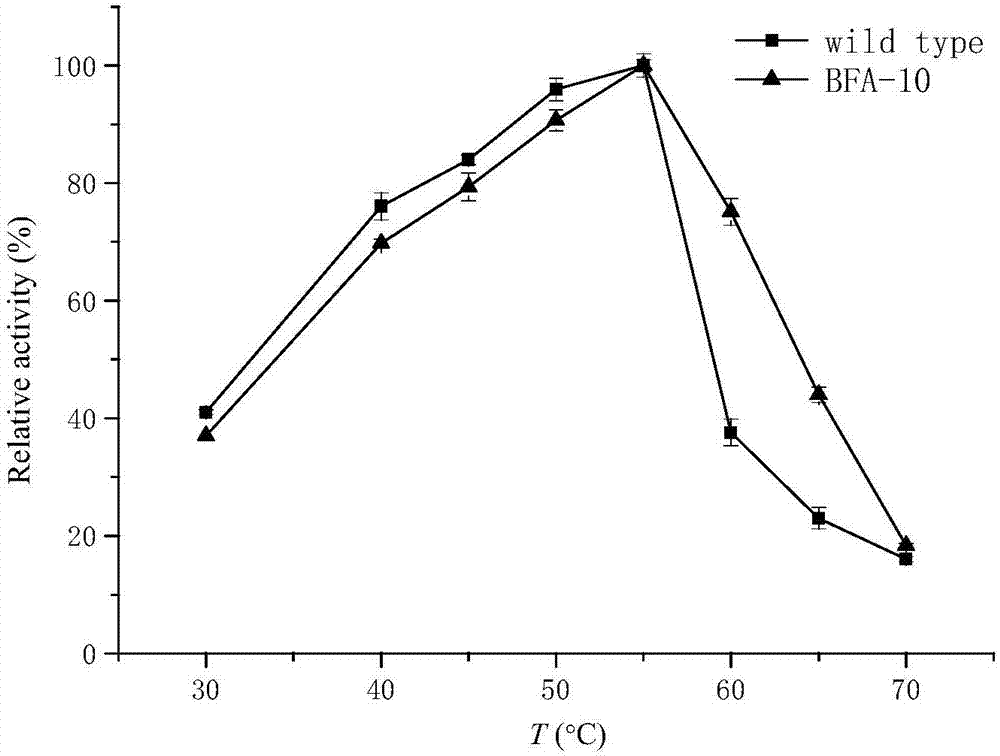
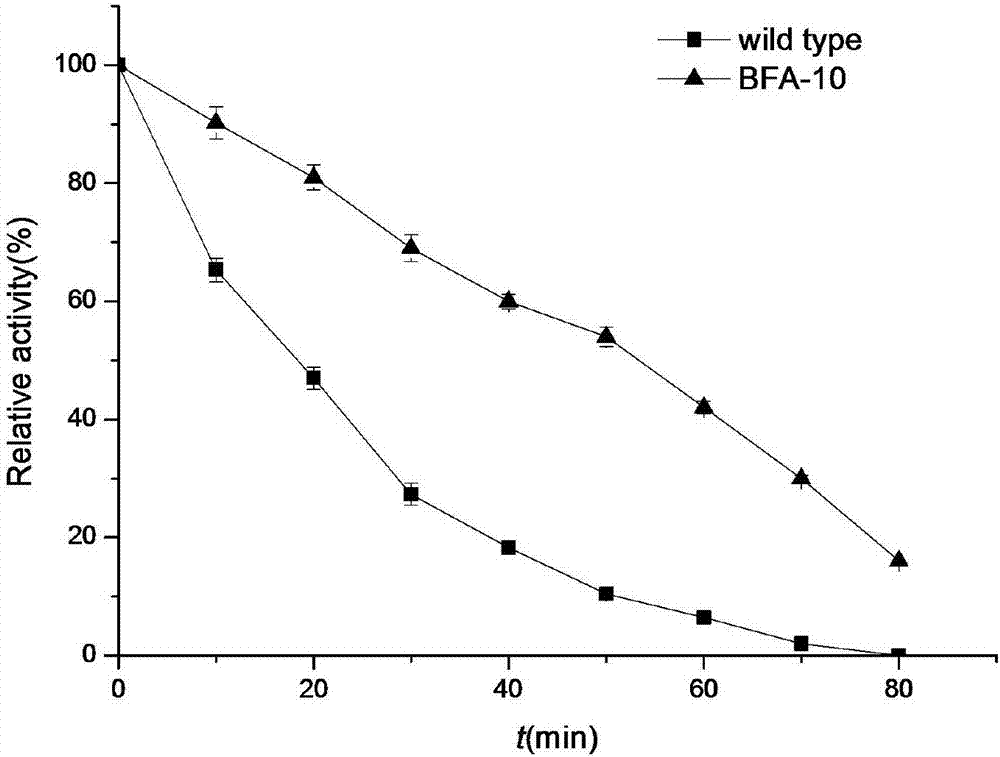
Beta-amylase mutant with improved heat stability
An amylase and mutant technology, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, and can solve the problems of less molecular modification and no relevant literature reports.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1: Construction of β-amylase mutant library based on error-prone PCR technology
[0019] Using error-prone PCR technology to introduce nucleotide mutations into the Bacillus flexus β-amylase gene. The reaction conditions for error-prone PCR are as follows:
[0020]
[0021]
[0022] The sequences of the upstream primer F and the downstream primer R are:
[0023] F: (5′-aa ccatgg cggtaaatggacagtcgtt-3′);
[0024] R: (5′-aa ctcgag ttaccaattattcgtatacgttg-3').
[0025] The PCR amplification procedure is: 94°C for 4min; 98°C for 10s, 53°C for 10s, 72°C for 1min 40s, 30 cycles; 72°C for 10min extension and incubation at 4°C.
[0026] The error-prone PCR product was recovered by agarose gel kit, the target gene was ligated with the vector pMD-18T to transform JM109. After cloning and culture, the target gene fragment was recovered with restriction enzymes Nco I and Xho I and passed through Nco I and Xho I. The digested expression vector pET24a(+) was connected and transform...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: Screening of β-amylase mutants with improved thermal stability
[0029] The Escherichia coli expressing parent β-amylase in pET24a(+) was used as the control bacteria.
