Low anticoagulant heparin and oligosaccharides thereof, and preparation methods and application of low anticoagulant heparin and oligosaccharides thereof in preparation of anti-Alzheimer's disease drugs
A low anticoagulant and oligosaccharide technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of low anticoagulant heparin by-products, waste of biological resources, etc., and achieve the effect of abundant raw material sources, low cost, and avoiding bleeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Preparation of low anticoagulant heparin
[0035] The preparation method of low anticoagulant heparin of the present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
[0036] 1. Chondroitinase ABC enzyme removes chondroitin impurities: dissolve pig intestinal mucosa crude heparin (10g) purchased from a heparin production plant in 3L enzymolysis buffer (0.05mol L -1 Ammonium acetate, 2mmol·L -1 Calcium chloride), 50 Units of chondroitinase ABC were added thereto, reacted on a shaking table at 35° C. for 6 hours, and inactivated in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes.
[0037] 2. Hydrochloric acid precipitation to remove nucleic acid impurities: centrifuge the enzymatic solution and take the supernatant. Add 1 mol·L dropwise to the supernatant with stirring -1 hydrochloric acid until the pH of the enzymolysis solution is 3.0, centrifuge, take the supernatant and use 1mol·L -1 neutralized to pH 7.0 with NaOH.
[0038] 3. Ethanol precipitation: After co...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: Structural characterization of the low anticoagulant heparin
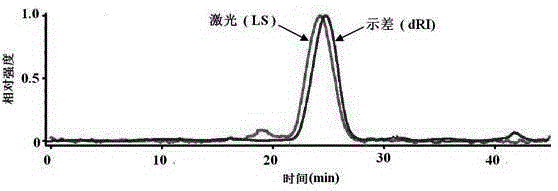
[0041](1) Absolute molecular weight determination and purity analysis: The absolute molecular mass of the low anticoagulant heparin was determined and the purity was analyzed by high performance gel permeation chromatography (HPGPC)-octadecanine laser light scattering method (MALLs).
[0042] Chromatographic conditions: Chromatographic column: ShodexOHPakSB804HQ column and ShodexOHPakSB802.5HQ column in series; mobile phase: 0.1mol L -1 Na 2 SO 4 Aqueous solution; The molecular weight of low anticoagulant heparin is detected and determined in series by a differential detector and an octagonal laser light scattering instrument in series; the sample is in the middle of a single symmetrical peak in the HPGPC spectrogram (such as figure 1 Shown), the sample purity is very high, and its absolute molecular mass is measured as 10.24kDa.
[0043] (2) Analysis of disaccharide composition: make low antic...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: Anticoagulant activity of low anticoagulant heparin
[0050] Follow the steps indicated in the kit to determine the inhibitory effect of the sample on the activity of FXa and FIIa, the initial concentration of the sample is 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10 and 100 μg·mL -1 . Add 20 μL of antithrombin III (ATIII) and 20 μL of sample solution to each well of a 96-well plate, incubate at 37°C for 1 min, then add 40 μL of FXa or FIIa, incubate at 37°C for 1 min, add 100 μL of FXa or FIIa substrate, and incubate at 37°C 4min, finally add 100μL stop solution, detect absorbance at 405nm wavelength, calculate inhibition rate: result ( Figure 4 ) showed that LAH had weak anticoagulant activity, which was much lower than that of HP and ES standards, and slightly higher than that of HS standards.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com