Rare earth in-situ leaching and enriching process for ionic rare earth ore
An ionic rare earth ore, in-situ leaching technology, applied in the field of mining technology, can solve the problems of lack of research on recycling, restricting the use of technology, and long production cycle, so as to solve the problem of ammonia nitrogen pollution, improve resource utilization, and shorten the leaching cycle. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
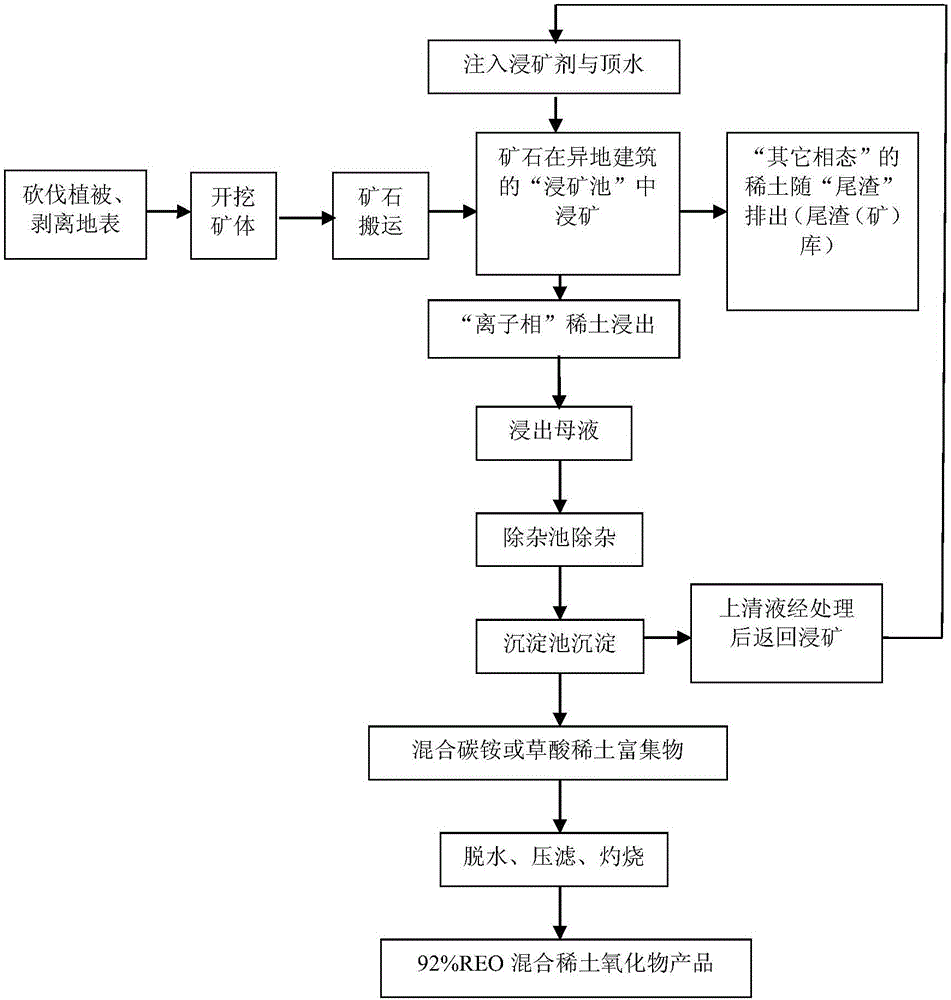
[0084] The ionic rare earth ore in this example comes from a rare earth mine in Xunwu, Ganzhou, and the main chemical composition of the ore sample is shown in Table 1.
[0085] Table 1 The main components of an ion-type rare earth ore in Xunwu
[0086]
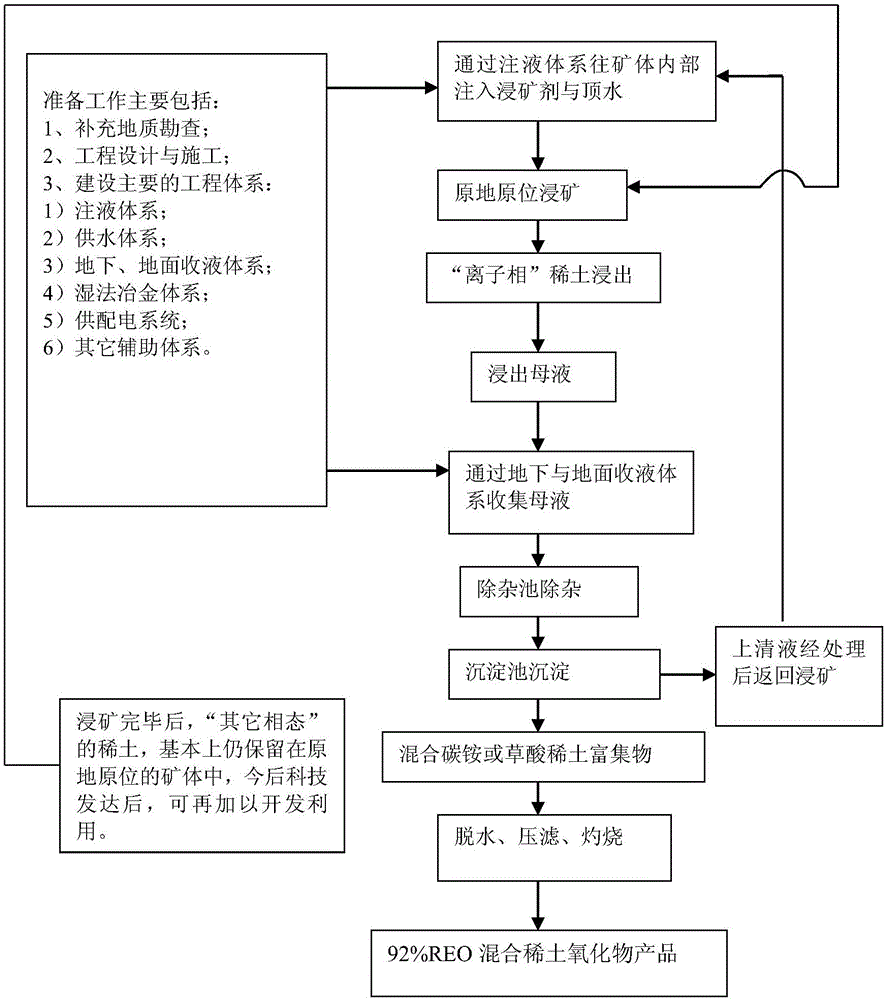
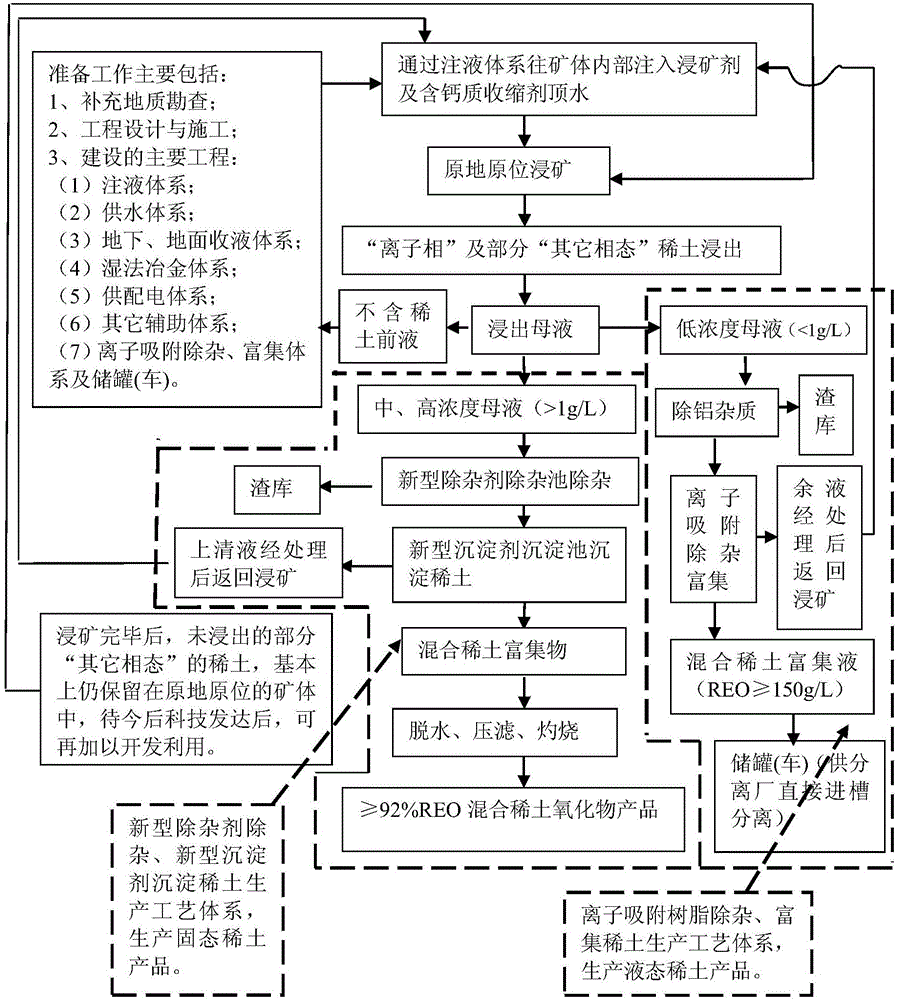
[0087] First, do the preparatory work:
[0088] 1. Supplementary geological exploration;
[0089] 2. Engineering design and construction;
[0090] 3. Main construction projects:
[0091] (1) Liquid injection system;
[0092] (2) Water supply system;
[0093] (3) Underground and ground liquid collection systems;
[0094] (4) Hydrometallurgy system;
[0095] (5) Power supply and distribution system;
[0096] (6) Other auxiliary systems;
[0097] (7) Ion adsorption and impurity removal, enrichment system and storage tank (vehicle).
[0098] Then, start the leaching and enrichment work:
