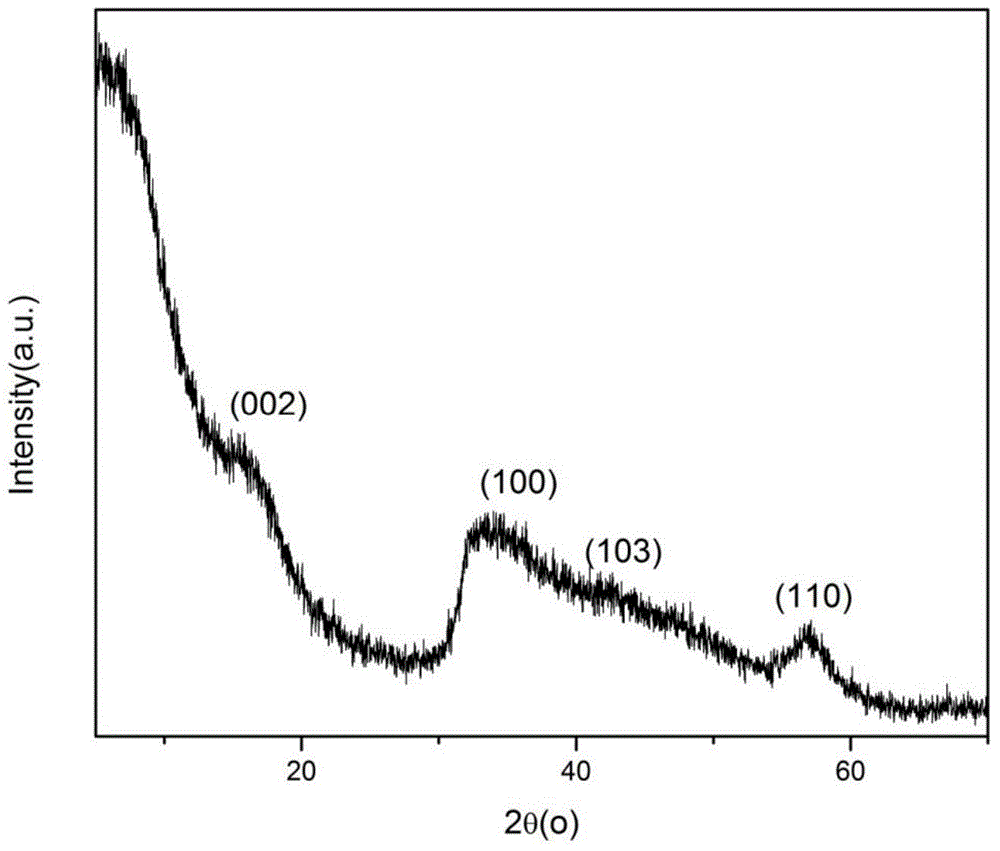
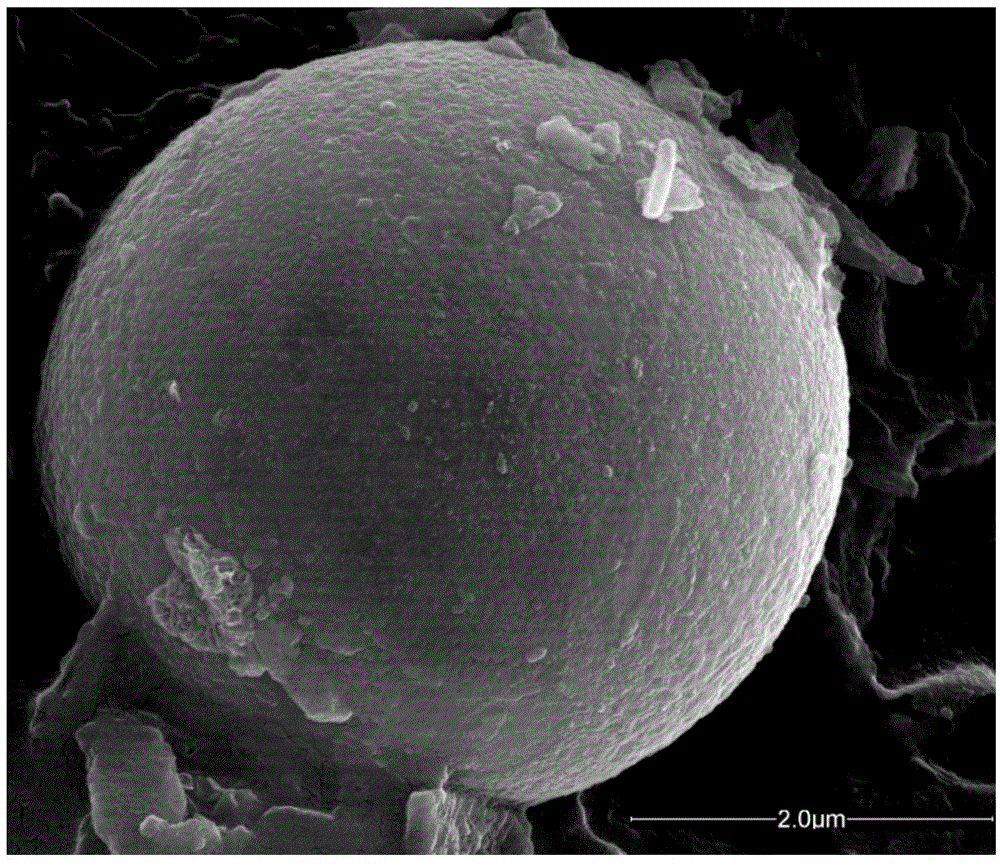
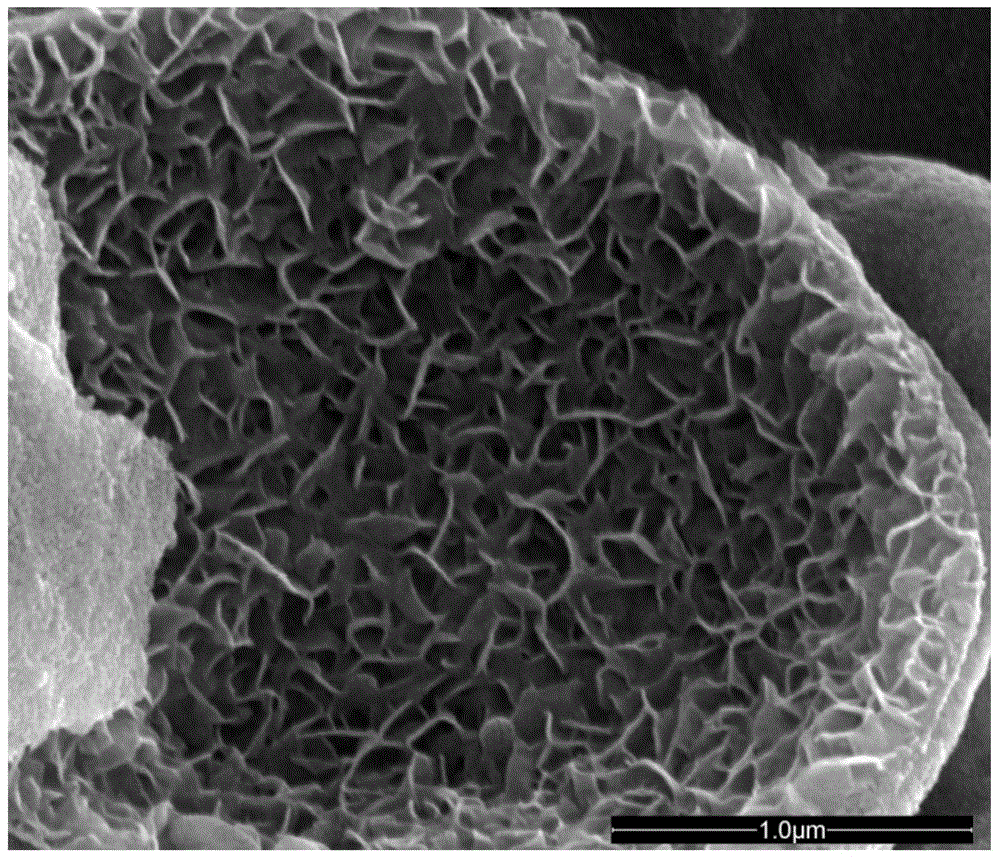
A method of preparing molybdenum disulfide microspheres in a reversed-phase microemulsion system
An inverse microemulsion and molybdenum disulfide technology, applied in the direction of molybdenum sulfide, etc., can solve problems such as complex operation, and achieve the effect of simple experimental equipment, controllable particle size and uniform size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether (TritonX-100), n-hexanol and cyclohexane were formulated into mixture A, wherein TritonX-100 was 58.75 g, n-hexanol was 48.61 g, and cyclohexane was 79.92 g. Add 6.55 mL of 0.15 mol / L ammonium tetrathiomolybdate aqueous solution B to mixture A under stirring at 500 rpm, and stir for 30 min to form microemulsion C. Add 1.65 mL of hydrazine hydrate solution D with a concentration of 0.56 mol / L to the above microemulsion C, and stir at 500 rpm for 30 min to form microemulsion E. Transfer the microemulsion E into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, the filling volume is 60% of the free volume of the reaction kettle, seal it and stand at 180° C. for 24 hours for crystallization. Cool down to room temperature naturally after taking out the kettle. After separation by filtration, it was washed three times with deionized water and absolute ethanol to obtain a black solid product, which was dried in vacuum at 70° C. for 12 hours to obtain molyb...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether (TritonX-100), n-hexanol and cyclohexane were formulated into mixture A, wherein TritonX-100 was 58.75 g, n-hexanol was 48.61 g, and cyclohexane was 79.92 g. Add 6.55 mL of 0.15 mol / L ammonium tetrathiomolybdate aqueous solution B to mixture