Method for preparing wheat straw cellulose microfibrils by auxiliary enzymatic pretreatment
A technology of cellulose microfibrils and enzyme pretreatment, which is applied in the direction of using microorganism/enzyme cellulose treatment, fiber raw material treatment, pulp beating/refining method, etc., can solve the increase of cost and environmental load, and high corrosion resistance , high energy consumption, achieve good economic and environmental benefits, reduce mechanical dissociation energy consumption, and reduce environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046]Sieve the wheat straw pulp, collect the fiber components trapped on the 100-mesh sieve, soak and swell with water for 12 hours, decompose for 30 minutes with a decomposer, squeeze out the water, and prepare the concentration with 0.05mol / L phosphate buffer solution 3% fiber suspension; then add domestic solid-state endoglucanase of 5% relative to the absolute dry mass of the fiber component for hydrolysis, keep the temperature at 45°C in a constant temperature water bath oscillating pot, and the oscillating frequency is 100r / min, the reaction The time is 120min. After the hydrolysis is completed, put it in a boiling water bath to boil and inactivate for 5 minutes, and then wash it thoroughly with distilled water to obtain the fiber slurry after enzyme pretreatment; then the fiber slurry is stirred by appropriate machinery, and the stirring speed is controlled at 8000r / min. 10min, and then it is prepared into 100mL of fiber suspension with a mass fraction of 0.5%. After t...
Embodiment 2
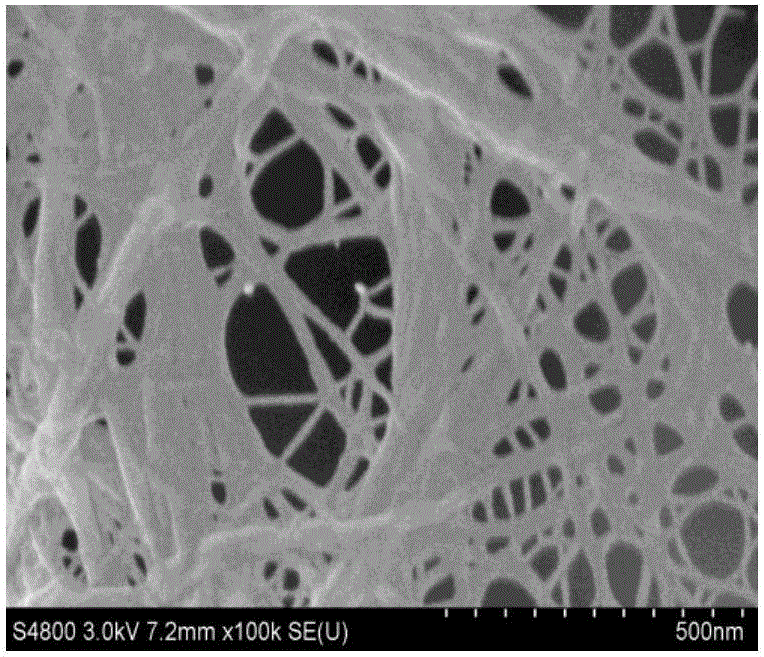
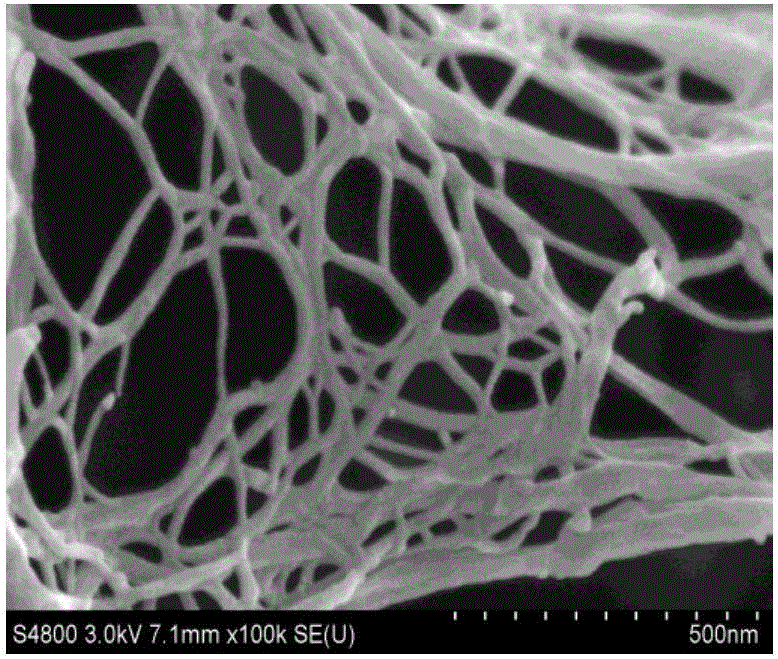
[0053] Other conditions are the same as in Example 1, only the addition amount of endoglucanase is 0.5%, 2%, ... 25% and 45% relative to the absolute dry mass of the fiber component, to prepare wheat straw cellulose microfibrils, and its performance The test results are shown in Table 1 below; wherein the scanning electron microscope picture (×100k) of the wheat straw cellulose microfibrils obtained by adding 25% enzyme amount and homogenizing 10 times is as attached image 3 shown.
