Method for comprehensively recycling lead and zinc containing blast furnace dust
A dust and blast furnace technology, which is applied in the field of comprehensive recycling of blast furnace dust containing lead and zinc, can solve problems such as sinter composition segregation, leaching agent consumption, and unit operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
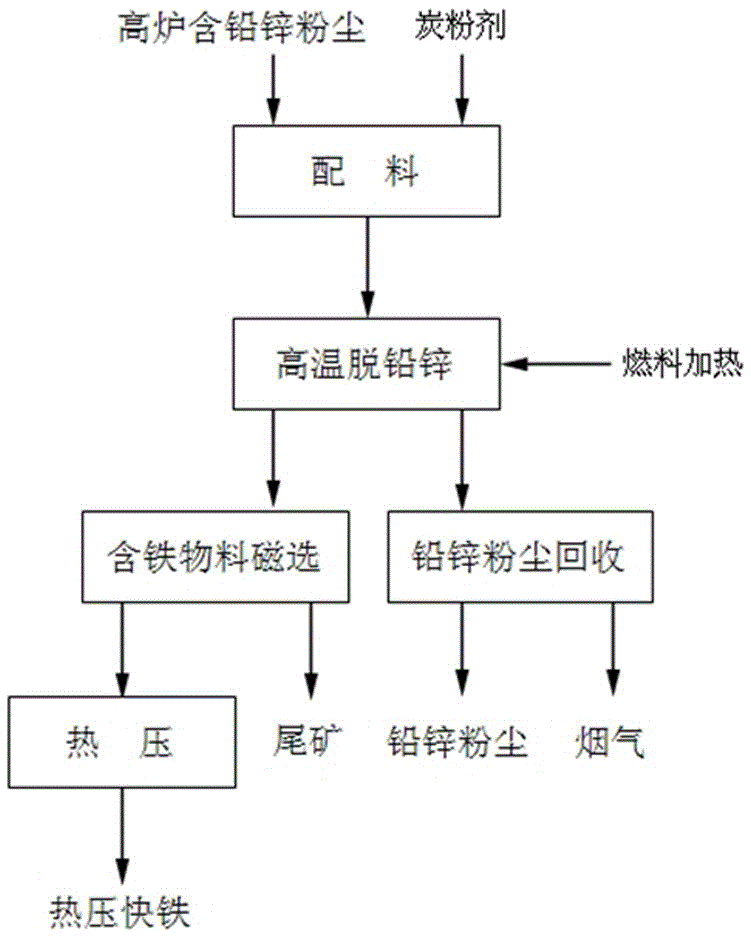
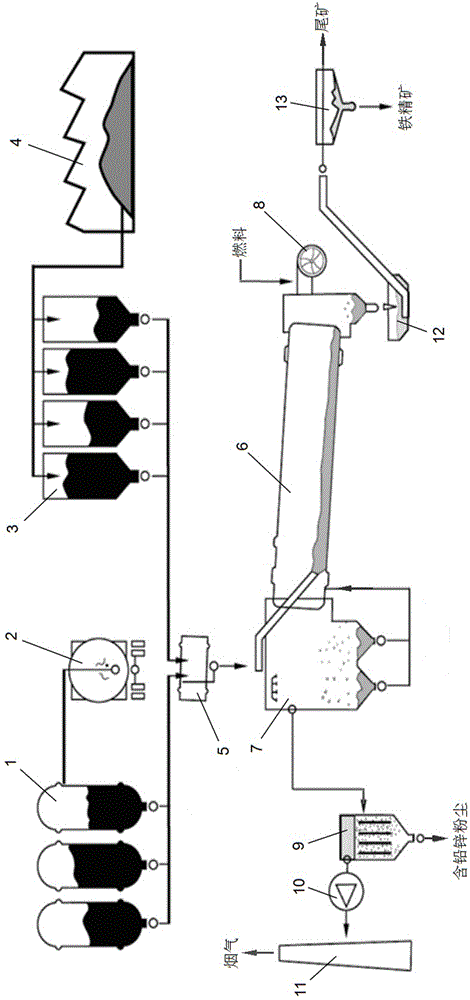
[0029] Such as figure 1 and 2 As shown, take the blast furnace bag dust removal powder containing lead and zinc dust with a TFe content of 25.2%, a Zn content of 12.74%, a Pb content of 4.06%, and a C content of 37.24%, and comprehensively recycle and utilize it through the following steps:
[0030] 1. Mix the above recovered blast furnace lead-zinc dust and coke powder with a fineness of 50 mesh and a fixed carbon content of 83% with water at a weight ratio of 10:1.5 to make pellets;
[0031] 2. Add the above-mentioned pellets from the kiln tail at a rate of 40-300 tons / h with an inclination angle of 3.5°, a rotation speed of 0.3-4m / min, and an outlet gas flow rate of 50-450m 3 / s Φ3.0×60 rotary kiln, and spray gas from the kiln head to heat the pellets. The pellets enter the drying and preheating section (650~750℃) through the continuous rotation of the rotary kiln, and then enter the medium temperature section (750℃) ~1100℃), and finally enter the high-temperature section ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Take the lead-zinc dust of the blast furnace bag dust removal powder with a TFe content of 39.57%, a Zn content of 15.81%, a Pb content of 2.12%, and a C content of 26.74%, and comprehensively recycle through the following steps:
[0038] 1. Mix the above recovered blast furnace dust containing lead and zinc with coal powder with a fineness of 200 mesh and a fixed carbon content of 45% by adding water at a weight ratio of 10:3 to make pellets;
[0039] 2. Put the above-mentioned pellets into the rotary kiln from the kiln tail, and spray propane from the kiln head to heat the pellets. The pellets enter the drying and preheating section (600-700°C) through the continuous rotation of the rotary kiln, and then enter the middle temperature section (700-850°C), and finally enter the high-temperature section (900-1000°C) for smelting for 50 minutes; with the rotation of the rotary kiln, the lead, zinc and some alkali metal oxides and sulfides in the pellets in the high-temperat...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Take the blast furnace bag dust removal powder containing lead and zinc dust with a TFe content of 20.23%, a Zn content of 16.93%, a Pb content of 3.68%, and a C content of 54.39%, and comprehensively recycle through the following steps:
[0046] 1. Mix the above recovered blast furnace lead-zinc dust and coal powder with a fineness of 120 mesh and a fixed carbon content of 78% with water at a weight ratio of 10:2 to make pellets;
[0047] 2. Put the above-mentioned pellets into the rotary kiln from the kiln tail, and spray natural gas from the kiln head to heat the pellets. The pellets enter the drying and preheating section (600-700°C) through the continuous rotation of the rotary kiln, and then enter the middle temperature section (700-950°C), and finally enter the high-temperature section (950-1100°C) for smelting for 45 minutes; as the rotary kiln rotates, the lead, zinc and some alkali metal oxides and sulfides in the pellets in the high-temperature section are red...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com