Anti-oxidation polysaccharide in boletus subsplendidus as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology for tawny boletus and oxidized polysaccharide, which is applied in the field of extraction and purification of antioxidant polysaccharides in chrysanthemum boletus, can solve problems such as research difficulties, achieves simple preparation, is suitable for large-scale production, and has good safety Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1. Preparation of antioxidant polysaccharide of the present invention
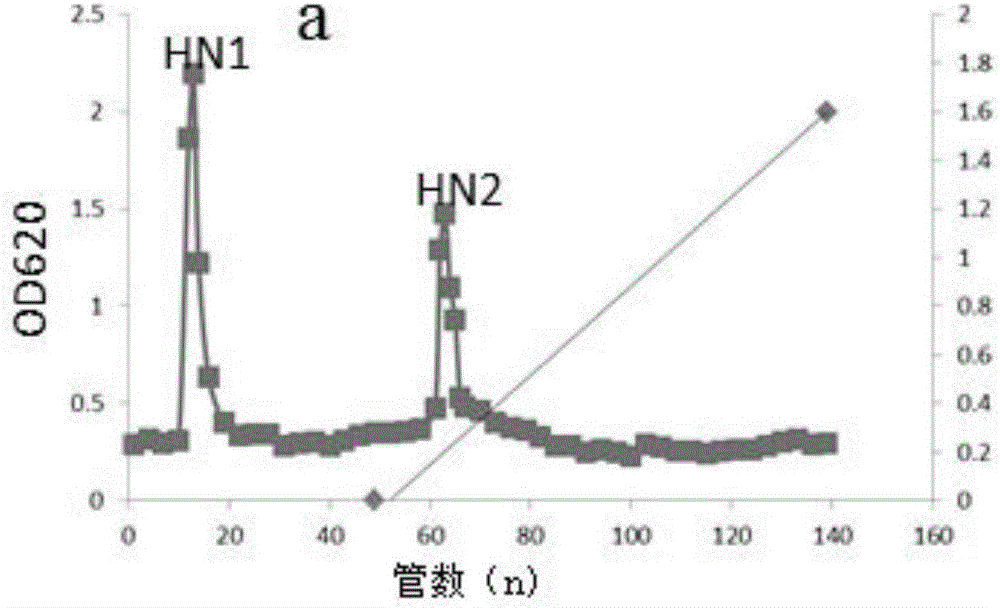
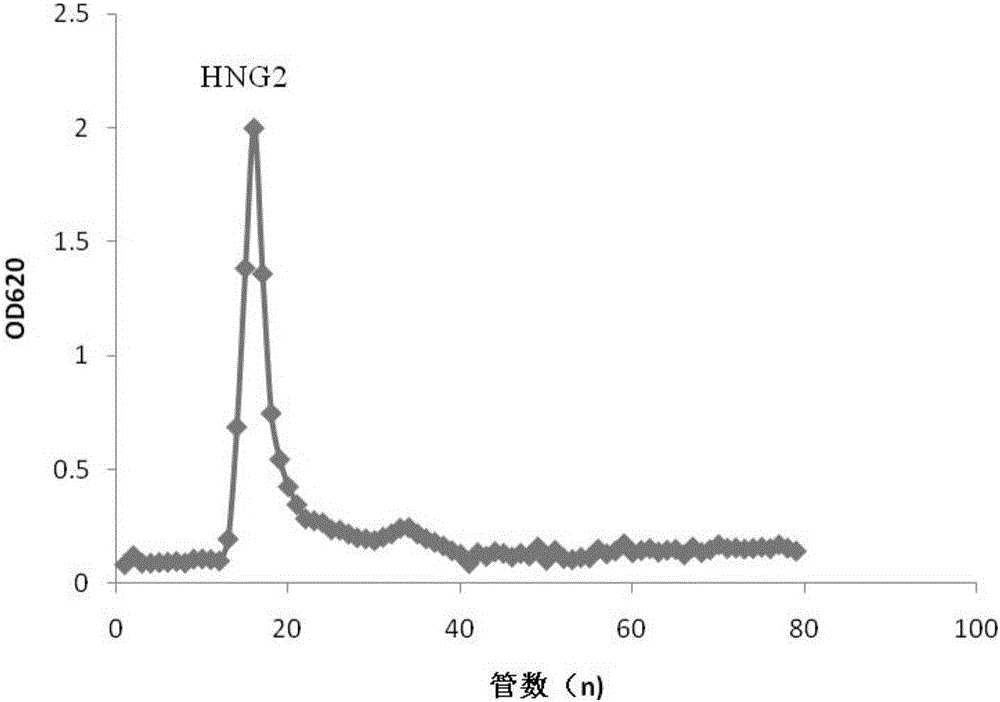
[0037] (1) Dry the fruiting bodies of Boletus edulis, pulverize with a high-speed grinder, add 30 times volume of distilled water, shake in a water bath at 80℃ for 5h, centrifuge at 8000r for 10min, take the supernatant, and repeat the extraction 2-3 times , Combine the centrifugal supernatants, use a rotary evaporator for rotary evaporation, concentrate to a certain volume, add 4 times the volume of absolute ethanol and let stand overnight at 4°C. After centrifugation, the precipitate was reconstituted to obtain a polysaccharide solution. To remove protein by sevage method, Sevage reagent was prepared according to the ratio of chloroform: n-butanol=4:1, and Sevage reagent was added according to the ratio of crude solution: Sevage reagent=4:1, vigorously shaken for 8-10min, and left to stand. When the interface between the aqueous and organic phases appears white, open the separatory funnel to...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2. Determination of the purity and molecular weight of the antioxidant polysaccharide of the present invention