[0099] Step 1: inject ore leaching agent and shrinkage agent into the ore body, in situ leaching ore leaching to leach "ionic phas...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Weigh 18 kg of rare earth ore samples (as shown in Table 1) and put them into the leaching column, and leach the rare earth ore samples with the configured ore leaching agent. The test conditions for leaching are raw ore weight 18kg, leaching agent concentration 4wt%, leaching agent flow rate 3ml / min, liquid-solid ratio (ie volume ratio of ore leaching agent to rare earth ore sample) 1:3.25. Under the above test conditions, the leaching rate of rare earths in the ionic phase was 99.45%, the leaching rate of rare earths in "other phases" was 30.02%, and the corresponding leaching rates of Fe, Al, and Si impurities in the leaching mother liquor were 0.73%, 0.37%, and 1.93%, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0116] Weigh 18 kg of rare earth ore samples (as shown in Table 1) and put them into the leaching column, and leach the rare earth ore samples with the configured ore leaching agent. The test conditions for leaching are raw ore weight 18kg, leaching agent concentration 2.5wt%, leaching agent flow rate 3ml / min, liquid-solid ratio 1:2.5. Under the above test conditions, the leaching rate of rare earths in the ionic phase was 91.04%, that of “other phases” was 12.5%, and the corresponding leaching rates of Fe, Al, and Si impurities in the leaching mother liquor were 0.68%, 0.32%, and 1.86%, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com