[0030] Preliminary screening on LB agar starch plate: Recombinant strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET24a(+)-BFA was induced and expressed in TB fermentation medium for 48h, centrifuged to obtain extracellular supernatant, and 96 empty plates were obtained by high-throughput screening system The fermentation broth of each mutant was transferred to the LB agar starch plate one by one. Incubate overnight at 37°C for about 8 hours, coat the agar starch plate with iodine solution (0.03% w / v), observe the transparent circle, and select the mutant strain corresponding to the transparent circle that is significantly larger than the control.
[0031] Quantitative screening by DNS method in 96-well plate: select mutant strains with a higher transparent circle than the control, and quickly transfer the fermentation s...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Enzyme activity analysis method
[0033] A β-amylase enzyme activity unit (1U) definition (U / mL): 1mL enzyme solution at pH 7.0, temperature 55 ℃, 1h hydrolyze soluble starch to produce 1mg maltose enzyme amount is called an enzyme activity unit.
[0034] Determination method: accurately draw 0.5mL of 2% soluble starch solution, place it in a 15mL colorimetric tube, add 0.4mL of 50mM pH 7.0 phosphate buffer solution, shake well, preheat in a 55℃ water bath for 5 minutes, accurately add 100μL of enzyme solution, and count immediately , Shake well, accurately heat the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction in a 55℃ water bath for 10 minutes, immediately add 1 mL of DNS, shake well, boil for 5 minutes, and cool in ice water. A reaction system with buffer solution instead of enzyme solution under the same conditions was used as a control. The above reaction system was added with 10 mL of distilled water, mixed well, and the absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 540 nm in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com