[0041] Prepare standard dextran (Dextran T-10, T-50, T-70, T-100, T-200) of known molecular weight with double-distilled water to prepare a standard solution with a concentration of 10 mg / mL. After the filter membrane was filtered, the sample was loaded on the SUGAR KS-804 sugar column, the injection volume was 20μl, the molecular weight Mw of different dextran was used as the ordinate, and the retention time t of the standard dextran was used as the abscissa to draw a standard curve ( Figure 4 ).
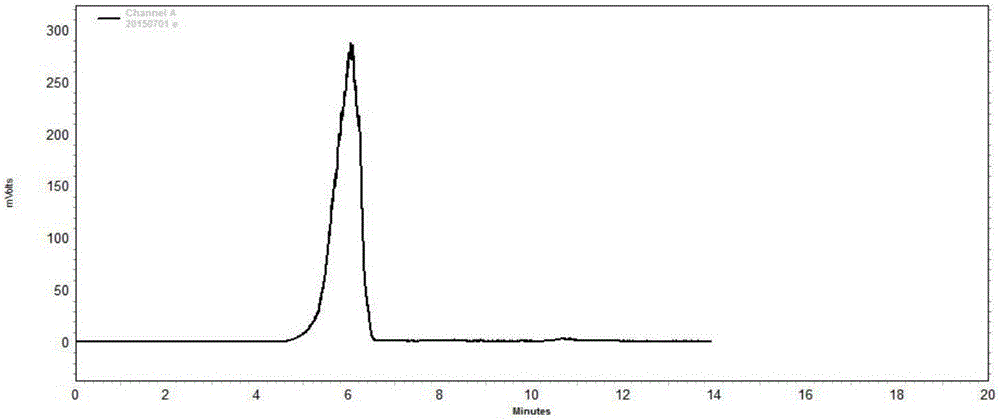
[0042] Prepare a solution with a concentration of 10mg / mL with double distilled water, filter it through a 0.22μm filter membrane and load the sample, collect the spectrum, and determine the purity according to the peak situation. image 3 Shows a single narrow symmetrical peak, it can be judged that the polysaccharide is pure product, the retention time is 6.0...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3. The DPPH free radical scavenging effect of the antioxidant polysaccharide of the present invention
[0044] (1) Use anhydrous methanol as a solvent for the antioxidant polysaccharide to prepare a solution with a concentration of 0.5 mg / mL, and use anhydrous methanol for DPPH to prepare a final concentration of 1×10 -4 mol / L solution.
[0045] (2) Take 0.06, 0.12, 0.18, 0.3, and 0.6 mL of the above polysaccharide solution in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, make up 1.2 mL with DPPH solution, and use an equal volume of anhydrous methanol to replace the sample solution as a blank control, and ascorbic acid as a positive control , Placed in the dark for 30 minutes.
[0046] (3) Measure the absorbance of each treatment at 517nm.
[0047] (4) Press "Removal rate=[1-(A s -A b ) / A i ]×100%" formula to calculate DPPH clearance rate, where A i Is the absorbance value of DPPH solution without sample, A s Is the absorbance of the sample after reaction with DPPH, A b Is the absorbance o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com