[0054] Table 1 Performance test results of wheat straw cellulose microfibrils prepared with different enzyme additions
[0055] Enzyme addition 0.5% 2% 15% 25% 30% 45% Yield (%) 93 87 68 52 48 42 Width (nm) 40~120 40~110 35~85 30~80 30~65 25~60 Crystallinity 71.68 73.53 75.76 76.86 76.32 75.13 Polymerization 287 245 221 210 189 177 Energy consumption value (W h) 955.0 794.3 813.5 672.9 634.3 624.6
[0056] From the analys...
Embodiment 3
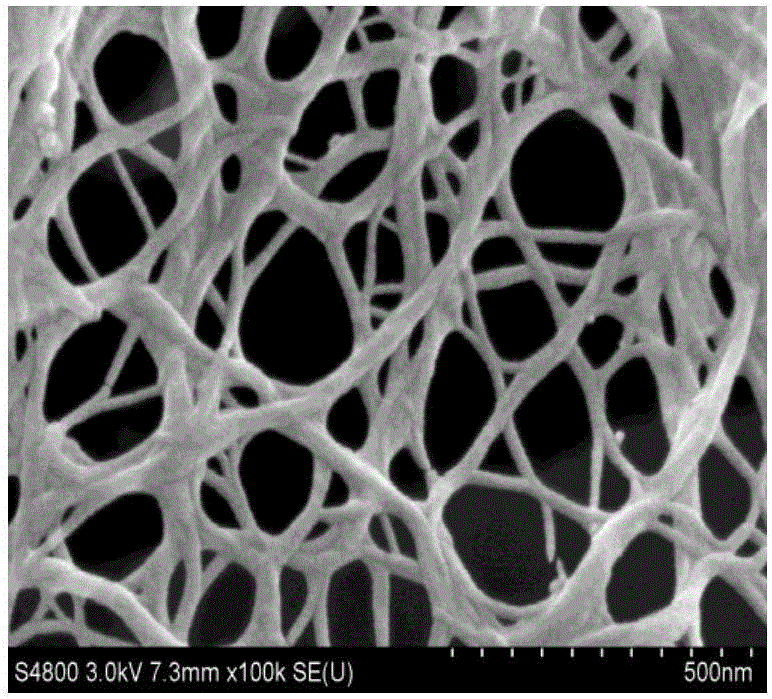
[0059] Other conditions are the same as in Example 1, only the amount of enzyme added is changed to 25% of the absolute dry mass of the relative fiber component, and the number of cycles of homogenization is successively 5, 10, 20, 30 and 40 times to prepare wheat straw cellulose microfibrils. The scanning electron microscope picture (×10k) of the wheat straw cellulose obtained by adding enzyme amount 25% and homogenizing 5 times is as attached Figure 4 As shown, the scanning electron microscope pictures (×100k) of the wheat straw cellulose microfibrils obtained by adding 25% enzyme amount and homogenizing 30 times are as attached Figure 5 shown.
[0060] The results showed that: when the number of homogenization was 5 times, the surface of the wheat straw fiber was obviously divided and fluffed, the fiber became shorter, and the microfibril structure was exposed, but the microfibrils were not completely dissociated; with the increase of the number of homogenization, When t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com