A under stirring at 500 rpm, and stir for 30 min to form microemulsion C. Add 1.65 mL of hydrazine hydrate solution D with a concentration of 1.4 mol / L to the microemulsion C above, and stir for 30 min to form microemulsion E. Transfer the microemulsion E into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, the filling volume is 60% of the free volume of the reaction kettle, seal it and stand at 180° C. for 24 hours for crystallization. Cool down to room temperature naturally after taking out the kettle. After separation by filtration, it was washed three times with deionized water and absolute ethanol to obtain a black solid product, which was dried in vacuum at 70° C. for 12 hours to obtain molybdenum disulf...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether (TritonX-100), n-hexanol and cyclohexane were formulated into mixture A, wherein TritonX-100 was 58.75 g, n-hexanol was 48.61 g and cyclohexane was 79.92 g. Add 6.55 mL of 0.15 mol / L ammonium tetrathiomolybdate aqueous solution B to mixture A under stirring at 500 rpm, and stir for 30 min to form microemulsion C. Add 1.65 mL of 2.24 mol / L hydrazine hydrate aqueous solution D to the microemulsion C above, and stir at 500 rpm for 30 min to form microemulsion E. Transfer the microemulsion E into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, the filling volume is 60% of the free volume of the reaction kettle, seal it and stand at 180° C. for 24 hours for crystallization. Cool down to room temperature naturally after taking out the kettle. After separation by filtration, it was washed three times with deionized water and absolute ethanol to obtain a black solid product, which was dried in vacuum at 70° C. for 12 hours to obtain molybdenum disulfide p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com