Thin-layer composite film based on gas-liquid interface reaction, and preparation method and applications thereof
A technology of liquid interface and composite membrane, which is applied in the field of membrane separation, and achieves the effect of simple preparation method, strong controllability and improved scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
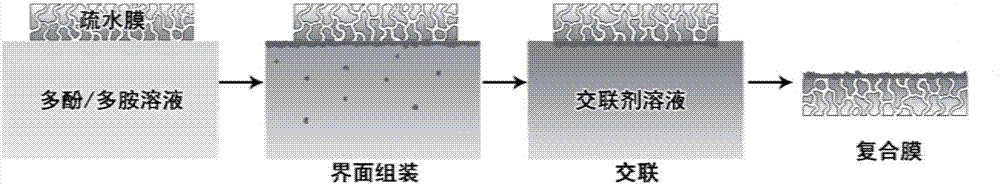
[0040] The preparation method of the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, first configure the polyphenol / polyamine solution according to a certain ratio, and float the hydrophobic basement membrane on the surface of the solution. After reacting for a certain period of time, the base film is placed in an aqueous solution of glutaraldehyde for cross-linking for a certain period of time to obtain a thin-layer composite membrane.
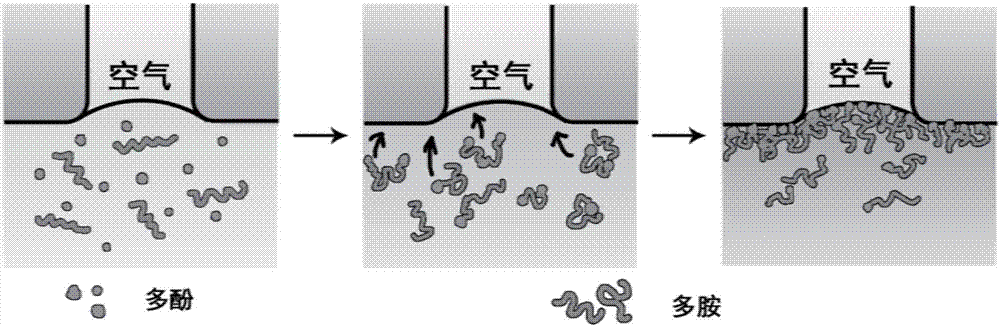
[0041] The mechanism of its reaction is as figure 2 As shown, oxygen diffuses downward through the gas / liquid interface, and the polyphenols in the solution are oxidized to form quinones, which then undergo Michael addition or Schiff base reactions with polyamines, and the polyphenol / polyamine complexes further develop at the gas / liquid interface. reaction, a cross-linked thin film structure is formed at the air / liquid interface of the polymer porous base membrane; the thin-film structure forms a dense selective functional skin layer through cro...
Embodiment 1
[0048] Select dopamine and polyethyleneimine (weight average molecular weight 600) as polyphenols and polyamine monomers, dissolve dopamine and polyethyleneimine in Tris-HCl buffer solution according to the mass concentration ratio of 4:1, wherein dopamine and polyethyleneimine concentrations were 2g / L and 0.5g / L.
[0049] Float the polyvinylidene fluoride microporous membrane on the surface of the deposition solution and deposit it at 20° C. for 4 hours.
[0050] Finally, the prepared film was cross-linked in 10% glutaraldehyde solution at 70°C for 2 hours.
[0051] Finally, after washing with water and drying, a thin-layer composite film is obtained.
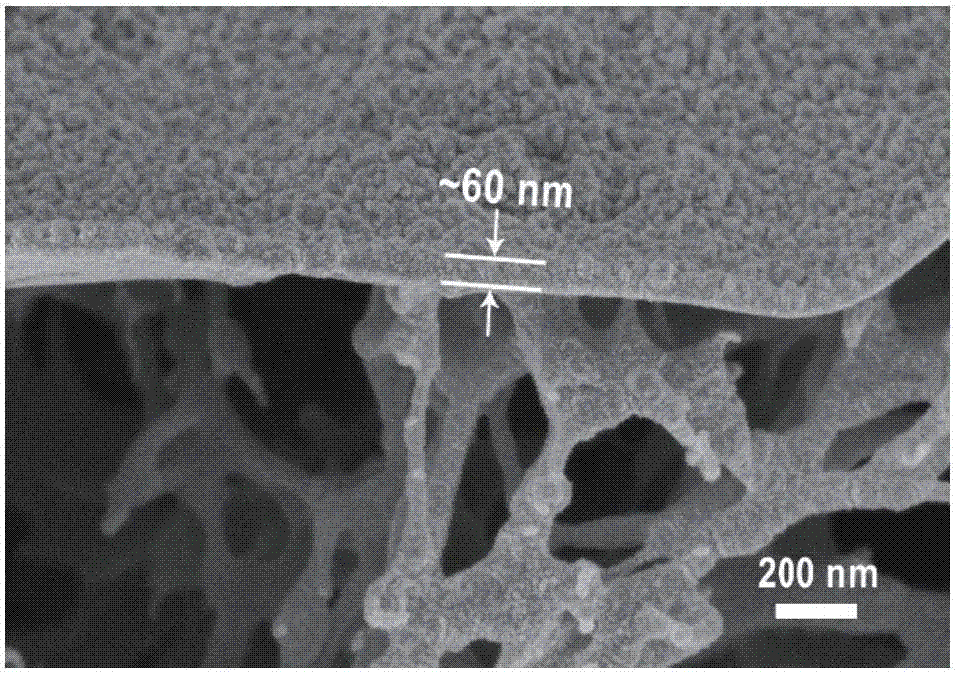
[0052] The cross-sectional morphology (SEM) of the prepared thin-layer composite film is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the thickness of the selective functional cortex on the basement membrane is about 60nm. Its water flux is 53.3Lm -2 h -1 , the desalination rate of magnesium chloride is 95.1%.
Embodiment 2~4
[0054] The polyvinylidene fluoride microporous membrane was replaced with polypropylene, polyethylene, and polyvinyl chloride microfiltration membranes, and the rest of the conditions were the same as in Example 1.
[0055]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Water flux | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com