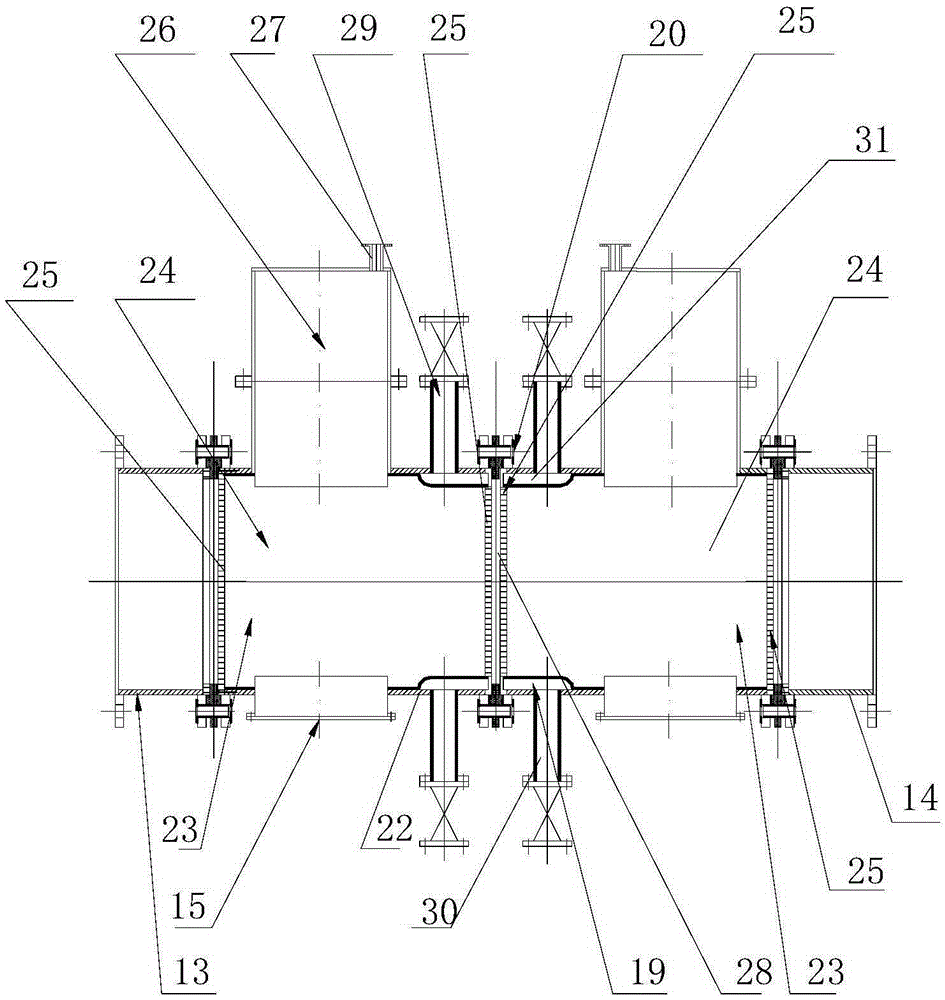
[0057] The synchronous desulfurization and denitrification reaction tower of the present invention includes a tower body 1, the top of the tower body is provided with a flue gas outlet 3, the middle of the tower body is provided with a flue gas inlet 2, and the bottom of the tower body 1 is provided with a circulating absorption liquid outlet 10, the circulating absorption liquid outlet 10 The circulating pump 4 is connected to the spray layer 8 on the upper part of the tower body, above the spray layer 8 an electrostatic defogging and reaction layer 9 is arranged in the tower body, and a washing layer is arranged above the electrostatic defogging and reaction layer 9; Below the spray layer 8 there is a packing layer 7 in the tower body, and at least one layer of absorption and electrochemical reaction layer 6 is arranged below the packing layer 7 (in this embodiment, there are two layers, two adjacent layers of ab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com